Biology - Chapter 1 - Principles and the basic structures of life
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
bacteria
unicellular microorganisms some of which are pathogenic in humans, animals and plants
cell membrane
A selectively permeable membrane surrounding the cell and controlling the entry and exit of materials
chloroplast
contains green pigment chlorophyll, the site of photosynthesis
nucleus
controls what happens in the cell, where the chromosomes are located
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
The adaptation of the cells lining the small intestine
Has a large surface area to absorb more food faster
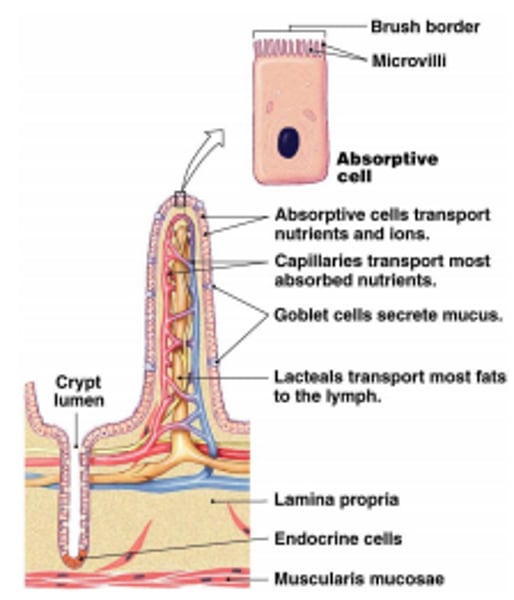
Why are unicellular organisms at a disadvantage?
They do not live for long as it gets tired easily and there is no other cell to replace it.
Epithelium
Forms the coverings and linings of the body
adaptation
A feature of an organism's body which helps it to survive.
cell
Basic unit of life
unicellular
A single celled organism
multicellular
Made up of more than one cell.
cell wall
provides support and prevents bursting by osmosis. Keeps the plant cell turgid
cytoplasm
the living substance inside a cell, where chemical reactions take place
mitochondria
where respiration takes place (powerhouse)
specialised cell
A cell that has become differentiated to carry out a particular function, eg red blood cell.
tissue
A group of similar cells that perform the same function.
vacuole
a space in the cytoplasm of plant cells that contains cell sap
prokaryotic cell
cell without a nucleus that is found in single-celled organisms, ex bacteria
eukaryotic cell
cell with nucleus and organelles present. Found in all other living organisms apart from bacteria.
Animal cell division step 1
Nucleus divides
Animal cell division step 2
The cytoplasm pinches off between the two nuclei and two daughter cells are formed.
Animal cell division step 3
Two daughter cells are now individual, where one of them becomes a specialized cell.
Plant cell division step 1
The nucleus divides to become two, and a new cell wall forms to separate them.
Plant cell division step 2
One of the cells enlarges, vacuoles form and force the cell to expand, and eventually the two cells separate
The adaptation of red blood cell
No nucleus for more space for haemoglobin to carry more oxygen
The adaptation of a muscle cell
Has a lot of mitochondria
Adaptation of nerve cell
Long cytoplasm to carry messages easily
Adaptation of palisade cell
Contains chloroplasts
Adaptation of root hair cell
Bigger surface area to absorb more water and nutrients from the soil
How do unicellular organisms carry out all the functions?
They have a large surface area to volume ratio
Multicellular organisms (animals) consist of:
organelles-cells-tissues-organs-organ systems-organism
Connective tissue
Found between the body organs binding the parts together
Muscle tissue
Contracts, resulting in movement
Nervous tissue
Transmits messages/nerve impulses
Mesophyll tissue
Photosynthesis occurs here
Epidermis (plant tissue)
The outer layer of the root