Primary Teeth (objectives + highlights + quiz)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Age of eruption and shed for primary maxillary central incisor
E: 7.5 months
S: 6-7 years
Age of eruption and shed for primary maxillary lateral incisor
E: 9 months
S: 7-8 years
Age of eruption and shed for primary maxillary canine
E: 18 months
S: 10-12 years
Age of eruption and shed for primary maxillary first molar
E: 14 months
S: 9-11 years
Age of eruption and shed for primary maxillary second molar
E: 24 months
S: 10-12 years
Age of eruption and shed for primary mandibular central incisor
E: 6 months
S: 6-7 years
Age of eruption and shed for primary mandibular lateral incisor
E: 7 months
S: 7-8 years
Age of eruption for primary mandibular canine
E: 16 months
S: 9-12 years
Age of eruption and shed for primary mandibular first molar
E: 12 months
S: 9-11 years
Age of eruption and shed for primary mandibular second molar
E: 20 months
S: 10-12 years
The maxillary primary first molar generally resembles which permanent tooth?
maxillary premolar
The primary second molars in each arch (maxillary and mandibular) resembles which permanent teeth?
first molar in the same arch
True or False: The mandibular first primary molar does not resemble any other tooth.
True
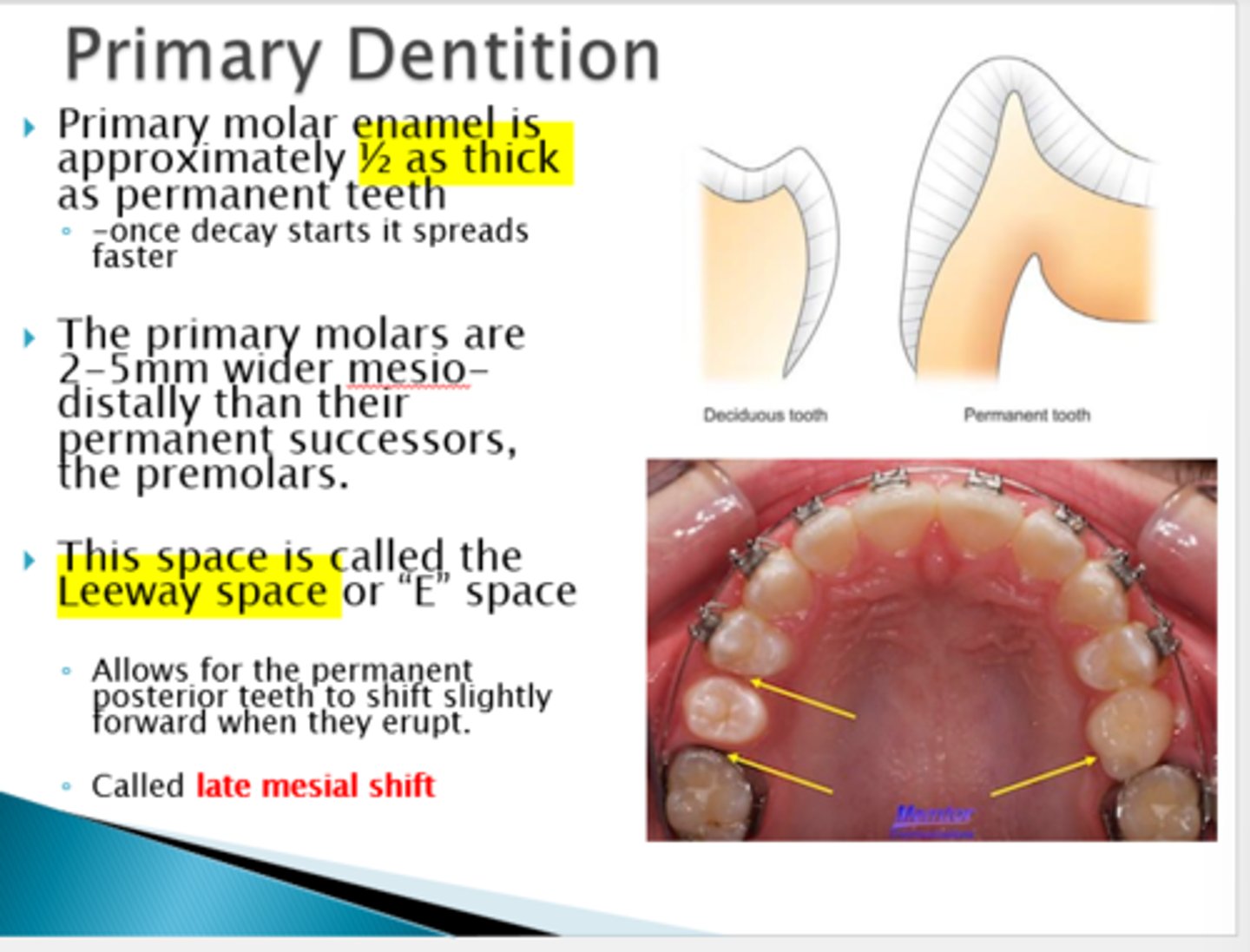
Primary molar enamel is about ________ as thick as permanent teeth.
half
Why does decay spread fast in primary molars?
enamel is 1/2 as thick as primary enamel
_____(2 names)_____ allows for permanent posterior teeth to shift slightly forward when primary teeth erupt.
Leeway space or "E" space
(allows permanent teeth to come in straighter)
On the primary crowns, what is the distinct buccogingival ridge called?
buccal bulge
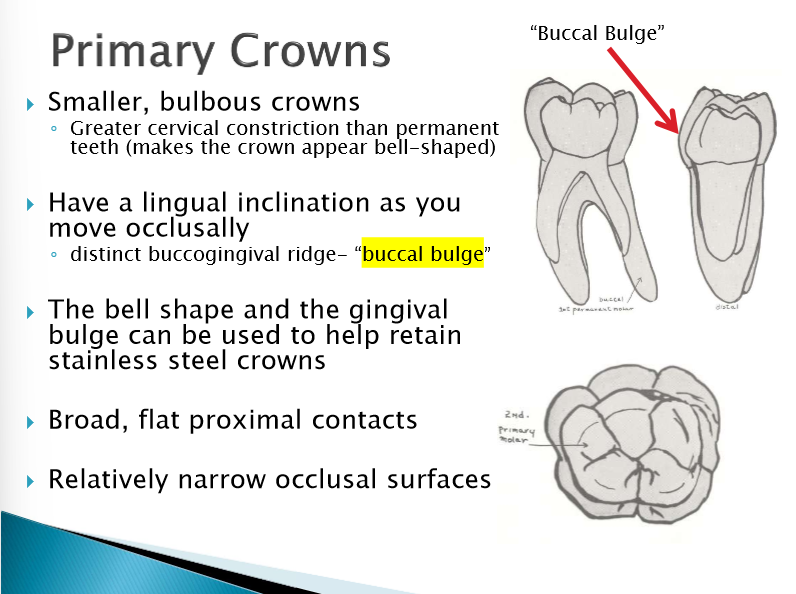
As you move occlusally, what inclination (direction of angle) will the primary crowns have?
lingual
The bell shape and the gingival bulge can be used to help retain _________.
stainless steel crowns
Pulps of primary teeth are proportionally _________ than the permanent teeth.
larger
Primary second molars are smaller versions of what permanent teeth in the same arch?
permanent first molars (can easily be confused)
Primary tooth roots are _______ in proportion to the crown, than in the corresponding permanent teeth.
longer
How do the primary molar roots allow room for the underlying premolars?
roots will diverge and bulge to envelope the developing crowns
What treatment will be given to the patient for attrition (wear from tooth to tooth contact) of the primary teeth?
trick question - no treatment
The most common congenitally missing primary tooth is the ____________.
primary maxillary lateral incisor (rare)
Note: if the primary tooth is congenitally missing, the permanent tooth will be missing as well
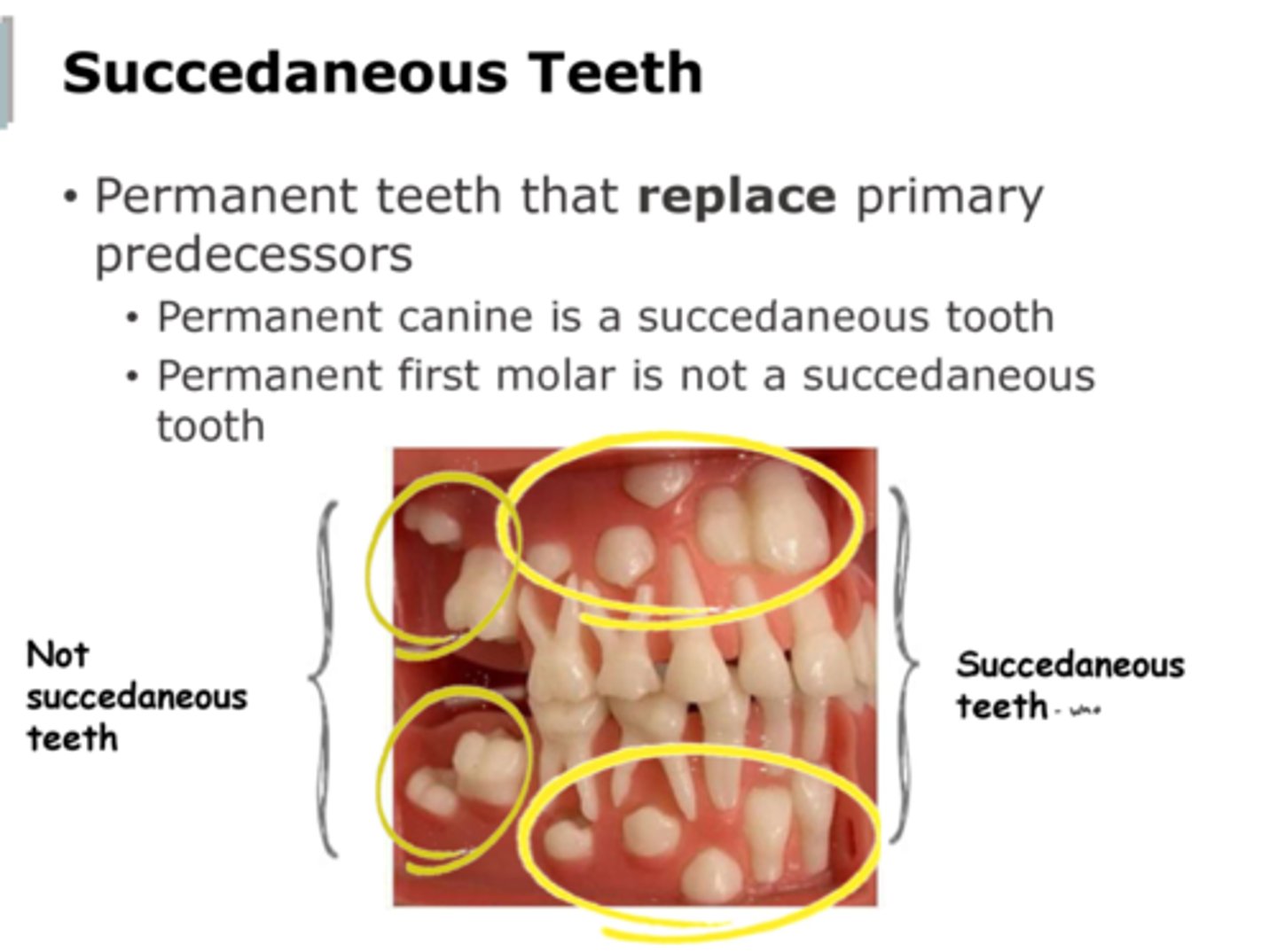
__________ teeth replace primary teeth.
Give 3 examples.
Succedaneous teeth
Example: permanent premolars, canines, incisors
What is primate space?
important space for canine and bicuspid eruption
Where should the "primate" space be for the maxillary canines?
mesial
Where should the "primate" space be for the mandibular canines?
distal
Enamel forms in layers called ___________.
incremental lines of Retzius
A dark band that that appears on the enamel of teeth and develops at birth is called:
neonatal line
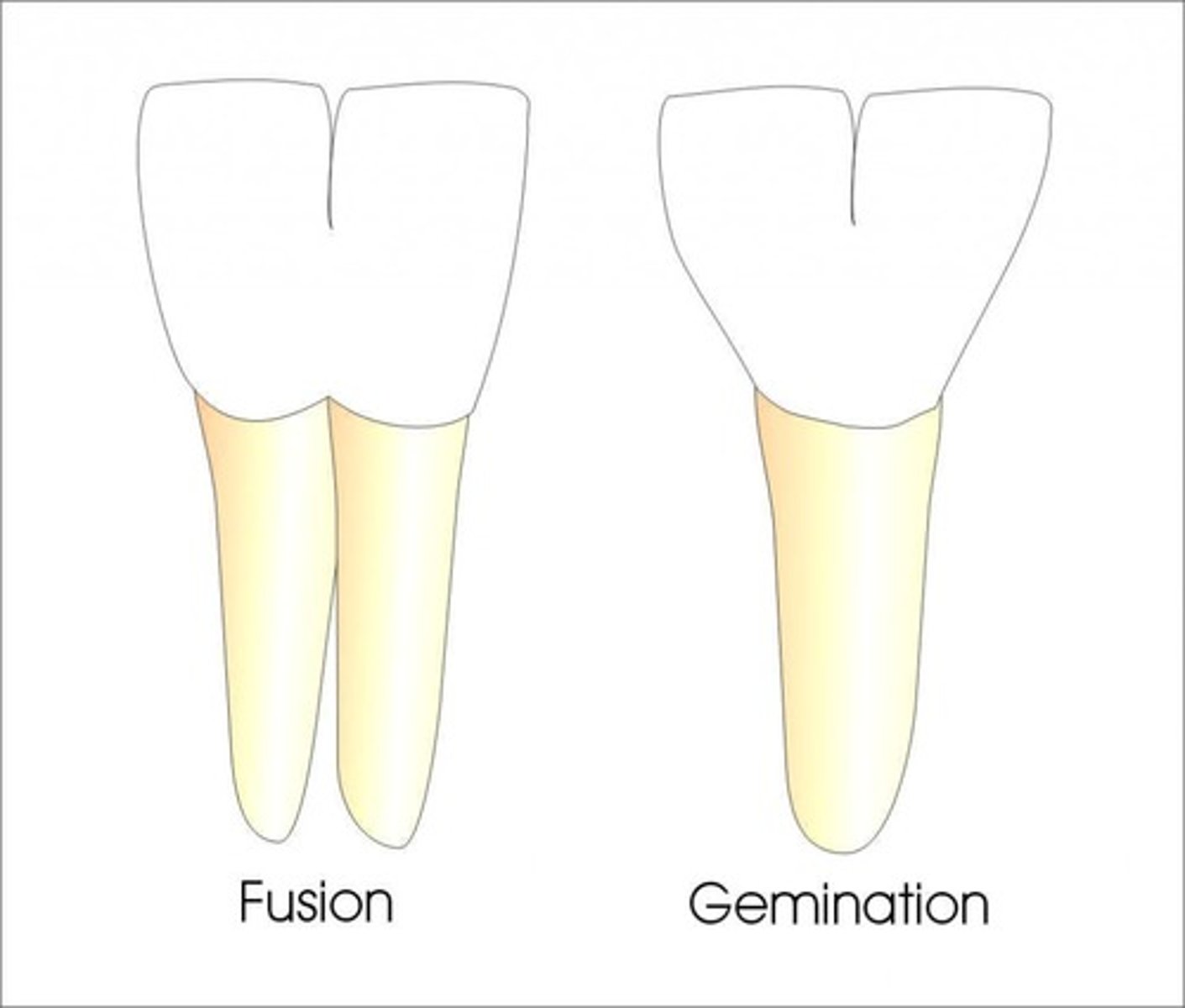
What is gemination?
One tooth bud divides into an incomplete formation of two teeth
(aka one root, one tooth), abortive attempt by a single tooth bud to divide, heredity
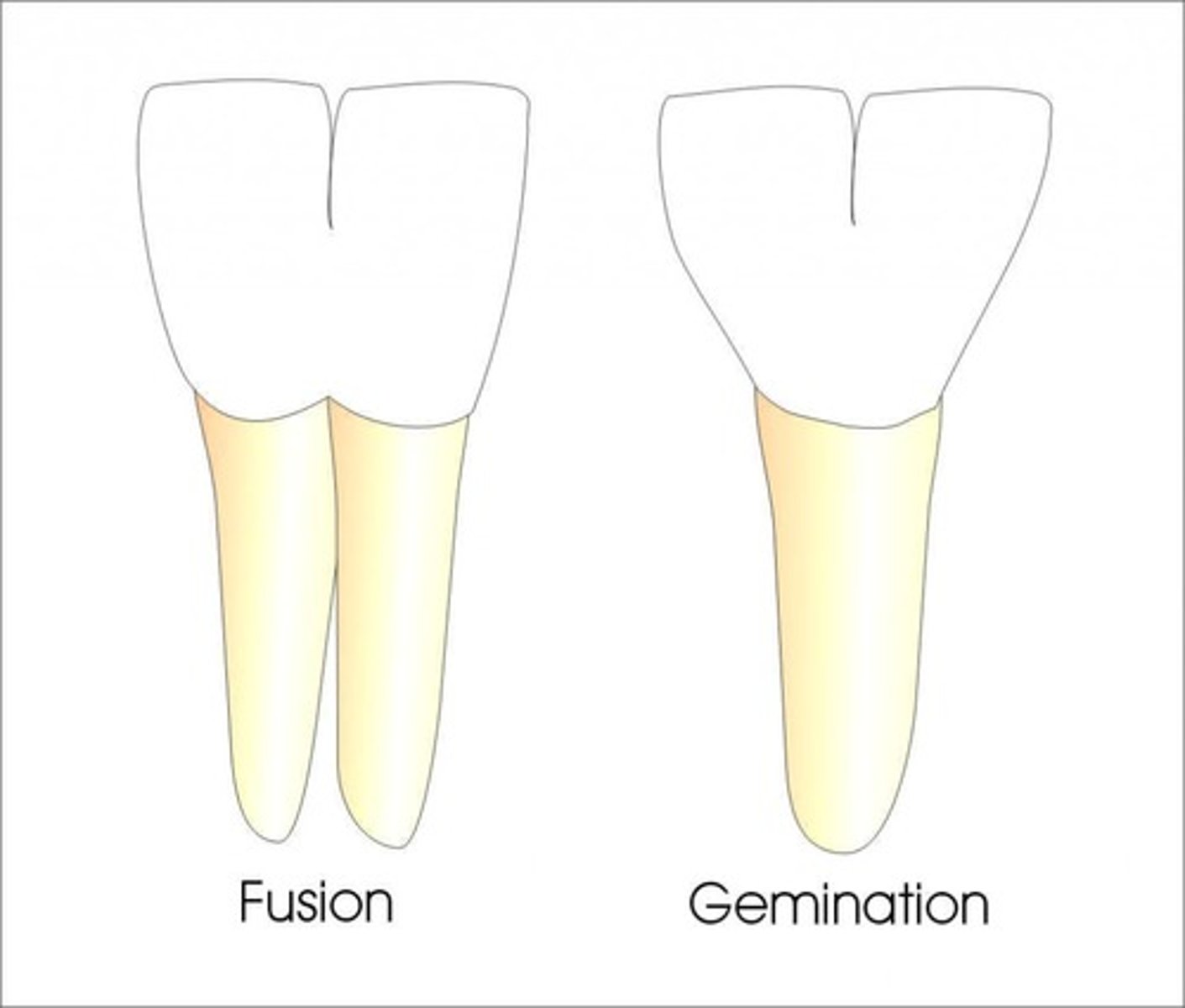
What is fusion?
Union of 2 normally discrete teeth, has 2 roots, potentially congenitally missing permanent tooth
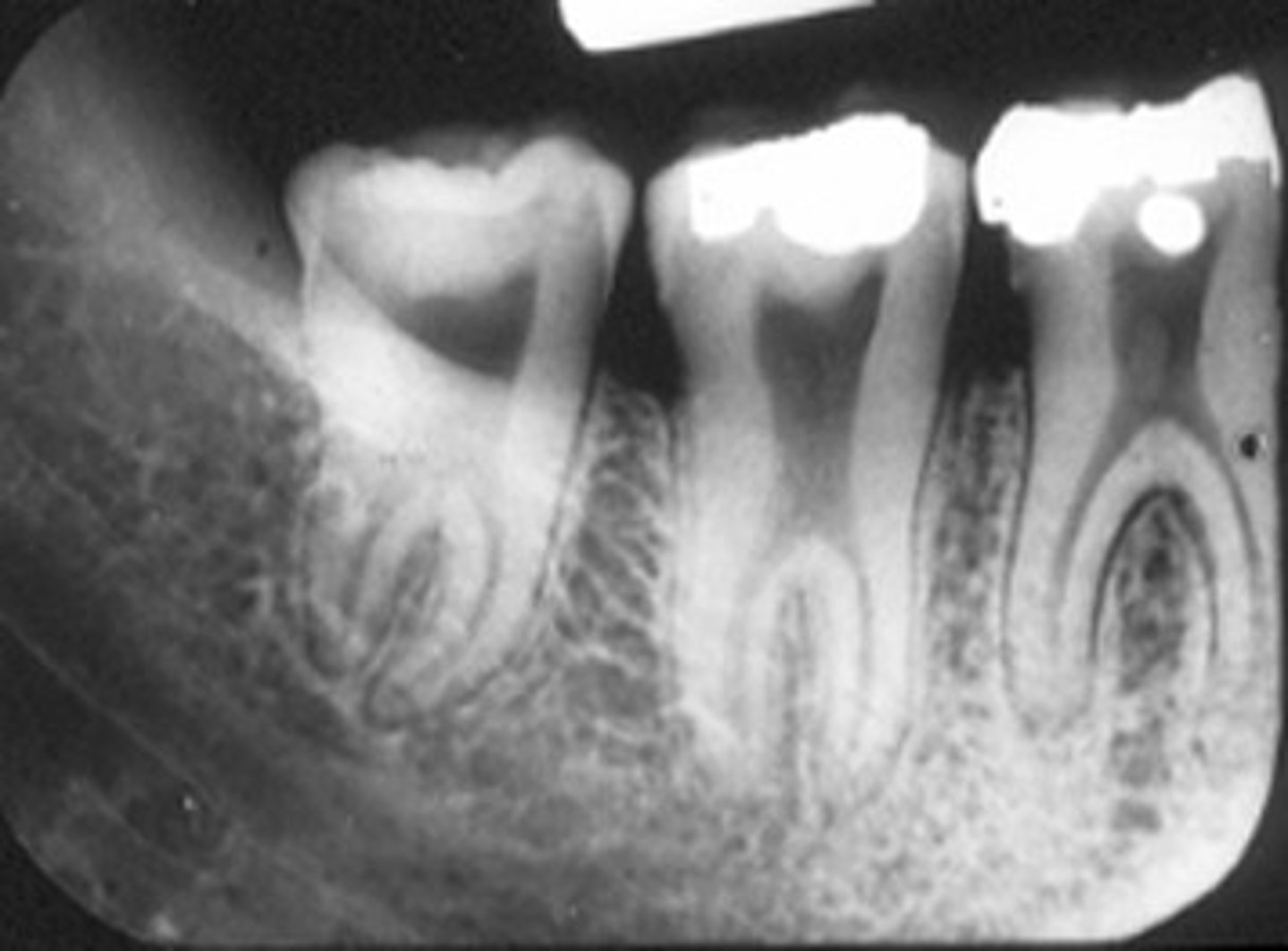
What is concrescence?
Union of root structure of two or more teeth by cementum, can occur during root formation
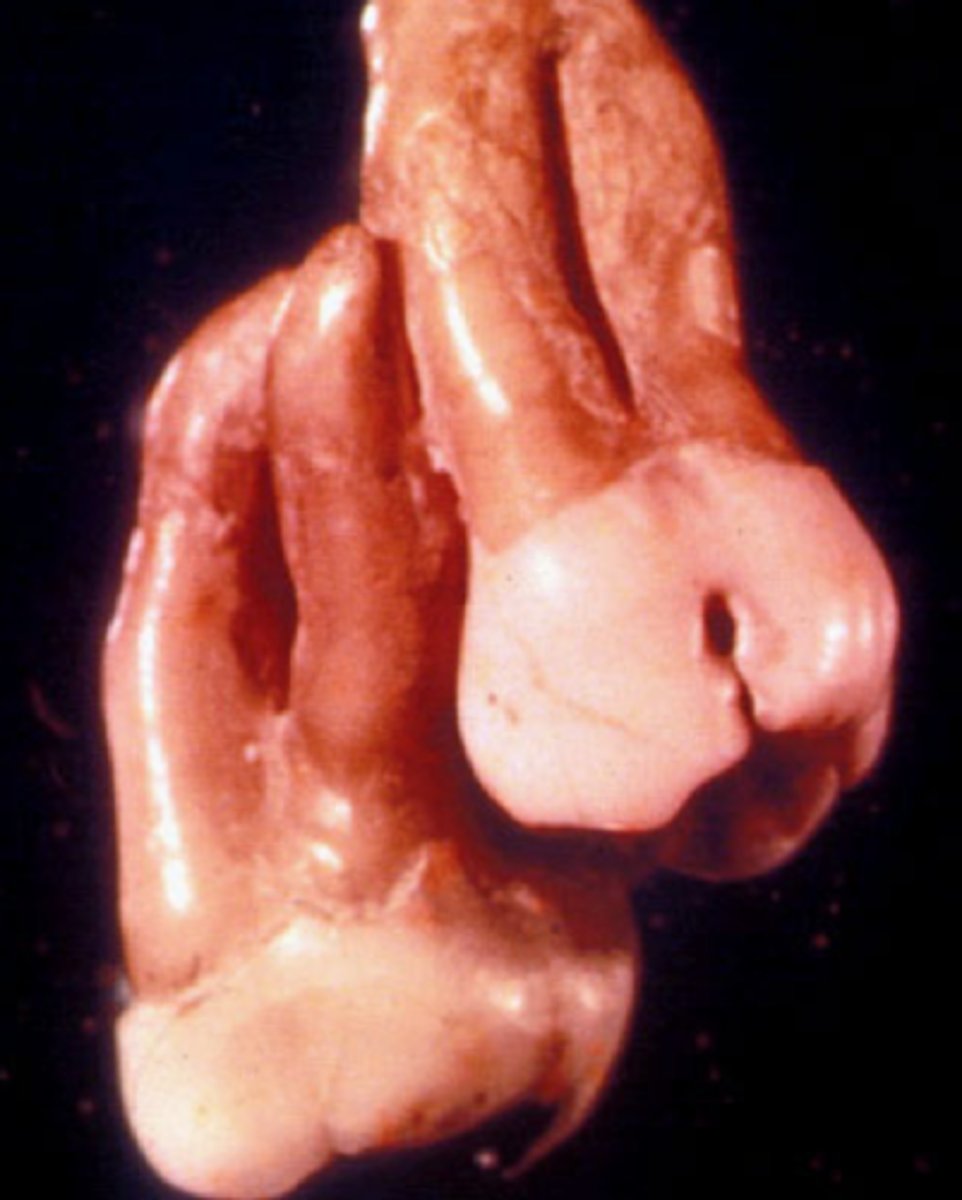
What is taurodontism?
Elongated root trunk, both primary and permanent tooth can be involved
Hutchinson Incisors and Mulberry molars has been associated with:
congenital syphilis
Define anodontia
all teeth missing, associated with ectodermal dysplasia
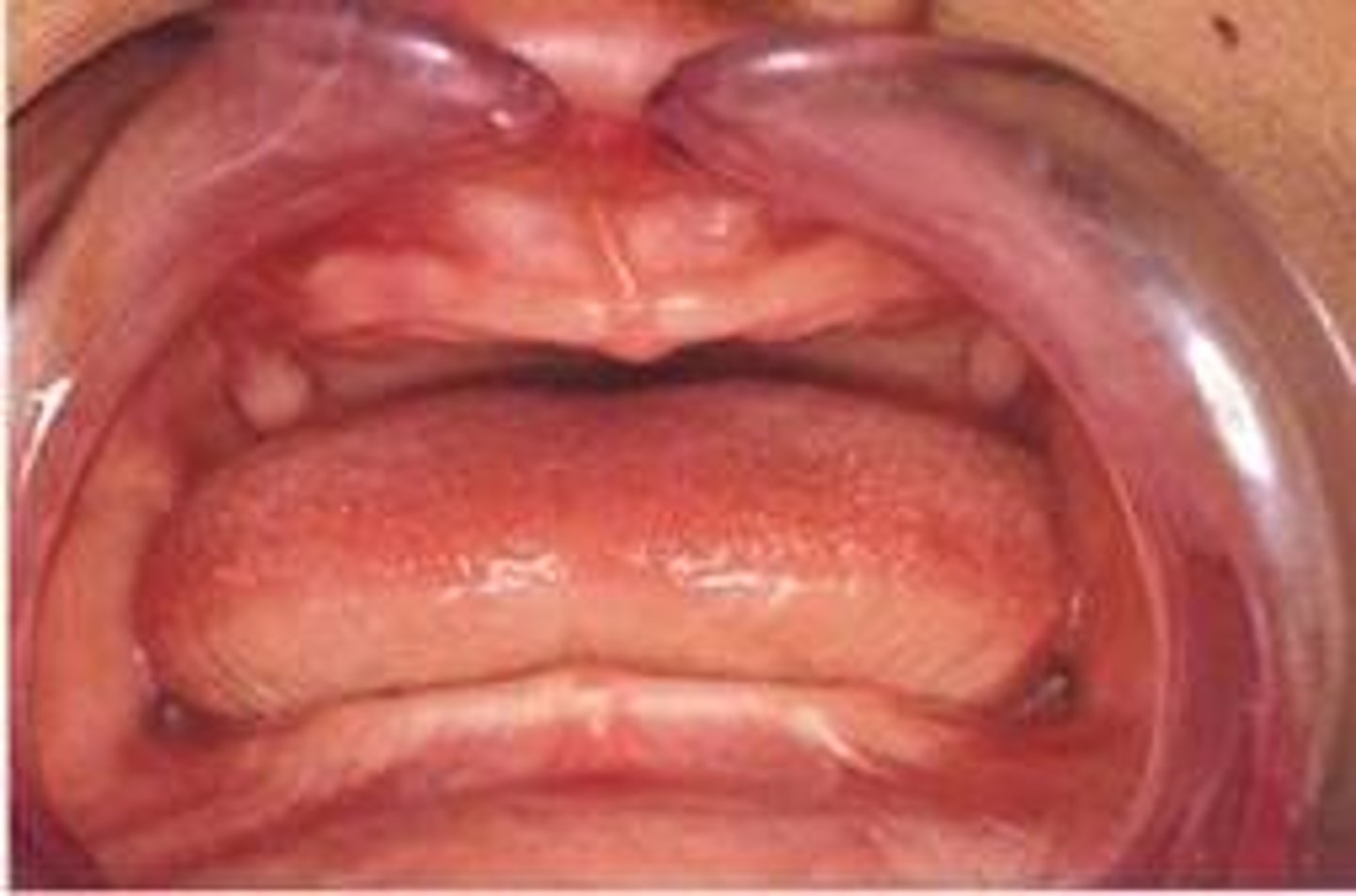
What disorder is associated with anodontia?
ectodermal dysplasia
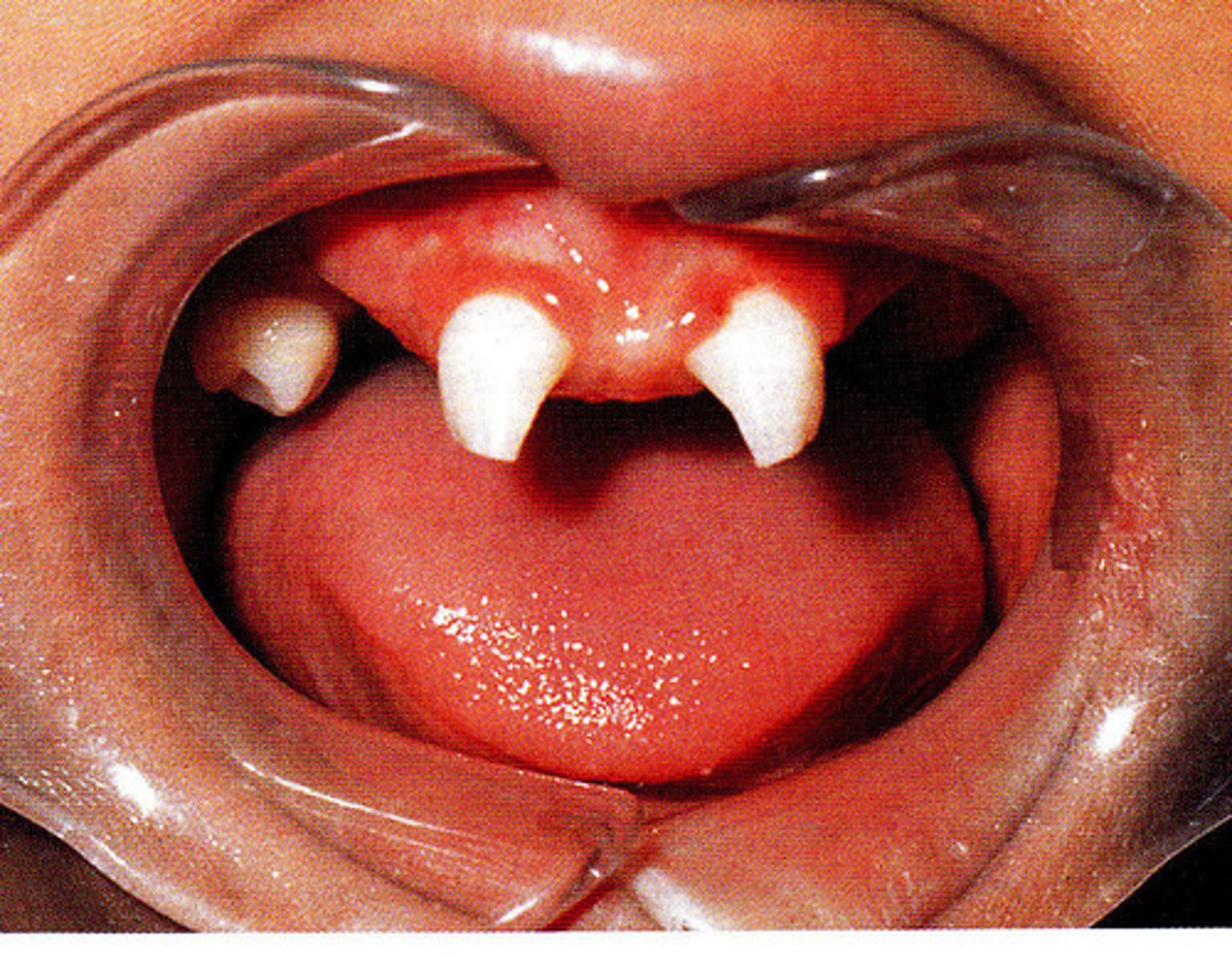
Overbite is a ____________ measurement.
vertical
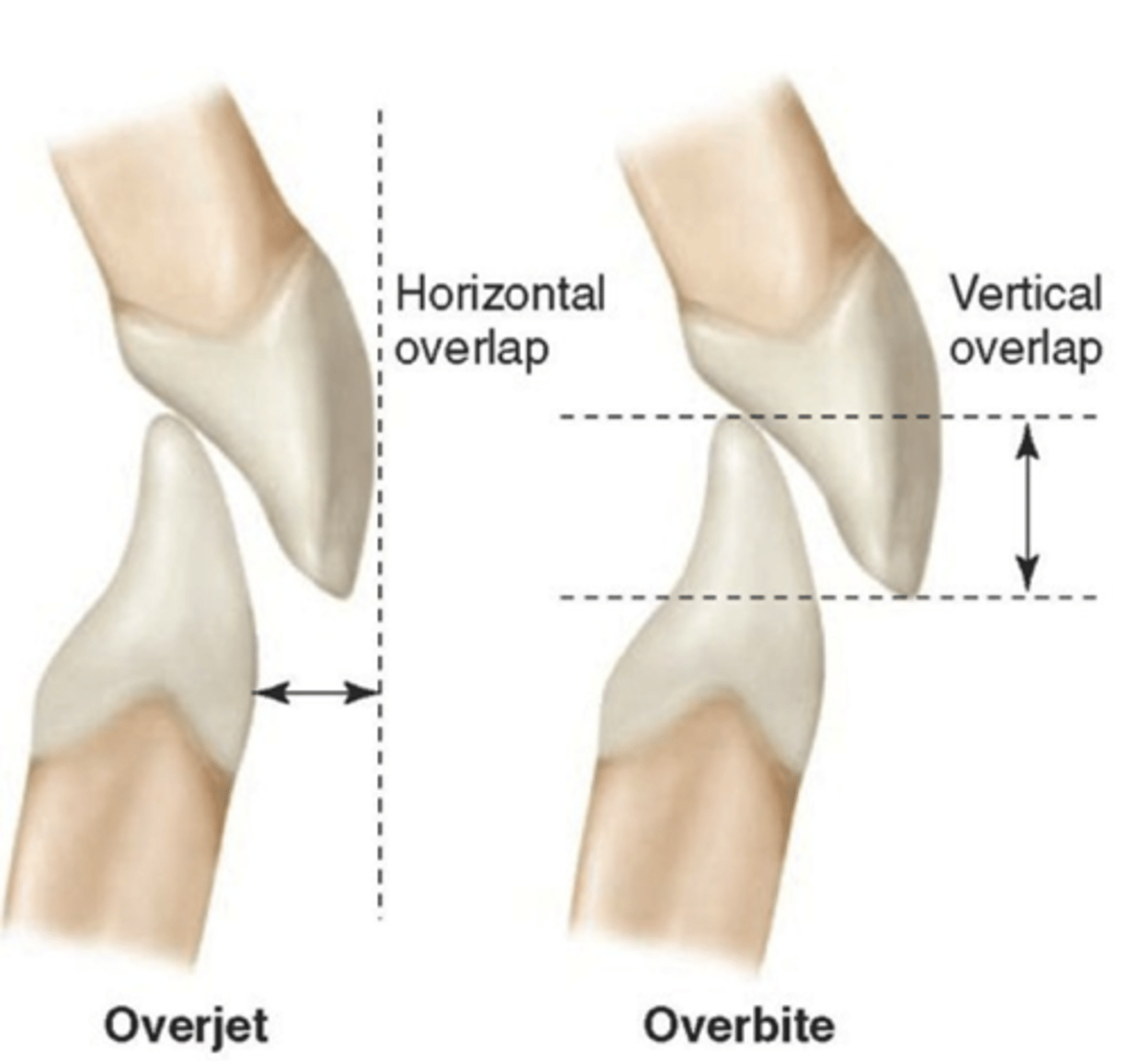
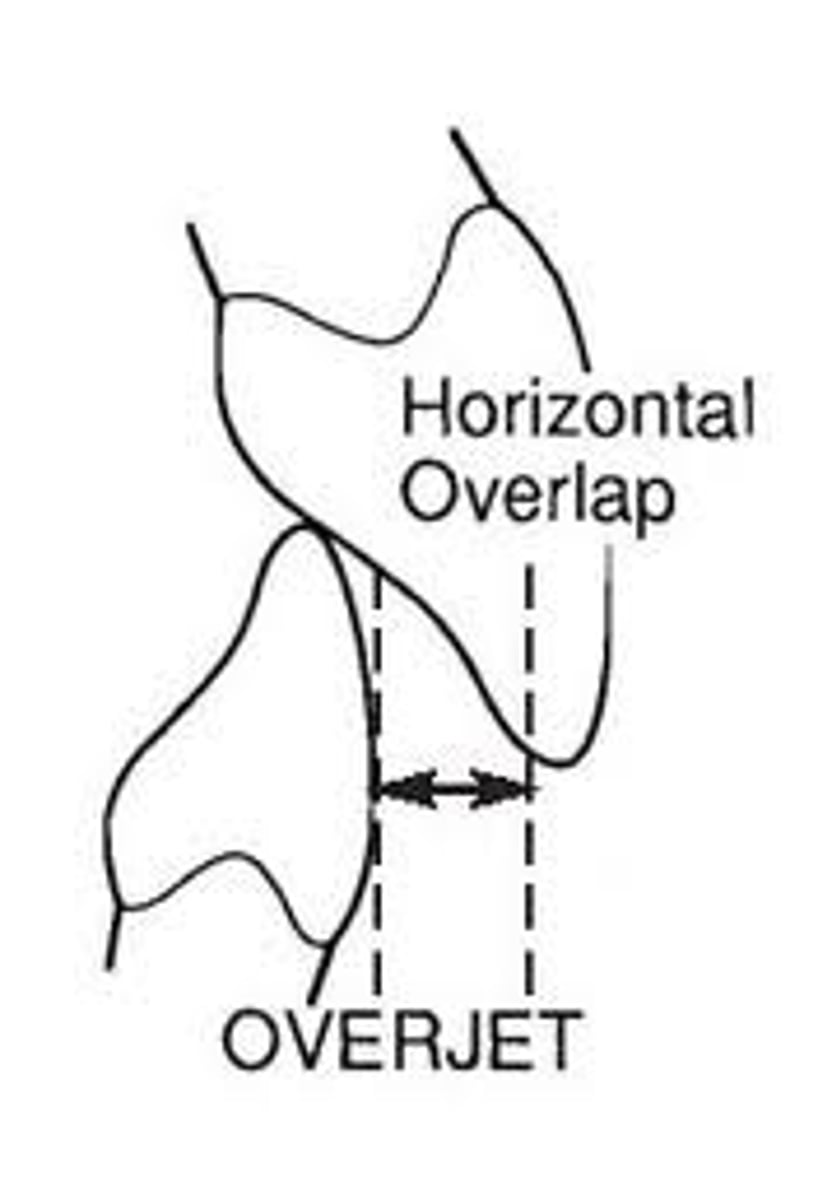
Overjet is a _________ measurement.
horizontal
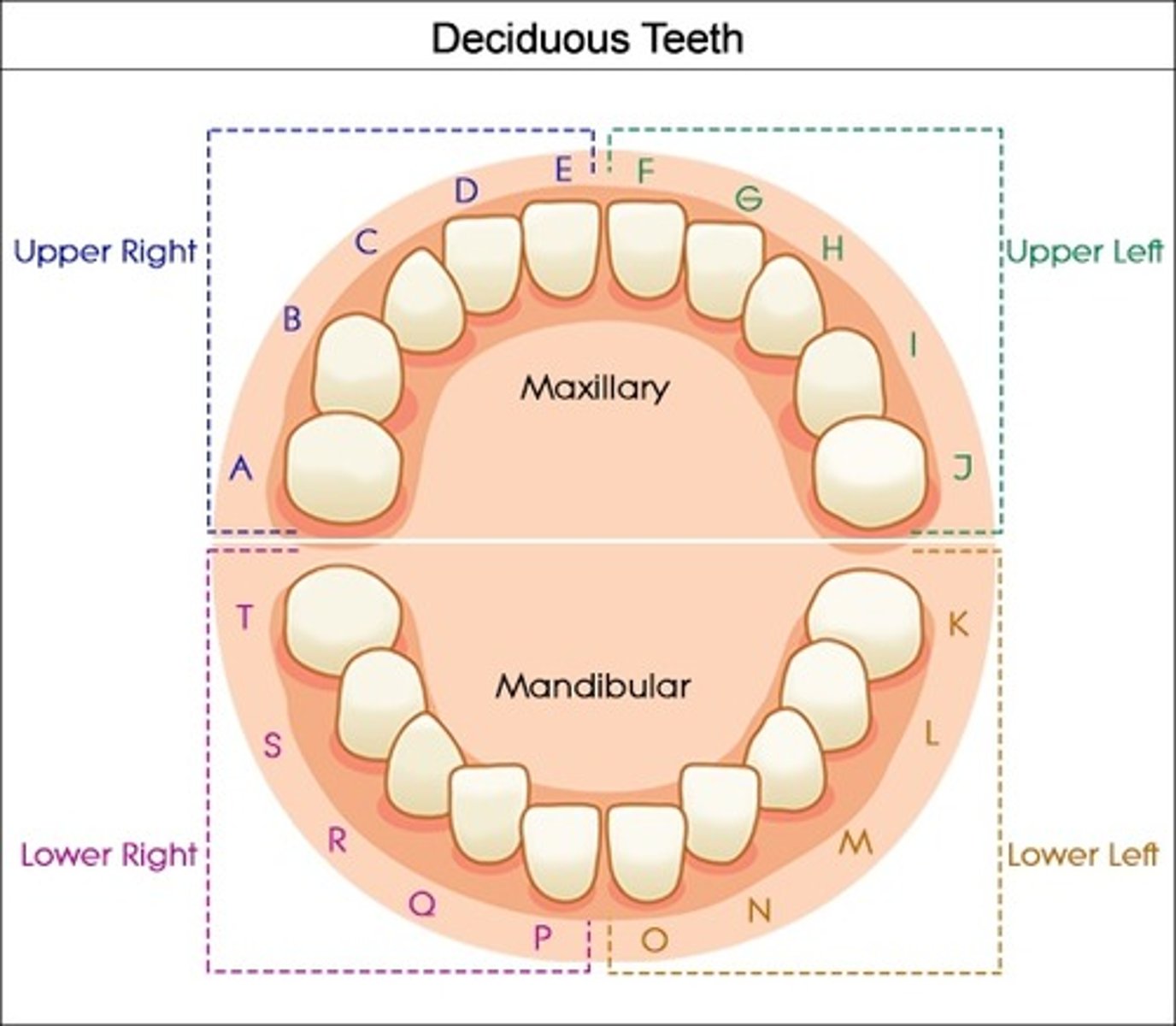
All the following are succedaneous teeth except:
a. #4
b. #12
c. #19
d. #28
c. #19
The primary teeth that typically erupt first are the _____.
Mandibular central incisors
The space associated with primary canines is known as:
primate space
You are completing a periodic oral examination on woman who had her first baby two months ago. She asks when she can expect her baby to get its first teeth. You reply that they generally appear at:
7 months
Primary molars generally resemble a permanent tooth. Which tooth would be the exception to this? (use universal notation to answer)
S
You hear your child singing about only wanting his/her front teeth for Christmas. You reassure them that the permanent maxillary central incisors generally erupt at what age?
7-8 years old
The horizontal measurement of distance between the edge of the maxillary incisors to the mandibular incisors is known as:
overjet
Which tooth out of the primary or permanent dentition is the only tooth wider mesiodistally than it is incisocervically?
primary maxillary incisors
shape of primary upper central incisor
large and shovel shaped
shape of primary lower central/lateral incisors and upper lateral incisors
more chisel shaped, more slender and relatively smaller than the upper central incisor