UCSD BILD 1 Midterm 1
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
What are the characteristics of living things?
have an orderly structure made of cells, produce offspring, grow and develop, and adjust to changes in the environment
How is life organized, from atoms to organisms?
atoms > molecule > macromolecule > organelle > cell > tissue > organ > organ system
Where do organisms get more matter/atoms as they develop?
nutrients in food
What are the unique properties of water?
It is a polar molecule, has a high specific heat, and is denser as a solid
hydrophobic
having an aversion to water; tending to combine and form droplets in water
hydrophillic
having an attraction to water
covalent bond
a chemical bond formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons
ionic bond
a chemical bond resulting from the attraction between oppositely charged ions
Why do chemical bonds require more energy to break than hydrogen bonds?
hydrogen bonds are only held together by partial charges (polarity); ionic chemical bonds have lattice energy and covalent chemical bonds have bond enthalpies that make them stronger
hydrogen bond
weak attraction (van der Waal forces) between a hydrogen atom and another atom; causes cohesive forces in water
meniscus
the curved upper surface of a liquid in a graduated cylinder
surface tension
the force that acts on the surface of a liquid and that tends to minimize the area of the surface
Ex:water freezes
cohesion
water is sticky to other polar or charged things. Water forming hydrogen bonds with each other
adhesion
water is sticky to itself. surface tension leads to distributing broadly.
diffusion
the process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
osmosis
the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
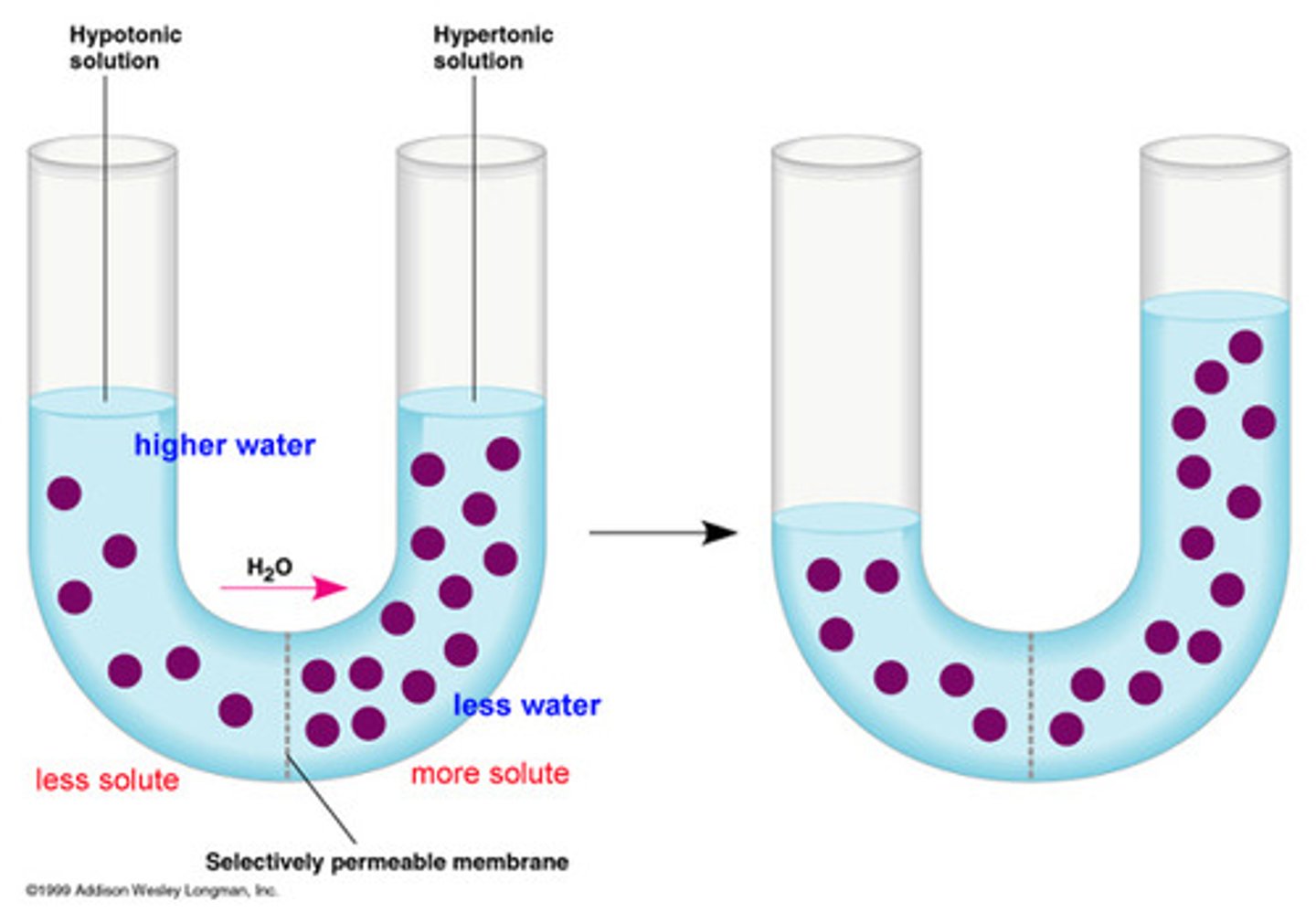
In a "U" shaped cylinder with a semipermeable membrane separating concentrations of sugar, will water move to a higher or lower concentration of sugar?
water will move from the lower concentration to the higher concentration; this will make the concentrations equal
What are the main types of biomolecules?
lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, proteins
lipids
fats; free fatty acids, triglyceride, phospholipids, and cholesteryl ester
what is the function of lipids?
to store energy, make cells compartmentalize, and insulate
trigylceride
lipids containing three fatty acids and a glycerol; how an organism stores fat
amphipatic, fluid mosaic model of phospholipids.
having both a hydrophilic region and a hydrophobic region
phospholipid
fatty acid with glycerol
What is unique about the structure of phospholipids?
they have a hydrophillic head and hydrophobic tail; form phospholipid bilayers to maintain a barrier between inside/outside a cell
saturated fatty acid
a long-chain hydrocarbon with single covalent bonds in the carbon chain; solid, tightly packed physical properties
unsaturated fatty acid
a fatty acid whose hydrocarbon chain contains one or more double covalent bonds in the carbon chain; fluid and chaotic physical properties
CHOLESTEROL/LIPIDS
cholesterol is a lipid, In animal cell
nucleic acids
nucleotides five carbon, phosphate groups, nitrogen bases(pyramidine/purine): links phosphodiester linkages which is the phosphate links sugar of 2 nucleotides:sugar with phosphate backbone:, DNA, RNA.
pyrimidines,purines
pyramidine:cytosine and thymine; single ring structure
purine:guanine and adenine; double ring structure
amino acid
monomers of proteins, amino and carboxyl group
Two amino acids joined by what
dehydration reaction:losing a water molecules.
hydrolysis: addition of water to break glucose monomers
enzymes
proteins that act as biological catalysts
what is the structure of an amino acid?
central carbon, amino group, carboxyl group, side chain (R-group)
what determines and amino acids's charge?
the side-chain (R-group), which makes the amino acid unique in chemical structure
how is a protein made?
transcription (nucleus), translation (cytoplasm), and protein folding
polymer
molecules composed of many monomers; makes up biomolecules
monomer
a simple "building block" compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
DNA and RNA
Thymine in DNA, Uracil RNA.
DNA struc: double helix
RNA struc: roughly L-shaped.
same: cytosine, guanine, adenine.
carbohydrates (CH2O)n
sugars and starches, in simple monosacchrides, disacchrides or complex structures polysaccharides
what is the function of carbohydrates?
energy, cell markers/communication, structure support (cell walls)
proteins
chains of amino acids
primary structure of protein
sequence of amino acids
secondary structure of protein
protein structure that forms when by folding and twisting the amino acid sequence; alpha helix and beta pleated sheet
what is the difference between an alpha-helix and beta-pleated sheet in a protein's secondary structure?
alpha-helix is weaker than a beta-pleated sheet because there are less amino acid sticking to one another
tertiary structure of protein
protein structure that forms from the secondary structure folding again to from a larger 3D structure.
quaternary structure of protein
protein structure consisting of several 3D protein structures
RNA world hypothesis
hypothesis that RNA served as the genetic information of early life
What are the three domains of life?
Eukarya, Archaea, Bacteria
what are the functions of the endomembrane system?
protein synthesis/transport, lipid synthesis/transport, detoxification, and other metabolic processes
what components are in the endomembrane system?
nuclear membrane, rough ER, smooth ER, golgi appartus, vesicles, and cell membrane
nuclear envelope
layer of two membranes that surrounds the nucleus; covered in pores to allow ribosomes/RNA to exit
smooth ER
the portion of the endoplasmic reticulum that is free of ribosomes; synthesizing lipids, metabloize carbohydrates, detoxify, store calcium
rough ER
the portion of the endoplasmic reticulum studded with ribosomes; synthesizes proteins in cysternal space
endoplasmic reticulum
a system of membranes that is found in a cell's cytoplasm and that assists in the production, processing, and transport of proteins and in the production of lipids
golgi apparatus
a system of membranes; receives vesicles from ER that fuse with Golgi, modifies/stores/transports products of ER, and move from cis to trans side
cell membrane
thin, semipermeable barrier around a cell that is made of phospholipids; regulates what enters/leaves the cell
what differs between cell membranes with saturated or unsaturated fats in the cell membrane?
unsaturated fats cause "kinks" in the membrane that allows it to be more fluid; saturated fats are tightly packed and make the membrane viscous
active transport
the movement of materials through a cell membrane using energy
passive transport
the movement of materials through a cell membrane without using energy
what are the components of the cytoskeleton?
microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules
what makes mitochondria and chloroplast unique?
they were originally bacteria engulfed by a eukaryotic cell that developed a symbiotic relationship
how are vesicles transported?
actively transported by motor proteins (dynein) that move along the cytoskeleton
Polysacharides-glycogen
Animals store a polysaccharide called glycogen, a poly-mer of glucose that is like amylopectin but more extensively branched Vertebrates store glycogen mainly in liver and muscle cells.
An amino acid is an organic molecule with both an amino
group and a carboxyl group. how to form a peptide bond?
An amino acid is an organic molecule with both an amino
group and a carboxyl group. Peptide bond is through amino acids.
Primary structure
sequence of amino acids
secondary structure
Regions of repetitive coiling or folding of the polypeptide backbone of a protein due to hydrogen bonding between constituents of the backbone (not the side chains). Alpha and beta sheets.
tertiary structure
The third level of protein structure; the overall, three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain. Hydrophobic reaction
Interactions between side chains
four types of interaction:
polar side chains- hydrogen bonds
two nonpolar- hydrophobic interactions: water squishes hydrophobic bits they have less surface and they don't touch them.
polar ones on the surface and hydrophobic in the middle
acid amino acids negative with a basepositive- they form ionic bond
Disulfide bridges
A strong covalent bond formed when the sulfur of one cysteine monomer bonds to the sulfur of another cysteine monomer.
Denaturation of proteins
proteins go to inactive form (back to their primary sequence) Can take place with changes to pH, salt concentration, temperature, or exposure to toxic compounds
Protien dentures mean break. Acidic upping hydrogen ions. Postiive charges get in between hydrogen bonds and distrupt them.Secondary and tertiary break apart. Disruption of hydrogen bonds is highly severe than ionic bonds.
Nucleic acids
store and transmit genetic information. Made of nucleotides.
DNA/RNA structure
- the nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, are polymers of nucleotides
- linked together by phosphodiester bonds
- Structure of DNA: storing, deoxyribose sugar, only has thymine nitrogenous base, double stranded("helix shape).
2 line of nucleotides, Orientated inversely , hold together by hydrogen bonds nitrogenous bases, G-C, A-T,
Structure designed to be stable
Structure of RNA: transmitting, ribose sugar, only has uracil nitrogenous base,single stranded- variable, G-C, A-U.
Similar: guanine, adenine, cytosine
Hydrocarbons
Compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen
Fat molecule: hydrophobic molecules that don't form true polymers, glycerol linked to fatty acid tails. Hydrocarbon
Tails is the reason it makes hydrophobic.
hydrocarbon chains are
hydrophobic, nonpolar
Phospholipid/steroids
Phospholipids:
The core building block of cell membrane, it has glycerol, two fatty acid tails, very hydrophobic Tails, charged polar hydrophilic head(glycerol and phosphate). Amphipathic(half interacts with water and
Half does not).
Steroids: characterized by four fused rings at the core. Ex: Cholesterol, steroids
This one is cholesterol in the image, unique it has membrane function rather than communication function.
Difference between prokaryote and eukaryote cell
Prokaryote
Traits:
Nuclous free floating in cytoplasm.
Does not have membrane bound organelles
Single circular chromosome
Eukaryote:
more complex multicellular karyotes, they can be both.
On average 10x bigger than pro.
Have nucleus- protects DNA
Membrane bound organelles- substructure
Multiple linear chromosomes
Difference between plant and animal cells
Plant cells have larger vacuoles, a cell wall, and chloroplasts
Cell wall
Chloroplasts- capture light make it into complex molecules
Central vacuole
ribosomes, nucleus, cytoplasm
Nucleus: houses the cells genetic information(dna).
Prevent damage, what comes in and out of the cell.
Nucleolus- assemble ribosomes.
DNA wrapped around
Ribosomes:
Large complexes of protein and RNA that synthesize proteins. Structure not an organelle.
Two places, free floating in cytoplasm, others attached to the ER .Ribosomes job is making proteins on the ER than the cytoplasm.
Smooth and rough ER
Rough ER (rER)• Bound Ribosomes• Glycoprotein Synthesis • Transport Vesicles• Synthesize Membrane
Smooth ER (sER)• No ribosomes• Synthesizes Lipids • Metabolizes Carbs • Detoxifies Drugs
Golgi apparatus
Modifies proteins, Sorts and packages materials into vesicles3 types:
Microtubules, Microfilaments, Intermediate filaments.
Lysosomes
cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell.
sphere of membrane contain digestive enzymes.
Enzymes breaking large proteins,
-Used for food vacuole
-Autophagy: auto-self phagy-eating, in all eukaryotes, any organism.
Breaking down organelles and replacing them, and lysosomes are part of that process.
Do it in contained membrane structures to protect your self .
Difference between mitochondria and chloroplasts
Mitochondria:
Different from organelles
Two membrane layers, outer and inner. Outer highly structured Inner is folded In between is inter-membrane space. Inside the inner membrane is the matrix.They have their own DNA. Core of genetic material is in the DNA.. Eukaryotic have circular DNA and they have their own ribosome. Ribosomes in the mitochondrial matrix more look like prokaryotic ribosomes.Replicate their own sleeves, control their own production.Your cell can't make mitochondria.
Chloroplast:
convert light and water into sugar.
-produce independently
- two membranes sepa- rated by a very narrow intermembrane space.
- Inside the chloroplast is another membranous system in the form of flattened, interconnected sacs called thylakoids. In some regions, thylakoids are stacked like poker chips;
- The fluid outside the thy- lakoids is the stroma, which contains the chloroplast DNA and ribosomes as well as many enzymes.
- The membranes of the chloroplast divide the chloroplast space into three com- partments: the intermembrane space, the stroma, and the thylakoid space. This compartmental organization enables the chloroplast to convert light energy to chemical energy
Cytoskeleton
cytoskeleton is to give mechanical support to the cell and maintain its shape. This is especially important for animal cells, which lack walls.
Membrane proteins
Transporter- move things across membranes
Enzymes- attached to membrane to complete a job
Sing- proteins on surface of cell, release a signal
Cell-recognition- glycoproteins
Inter join- hold cells together
viscous fluid
fluid: Unsaturated hydrocarbon tails (kinked) prevent packing, enhancing membrane fluidity. decreased temperature
Viscous
Saturated hydrocarbon tails pack together, increasing membrane viscosity.
Cholesterol reduces membrane fluidity at moderate temperatures, but at low temperatures hinders solidification.
Diffusion, osmosis, isotonic, hypotonic vs hypertonic
Diffusion
Molecules generally move from high conc, to low concentration areas.
Molecules moving randomly, evenly dispersed. In balance everyone is dispersed-equilibrium
Net diffusion, more likely fluid
Solution(soln): 1 or more things dissolved in another.
Ex: salt water
Solute: thing being dissolved, lesser amount. Ex:salt
Solvent: the things doing the dissolving, present in the greatest amount. Ex:Water
Osmosis: special case of diffusion, when water moves across a semi-permeable barrier. Semi permeable means Somethings cross and some things can't, cell membrane is also a semi-permeable.
Water is following its diffusion gradient, to dissolve.
Water moves to higher solute concentration, diluting down the solute concentration.
Hypotonic vs. Hypertonic
Concentration of solutes outside a cell compared to insdie directs the movement of water.
Hypotonic: Concentration inside a cell is greater than the concentration outside the cell. Water is going to rush inside the cell. lysis: break.
Hypertonic: Concentration inside the cell is less than the outside of the side. Water is going to rush outside the cell. Shriveled.
Isotonic solution: equilibrium state, concentrations balanced. Water moving In and outside of cell.
CO2, O2, Glucose, amino acids, cholesterol, and digestive enzymes, large cargo.
Diffusion with CO2, nonpolar,
O2 simple diffusion
Glucose active transport, pancreative cells(passive transport)
Amino acids, active transport (active backbone is always polar, nutritionally needed).
Cholestrol, simple diffusion, lipids are nonpolar.
Enzymes: active process, usse transport vessicles, are protiens.
Large Cargo
Crosses the membrane using transport Large things in the cell, tons of energy. Phagocytosis- build up cytoskeletons.
Penocytosis- cells sipping little droplets.
Na+/K+ pump
Active transporter that moves three Na+ out of a cell and two K+ into the cell against their respective concentration gradients. Outside is slightly positive and inside negative.
Co-transport with glucose.
Cotransport
Moving 2 different things at the same time. Simultaneous, we want sucrose but it can't cross on its own. Electrochemical gradient does is move the hydrogen ions with a sucrose. Use as a energy source.Each hydrogen ion needs 1 sucrose.
active and passive transport
Passive- following rules of diffusion always take high con to low con, don't need any energy.
Active transport- low con to high con, pumping action, requires energy.
Membrane synthesis
occurs mostly in ER w/ modifications in Golgi Apparatus transport of membrane "pieces" occur in vesicles - inner face of vesicle become outer face.
Vacoules
Food Vacuole-Product of phagocytosis
• Central Vacuole-Large storage organelles found
in plant cells
endosymbiotic theory
The theory that mito- chondria and plastids originated as prokary- otic cells engulfed by a host cell. The engulfed cell and its host cell then evolved into a single organism.
Membrane Selectivity
Nonpolar things move freely across
Polar or charged things can't pass the hydrophobic region of the membrane
without help
polysaccharides links with
macromolecules of 100-1000 monosaccharides linked by glycosidic linkages which is a covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction (glycorefers to carbohydrate).
isotopes
different versions of elements and different number of neutrons. its important because some are used by organisms for radioactive decay and carbon dating(C12-13)is ate and determine how long organisms have died. Used in pet scans as well.
High heat capacity
amount of energy needed to change 1kg of a substance 1celcius. hydrogen bonds increase and temperature increases.
Solvent of life
water attracts anything polar and charged. water is solvent of life.
hydrogen bonds
weak attraction between positive and negative covalent bonds.
Electronegativity
tendency of an atom to pull shared electrons to itself.
CH- weak electro
NO- strong