lf206 lecture 13 - proteostatsis and autophagy
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
proteostasis is the dynamic regulation of the ______ _________ within the cell
balance is maintained by biosynthetic pathways and degradation pathways i.e. proteasomal _______ and _______
protein compliment
degradation
autophagy
what is autophagy?
process of self-digestion within the cell involving delivery to lysosome for degradation
cytoplasmic material is recycled
why do cells use autophagy? [3]
provides amino acids, nucleotides, lipids and sugars under low nutrient conditions
removes aggregates, damaged organelles and invading pathogens
cell differentiation and developmental remodelling (e.g. removing nucleus from an erythrocyte)
types of autophagy?
chaperone-mediated autophagy (proteins that display a particular motif, transported to lysosome)
microautophagy (direct interaction between lysosome and what needs to be degraded, i.e vesicles, small aggregates)
macroautophagy (isolation membrane encapsulates cell contents to be degraded)
during macroautophagy, a __________ forms to encapsulate cell contents
types of macroautophagy [2]
autophagosome
canonical autophagy - non-specific
xenophagy - of proteins
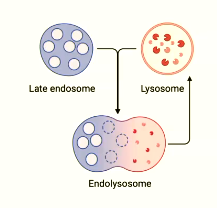
lysosome is central for intracellular _________
proteins enter vesicles called early _______ which will mature into late endosome
as pH ________, enzymes within late endosome _______
late ______ fuses with lysosome to form an _________
degradation
endosome
decreases
activates
endosome
endolysosome
how is lysosome pH maintained?
__-type ATPases hydrolyse ___ to pump protons ___ the lysosome
this creates a _____ gradient
this is maintained by losing _____ or gaining _____
V-type
ATP
into
voltage
cations (positive)
anions
CHAPERONE MEDIATED AUTOPHAGY RECOGNITION
Hsc70 identifies ______ motifs of LAMP (_______ ______ ______ _______) proteins on _____ surface
describe the motif
has up to 2 ______ charged residues - _ & _
up to 2 _______ resides - I, F, _ or _
a single _______ charged residue- _ or _
a single _ on either the N or C terminus
the motif can be in any _____
KFERQ
lysosome associated membrane proteins
lysosome
positively - K, R
hydrophobic - L, V
negatively - E, D
Q
order
CHAPERONE MEDIATED AUTOPHAGY
inactive _____-2A
Hsc70 recognises ______ motif and delivery of _____ to LAMP-2A
_______ of LAMP-2A by Hsp__
_________ of protein mediated by Lys-Hsc70
unused LAMP-2A is captured by ___ and transferred to lipid ______ to break them down by ______ A and a metalloproteinase
LAMP
KFERQ, protein
multimerisation, 90
translocation
Hsc70, microdomain, cathepsin
DOWN-REGULATION OF CHAPERONE MEDIATED AUTOPHAGY
mTORC2 complex ______ Akt1 by __________
Akt1 phosphorylates ____
phosphorylated ___ keeps LAMP-2A _____
this occurs in ____ nutrient conditions as the conditions _____ mTORC2
activates, phosphorylation
GFAP
GFAP, inactive
high, stimulate
Tau is a ______ in _____-mediated autophagy
in neurodegenerative diseases we see CMA dysfunction meaning Tau ______ → Alzheimer’s
too much up-regulation of CMA, degradation of tumour _____ and pro-_______ proteins favour/promote _______
substrate
chaperone
accumulates
suppressors
apoptotic
cancers
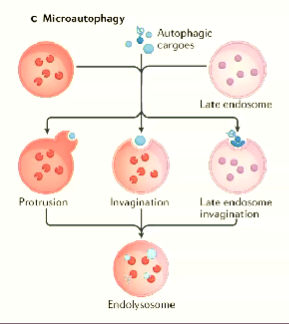
in microautophagy, autophagic ______ are taken up directly by late _____ and lysosomes
some microautophagy substrates have ______ motifs and are delivered by _____ - it binds to ________ in late endosome membrane
cargo is degraded in _______ or lysosomal lumen
cargoes
endosomes
KFERQ
Hsc70
phosphatidylserine
endolysosomal
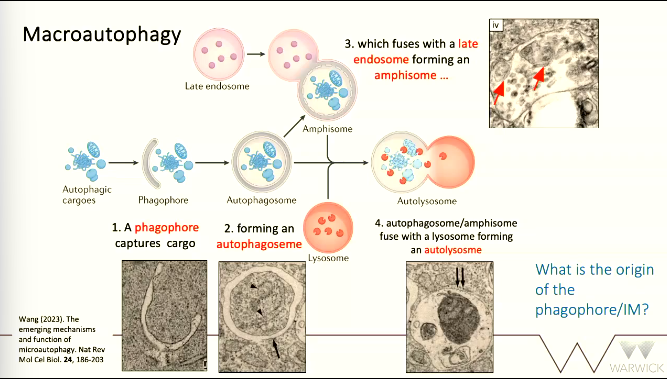
MACROAUTOPHAGY
a ______ grows and captures cargo
it fuses with itself forming an __________
autophagosome fuses with a late ______ to form an _______
the autophagosome/_______ fuse with a lysosome to form an _______
_______ occurs
phagophore
autophagosome
endosome, amphisome
amphisome, autolysosome
degradation
steps of forming autophagosomes [4]
autophagosomes are used only in which type of autophagy?
initiation
nucleation
elongation
closure
macroautophagy
INITIATION
mTORC2 phosphorylates ______ which activates mTORC_
mTORC1 phosphorylates ____ in ___ places
phosphorylation of ____ inhibits _________
________ is stimulated during starvation
ULK1 complex associate at __ membrane and capture _____ vesicles
these vesicles are cycled between ____ membrane and trans-_____ network as they maintain membranes
____ is associated with these vesicles
ULK1 ____ phosphorylates ____ (BECN) which activates PI3K
PI3K is a _____ kinase,
adding ______ to lipids
turning phosphatidylinositol to phosphatidylinositol (3)-phosphate (PI3P)
Akt1
mTORC1
ULK1, 2
ULK1, macroautophagy
macroautophagy
ER, ATG9
plasma, Golgi
PI3K
kinase, Beclin
lipid
phosphates
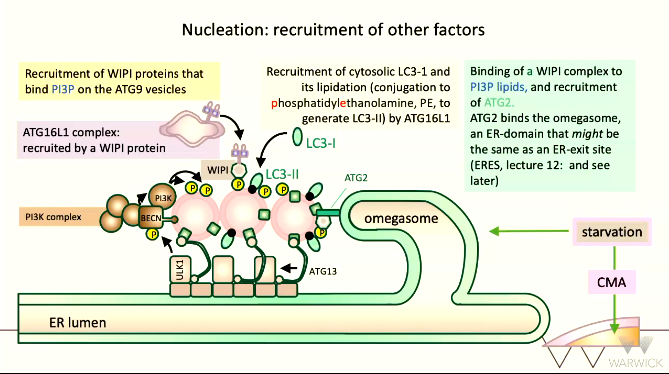
NUCLEATION
____ proteins bind to PI3P on the ATG9 vesicles
_______ is recruited by WIPI proteins
LC3-1 is recruited by ATG16L1
binding of WIPI and PI3P lipids also recruit ___ which binds the ______some
WIPI
ATG16
ATG2, omegasome