the labour market
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
How is labour a derived demand?
The demand for labour comes from the demand for what is produces
what does a change in wage rates do to demand for labour?
contraction/expansion in quantity demanded
what are the factors affecting the demand for labour
demand for the product
labour productivity
capital productivity
the price of the product
how does shift in the demand for a product lead to a shift in the demand for labour
if consumers demand more or less of a product, then the firm demands more or less labour to produce the product
∴ shift
How could a change in labour productivity lead to a shift in the demand for labour
If labour becomes more productive, more of that labour may be demanded because each worker can produce more output in the same amount of time
∴ MRP increases as MRP= MP of labour X Price
∴ firms demand more of this labour at every wage level
how can change in productivity of capital lead to a shift in the demand for labour
increase in capital productivity can lead to replacing labour as firms may substitute capital for labour
- Labour is then substituted
- MP_L falls
- MRP_L falls
- Demand for labour curve shifts left
how can a change in the price of a product lead to a shift in the demand for labour
if the price of a product increases
MRP_L = MP_L x P
If P (price) increases, then MRP increases, making workers more valuable to firms so firms demand more labour at all wage levels causing demand to shift right
what is MRP_L
what is the formula?
MRP is the amount of revenue created by one additional unit of labour that has been produced
MRP_L = MP_L x P
MRP curve
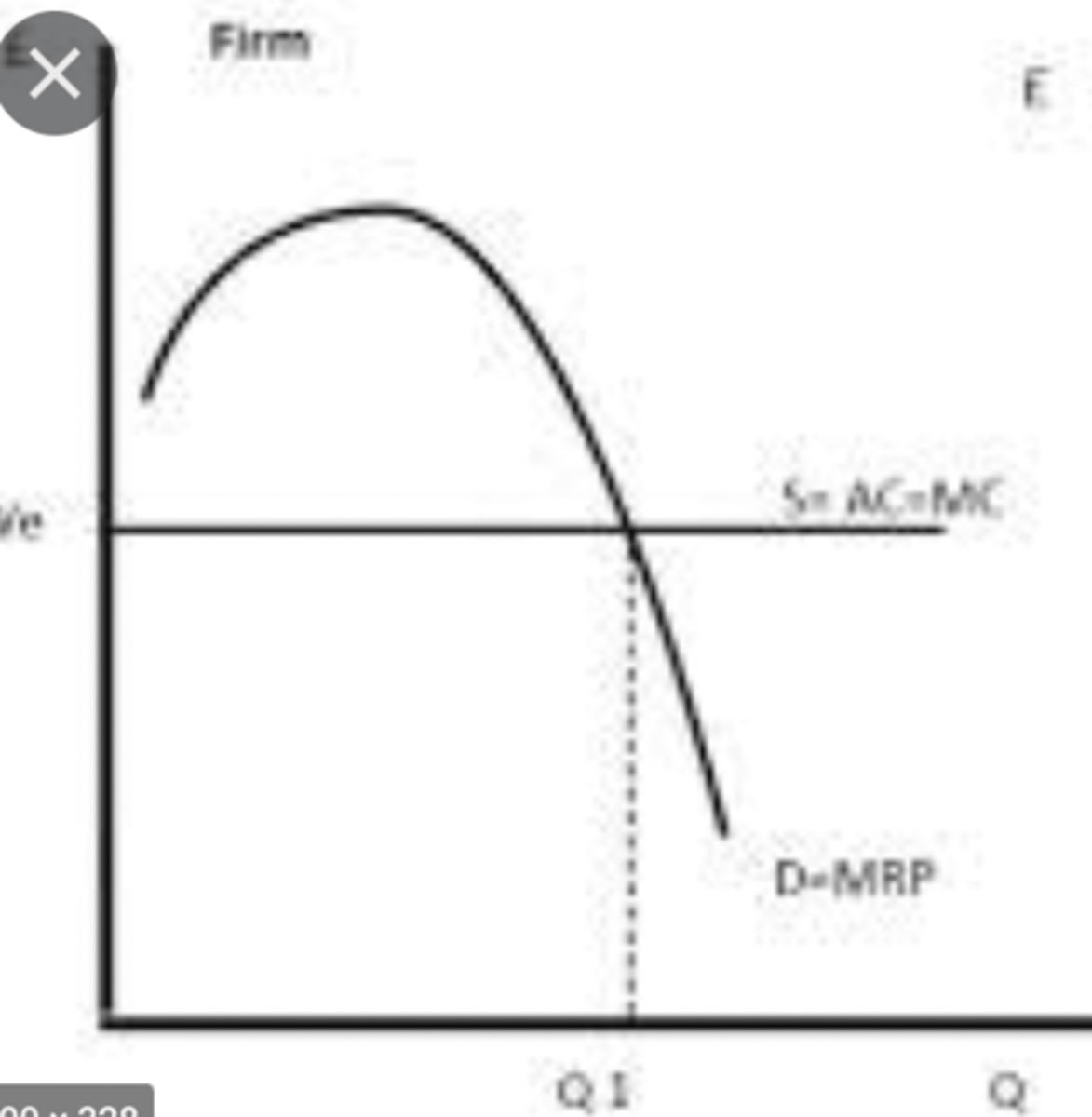
whys MRP curve shaped the way its shaped?
what point will porfit max firms act?
- law of diminishing marginal returns as each extra worker beyond the optimum produces less output MP_L falls to MRP_L falls
- Profit max firm will employ at at least MRP_L = MC_L to not make any loss
define wage elasticity of demand for labour
a measure of how responsive the quantity of labour demanded is to a change in the wage rate
what are the factors affecting the elasticity of labour demanded?
- substitutability
- proportion of labour costs to total costs
- Time period
How does substitutability of labour affect the wage elasticity of demand for labour
if labour can be easily replaced by capital then demand is more elastic
How does the proportion of labour costs relative to total costs affect the wage elasticity of demand for labour
If labour costs make up a larger portion of total costs, firms will be more sensitive to wage changes, leading to more elastic demand
how is the elasticity of demand for labour different in the short-run and long-run
In the short run, firms have less flexibility to adjust, so labour demand is inelastic
In the long run, firms can adjust more by adopting technology so labour demand is more elastic
define labour supply
the ability and willingness of households to work at different wage levels
what are the factors affecting the supply of labour
- non-pecuniary benefits
- wages in other industries
- demographics
How do wages in other industries affect supply of labour in an industry?
if a worker can earn a higher wage in a different industry, they will leave their current one shifting supply left and right to the industry they moved too
how do non-pecuniary benefits affect the supply of labour to an industry?
If a job offers great non-monetary benefits, more workers might be willing to work even if wages are lower
Non-pecuniary factors are job satisfaction, flexible working hours, health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave, and job security
more non-pecuniary benefits will shift supply right in an industry
How do demographics influence the supply of labour in an industry in the economy
- Older workers would be less likely to work - supply shifts left
- Certain industries may attract one gender over the other - can shift supply left
- could be a growing population from migration - shift supply right
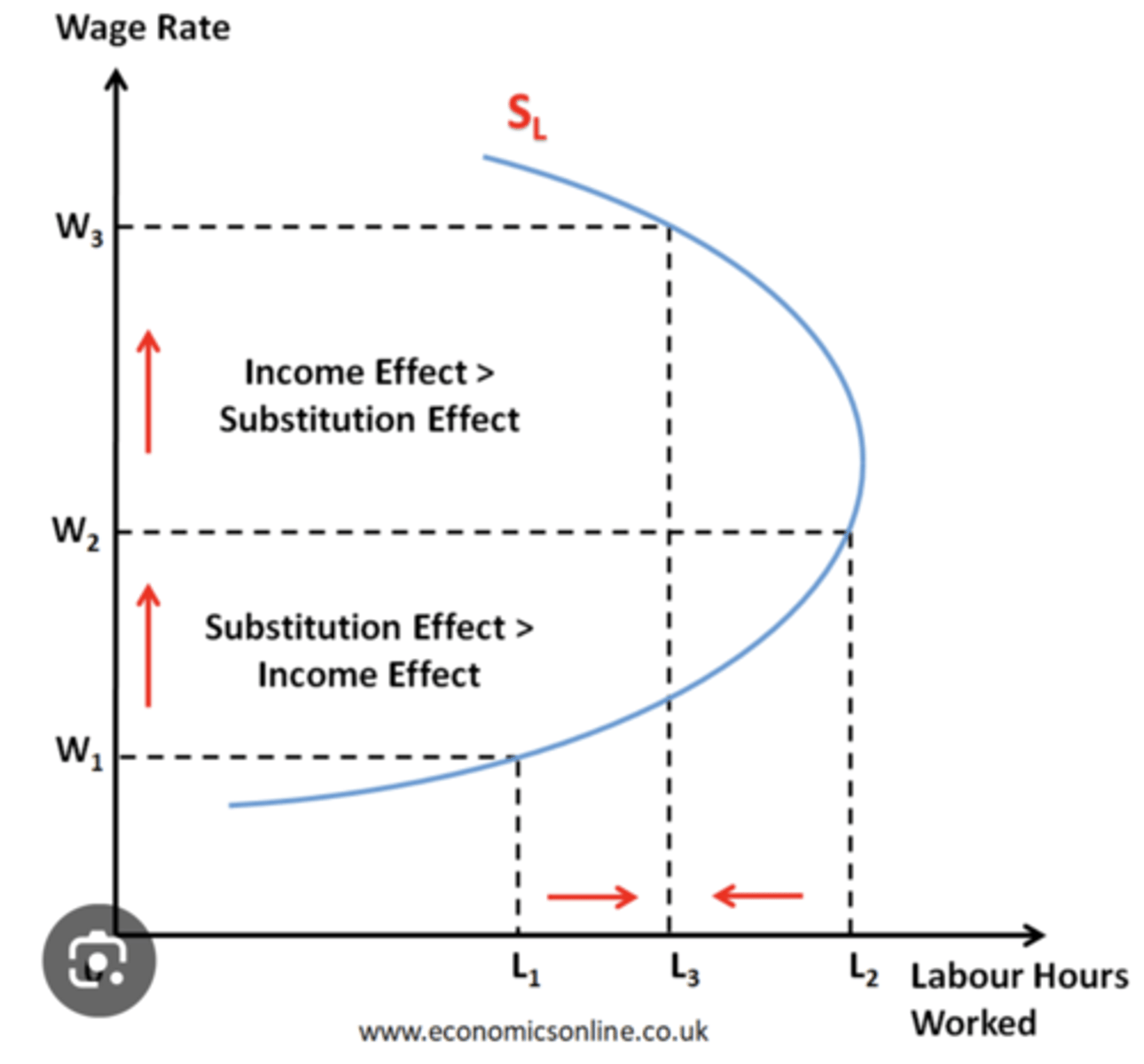
explain the diagram for wage rate against the number of hrs of labour worked
- As the wage rate increases, a worker would substitute leisure time for work time = substitution effetc
- as the wage rate increases further, the worker will have enough money so will begin to substitute work time for leisure = income effect
how does the availability of workers affect the elasticity of labour supplied
If there is a large pool of available workers, the labour supply will be more elastic because firms can easily hire workers when wages rise
if there is a shortage of workers, labour supply is inelastic because even if wages increase, there arent enough people to fill the roles
how do skills and qualifications affect the wage elasticity of the supply of labour
Jobs requiring low skills tend to have an elastic labour supply because many people can do the job
jobs requiring high skills and qualifications tend to have inelastic labour supply because even if wages rise, new workers cant enter the profession quickly
how does the nature of a job affect the wage elasticity of supply of labour
If a job is considered to be attractive (good working conditions, low stress), more people are willing to do it, making labour supply more elastic
How does labour immobility affect the wage elasticity of the supply of labour
if workers find it hard to move to areas where jobs are available, the supply of labour is more inelastic (geographical immobility)
if workers struggle to switch industries due to lack of transferable skills, labour supply is also inelastic
how does the wage elasticity of the supply of labour curve differ in the short run and long run
short-run = inelastic because people can't switch their occupation easily
long run = elastic becuase people can enage in trianing or gain qualifications for higher paid work
define economic rent
the extra income a worker earns above the minimum required to keep them in their current job
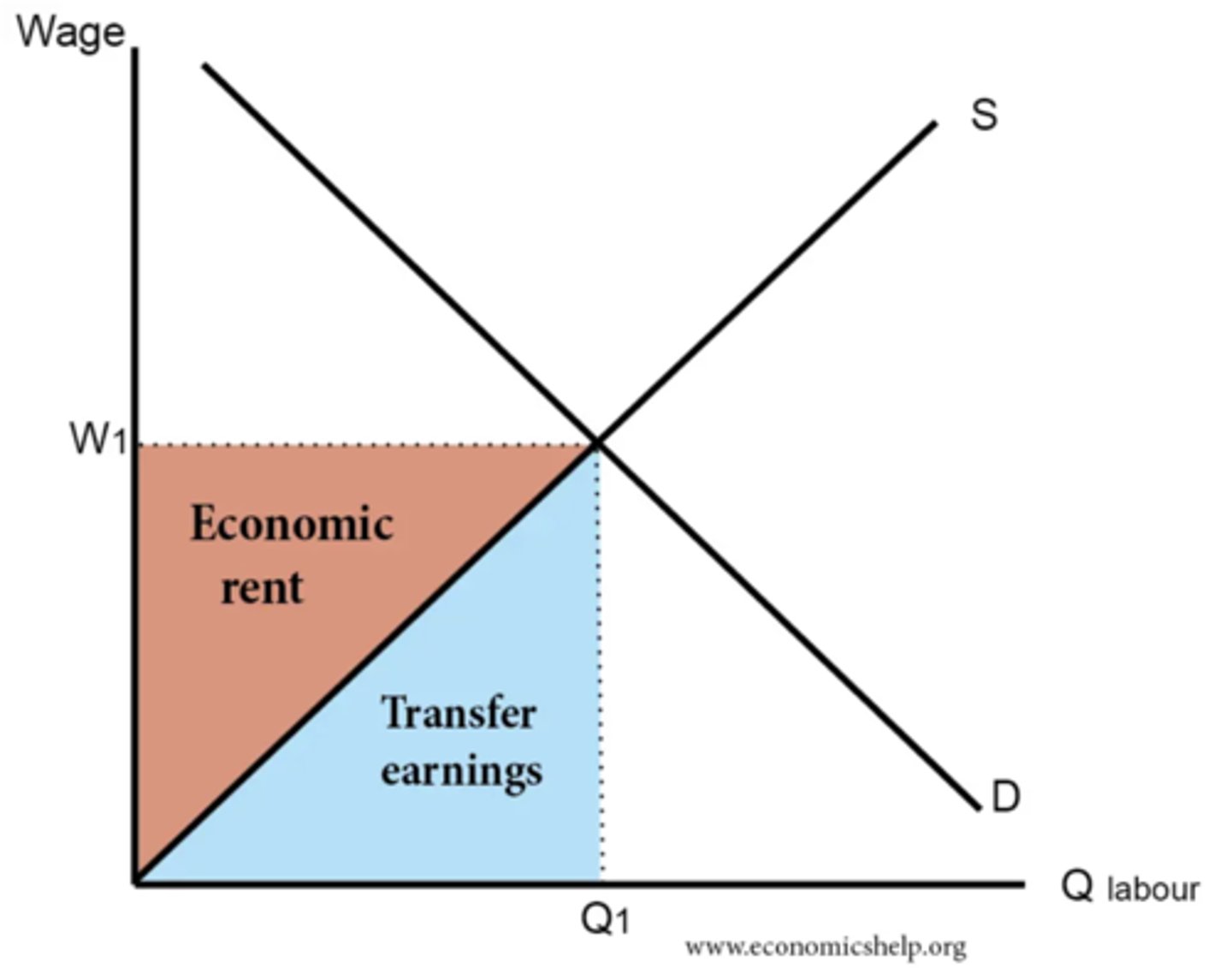
define transfer earnings
The minimum payment required to keep a factor of production in its present use
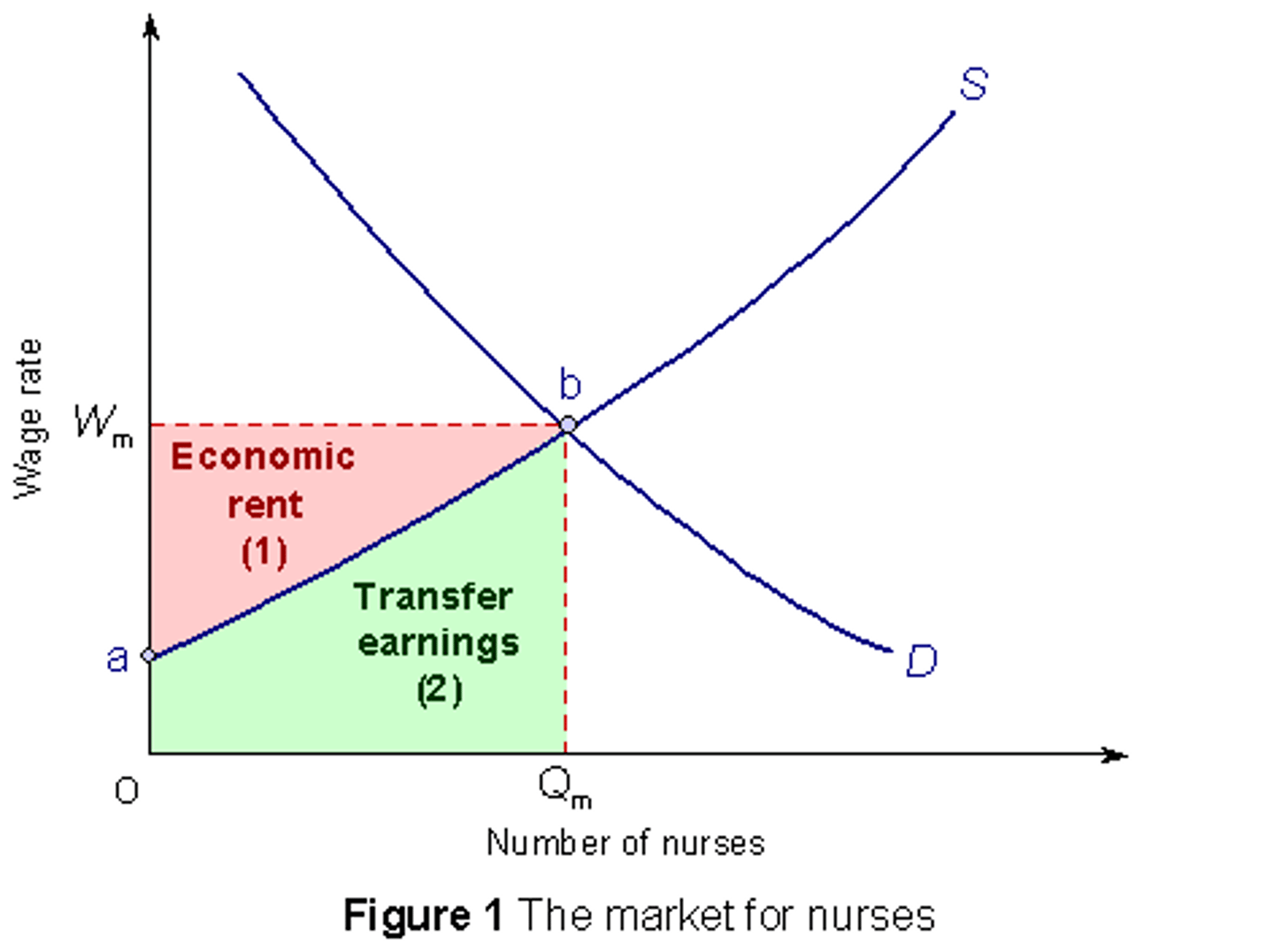
how does the elasticity of labour supply impact level of economic rent and transfer earnings
more elastic labour supply curve decreases the proportion of total earnings that is economic rent and increases the proportion of transfer earnings
What is a wage differential?
The difference in wages between workers with different skills in the same industry, or between workers with comparable skills in different industries or localities.
what are some reasons for wage differentials
- differences in the level of skills, qualifications and training
- differences productivity
- differences in the marginal physical product of labour
- differences in conditions of work
- discrimination against due to gender, age, disabilities and race
What is a monopsony
so what is a monopsony labour market
a market situation in which there is only one buyer
- a monopsony labour market is a market situation where there is a single employer
what are some examples of monopsony employers
- NHS
- State schools
- army
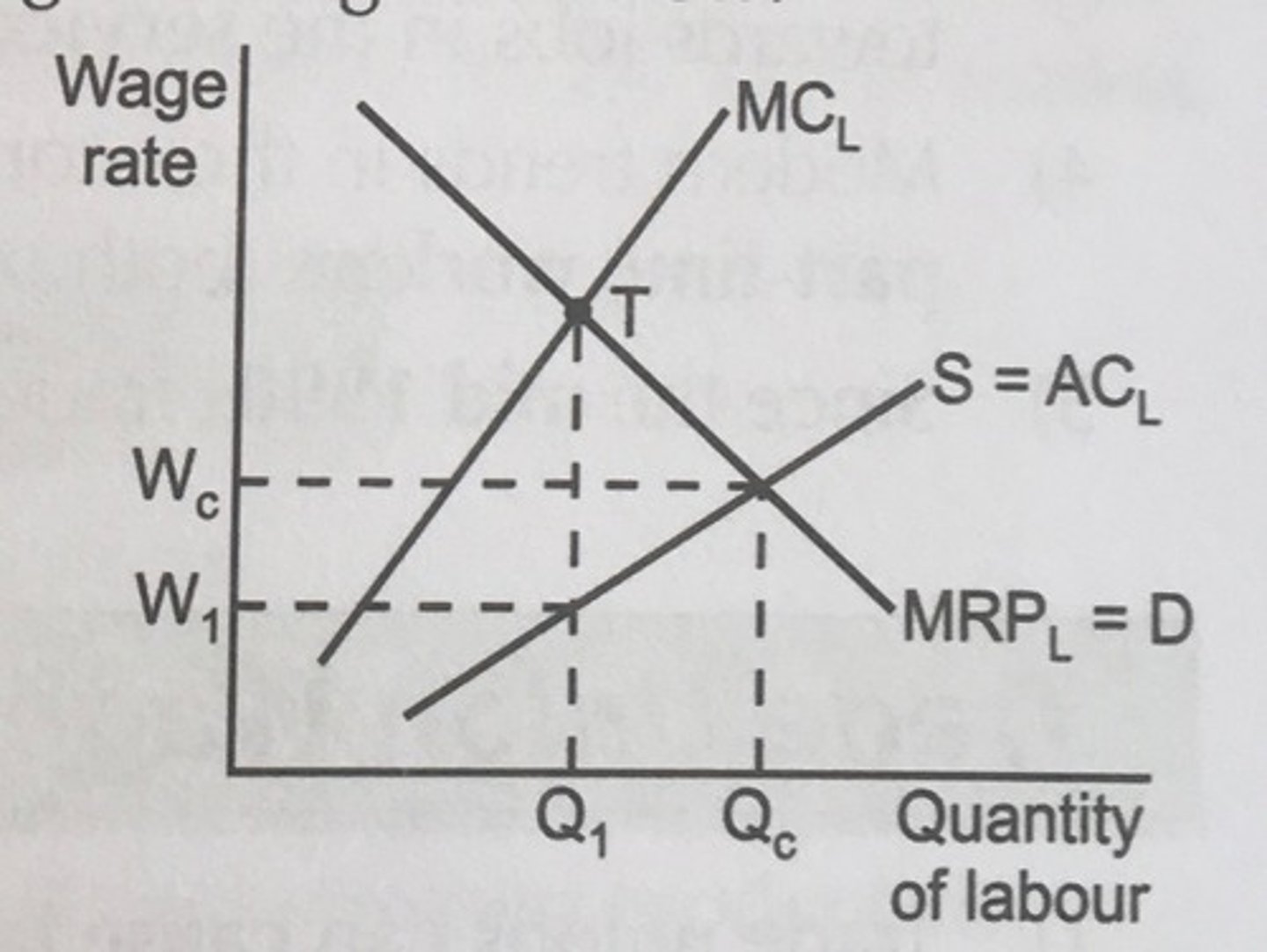
how are wages determined in a monopsony labour market
- monopsonist has the wage-setting power
- they can pay wages less than a worker's MRP and drive down the level of employment than what would be in a perfectly competitive labour market
- the monopsonist will hire the number of workers that will maximise their profits, where MRP = MC, so the quantity of workers employed is Q1 and wage is W1
- this causes unemployment in this labour market and labour market failure
what is labour market failure
labour market failure occurs when the labour market does not allocate labour efficiently meaning that there is not an optimal outcome for society or the economy
What is a trade union?
an organisation of workers that negotiates with employers on behalf of its members
what are the objectives of trade unions
- wage bargaining
- improvement of working conditions
- job security
what is collective bargaining
when a trade union negotiates with an employer
what are factors affecting trade union bargaining power
union density due to the credible threat of strike power
- economic climate, low levels of unemployment mean unions have more bargaining power due to scarcity of skilled workers
what are the reasons for the massive fall in trade union membership in the UK over time
(legal changes, changing workforce demographics, and globalisation)
- legal changes - the UK have implemented labour laws & and reforms that have made it more difficult for unions to recruit and maintain members
- changing workforce demographics - composition of the workforce has changed with more part-time, temporary and gig economy jobs
- globalisation - reduced bargaining power of employees due to the growing monopsony power of large MNCs
what is the gig economy
what are some examples
A flexible market that allows you to work short-term, independent jobs on a freelance basis where you get paid per task/ per 'gig'
e.g. uber, deliveroo
what are some factors contributing to the rise of the gig economy
- technological advancements
- cost reduction for employers
- desire for work-life balance
- entrepreneurial opportunities
how can trade union negotiations lead to labour market failure
how does elasticity of demand for labour affect?
- trade unions can cause labour market failure by forcing wages up to a level higher than the market equilibrium wage causing an excess supply of labour, and insufficient demand for the number of workers willing and able to work so there is unemployment and therefore labour market failure
- the elasticity of the demand for labour affects the extent to how much unemployment occurs
- an inelastic demand curve, does not lead to major unemployment whereas an elastic one does
how can a trade union help to increase wages but not lead to unemployment
can persuade their members to agree to more efficient working practices which increase worker productivity
MPP increases so MRP increases so shifts so demand shifts so the new wage rate at a higher equilibrium
- firms can afford to pay higher wages
what is a factor affect trade union bargaining power
union density & and membership giving a credible threat of strike power
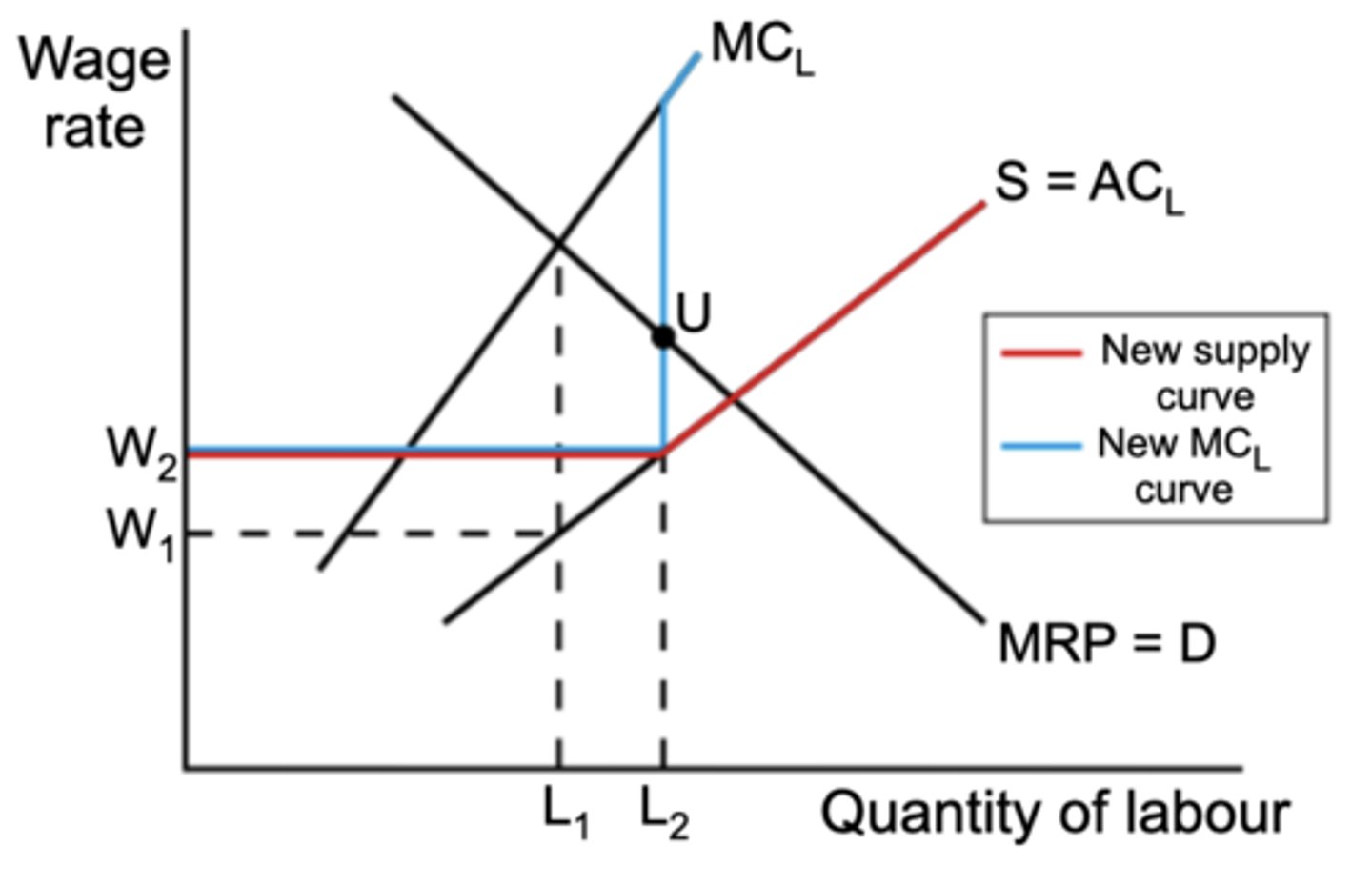
what is a bilateral monopoly
what is the diagram to show the impact of increased wages in a bilateral monopoly
- where would have they been employed at
- what impact was there on the market
when a trade union enters a monopsonistic labour market is an example of a bilateral monopoly, when there is a single buyer and a single seller; the buyer is the monopsonist and the seller is the trade union
- W1L1 is where the monopsonist would've employed without a trade union
- the union bargains for a wage of W2, and they ensure no one is willing to work below this wage rate, creating a kinked supply curve with the kink at W2L2
- this also changes the shape of the MC curve with two kinks
- the inion has increased wages from W1 to W2 and increased employment from L1 to L2
- the trade union has had a positive impact on the labour market
What is wage discrimination?
paying different workers different wage rates for doing the same job
what is labour market discrimination
how can it cause labour market failure
When a specific group of workers is treated differently from other workers in the same job
- due to race, gender, sexuality, religion, age, disability
- against law
- cause unequal distribution of wealth, misallocation of resources, reduced efficiency, increased costs
how can employers that discriminate incur increased costs
- employers influenced by prejudices believe that the MRP of the discriminated group is lower than it really is, shifting MRP left
- by ignoring workers who may have been more suited to a job and more efficient, they increase their costs of production which can increase prices
- misallocation of resources, the firm loses out on more productive and allocative efficiency, passing on higher costs onto consumers as higher prices, reducing consumer surplus, competitiveness and profits
how does discrimination cause increased cost for gov
- gov may need to increase welfare payments to support discriminated workers which is unnecessary if discrimination didn't happen
- discriminated workers working for unfairly low wages will also reduce gov tax rev
what is geographical immobility of labour
what are the reasons for geographical immobility
what impact does this have on the labour market
geographical immobility of labour is when workers are not able to or are reluctant to move to different locations to find jobs suited to them
- When this happens, they end up unemployed or in jobs that are not suited to them causing a misallocation of resources and market failure
- The reasons for geographical immobility are that people do not want to move away from friends and family and that it is expensive to move, there may also be imperfect knowledge of the work in different regions
- this can lead to labour shortages in one area and surpluses in another area
what is occupational immobility of labour
what are the reasons for occupational immobility of labour
how can occupational immobility of labour be affected by age
what is the impact of occupational immobility of labour on the labour market
occurs when workers find it difficult or impossible to move from one occupation to another with ease
- reasons for this may be that workers cannot easily transfer their skills from one job to another, or they do not have the skills and qualifications which may be high level taking a long time to train
- occupational immobility can be affected by age, as younger workers are more likely to retrain but older workers may lack the confidence and motivation to do so
- occupational immobility can contribute to mass structural unemployment if highly specialised jobs get replaced by capital
what is the flexibility of the labour market
how does the gov try to increase this
what is the flexibility of the labour market in the eyes of a firm
How willing and able labour is to respond to changes in the conditions of the market
- gov acts to increase the flexibility of the workforce by the provision of education and training schemes to help workers gain skills and knowledge
- for employers, a flexible workforce is one that can be hired and fired easily, which due to the efficiency, encourages employers to take on more workers as they can change the size of their workforce quickly and cheaply