Skeletal System Sci Oly Info
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
80
how many bones are in axial skeleton
126
how many bones are in the appendicular skeleton
skull, auditory ossicles, hyoid, thorax, vertebral column
5 types of bones in axial skeleton
cervical vertebrae
transverse foramen, bifid spinous process
atlas
supports head c1
axis
dens pivots to turn head c2
thoracic vertebrae
long spinous processes, rib facets
osteoblasts
bone forming cells synthesize and secrete unmineralized ground substance and are found in areas of high metabolism within the bone
osteocytes
mature bone cells made from osteoblasts that have made bone tissue around themselves. They maintain healthy bone tissue by secreting enzymes and controlling the bone mineral content; they also control calcium release from bone to blood
osteogenic cells
respond to traumas by giving rise to bone forming cells and bone destroying cells
osteoclasts
bone absorbing cell large cells break down bone tissue important to growth healing and remodeling
bone lining cells
made from osteoblasts along the surface of most bones in an adult, regulate mvmt of calcium and phosphate into and out of the bone
hematopoiesis
takes place in red marrow
hyaline cartilage
fine collagen fiber matrix- most abundant type- found in articular (movable joint) cartilages, costal cartilages (connect ribs tosternum), respiratory cartilages (in larynx & upper respiratory passageways) & nasal cartilages
elastic cartilage
similar to hyaline cartilage, more elastic fibers (very flexible) – found in external ear & epiglottis (larynx covering
fibrocartilage
rows of chondrocytes with thick collagen fibers; highly compressible with great tensile strength- found in menisci of knee, intervertebral discs & pubic symphysis
hairline

oblique displaced
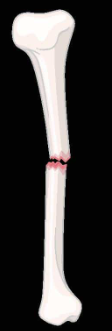
oblique nondisplaced
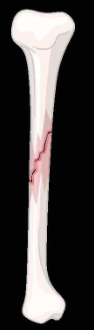
linear
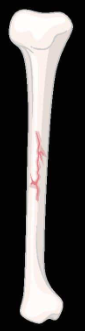
comminuted

spiral
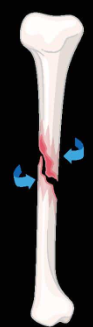
segmental

osteoarthritis
degeneration of joint cartilage and the underlying bone, most common from middle age onward. It causes pain and stiffness, especially in the hip, knee, and thumb joints
osteoporosis
develops when bone mineral density and bone mass decreases, or when the structure and strength of bone changes
disk herniation
occurs when some of the nucleus pushes out through a tear in the annulus
scoliosis
abnormal lateral curvature of the spine
ACL injury
Pain on the outside and back of the knee.
Knee swelling within the first few hours of the injury.
Limited knee movement because of swelling and/or pain.
Loss of full range of motion.
Discomfort while walking.
treated with rehab and surgery
mcl injury
Knee swelling
Locking or catching of the knee when you move it
Pain and tenderness along the inside of the joint
A knee that gives way or feels like it is going to give when it is active or stressed in a certain way