Macromolecules: Proteins Structure, Function, and Mutations
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What are the basic building blocks of proteins?
Amino acids
How many different amino acids are used to build proteins?
20 different amino acids
What are essential amino acids?
9 amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own
What are the three main components of an amino acid?
Amino group (-NH2), Carboxyl group (-COOH), and R group
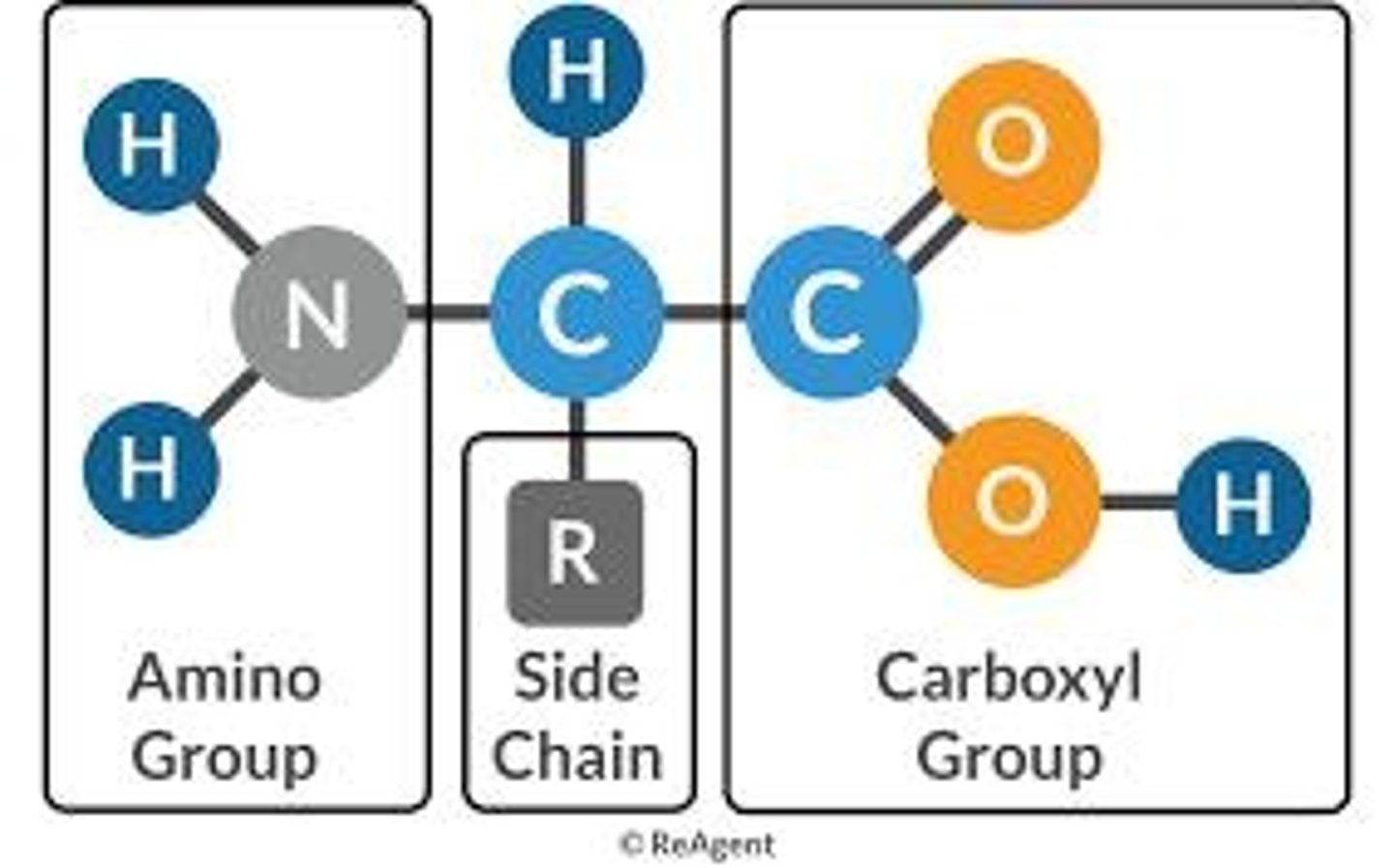
What is the significance of R groups in amino acids?
Different R groups give amino acids different properties
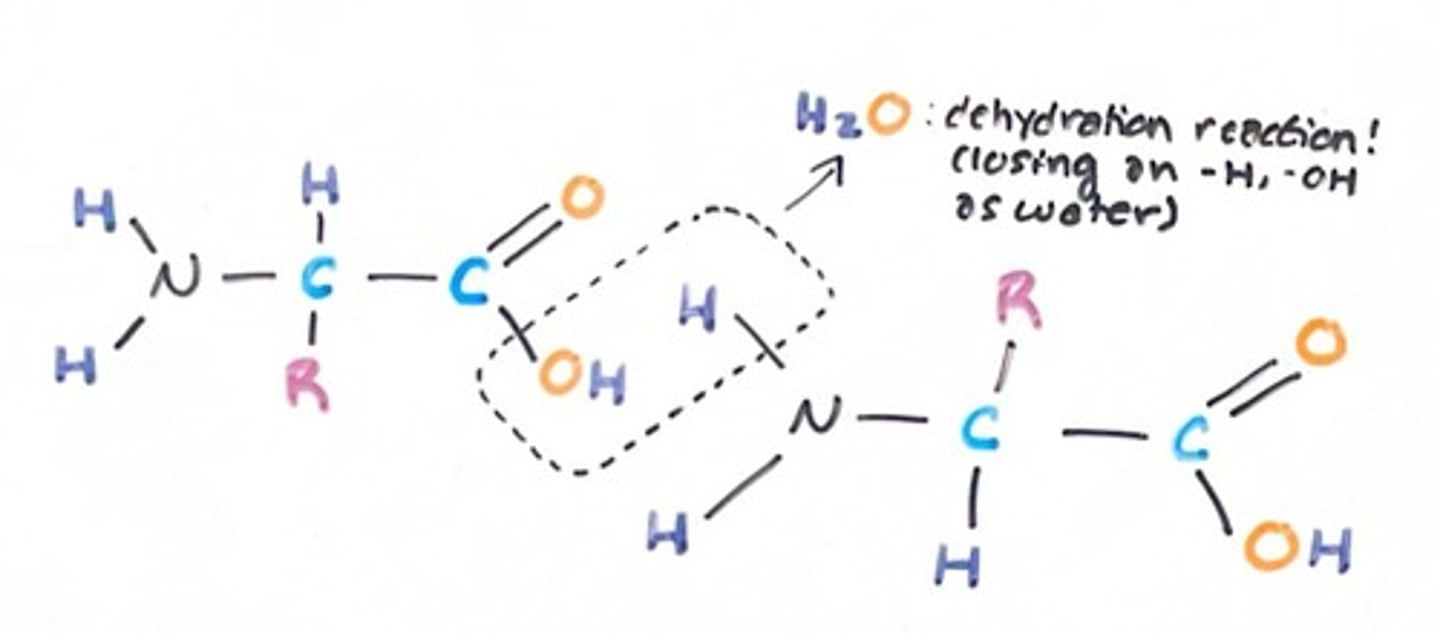
What type of bond links amino acids into peptide chains?
Peptide bonds, which are covalent bonds
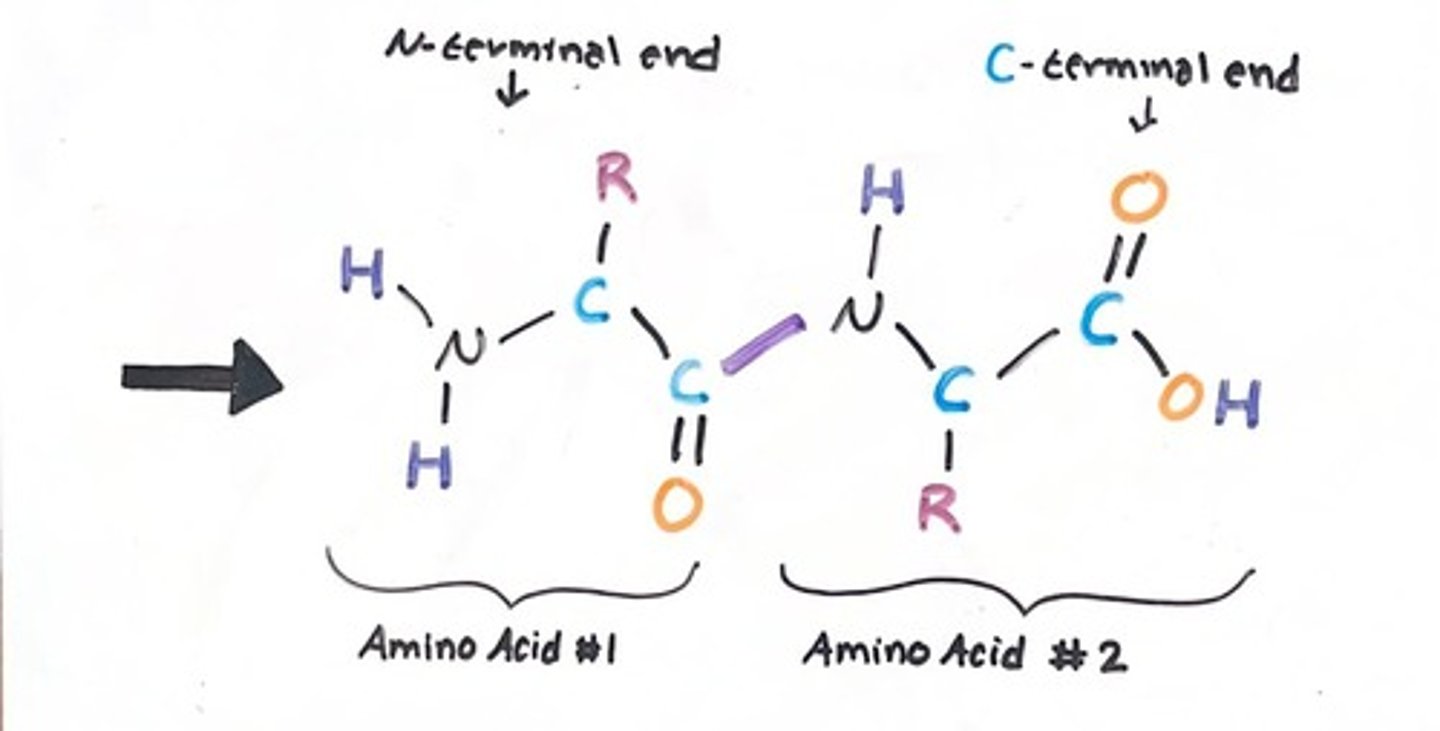
What are the two ends of a polypeptide chain called?
N-terminal end and C-terminal end
What are the two common secondary structures of proteins?
α-helix (twisted spiral) and β-pleated sheet (zig zags on a flat plane)
What is the role of chaperonin proteins?
They assist in the proper folding of proteins into their three-dimensional structure
What is a functional domain in proteins?
A conserved region of a peptide sequence that folds into a 3D shape and performs a specific biological function
What are motifs in protein functional domains?
Highly specialized regions within a functional domain that might be shared across different proteins with similar functions
What are lipoproteins?
Combinations of lipids and proteins that form parts of the cell membrane
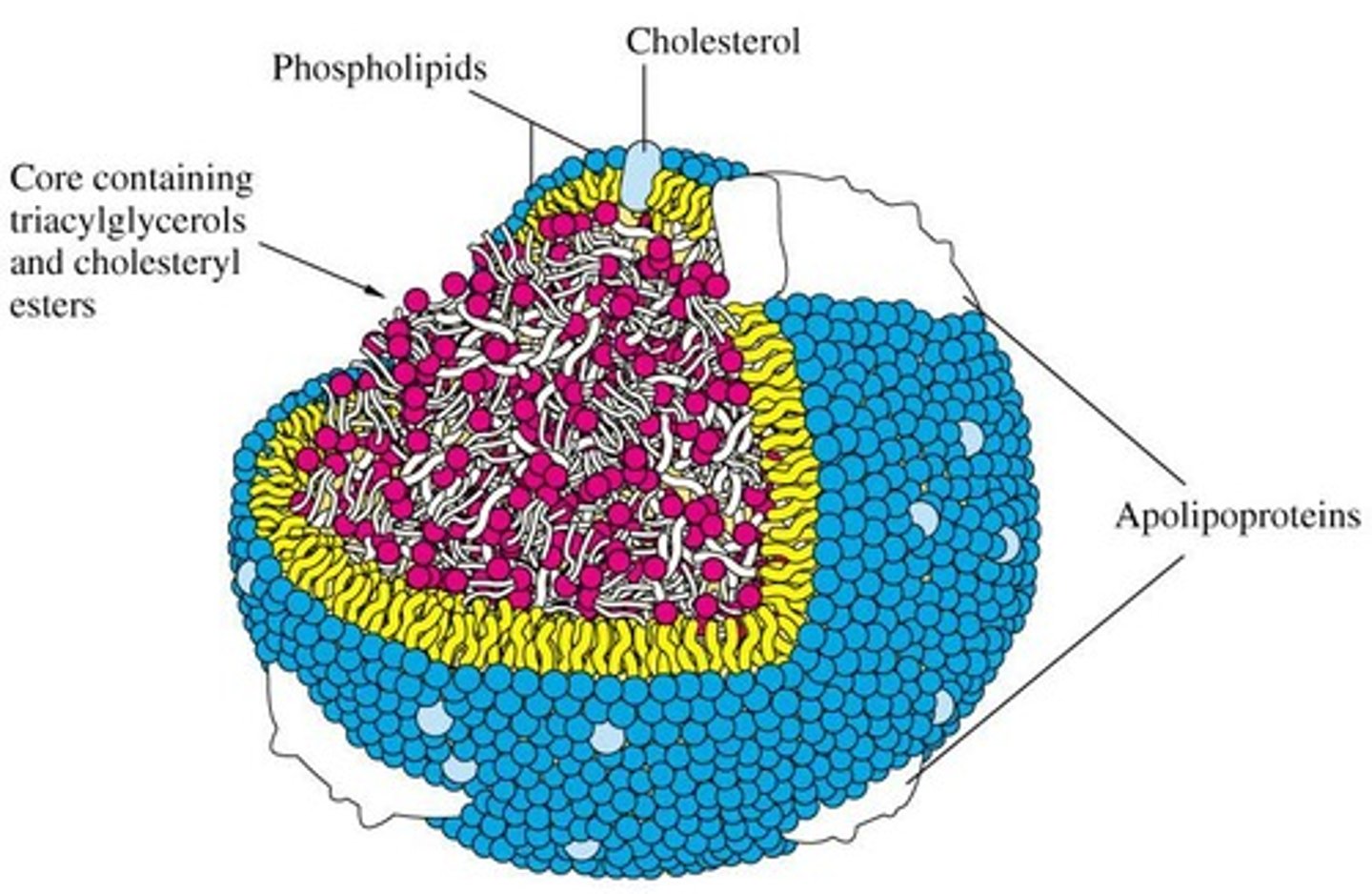
What are nucleoproteins?
Combinations of nucleic acids and proteins that form structures like chromosomes
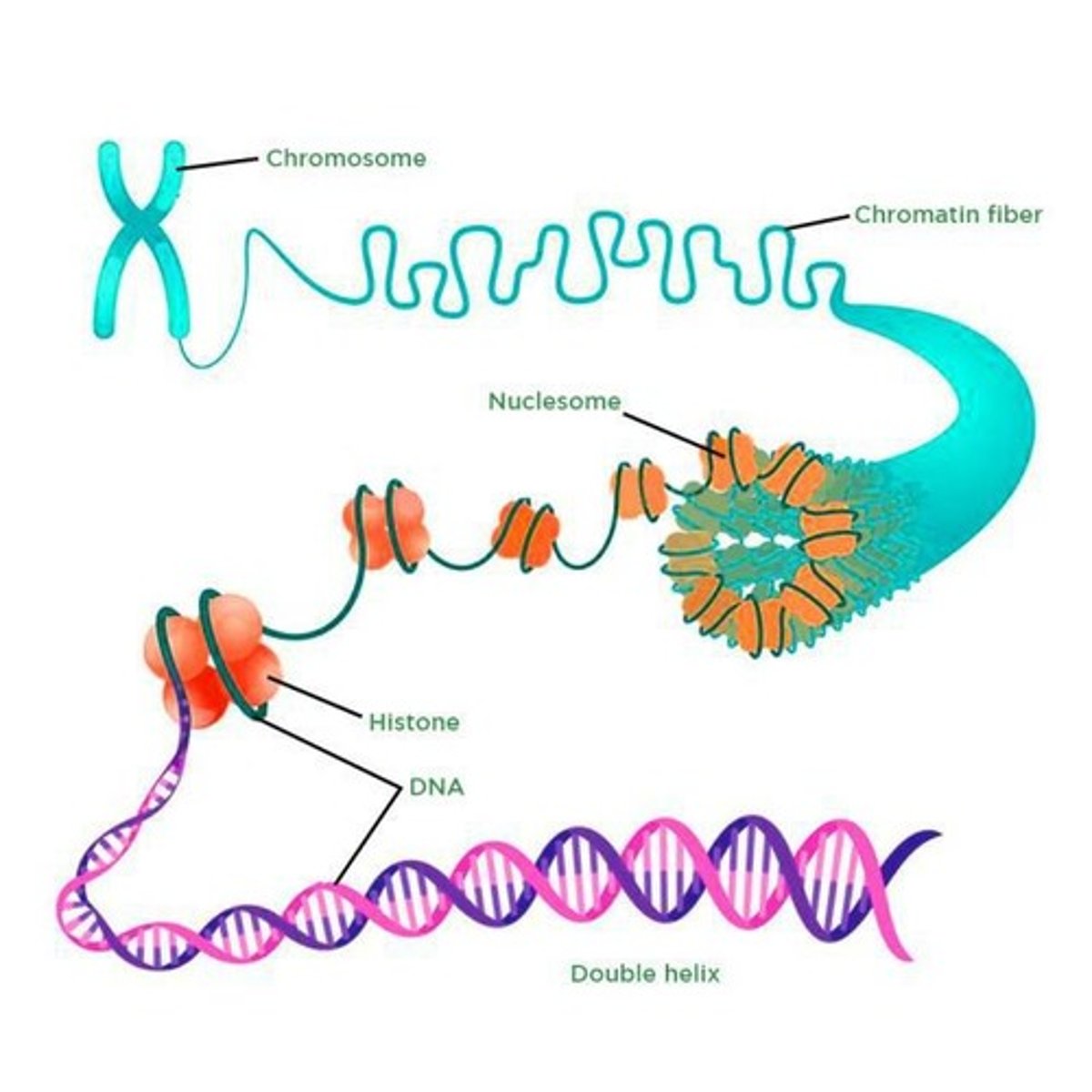
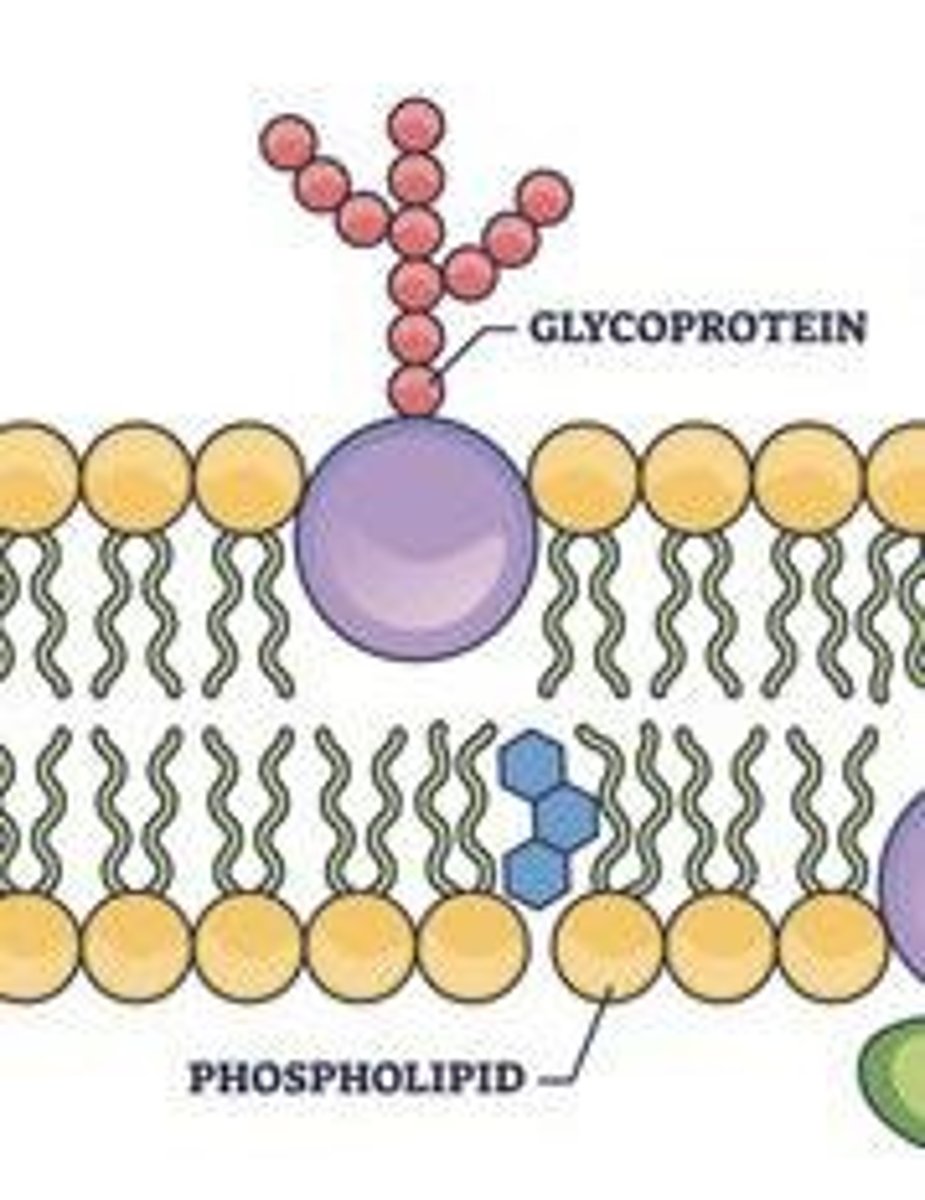
What are glycoproteins?
Combinations of carbohydrates and proteins that form antibodies and recognition/receptor molecules
What is the impact of mutations on proteins?
They can cause genetic variation, some of which may be harmful or beneficial
What is misfolding in proteins?
A problem where proteins are not folded in the specific way needed for functionality
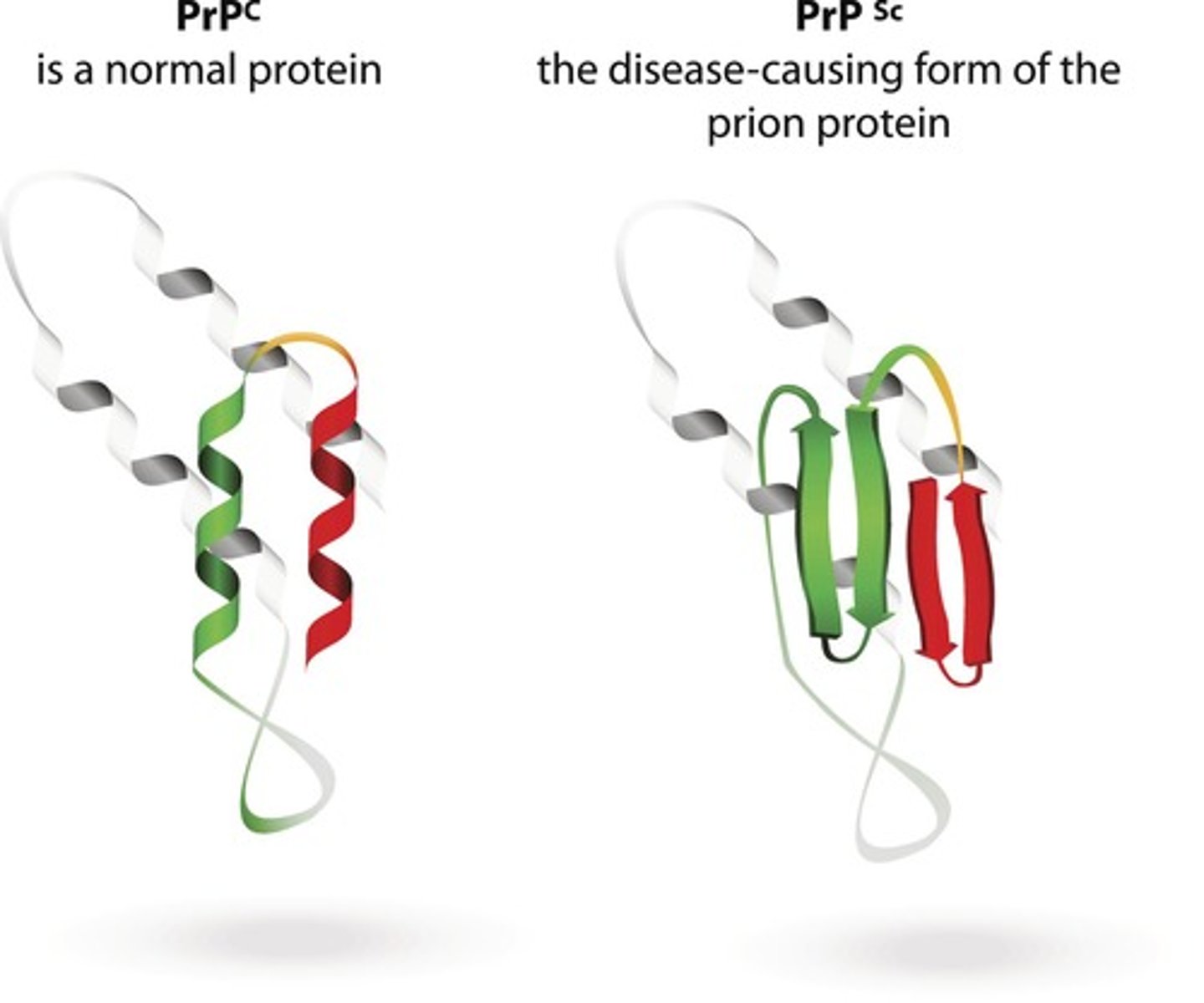
What can happen if a protein's structure is disturbed?
It can alter the protein's function
What are the interactions that stabilize protein structure?
S-S linkages, hydrogen bonds, and attractions between R groups