Chapter 1
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
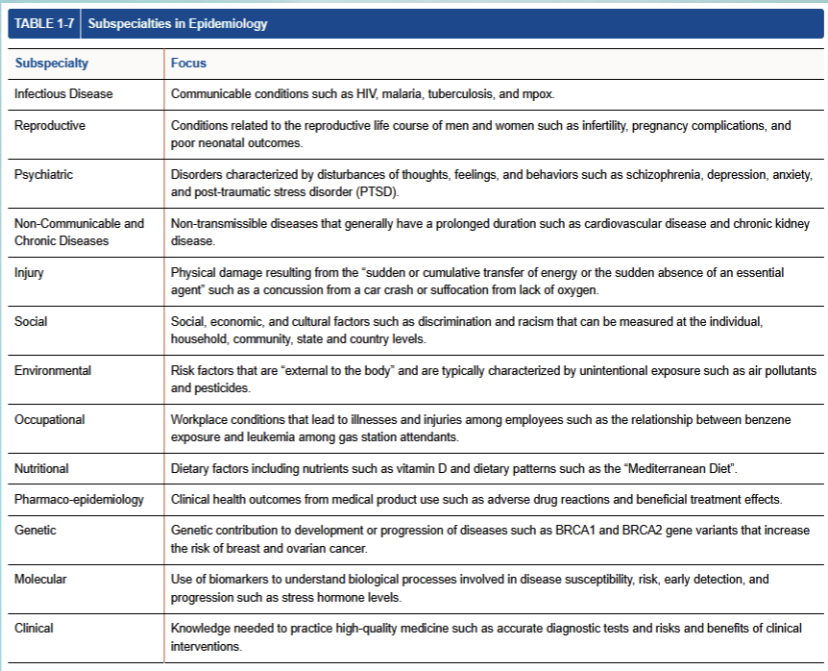
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Epidemiology:
the study of the distribution and determinants of disease frequency in human populations and the application of this study to control health problems
descriptive
analytic/ scientific
Epidemiology is based on what two fundamental assumptions?
human disease does not occur at random
factors or determinants can be identified by systematic investigation of populations or subgroups within populations
Human populations:
a group of people with a common characteristic such as residence, age, gender, group membership, etc
Disease frequency:
counting the number of cases of a disease in a population over a specific time period
Determinants:
factors that cause some people to get disease or factors that prevent in getting a disease
exposures
Disease distribution:
the pattern of disease according to the characteristics of a person, place, and time
who is getting sick
where is it occurring
how is it changing over time
Disease control:
the reduction or elimination of disease occurrence
accomplished through epidemiology research and surveillance
Hypothesis:
a testable statement that tries to explain a set of observations and can be tentatively rejected (or not rejected) through scientific research
project expected association between two or more measurable variables
carry clear implications for testing stated relations
Historical Development of Epidemiology:
spans 400 years
progress slow and unsteady
key figures
John Graunt
James Lind
William Furr
John Snow
Cholera:
swept into Europe in early 1800s, specifically London and Paris
symptoms include
nausea, dizziness
violent vomiting and diarrhea
“Rice water” stools
death
cardiovascular collapse
What were the beliefs about transmission of Cholera?
believed to be person-to-person via respiratory system
miasmas → mysterious vapors from swamps, cemeteries, cesspools
John Snow:
London physician to the poor who studied cholera outbreaks in the 1830s and saw it was transmitted by fecal contamination of drinking water
reasoned it might be transmitted by water or food due to gastrointestinal symptoms
conducted landmark series of studies
tested his hypothesis about mode of transmission
led to investigation
London Water Supply:
some families carried water from community pumps, but others got water from companies that pumped water from the Thames River via pipes
snow compared rates of mortality from cholera based on water supply companies in subdistricts of London
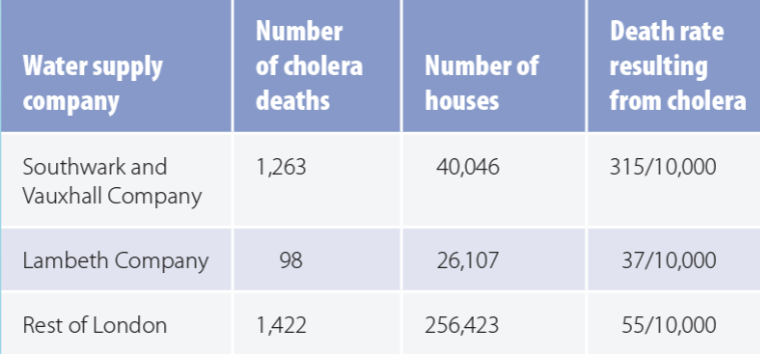
What were the significance of John Snow’s endeavors?
based on observation and reason he proposed a new hypothesis for how cholera was transmitted → one of the first observational studies
tested hypothesis by collecting data systematically and comparing groups of people
established an association between certain drinking water and getting cholera
never found direct evidence
argued for an intervention that prevented more cases
What is the cause of cholera?
bacterium, Vibrio cholera, which is transmitted by ingestion of water or food contaminated with sewage
What have been some Epidemiological Milestones?

Descriptive Epidemiology:
describe disease patterns; identify and count cases of disease in populations and conduct simple studies
monitor public’s health
evaluate success of intervention programs
generate hypotheses about causes of disease

Analytic Epidemiology:
search for disease causes and preventions; compare groups and systematically determine if there is an association
evaluate hypothesis about causes of disease
evaluate success of intervention programs

Closer look at Descriptive Epidemiology:
main uses
identify problems, trends, and high-risk groups
public health planning: where to spend resources
generate hypotheses for analytical epidemiology
questions asked
what are the main diseases in a population?
who is getting disease?
how does it vary across place and time?
limitation: CANNOT identify the causes of disease

Is the following data of the Nile Virus considered an outbreak?
Yes

Is the following data of Tuberculosis considered an outbreak?
No
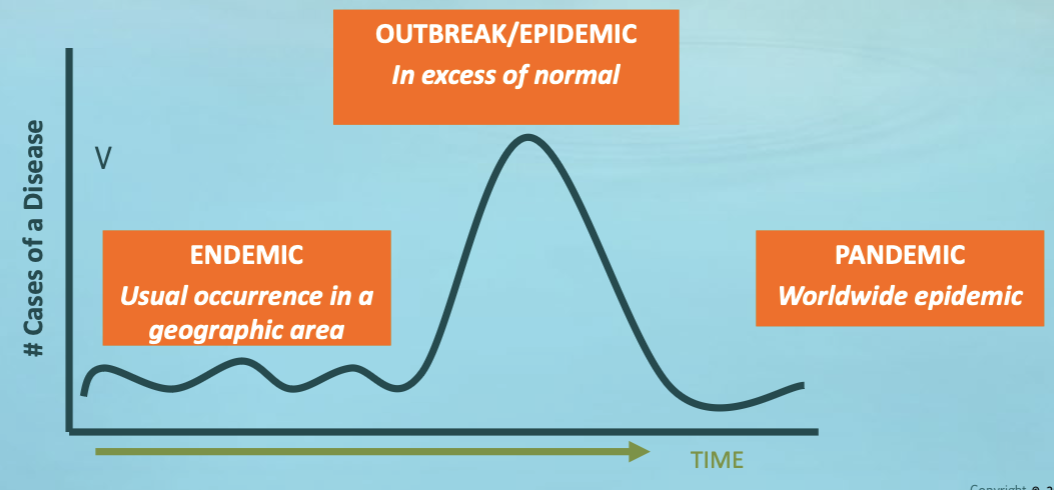
Closer look at Descriptive Studies (outbreak):
the occurrence of cases of an illness clearly in excess of what is normally expected
endemic
epidemic
pandemic
What is the goal of public health?
focuses on preventing illness of the population and implementing solutions typically involving community-level interventions that control or prevent cause of problem
assessing health status of population
educational programs
Basic health research:
study disease in a laboratory setting by conducting experiments on cells, tissues, and animals in order to understand disease mechanisms or processes
regulate all important aspects of the experimental conditions
results are often difficult to extrapolate to real-life situations involving humans
Clinical health research:
focus research questions mainly on disease diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis in individual patients
usually based on people who come to a medical care facility
often unrepresentative of the full spectrum of disease in the population
Public health research:
study ways to prevent disease and promote health in the population at large
mainly disease prevention not treatment
units of community rather than individual
John Graunt:
summarized the patterns of mortality in 17th-century London and discovered the regularity of deaths and births
James Lind:
conducted one of the earliest experimental studies on the treatment of scurvy among sailors using sound experimental principles
found that the consumption of oranges and lemons was the most effective remedy for scurvy in this population
William Farr:
pioneered many activities encompassed by modern epidemiology
calculation of mortality rates using census data for denominators
fair comparisons
Streptomycin Tuberculosis Trial:
one of the first modern experimental studies on the use of streptomycin to treat pulmonary tuberculosis
used random assignment
placement of restrictions on the type of patient eligible for the trial
free of bias
considered the ethical issues involved in conducting the trial
Doll and Hill Studies:
conducted groundbreaking studies on cigarette smoking and lung cancer in the 1950s
Framingham Study:
notable for bringing about a shift in focus from infectious to noninfectious diseases following World War II
development of appropriate methods for measuring the major risk factors for coronary heart disease
solving problems associated with measurements that vary over time
What are some of the current challenges of modern epidemiologists?
air, water, and soil pollution
global warming
population growth
poverty and social inequality
civil unrest and violence