GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING - TOPIC 3
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
This is the strength with which soil materials are held together or the resistance of soil to deformation and rupture.
Soil consistency
Four stages of consistency
Liquid state
Plastic state
Semi-solid state
Solid state
Identify the consistency of the soil based on the strength (kPa)
0-24 kPa
24-48 kPa
48-96 kPa
96-192 kPa
192-383 kPa
>383 kPa
Very soft
Soft
Medium
Stiff
Very stiff
Hard
When a fine-grained soil is mixed thoroughly with a large quantity of water, the resulting suspension is in a liquid state, and offers practically no resistance to flow. The soil has ____.
No shear strength
The water content of the suspension is gradually reduced to keep the consistency of the sample uniform. At this point, the soil starts to develop resistance to flow. The soil has ___ and change from liquid state to plastic state.
The soil can be molded into different shapes without rupturing because of plasticity.
Small shear strength
After further reducing the water content of the soil, the soil also loses plasticity and now becomes ___ .
The soil becomes brittle and molding the soil will result into cracking of the surface.
Semi-solid
In the ____, the soil cannot be remolded at all as it would lead to the soil specimen getting broken.
Solid state
The ___ are water contents at a certain limiting or critical stage in the soil behavior.
Atterberg limits
This is also known as the upper plastic limit, it is the water content at which the soil changes from the liquid state to a plastic state. It is the minimum moisture content at which a soil flows upon application of every small shear force.
Liquid limit
This is also known as the lower plastic limit, the water content at which the soil changes from the plastic state to a semi-solid state.
It is performed by repeatedly rolling an ellipsoidal-sized soil mass by hand on a non-porous surface. Casagrande defined the plastic limit as the water content at which a thread of soil just crumbles when it is carefully rolled out to a diameter of 3 mm (⅛”)
Plastic Limit
This is the arbitrary limit of water content at which the soil tends to pass from the semi-solid to solid state. It is the water content at which a soil, regardless of further drying, remains constant at volume.
Shrinkage limit
Formula for shrinkage limit
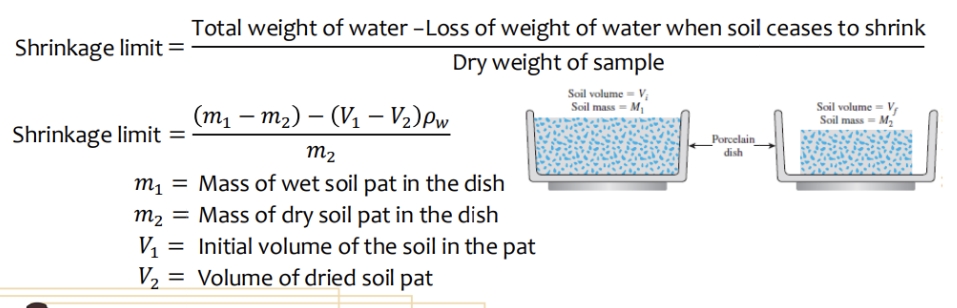
It is the ratio of the volume change of soil as a percentage of the dry volume to the corresponding change in moisture content.
Shrinkage ratio
formula for shrinkage ratio and specific gravity
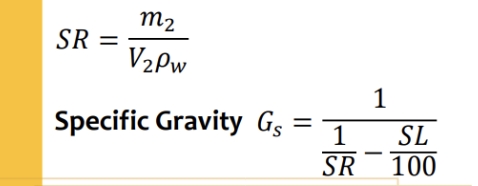
It is the range of water content within which the soil exhibits plastic properties (i.e. difference between liquid and plastic limit)
Plasticity Index (PI = LL - PL)
It is the range if water content within which the soil is in a semisolid state of consistency (i.e. difference between the plastic and shrinkage limit)
Shrinkage Index (SI = PL - SL)
It is defined as the ratio of the difference between the liquid limit and the natural water content to the plastic limit of a soil.
Consistency Index (relative consistency)
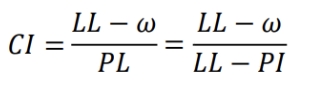
It is defined as the ratio of the difference between the natural water content and the plastic limit to the plasticity index.
Liquidity Index (water-plasticity ratio)
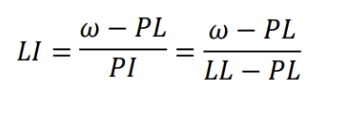
Characteristics of Soil
LI < 0 Brittle Solid
LI < 1 Plastic
LI > 1 Liquid