AP World History "-Isms"
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Absolutism
a form of government in which the ruler is an absolute dictator (not restricted by a constitution or laws or opposition etc.)

Anarchism
a political theory favoring the abolition of governments

Anti-Semitism
policies, views, or actions that harm or discriminate against Jews

Colonialism
-The practice of having and running colonies.
New Imperialism
Historians' term for the late-nineteenth- and early-twentieth-century wave of conquests by European powers and the United States, which were followed by the development and exploitation of the newly conquered territories.

Pan-Slavism
A movement to promote the independence of Slav people. Roughly started with the Congress in Prague; supported by Russia. Led to the Russo-Turkish War of 1877.
Communism
a theory or system of social organization based on the holding of all property in common, actual ownership being ascribed to the community as a whole or to the state.

Conservatism
a political or theological orientation advocating the preservation of the best in society and opposing radical changes

Racism
discriminatory or abusive behavior towards members of another race
Corporatism
a political system in which interest groups become an institutionalized part of the state or dominant political party;public policy is typically the result of negotiations among representatives of the state and key interest groups

Realism
This was the new style of literature that focused on the daily lives and adventures of a common person. This style was a response to Romanticism's supernaturalism and over-emphasis on emotion

Deism
The religion of the Enlightenment (1700s). Followers believed that God existed and had created the world, but that afterwards He left it to run by its own natural laws. Denied that God communicated to man or in any way influenced his life.

Empiricism
the view that (a) knowledge comes from experience via the senses, and (b) science flourishes through observation and experiment.

Existentialism
A philosophy that values human freedom and personal responsibility. A few well known _______ writers are Jean-Paul Satre, Soren Kierkegaard ("the father of _______"), Albert Camus, Freidrich Nietzche, Franz Kafka, and Simone de Beauvoir.

Romanticism
An artistic and intellectual movement originating in Europe in the late 18th Century and characterized by a heightened interest in nature, emphasis on the individual's expression of emotion and imagination, departure from the attitudes and forms of classicism, and rebellion against established social rules and conventions.

Social Darwinism
The application of ideas about evolution and "survival of the fittest" to human societies - particularly as a justification for their imperialist expansion.

Socialism
a theory or system of social organization that advocates the vesting of the ownership and control of the means of production and distribution, of capital, land, etc., in the community as a whole.

Utilitarianism
The theory, proposed by Jeremy Bentham in the late 1700s, that government actions are useful only if they promote the greatest good for the greatest number of people.

Zionism
A worldwide movement, originating in the 19th century that sought to establish and develop a Jewish nation in Palestine. Since 1948, its function has been to support the state of Israel.

Fascism
A system of government characterized by strict social and economic control and a strong, centralized government usually headed by a dictator. First found in Italy by Mussolini.

Feminism
the belief that women should possess the same political and economic rights as men

Humanism
an intellectual movement at the heart of the Renaissance that focused on education and the classics

Imperialism
A policy in which a strong nation seeks to dominate other countries poitically, socially, and economically.

Isolationism
a policy of non-involvement in foreign affairs

Impressionism
Major Western artistic style that gained prominence in the second half of the 1800s and into the 1900s.Against Realism, visual impression of a moment, style that seeks to capture a feeling or experience, often very colorful.

Liberalism
A political ideology that emphasizes the civil rights of citizens, representative government, and the protection of private property. This ideology, derived from the Enlightenment, was especially popular among the property-owning middle classes.

Marxism
the economic and political theories of ______ __________and Friedrich Engels that hold that human actions and institutions are economically determined and that class struggle is needed to create historical change and that capitalism will untimately be superseded

Mercantilism
an economic system (Europe in 18th C) to increase a nation's wealth by government regulation of all of the nation's commercial interests
Militarism
a political orientation of a people or a government to maintain a strong military force and to be prepared to use it aggresively to defend or promote national interests

Modernism
practices typical of contemporary life or thought

Nationalism
love of country and willingness to sacrifice for it

Nazism
a form of socialism featuring racism and expansionism, The doctrines of nationalism, racial purity, anti-Communism, and the all-powerful role of the State. The National Socialist German Workers Party encouraged this and it was advocated by Adolf Hitler in Germany.

Daoism
Chinese philosophy based on the teachings of Laozi; taught that people should turn to nature and give up their worldly concerns

Confucianism
the system of ethics, education, and statesmanship taught by Confucius and his disciples, stressing love for humanity, ancestor worship, reverence for parents, and harmony in thought and conduct

Legalism
In China, a political philosophy that emphasized the unruliness of human nature and justified state coercion and control. The Qin ruling class invoked it to validate the authoritarian nature of their regime

Animism
Belief that objects, such as plants and stones, or natural events, like thunderstorms and earthquakes, have a discrete spirit and conscious life.

Zoroastrianism
A religion originating in ancient Iran. It centered on a single benevolent deity-Ahuramazda, Emphasizing truth-telling, purity, and reverence for nature, the religion demanded that humans choose sides between good and evil

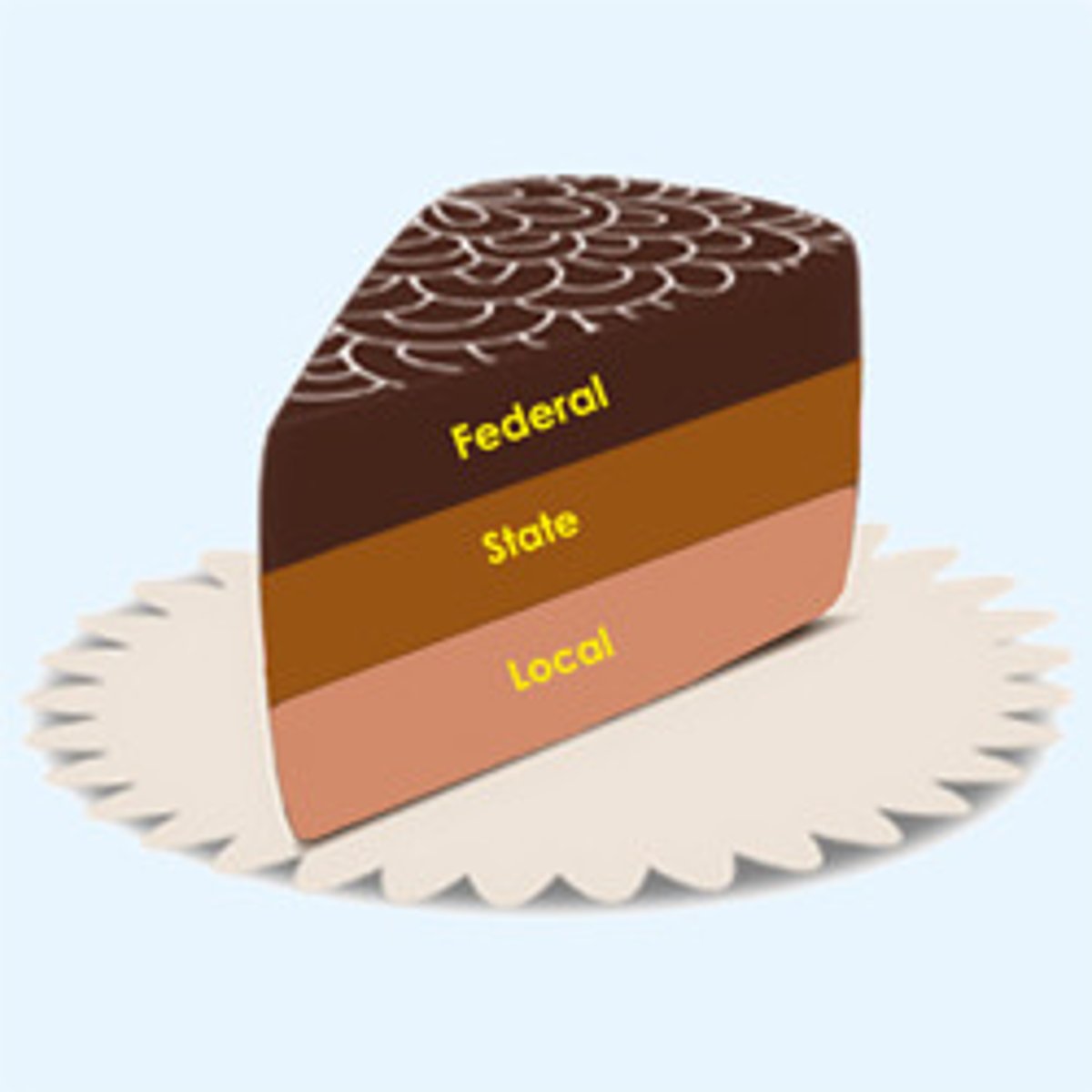
Federalism
A system of government in which a written constitution divides power between a central, or national, government and several regional governments
Centralism
denotes the concentration of a government's power into a centralized government. This takes away some of the powers of the states and puts more power into the hands of the executive leader
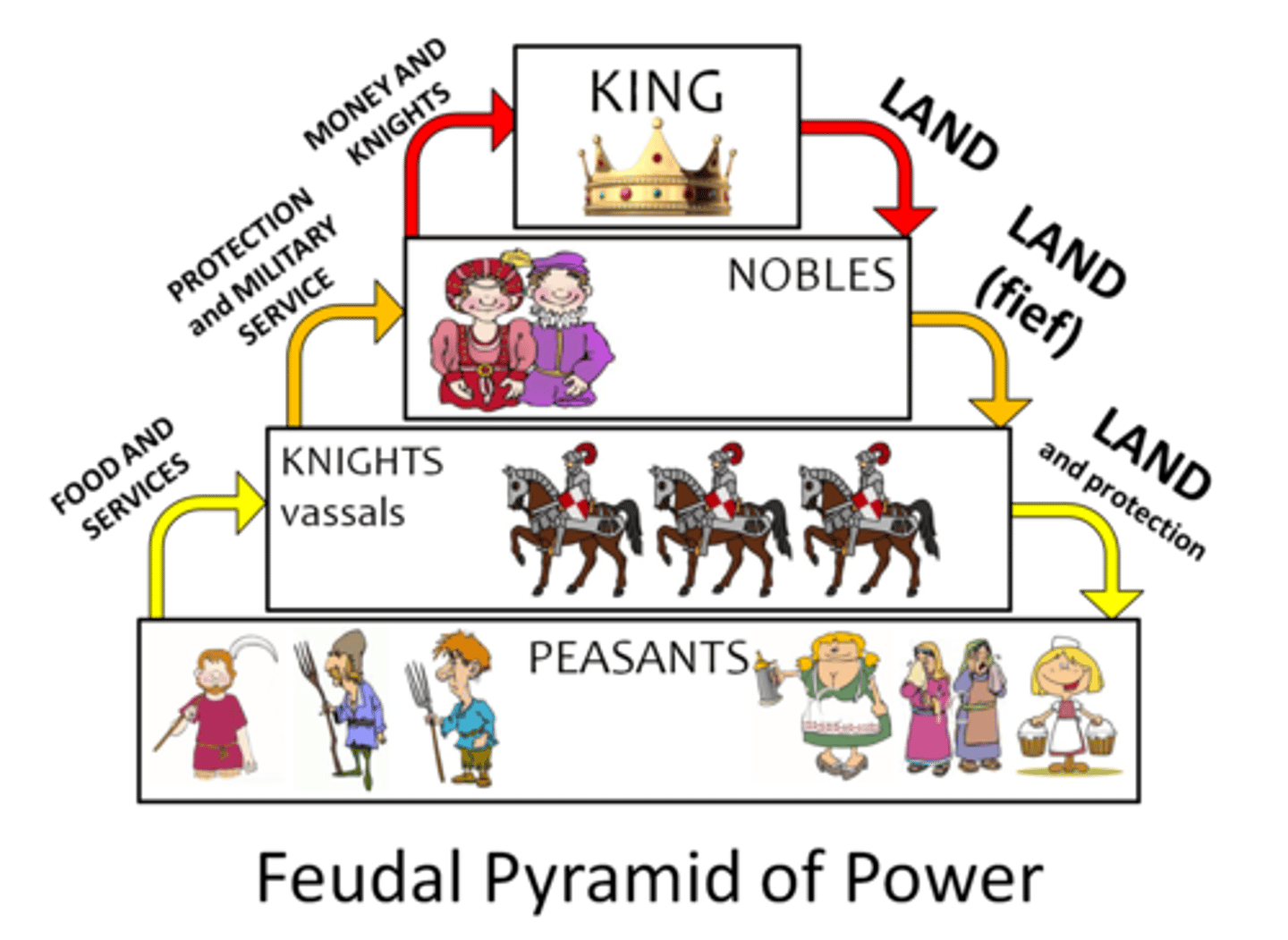
Feudalism
A political system in which nobles are granted the use of lands that legally belong to their king, in exchange for their loyalty, military service, and protection of the people who live on the land
Protectionism-
government policy of insulating domestic industries from the world market through import tariffs and taxes.

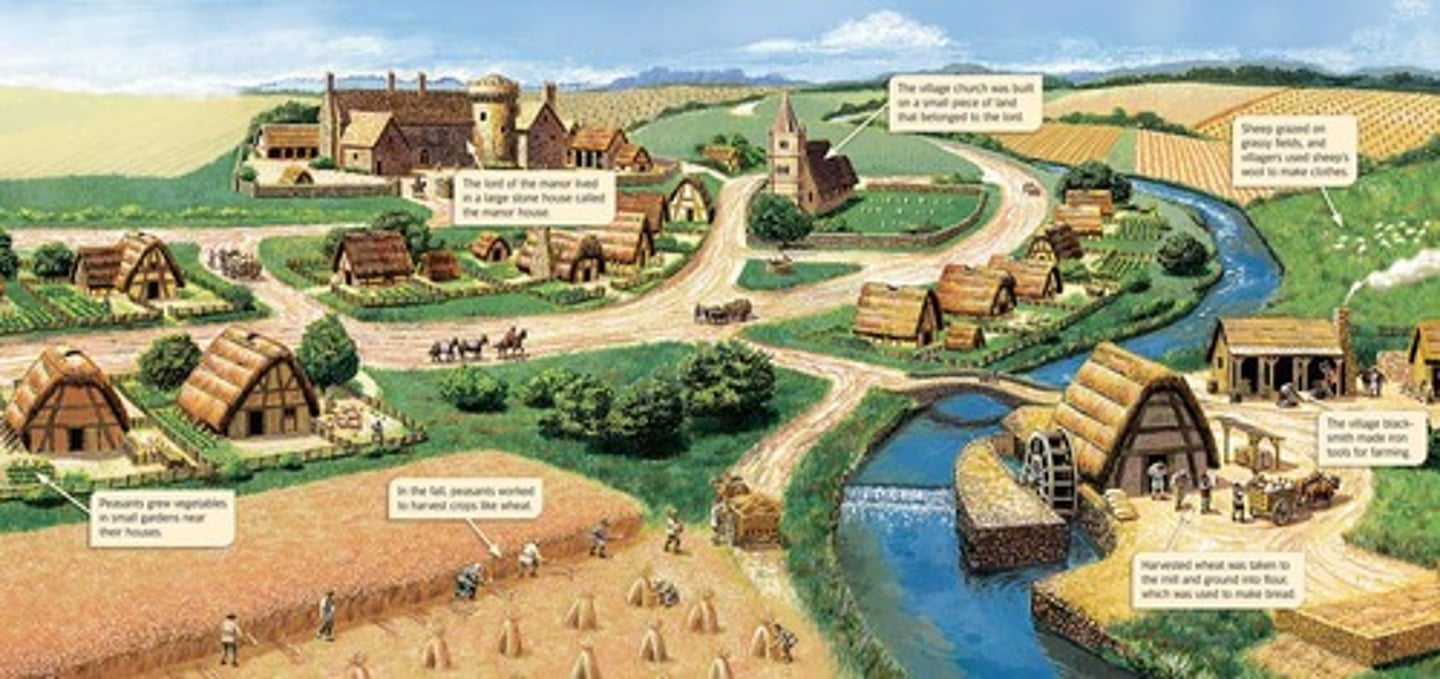
Manorialism
An economic system based on the manor and lands including a village and surrounding acreage which were administered by a lord. It developed during the Middle Ages to increase agricultural production.
Radicalism
a political philosophy that emphasizes the need to find and eliminate the basic injustices of society; seek what they consider the roots of the economic, political, and social wrongs of society and demand immediate and sweeping changes to wipe them out; a belief that rapid, dramatic changes need to be made to existing society, usually think current system cannot be saved and must be overturned

Protestantism
- religions born of protests to the practices of Catholicism
