Lesson 6.3: Taxes and Spending in Fiscal Policy
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards made from a presentation segment created as a lesson on taxes and spending in fiscal policy.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms

Fiscal policy
Policies the government adopts to speed up or slow down economic growth for stable aggregate supply and aggregate demand
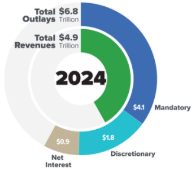
Government revenue
Funds that flow into the government from personal income, social insurance, and corporate profit taxes
Education and defense
The largest purchases of the United States using tax revenue
Medicare and Social Security
The largest transfers of the United States using tax revenue
GDP
The sum total of net exports, consumer spending, government spending, and investment spending
Government spending
Spending performed by the government as it purchases goods and services
Consumer spending
Spending performed by consumers
Can be influenced by the government through effects on disposable income with taxes and government transfers

Expansionary fiscal policy
Fiscal policy that increases aggregate demand, decreasing a recessionary gap to shift aggregate demand rightward for a restoration to LRAS
Seen through:
Increasing government spending
Reducing taxes
Increasing government transfers
These all indirectly boost consumer, investment, and government spending

Contractionary fiscal policy
Fiscal policy that reduces aggregate demand, decreasing an inflationary gap to shift aggregate demand leftward for a restoration to LRAS
Seen through:
Reducing government spending
Increasing taxes
Reducing government transfers
These all indirectly lower consumer, investment, and government spending
Discretionary fiscal policy
Fiscal policy that is the result of deliberate actions by policy makers, which can modify taxes or legislation to shift AD to the left or the right
Often used sparingly due to the problems associated with time lags
Time lag
The time between an incident and the adoption of discretionary fiscal policy, caused by:
Delays in the realization of an output gap
The time used to agree on an expansionary or contractionary plan
The time taken to adjust its spending
This can result in a significant delay, potentially even long enough for a market self-correction
Automatic stabilizers
Government spending and taxation rules that cause fiscal policy to be automatically expansionary or contractionary when the economy contracts or expands
Progressive tax policies are an example of this, where lowered tax rates and aid programs apply to the lower income
These can allow for aggregate demand to shift according to this increased or reduced spending