11/4 buad 280 exam 2
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
land
tangible
land improvements
tangible
buildings
tangible
equipment
tangible
natural resources
tangible
patents
intangible
trademarks
intangible
copyrights
intangible
franchises
intangible
goodwill - intangible or tangible
intangible
appraisal fee
cost to provide opinion on market value of property
fair value
estimated stand alone selling price
as natural resources are used, cost is allocated to an expense through a process called
depletion
land capitalized costs
purchase price + closing costs - sale of salvaged materials
closing costs
attorney fees, agent commissions, title, title search, recording fees, back taxes, other obligations, clearing, filling, leveling, removing old buildings
how to record amount for fair values for basket goods
estimated fair value / allocation % out of total fair values
multiply by amount of basket purchase (price when sold together)
record amount
purchase of intangible assets
purchase cost + legal fees
how are internally developed intangible assets recorded?
expensed on income statement as incurred
when is goodwill recorded
when part of the acquisition of another business
when the purchase price exceeds the fair value of net identifiable assets
how to calculate goodwill
fair value of assets acquired - fair value of liabilities assumed = fair value of identifiable net assets
purchase price - fair value of identifiable net assets = goodwill
when to capitalize
expenditures are capitalized if it benefits future periods
when to expense
expenditures are expensed if it benefits only the current period
repairs and maintenance - capitalize or expense?
when maintaining a given level of of benefits → minor → current → expense
making major repairs that increase future benefits → capitalize
addition - capitalize or expense?
adding a new major component → capitalize
improvement - capitalize or expense?
replacing a major component → capitalize
legal defense of intangible assets - capitalize or expense?
incurring litigation costs to defend the legal right to the asset → capitalize
if defense is unsuccessful → expense
depreciation
the process of allocating the cost of an asset to an expense over its service life
accumulated depreciation
contra asset account that represents total depreciation since the equipment was purchased
entry to record annual depreciation for equipment
debit depreciation expense, credit accumulated depreciation
book value
cost of asset - current balance in accumulated depreciation
depreciable cost
asset’s cost - residual value
straight line method when reestimating
depreciation expense = (cost - residual value) / initial service life
depreciation after x years = depreciation expense * x
book value after x years = cost - depreciation after x years
depreciation expense in the reestimate year = (book value after x years - residual value) / number of more years
double-declining balance method (depreciation rate)
calculate straight-line rate: 100 / useful life = x
2x = double-declining
depreciation rate per unit
(asset’s cost - residual value) / total units expected to be produced
when does impairment occur
book value > future cash flows or benefits
impairment loss
book value - fair value
what does the impairment loss entry look like
entry reduces net income and total assets by amount of impairment loss
net realizable value
market price - any additional costs necessary to sell it
estimating value of lost inventory
gross profit = gross profit ratio % * net sales
cogs = net sales - gross profit
ending inventory = beginning inventory + purchases - cogs
depreciation expense
total capitalized costs / useful life
adjusting net income from lifo to fifo
cogs under lifo - lifo reserve = cogs under fifo
income tax expense under lifo + (lifo reserve * tax rate) = income tax expense under fifo
net income under fifo = revenue - cogs - income tax expense
writing off uncollectible balance
debit allowance for doubtful accounts, credit accounts receivable
when costs are increasing, fifo results in
lower cogs, higher ending inventory values, higher net income
times interest earned (tie)
measures a company’s ability to meet its interest obligations with operating income
how to record an increase in the allowance for doubtful accounts
debit bad debt expense, credit allowance for doubtful accounts
ending allowance balance =
beginning balance + bad debt expense - write offs
activity based depreciation
depreciable base = cost - salvage value
depreciable rate per mile = depreciable base / total estimated miles
depreciation expense = miles driven * depreciable rate per mile
ammortization expense
depreciation rate * cost = expense
cost - expense = book value end of year one
book value end of year 1 * depreciation rate = book value end of year 2
repeat as necessary
under accrual accounting, revenue is recognized…
when earned
big bath accounting
taking large write offs in one period
when does depreciation stop?
when book value reaches salvage value
vertical analysis
income statement items as a percentage of net sales
balance sheet items as a percentage of total assets
horizontal analysis
percent change = (second year amount - base year amount) / base year amount
liquidity ratios
short-term
current ratio
quick ratio
operating cash flow to current liabilities
solvency ratios
long-term
debt-to-equity
times interest earned
profitability ratios
measures earnings or operating effectiveness of a company
accounts receivable turnover
how many times receivables have been collected during the period
inventory turnover
shows how quickly a company sells its products and restocks them over a period of time
ppet
how effectively a company uses its property, plant, and equipment to generate sales
sales allowance
contra revenue account - reduces revenue and current assets
2/10, net 30
customer will receive a 2% discount if amount owed is paid within 10 days
if customer does not take the discount, full payment is due within 30 days
nonrecurring items
employee layoffs
consolidating production facilities
reorganizing sales operations
outsourcing some activities
terminating or relocating employees
write-down of long-term assets
benefits of credit sales
increased sales
customer loyalty
competitor advantage
disadvantages of credit sales
loss of time value of money
risk of non-collection
allowance method
establish an allowance
debit bad debt expense, credit allowance for doubtful accounts
write off actual bed debts
reduce accounts receivable and allowance for doubtful accounts
re-estimate ending allowance balance and make adjusting journal entry
debit bad debt expense, credit allowance for doubtful accounts
percentage of receivables method
amount in accounts receivable * percentage uncollectible
aging of accounts receivable method
based on estimated uncollectible per aging bucket
more accurate than using a single percentage
accounts receivable write off
debit allowance for uncollectible accounts, credit accounts receivable
record collection of accounts receivable previously written off
debit accounts receivable, credit allowance for uncollectible accounts
debit cash, credit accounts receivable
inventory cost
sum of all the direct costs to bring the inventory to salable condition
inventory cost includes
purchase price
shipping costs
insurance while in transit
fees or taxes paid to get the inventory ready to sell
less returns, allowances, and discounts
inventory cost does not include
most administrative costs (liability insurance, utilities, salaries)
most marketing costs
research and development costs
balance sheet approach
fifo - amount it reports for ending inventory (which appears in the balance sheet) better approximates the current cost of inventory
when costs are increasing, lifo results in
higher cogs, lower ending inventory, lower net income, lower income taxes
income statement approach
lifo - the amount it reports for cogs (which appears in the income statement) more realistically matches the current cost of the inventory needed to produce current revenues
lifo conformity rule
requires a company that uses lifo for tax reporting to also use lifo for financing reporting
fob shipping point
ownership of goods transfers to the buyer when it is placed on the truck/carrier
fob destination
ownership of the goods transfers to the buyer when it is delivered at its destination
consignment inventory
supplier (consigner) physically provides inventory to a retailer (cosignee) for sale, but the supplier retains ownership of the inventory until the goods are sold to the end customer
tangible and not subject to depreciation
those with indefinite useful lives - land
intangible and subject to ammortization
those with finite useful lives
patents
copyrights
trademarks (with finite life)
franchises
intangible and not subject to amortization
those with indefinite useful lives
goodwill
trademarks (with indefinite life)
service life, useful life
estimated use the company expects to receive from the asset before disposing of it
residual value, salvage value
the amount the company expects to receive from selling the asset at the end of its service life
straight-line depreciation method
Depreciation base: cost - residual value
Depreciation rate: 1/estimated useful life
Depreciation base * depreciation rate = depreciation expense
double-declining balance method
depreciation expense = (cost * 2) / useful life
activity-based depreciation
Depreciation base: cost - residual value
Depreciation expense: depreciation base / total life in units
most companies use for depreciation
straight line for financial reporting
accelerated for tax reporting
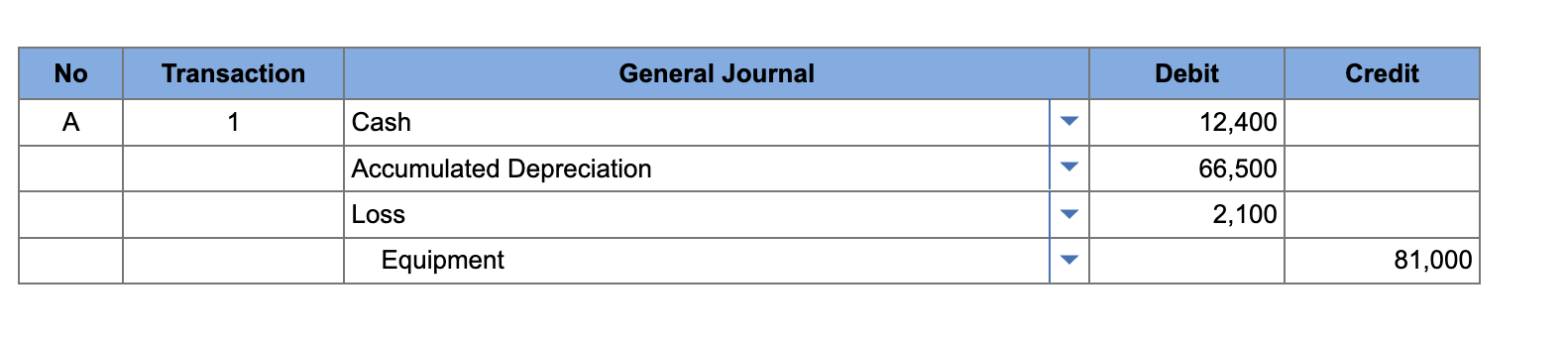
Hot Stone Creamery sold ice cream equipment for $12,400. Hot Stone originally purchased the equipment for $81,000, and depreciation through the date of sale totaled $66,500.
Record the gain or loss on the sale of the equipment.
debit cash 12400
debit accumulated depreciation 66500
debit loss 2100
credit equipment 81000
cash = sale amount
accumulated depreciation = amount depreciated
loss: purchase price - accumulated depreciation = book value → book value - sale amount = loss
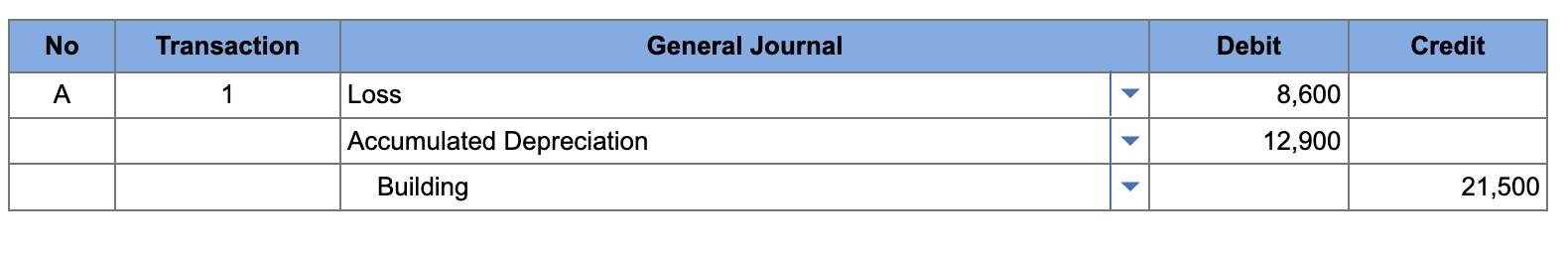
On January 1, Masterson Supply purchased a small storage building for $21,500 to be used over a five-year period. The building has no residual value. Early in the fourth year, the storage building burned down.
Record the retirement of the remaining book value of the storage building.
debit loss 8600
debit accumulated depreciation 12900
credit building 21500
loss = (purchase price / useful life) * years unused
accumulated depreciation = (purchase price / useful life) * years used
building = purchase price
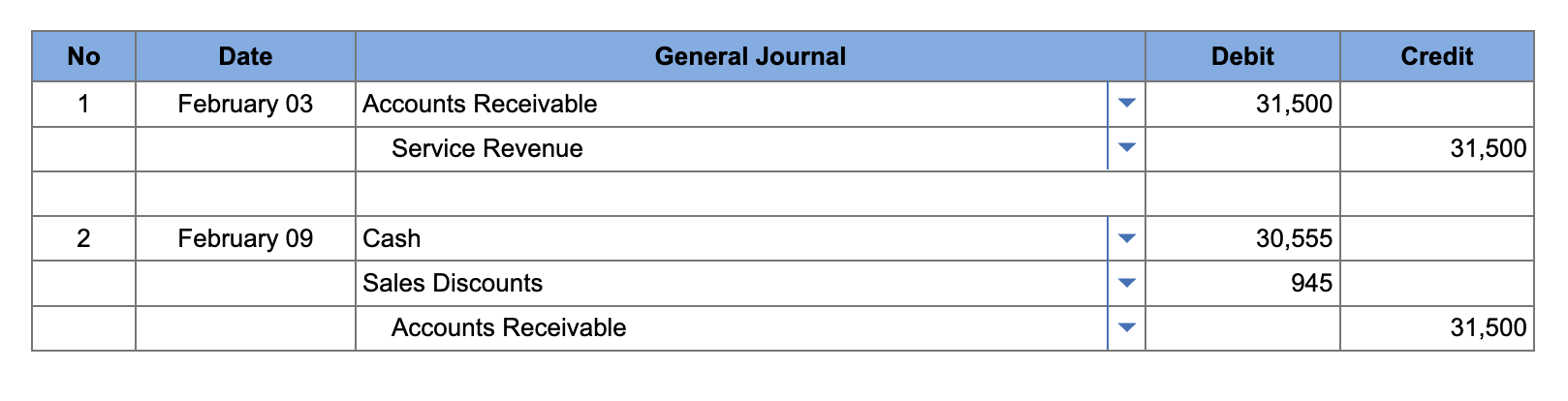
On February 3, a company provides services on account for $31,500, terms 3/10, n/30. On February 9, the company receives payment from the customer for those services on February 3.
Record the service on account on February 3 and the collection of cash on February 9.
feb 3
debit accounts receivable 31500
credit service revenue 31500
feb 9
debit cash 30555
debit sales discounts 945
credit accounts receivable 31500
A company has the following account balances at the end of the year:
Credit Sales = $400,000
Accounts receivable = $80,000
Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts = $400 credit
The company estimates future uncollectible accounts to be 4% of accounts receivable. At what amount would Bad Debt Expense be reported in the current year’s income statement?
2800
At the end of the year, an adjusting entry is recorded to reduce ending inventory from its recorded cost to net realizable value (NRV). The adjusting entry involves
Debit Cost of Goods Sold; credit Inventory
cogs =
beginning inventory + purchases - ending inventory
lower of cost/net realizable value method
multiply quantity by whichever is lower (unit cost or unit nrv)
add for each item
When a company determines that the net realizable value of its ending inventory is lower than its cost, what would be the effect(s) of the adjusting entry to write down inventory to net realizable value?
decrease total assets, decrease net income, decrease retained earnings
a trade discount results in…
revenue being recorded for the discounted price
closing costs acronym
arya always takes time roller blading on concrete floors like roads