Coordination and Response
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Homeostasis
Maintaining a stable internal environment to both internal and external conditions
Fill in the blanks: The body detects a _______ (change) then responds to it via either of the 2 _______ _______
The first system is the _______ system: the brain sends _______ _______ across the body. This system carries out _______ but _______-term changes
The second system is the _______ system: glands release _______ into the _______. This system carries out _______ but _______-term changes
The body detects a stimulus (change) then responds to it via either of the 2 control systems
The first system is the nervous system: the brain sends nervous impulses across the body. This system carries out fast but short-term changes
The second system is the endocrine system: glands release hormones into the bloodstream. This system carries out slow but long-term changes
Explain the function of Receptors, Coordination Centres, and Effectors
Receptors: Detect the stimulus
Coordination Centres: Receive information about the stimulus and coordinate a response
Effectors: Organs or glands that carry out the change conducted by the coordination centre
The nervous system is made up from two smaller systems. Name them and explain the difference between them
The nervous system is made up from the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) which includes the nerves throughout the body, and the Central Nervous System (CNS) which includes the brain and spinal cord
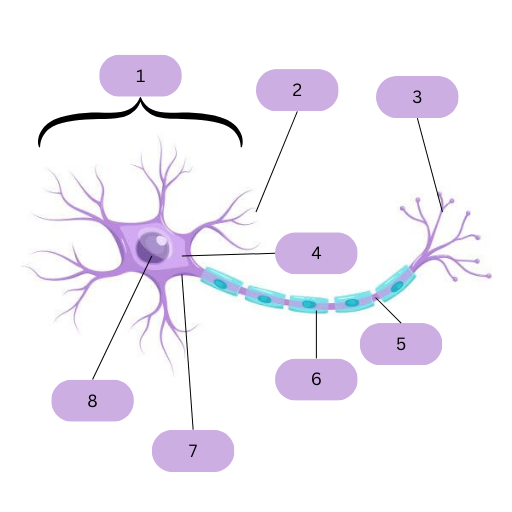
Nerves consist of neurons (nerve cells) that transmit the fast electrical impulses. Name labels 1-8 and explain all of them, but 3, 4, 7, and 8
Cell Body; Contains the main organelles
Dendrites: Branches of cytoplasm. The extended axon and dendrites help connect the cell to other neurons for the message to travel
Nerve Endings
Cytoplasm
Axon: Extended cytoplasm
Myelin Sheath: Insulates the impulses to make them travel faster and more efficiently
Cell Membrane
Nucleus
The Nervous System can perform voluntary (fully aware) and involuntary (no control over them) actions. Explain how the voluntary action works
Receptors detect the stimuli and send info to the brain via sensory neurons
The brain coordinates the response via the motor neurons which are connected to effector cells
The relay neurons (found in the CNS) connects the sensory to the motor neuron
Fill in the blanks: Between each neuron there is a _______ (gap) which cannot be crossed by _______ _______
When the _______ arrives at the gap, it release a chemical - _______ - these cross the synapse by _______. The _______ then regenerates the _______
Between each neuron there is a synapse (gap) which cannot be crossed by electrical impulses
When the impulse arrives at the gap, it release a chemical - neurotransmitters - these cross the synapse by diffusion. The neurotransmitters then regenerates the impulse
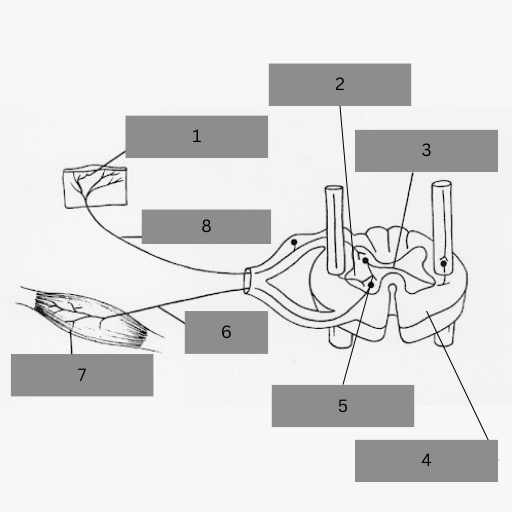
Reflexes are involuntary, rapid, and automatic responses - they travel in a nerve pathway called the Reflex Arc. Name labels 1-8
Receptor
Grey Matter
Intermediate/Relay Neuron
White Matter
Synapse
Motor Neuron
Effector
Sensory Neuron
The CNS is protected. What protects the brain and the spinal cord
The cranium protects the brain
The vertebral column protects the spinal cord
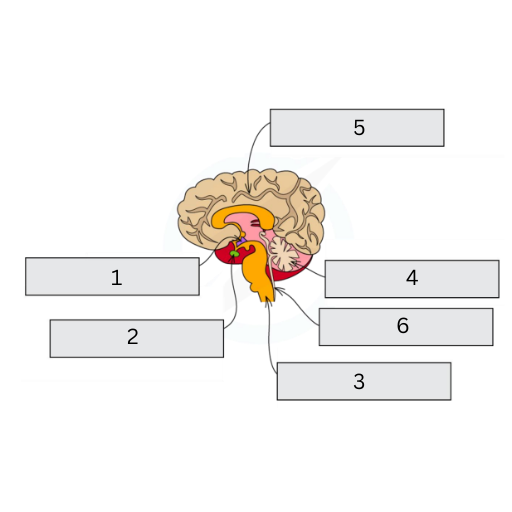
This is a diagram of the brain. Name labels 1-6, and explain the function of all, but 6
Hypothalamus: Involved in homeostasis
Pituitary (Master) Gland: Regulates many body functions
Medulla (Oblongata): Controls unconscious activities (e.g. breathing)
Cerebellum: Responsible for muscle coordination and movement
Cerebral Cortex: Responsible for consciousness, memory, intelligence, and language
Spinal Cord
Hormones
Chemical messengers secreted by glands in the body that regulate and coordinate various processes
What is the function of the blood in the endocrine system
The blood carries the hormones from the gland that secret them to the target destination through the bloodstream
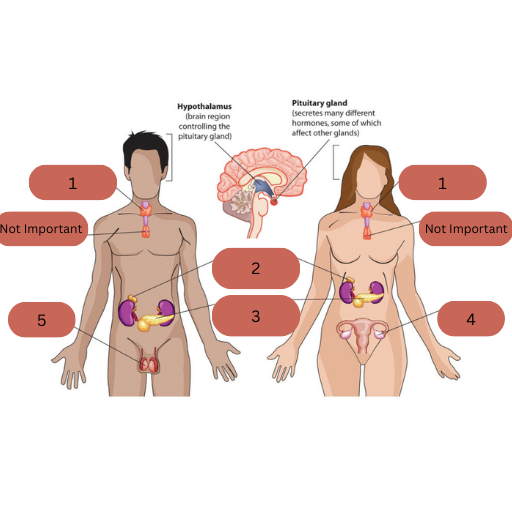
This is the main endocrine system. Name labels 1-5, state the hormone each gland secretes and why
Thyroid Gland: Secretes thyroxine which controls metabolic rate and affects growth
Adrenal Gland: Secretes adrenaline for a fight or flight response
Pancreas: Secretes insulin and glucagon to regulate blood glucose levels
Ovaries: Secrete oestrogen and progesterone for sexual development
Testicles: Secrete testosterone for sexual development
State all 5 hormones that the pituitary (master) gland releases
Growth Hormones - Control growth
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone - Stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete thyroxine
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone - Develops follicles in ovaries and increase sperm production
Luteinising Hormone - Stimulates ovulation and testosterone release
Anti-Diuretic Hormone - Causes kidneys to reabsorb water
Explain how Blood Glucose level regulation occurs
When the blood sugar levels are low, the pancreas secretes glucagon hormone which converts stored glycogen to glucose to increase the blood sugar levels
Alternatively, when the blood sugar levels are high, the pancreas secretes insulin hormone which stores the excess glucose to glycogen to decrease the blood sugar levels
This is a negative feedback mechanism
The conversion between glycogen and glucose occurs in the liver - the job of the pancreas is to release hormones
Negative Feedback
Negative feedback works to oppose something to restore homeostasis. For example, when the body temperature is too high, the body cools itself down by setting itself a low temperature