A&P Test 1 (Ch 1-2)
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
Atomic radiation
Energy released by unstable isotopes/radioactive isotopes
NaCl
Na lose one one electron (cation) and give to Cl (anion)
Na+ and Cl- attracts
Ionic compound NaCl (sodium chloride
Covalent bond examples
H2, O2, H20
Nonpolar covalent bonds
Same element atoms share electrons equally
Polar bonds
Electrons not shared equally bc of electronegativity, forming molecules with a slightly positive and slightly negative end
Hydrogen bonds
Positive H end of polar molecule attracts to negative N/O end of another polar molecule
Electrolytes
Release ions in water; NaCl → Na(+) + Cl(-)
Acids
Electrolytes that dissociate to release hydrogen ions; HCl → H(+) + Cl(-)
Bases
Electrolytes that release ions and combine w/hydrogen ions; NaOH → Na(+) + OH(-)
Salts
Electrolyte formed by reaction btw acid and base; HCl + NaOH → H2O + NaCl
Organic molecules
Contain C, H, dissolve in water/organic coumpounds, non-electrolytes; carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
Inorganic molecules
Don’t contain C, H, dissolve in water and forms electrolytes; water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, inorganic salts
Water
Most abundant inorganic molecule, 2/3 weight of human, medium for most metabolic reactions (intracellular and extracellular fluids), regulate body temperature
Oxygen
Inorganic element, organelles use to release energy from nutrients/food to drive cell’s metabolic activities; 1/5 of air
Carbon dioxide
Inorganic, waste product released during metabolic reactions
Inorganic salts
Abundant in body fluids; sources of necessary ions; help control H2O concentration, pH, blood clotting, nerve and muscle processes
Carbohydrates
Main source of cellular energy; supply materials to build cell structure; contain C,H,O (C6H12O6 = glucose)
Monosaccharides
Single sugars: glucose, fructose
Disaccharides
Double sugars: sucrose, lactose
Polysaccharides
Complex carbs: starch, glycogen, cellulose
Lipids
Soluable in organic substance; component of cell membrane; tryglycerides, phospholipids, steroids
Triglycerides
Most abundant lipid; used for cellular energy; more energy per gram than carbs; contain C,H,O; 1 molecule of glycerol and 3 fatty acids
Phospholipids
1 glycerol + 2 fatty acids + 1 phosphate group, main component of cell membrane
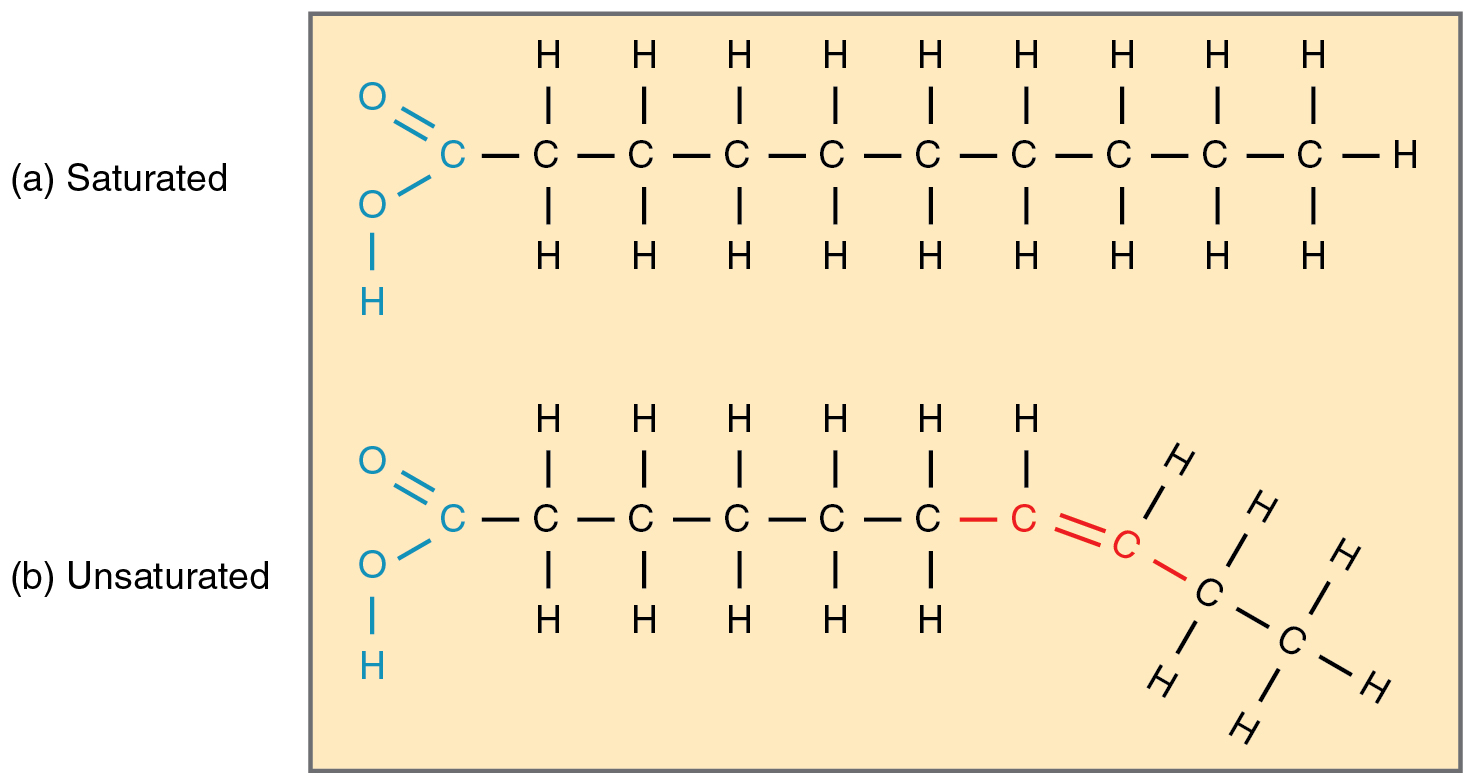
Saturated fat
Only a single carbon-carbon bond, solid at room temperature, most are of animal origin
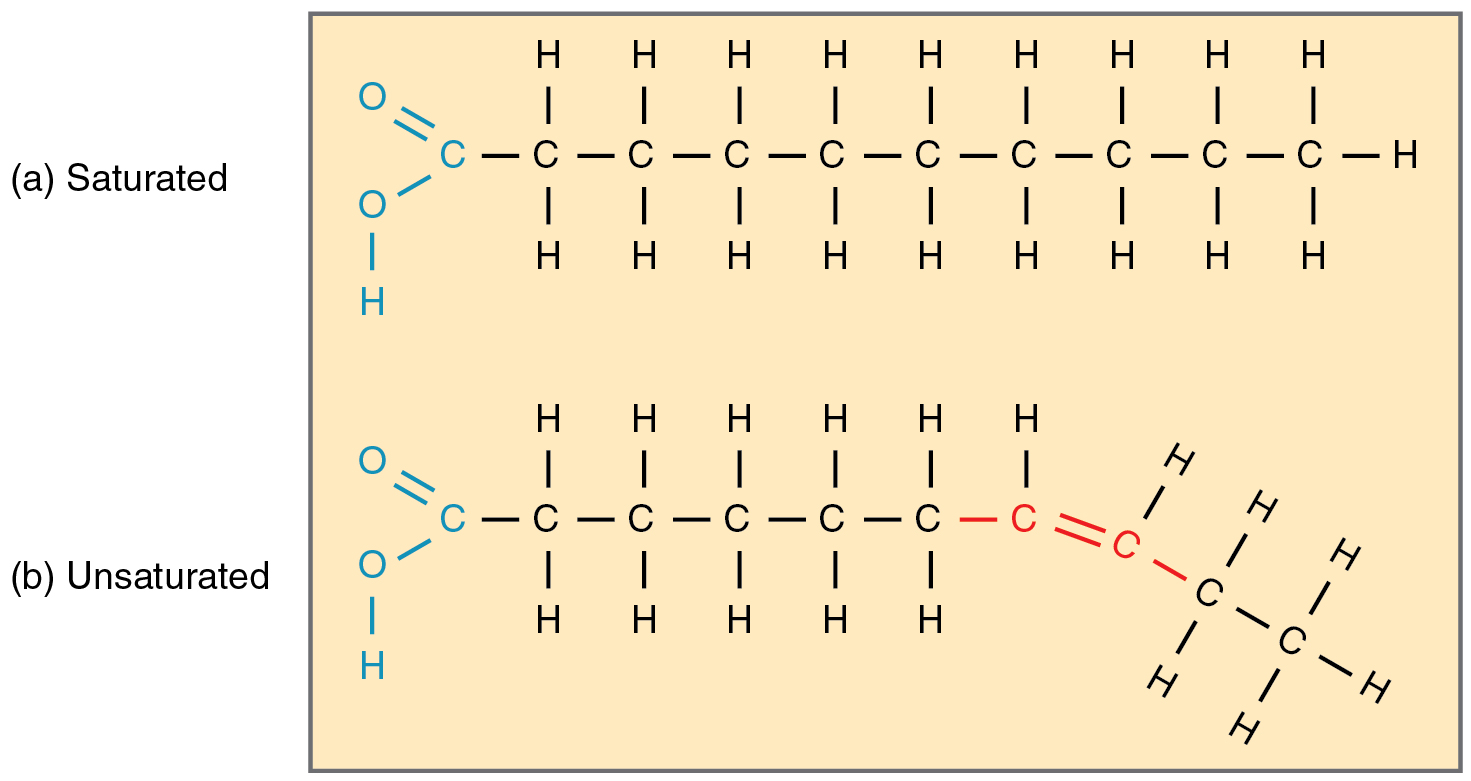
Unsaturated fat
One or more carbon-carbon double bond, liquid at room temperature, most are of plant origin
Steroids
4 connected rings of carbon, widely distributed in body, synthesize adrenal and sex hormones, cholestrol is main steroid in body
Protein structure
Amino acid building block contains an amino (-NH2) group, a carboxyl (COOP) group, and a unique R (side chain) group
Functions of protein
structural materials, energy source, hormones, receptors, enzymes, antibodies
What are amino acids bonded by
Peptide bonds
Primary
Amino acid sequence
Secondary
Pleated/twisted structure formed by H bonding between nonadjacent amino acids
Tertiary
Unique 3D shape (conformation) that determines function
Quaternary
2 or more polypeptide chains are connected to become 1 protein, can be reversible/irreversible
What is denaturation
Change in secondary, tertiary structure, caused by heat
What causes denaturation
Heat, radiation, pH changes, chemical
What does denaturation do
Stops function in enzymes
Nucleic acid structure
5-carbon sugar (S) , phosphate group (P), organic base (B)
DNA
Double chain of nucleotide that carry genetic code; deoxyribose sugar
RNA
Single chain of nucleotides that aid in protein synthesis; ribose sugar
Carbon atoms tend to form
covalent bonds
What does a radioactive element do
undergoes nuclear disintegration
Gamma radiation
Most penetrating and damaging to living things
Glycogen
Animal polysaccharides that consist of branched chains of sugar units and stores energy
Most chemical reactions are reversible in nature
True
The presence of electrolytes in the body is more important than the amount
True
Organic compounds must all contain the carbon atom
True
The fundamental unit of polysaccharide is glucose
True
Inorganic molecules usually contain fewer atoms than organic molecules
True
Ultrasound
High frequency sound waves that shoe soft internal structures
Magnetic Resonance
Magnetic field changes alignment of atoms, showing high-resolution images of internal structures; requires injection of dye
Computerized Tomography
X-Ray emitting device that makes 3D images of soft tissues; differentiates tissues with different densities/tumors
PET
Radioactive isotopes that emit positions (unusual postively charged electrons) to detect biochemical activity
Requirements of organisms
Water, food, oxygen, heat, pressure
Atmospheric pressure
Important for breathing
Hydrostatic pressure
Keeps blood flowing
Visceral peritoneum
Covers abdominal organs
Parietal peritoneum
Lines abdominopelvic cavity
Visceral pericardium
Covers heart
Parietal pericardium
Lines the space of the heart
Visceral pleura
Covers lungs
Parietal pleura
Lines chest wall where the lungs are
Orbital
Eye socket
Otic
Ear
Buccal
Cheek
Cervical
Neck
Axillary
Armpit
Brachial
Arm
Antecubital
Front of elbow
Antebrachial
Forearm
Carpal
Wrist
Cephalic
Head
Costal
Ribs
Inguinal
Groin
Coxal
Hip
Patellar
Knee
Crural
Leg
Pedal
Feet
Occipital
Lower back of the head
Acromial
Shoulder
Dorsum
Back
Cubital
Back of elbow
Lumbar
Lower back
Sacral
Between hips
Perineal
Between buttocks
Sural
Calf
Plantar
Sole
Calcaneal
Heel
Frontal
Forehead
Umbilical/Navel
Belly button
Tarsal
Ankle
Bilateral
Paired; on both sides
Proximal
Close to point of attachment to trunk
Distal
Farther away from point of attachment to trunk
Cross section
A cut across the structure
Oblique section
Angular cut
What do cell membrane mechanisms do
Determine entry of substances and responds to signal
What do energy processes do
Keep cells active
Characteristics of life
Growth, responsiveness, respiration, reproduction, movement, metabolism, digestion, circulation, assimilation, excretion
Respiration
Making energy