Prostaglandins & Leukotrienes
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
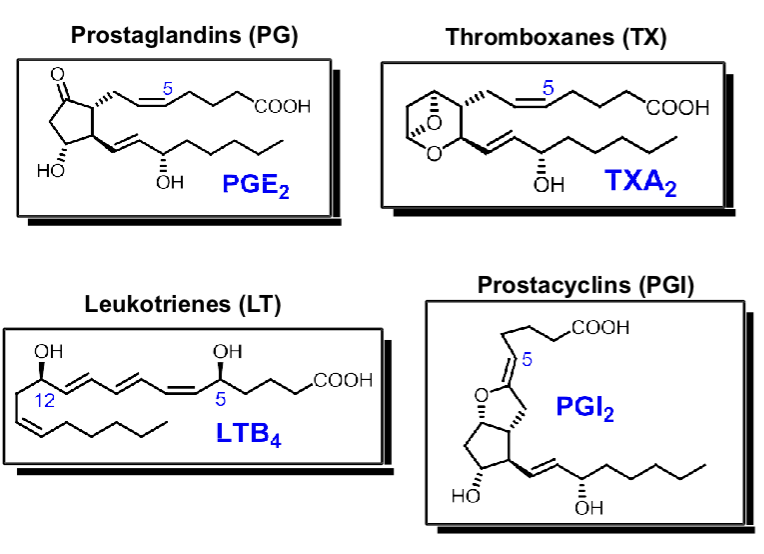
Eicosanoids
structurally simple but highly biologically ______, ______ substances
all structurally similar —> ____-carbon molecules
derived from ______ of lipids (fatty acids)
all are ______ (stable/unstable)
diverse, endogenous
20
oxidation
unstable
Eicosanoids are derived from:
Oxidation of lipids (fatty acids)
Which of the following is TRUE about eicosanoids?
They are structurally simple but biologically diverse
What is the carbon chain length characteristic of eicosanoids?
20 carbons
What do ALL eicosanoids have in common?
They are unstable
Each eicosanoid has own specific functions:
inflammation =
blood clotting/platelet aggregation =
inhibit platelet aggregation =
asthmatic + allergic rxns =
PG
TX
PGI
LT
Eicosanoids are the most important mediators of which process?
Inflammation
Eicosanoids exert their effects primarily through:
GPCRs
Prostaglandins (PGs) activate GPCRs that may be:
Either inhibitory or stimulatory
A single prostaglandin can:
Bind multiple receptor subtypes
Why can the same prostaglandin have different effects in different tissues?
Different receptors are expressed in different tissues
Which enzyme initiates prostaglandin metabolism by oxidizing the 15-OH group?
PG 15-OH dehydrogenase
Which statement best describes eicosanoids?
Eicosanoids = Local, short-lived signals → unstable → rapid breakdown → drugs = agonists OR antagonists
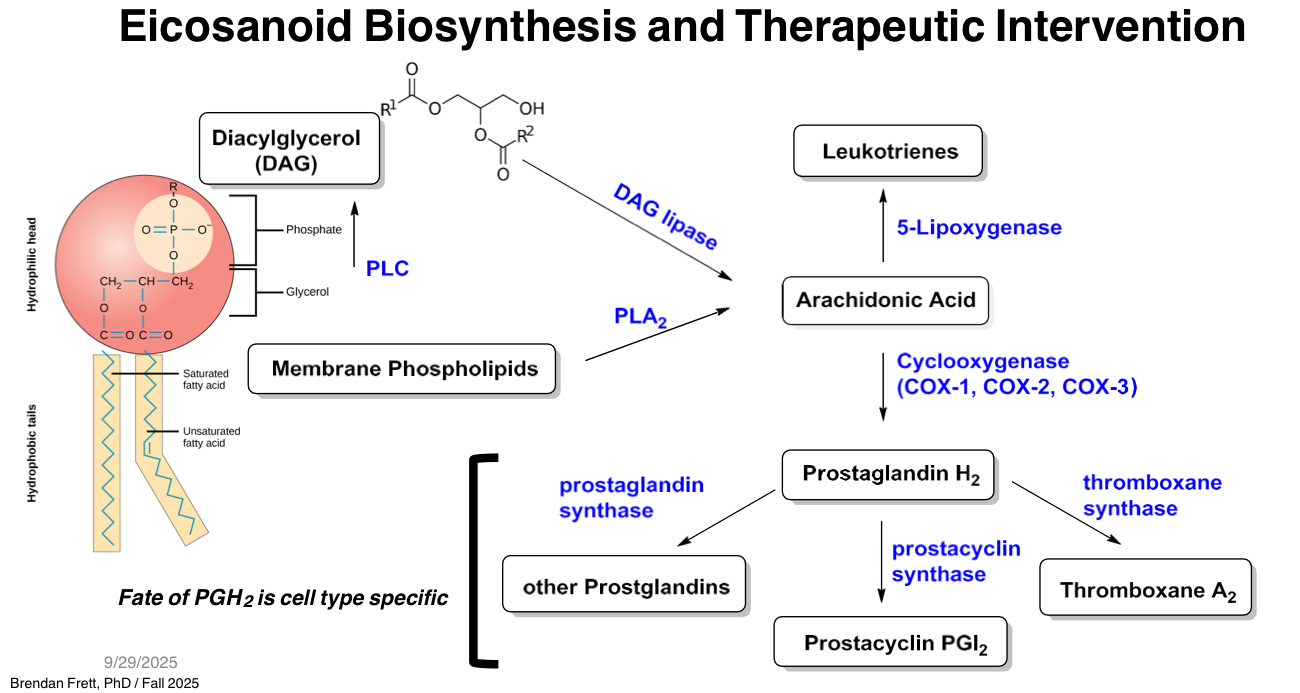
Which reaction type is used by phospholipases to cleave membrane phospholipids and release arachidonic acid?
Hydrolysis
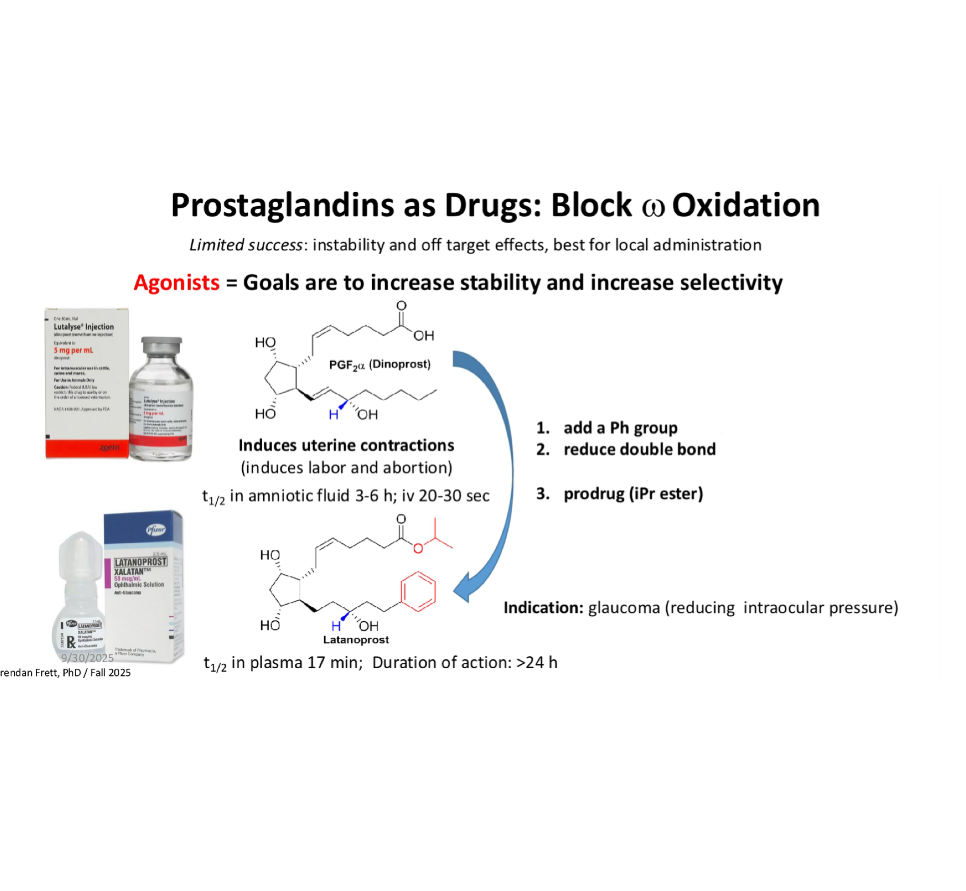
add a Ph group —>
reduce double bond —>
prodrug (iPr ester) —>
block oxidation
increase selectivity, slightly decrease potency
increase lipophilicity —> higher corneal permeability
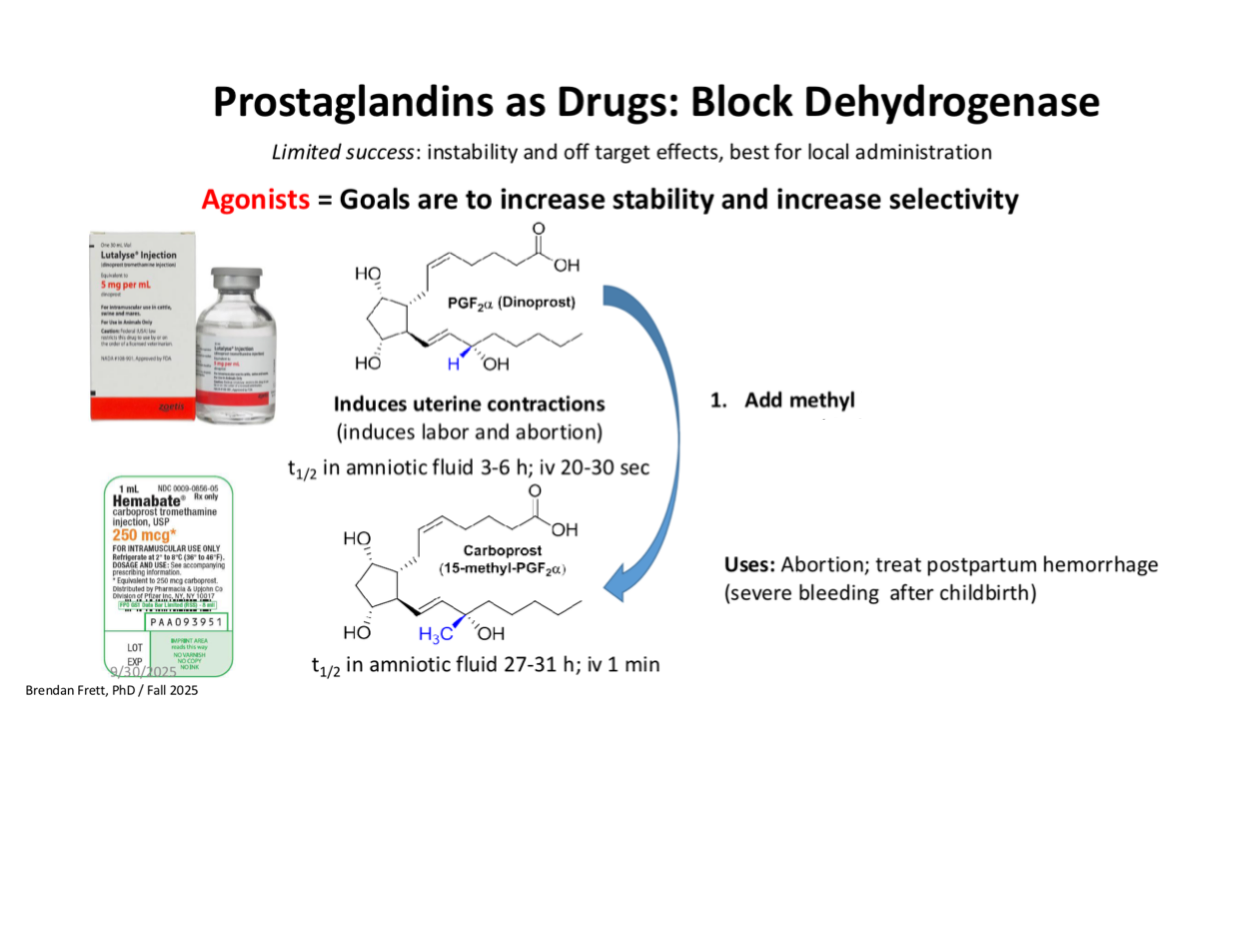
add methyl —>
in place of H —> block oxidation at carbon 15 by dehydrogenase
What is the major limitation of natural prostaglandins as drugs?
Instability and off-target effects
The therapeutic goal when using prostaglandin agonists is to:
Increase stability and selectivity
Latanoprost is primarily used to treat:
Glaucoma
PGF₂α (dinoprost) induces which physiological effect?
Uterine contractions
PGF₂α is used clinically to:
Induce labor and abortion
Carboprost’s major clinical use is:
Postpartum hemorrhage treatment
Bimatoprost is used for glaucoma and also for:
Eyelash lengthening & darkening
Which prostaglandin analog has the longest plasma half-life listed in the slide?
Bimatoprost (45 min)
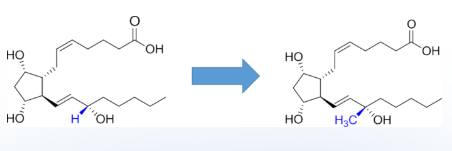
What is the effect on stability?
increase

Which has a higher corneal permeability?
B
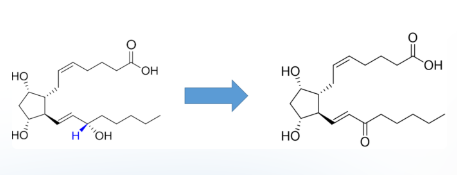
What is the effect on stability?
no effect
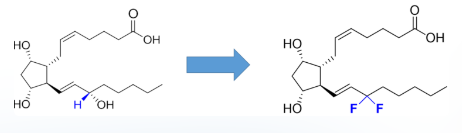
What is the effect on stability?
increase
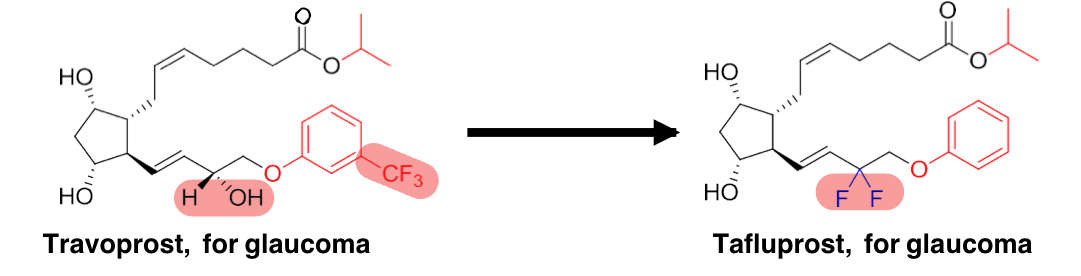
what does this mechanism increase?
stability
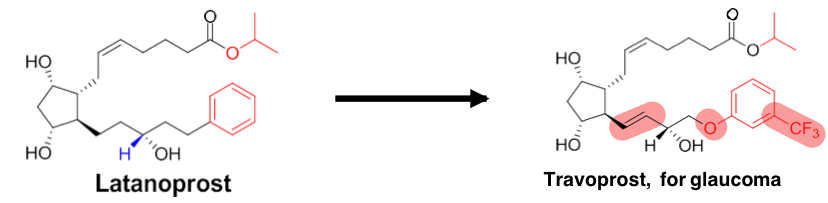
what does this mechanism increase?
selectivity

The modification in bimatoprost that increases both efficacy and stability is:
Ester → amide
Why is local delivery often required for eicosanoid-based therapeutics?
Receptor expression is tissue-specific
The term “local hormones” refers to eicosanoids because they:
Act near the site where they are produced
Which delivery route is commonly preferred for eicosanoid-based drugs?
Local/topical application
Eicosanoids are derived from fatty acids that are:
20-carbon polyunsaturated fatty acids
The double bonds in essential fatty acids that form eicosanoids are typically:
Cis
Which essential fatty acid is the primary precursor for most eicosanoids?
AA (Arachidonic acid)
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids must be obtained:
From dietary sources
Which fatty acid listed is an omega-3 precursor for eicosanoids?
α-Linolenic acid
Which of the following is an omega-6 fatty acid that forms eicosanoids?
Arachidonic acid