The Female Cycle
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1st powerpoint
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
most of interactions in female reproductive cycle (hormones and tissues) are based on…
negative feedback systems
where does the process of hormones start?
in the brain with signaling hormones (secreted by hypothalamus that stimulate anterior pituitary)
what do hormones from the anterior pituitary gland control?
the ovarian cycle
what do the ovaries, in turn, secrete?
hormones that control the uterine cycle
what is the “control center” of the endocrine system?
hypothalamus
what does the hypothalamus do?
monitors chemical and neural signals from the body
controls appetite
controls release of hormones to maintain homeostasis.
body temp (vasodilation/ vasoconstriction)
sweating and shivering
respiratory rate
what is the hypothalamus apart of/ where is it located?
part of diencephalon
located just inferior to thalamus (hypo= below; hypothalamus)
superior to pituitary gland
hypothalamus communicates with the…… via the…
anterior pituitary gland via the hypophyseal portal system
what is the hypophyseal portal system?
blood vessels that communicate between hypothalamus & anterior pituitary gland.
list steps of hypophyseal portal system:
hypothalamus hormones —> capillary bed of hypophyseal artery
blood with hormones —> hypophyseal portal system
hormones in portal system —> anterior pituitary
A.P. secretes its own hormones into the A.P. capillaries
these then empty into the systemic bloodstream.
what hormones do not enter the systemic blood circulation?
hypothalamic hormones
goes to pituitary gland which then release their hormones into blood circulation.
what does the anterior pituitary gland respond to and how does it respond?
responds to GnRH (from hypothalamus)
responds by secreting hormones that stimulate the ovaries (FSH and LH)
what is the anterior pituitary gland composed of?
glandular tissue
where is the pituitary gland located?
sits in sella turcica of sphenoid bone
what hormones does the anterior pituitary gland secrete?
gonadotropic hormones
FSH
LH
TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone)
Prolactin
what hormone does the hypothalamus secrete?
GnRH
what structure does GnRH target?
anterior pituitary
what does the anterior pituitary do in response to GnRH?
release FSH and LH
what do the gonadotropin hormones do (in general)?
stimulate gonads
gamete production
sex hormone secretion
what are the target cells of FSH?
ovarian follicles
target cells of LH?
ovarian follicles and corpus luteum
what is GnRH? (simple, one word answer)
neurohormone
how in GnRH secreted?
in pulsations- change frequency/ amplitude in different parts of cycle
early follicular phase- 1/90 min
late follicular/ ovulatory phase- 1/60-70 min
secretory phase- less frequent but higher in amplitude
what does the inhibition of FSH trigger?
LH surge
what does FSH do?
promotes follicle development in ovary
causes maturation of oocyte, corona radiata, and development of follicular antrum
what occurs as estrogen levels rise?
GnRH is inhibited
this leads to the fall of FSH and triggering of LH surge
What does LH do?
triggers ovulation and formation of corpus luteum
what are estrogen and progesterone secreted by?
the ovaries
what are estrogens?
class of hormones associated with female characteristics
cholesterol based steroid hormones
what is estradiol?
principle estrogen responsible for female sex characteristics and maturation of sex organs
where does estradiol come from?
developing follicles
adrenal cortex
placenta
what is estradiol important for?
bone health
what does estradiol (excess estrogen/ estradiol) contribute to?
endometriosis
fibroids
breast, ovarian, and endometrial cancer
what is estriol?
only produced during pregnancy and secreted by placenta
Aimee has estriol!
what is estrone?
only estrogen that remains in significant amounts after menopause (widely found in body)
Erin is closest to having estrone!
what is estrogen (mainly estradiol) secreted by?
the ovarian follicles that respond to FSH and mature
causes endometrium to develop a new functional layer
what is Progesterone secreted by?
corpus luteum after ovulation
only if fertilization occurs
how do you know if it is an ovulatory/ corpus luteal cyst?
with color, shows ring of fire
what does progesterone do?
prepares and maintains body for pregnancy
inhibits uterine irritability (tendency to contract)
blocks development of new ovarian follicles
causes formation of cervical mucous plug during pregnancy (protect against infection)
inhibits maternal immune system (prevents rejection of embryo)
stimulates growth of uterine wall and uterine blood vessels to support pregnancy
estrogen and progesterone have what kind of feedback?
negative feedback
reduces production
GnRH
LH
FSH
what are the phases of the menstrual cycle WITH days (7phases)?
menstrual phase: days 1-5
early mid proliferative phase: days 6-10
late proliferative phase: days 11-12
ovulatory phase: days 13-14
secretory phase: days 15-22
late secretory phase: days 23-25
late secretory phase: days 26-28
what happens to hormones during menstrual phase?
GnRH—pulsations increase
FSH—begins to rise
LH—low levels also secreted
Estrogen—low
Progesterone--low
what happens to ovaries during menstrual phase?
Early follicular phase- Follicles begin to respond to FSH
As follicles begin to mature, they begin to secrete estrogen (low levels)
what happens to uterus during menstrual phase?
Functional layer of endometrium from previous cycle is being shed (menstruation).
Endometrium = <4mm
what happens to hormones during early- mid proliferative phase?
GnRH—pulsations decrease
FSH—high, begins to fall
LH—low
Estrogen—rising
Progesterone--low
what happens to ovaries during early- mid proliferative phase?
Late follicular phase- Dominant follicle develops antrum (see larger follicle on ultrasound)
Progesterone still low, rises slightly near day 10
what happens to uterus during early- mid proliferative phase?
New functional layer develops in response to estrogen stimulation.
new endometrial glands & spiral arteries/veins.
Endometrium = 11mm
3 line sign seen
what happens to hormones during late proliferative phase?
GnRH—pulsations increase
FSH—begins to rise for surge
LH—begins to rise for surge
Estrogen—high (crest)
Progesterone—smaller peak
what happens to ovaries during late proliferative phase?
Very late follicular phase- Oocyte within Graafian follicle moves toward wall. Follicle measures 2.5-3cm
Estrogen secretion peaks prior to ovulation
Progesterone also rises and peaks, still lower than estrogen.
what happens to uterus during late proliferative phase?
New functional layer is nearly complete.
See “3 lines” on ultrasound w/ definite hypoechoic halo
Cervical mucus continues to thin
Endometrium = 11-12mm
what happens to hormones during ovulatory phase?
GnRH—pulsations increase
FSH—small surge followed by immediate fall back to baseline
LH—large surge followed by immediate fall back to baseline
Estrogen—falling for short time
Progesterone—falling for short time
what happens to ovaries during ovulatory phase?
Oocyte in Graafian follicle completes 1st meiotic division forming secondary oocyte.
LH surge causes Graafian follicle to rupture, releasing oocyte
Ruptured follicle forms corpus luteum under influence of LH
what happens to uterus during ovulatory phase?
Cervix slightly open, receptive to sperm.
Endometrium = 14 mm
See “3 lines” on ultrasound
very prominent hypoechoic halo around central echogenic line
what happens to hormones during secretory phase?
GnRH—pulsations low
FSH—low
LH—low
Estrogen—high but lower peak prior to ovulation
Progesterone—very high, coming to peak
what happens to ovaries during secretory phase?
Corpus luteum secretes primarily progesterone and some estrogen
CL appears:
thick walled
cystic
often complex/ containing debris
what happens to uterus during secretory phase?
Endometrial glands begin to secrete nutrients (prep for zygote implantation)
Endometrium becomes “thick and lush”
receptive to implantation
3 line sign replaced by thick echogenic endometrium on ultrasound
Cervical mucus becomes thick again
what happens to hormones during late secretory phase (days 23-25)?
GnRH—pulsations low
FSH—low
LH—low
IF NO Pregnancy:
Estrogen—beginning to fall
Progesterone—beginning to fall
what happens to ovaries during late secretory phase (days 23-25)?
corpus luteum begins to degenerate
Due to low LH (& FSH) levels
CL cystic structure begins to collapse, involute
often contains debris.
what happens to uterus during late secretory phase (days 23-25)?
As progesterone/estrogen levels fall, endometrial glands & spiral vessels begin to atrophy & die.
Endometrium still thick & hyperechoic.
Endometrium = 9-16mm
what happens to hormones during late secretory phase (days 26-28)?
GnRH—pulsations low
FSH—low
LH—low
IF NO Pregnancy:
Estrogen—low
Progesterone—low
what happens to ovaries during late secretory phase (days 26-28)?
Corpus luteum forms corpus albicans (“white body”), basically a scar.
No longer secreting progesterone or estrogen
what happens to uterus during late secretory phase (days 26-28)?
Endometrial glands & spiral vessels atrophy & die; functional endometrial endometrium begins to detach from basal layer.
Endometrium thick & hyperechoic w/posterior enhancement.
Endometrium = 9-16mm
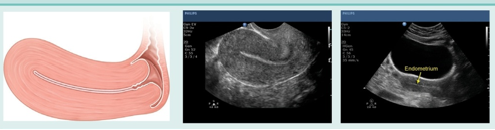
what uterine phase is this (and endometrial thickness)?
late menstrual phase (1-4mm)
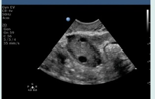
what ovarian phase is this (days included)?
follicular (day -15)
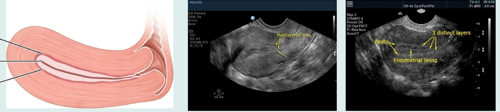
what uterine phase is this (and endometrial thickness)?
proliferative (5-8 mm)
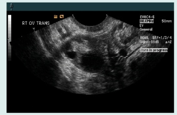
what ovarian phase is this (days included)?
follicular (6-13 days)
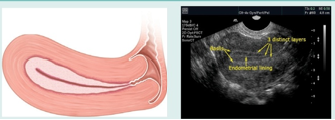
what uterine phase is this (and endometrial thickness)?
late proliferative (11 mm)
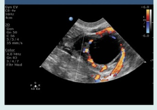
what ovarian phase is this?
follicular
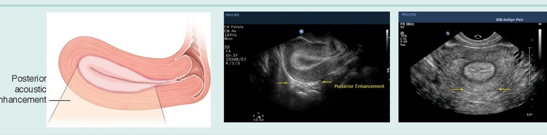
what uterine phase is this (endometrial thickness)?
late secretory (9-16 mm)
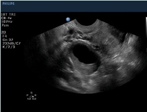
what ovarian phase is this (days included)?
luteal (days 14-25)
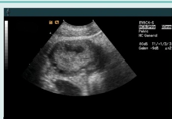
what ovarian phase is this (days included)?
ovulatory (day 14 ish)
different “types” of amenorrhea?
transient
intermittent
permanent
amenorrhea can be the result of…
a dysfunction of the hypothalamus, pituitary, ovaries, uterus or vagina
two categories of amenorrhea:
primary
secondary
what is primary amenorrhea?
when menstruation fails to take take place at all.
Menarche does not occur in a young girl aged 16
what is secondary amenorrhea?
occurs in women who have started menstruation but have had the absence of menses for the equivalent of three menstrual cycles or 6 months
what is oligomenorrhea?
infrequent or very light menstruation
when a woman has menstrual periods that occur at intervals of greater than 35 days, with only 4-9 periods in a year, she is considered to have oligomenorrhea
what is premature ovarian failure?
POF
primary ovarian defect characterized by a lack of menarche (primary amenorrhea) or premature depletion of ovarian follicles before the age of 40 years (secondary amenorrhea.
why does POF put women at risk for other health conditions?
because drop of estrogen and progesterone
POF puts women at risk for other health conditions such as:
Osteoporosis
Low thyroid function
Addison’s disease
Heart disease risk
what is menopause?
A transition period in a woman’s life usually (but not always) occurring during her late 40s or early 50s.
what occurs during menopause?
ovaries cease to produce ova
less estrogen and progesterone
Hormone levels become unstable
estrogen and progesterone levels keep surging; then reach a low point until levels become permanently low
ovaries slowly stop responding to FSH and LH
endometrium not stimulated to proliferate or grow
No menses occurs
what occurs post menopause?
uterus becomes small and fibrotic due to muscle atrophy
ovaries fail to produce any follicles after menopause
makes the estrogen level in the blood reduced
causes the endometrial lining to become thin and atrophied
What occurs the further into menopause a woman is?
the smaller their uterus becomes
the smaller the ovaries become
decrease in size due to absence of folliculogenesis
what does the postmenopausal ovary look like on US?
hypoechoic
ovoid structure
can be difficult to image/identify due to absence of follicles
what is the exception to the ovaries getting smaller in menopause?
if patient is receiving HRT (hormone replacement therapy), there may not be any changes to ovarian volume
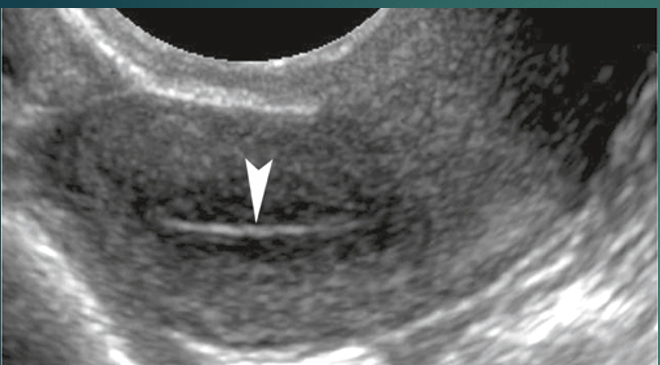
what does this image depict?
post menopausal uterus
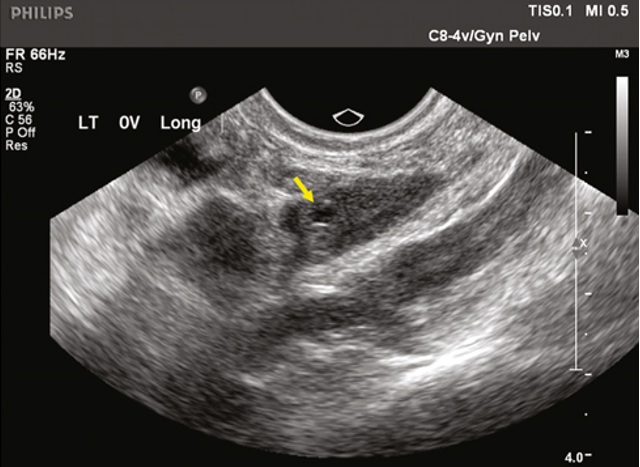
what does this image depict?
post menopausal ovaries
how does endometrium appear post menopause? exception to this?
Endometrium appears as a thin, homogeneous, and echogenic line
should measure 4 mm or less
be smooth and uniform
Exception: women on HRT (7 mm or less)
reasons for post menopausal bleeding?
Endometrial atrophy
Endometrial polyps
Submucosal fibroids
Endometrial hyperplasia
Endometrial carcinoma
Estrogen withdrawal
when is the best time to image a PMB patient?
directly after bleeding has stopped
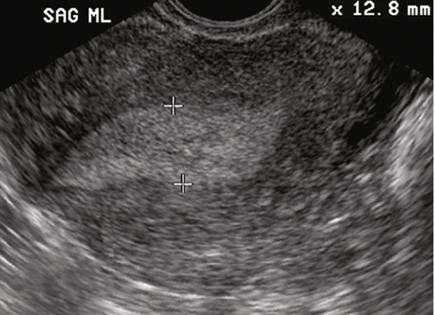
in normal PMB patient, if endometrium is greater than 5mm or appears irregular, what may be needed?
further investigation may be needed
sonohysterography
biopsy
hysteroscopy.