AP Psychology: Topic 4.7 - Emotion
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Affect
the feelings and emotions that people experience, and how a clinician interprets a client's expression of those feelings through non-verbal language

Physiological experiences
internal factors regulated by the autonomic nervous system (e.g., heart rate, perspiration, stomach activity) that influence emotion
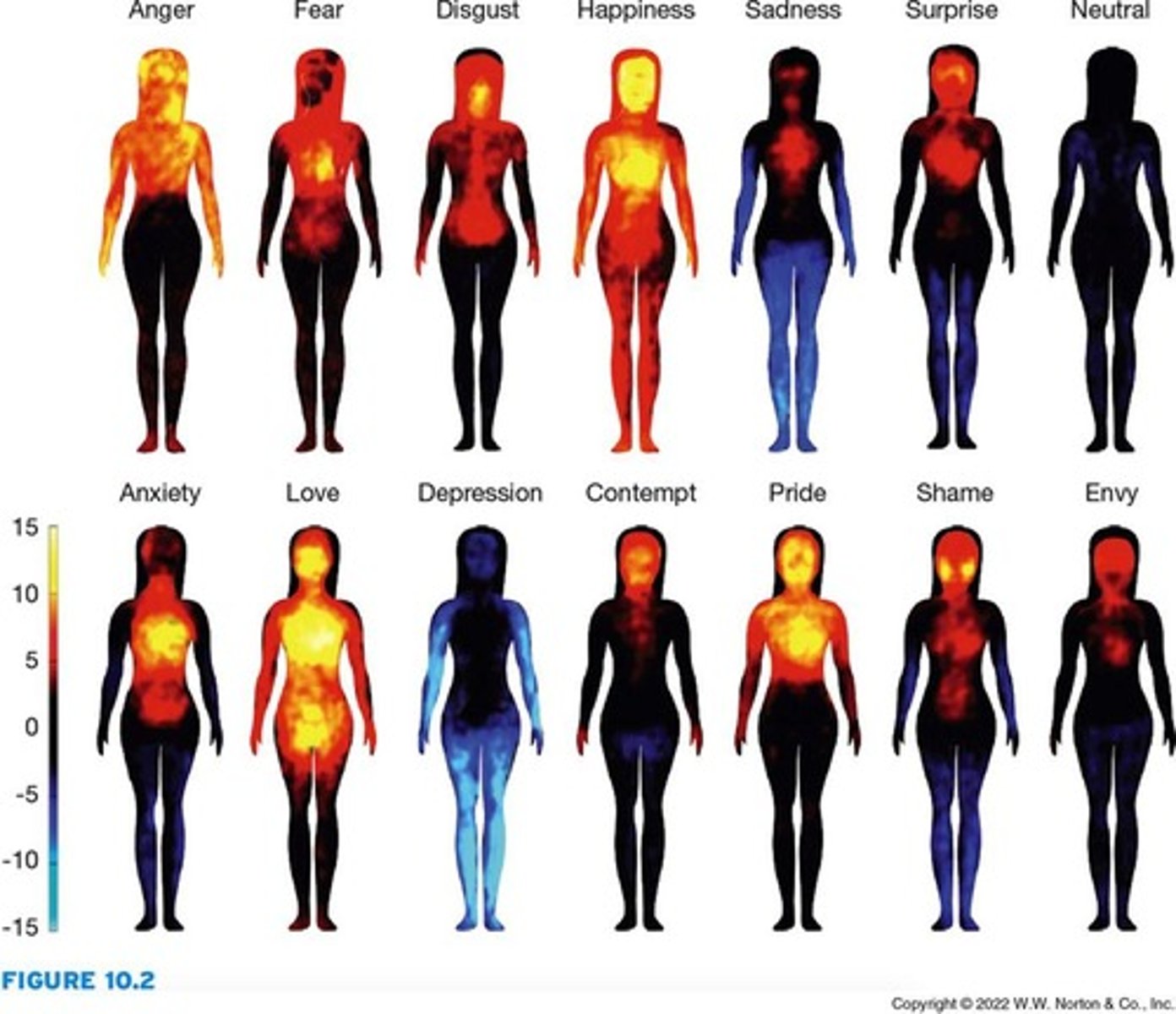
Cognitive experiences
how people think about and interpret external stimuli and how their thoughts influence the emotions they feel
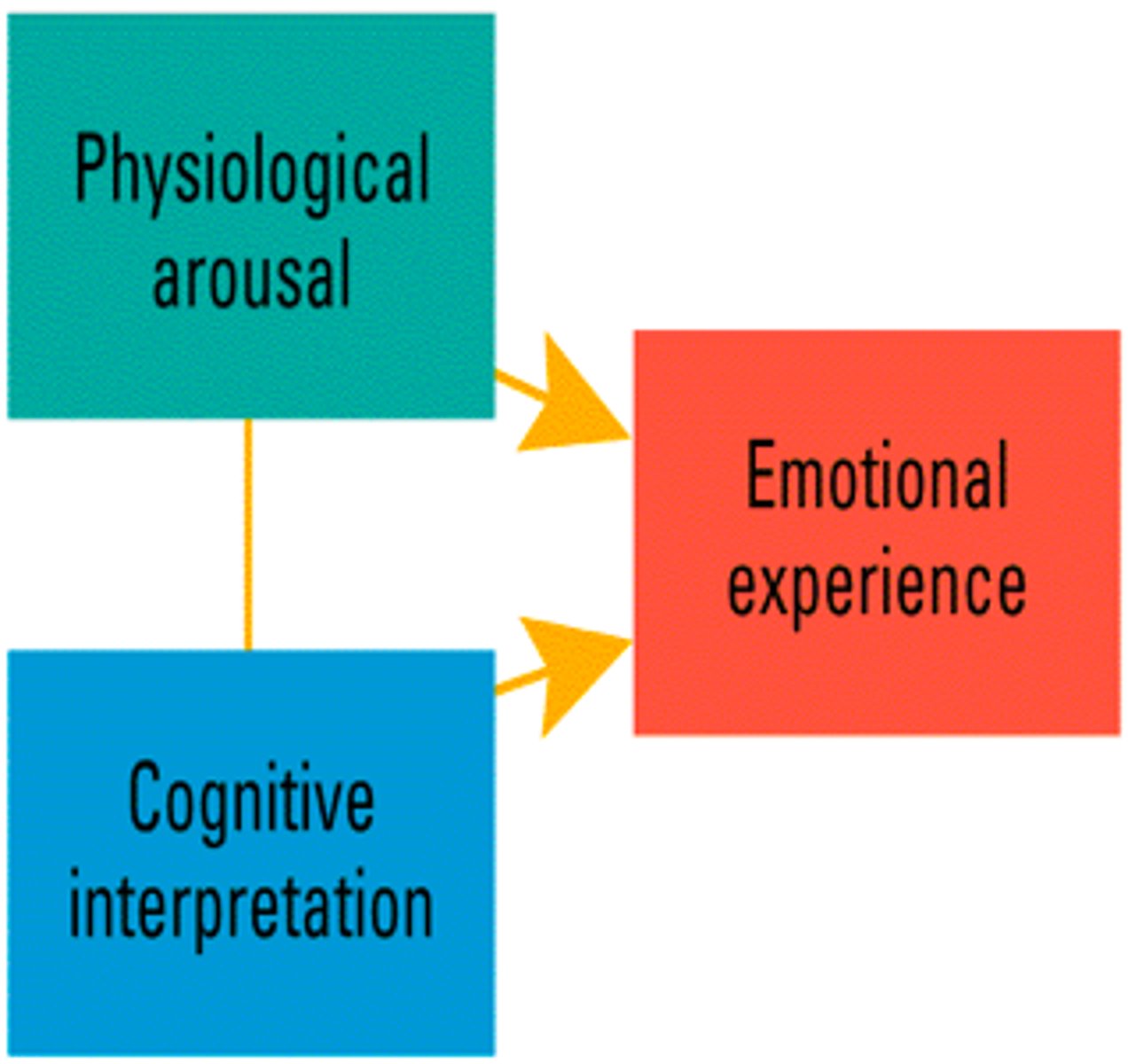
Cognitive label
According to the Schachter-Singer's theory, a person experiences an emotion when they have a physiological response and label it
Facial-feedback hypothesis
the idea that facial expressions can influence emotions as well as reflect them

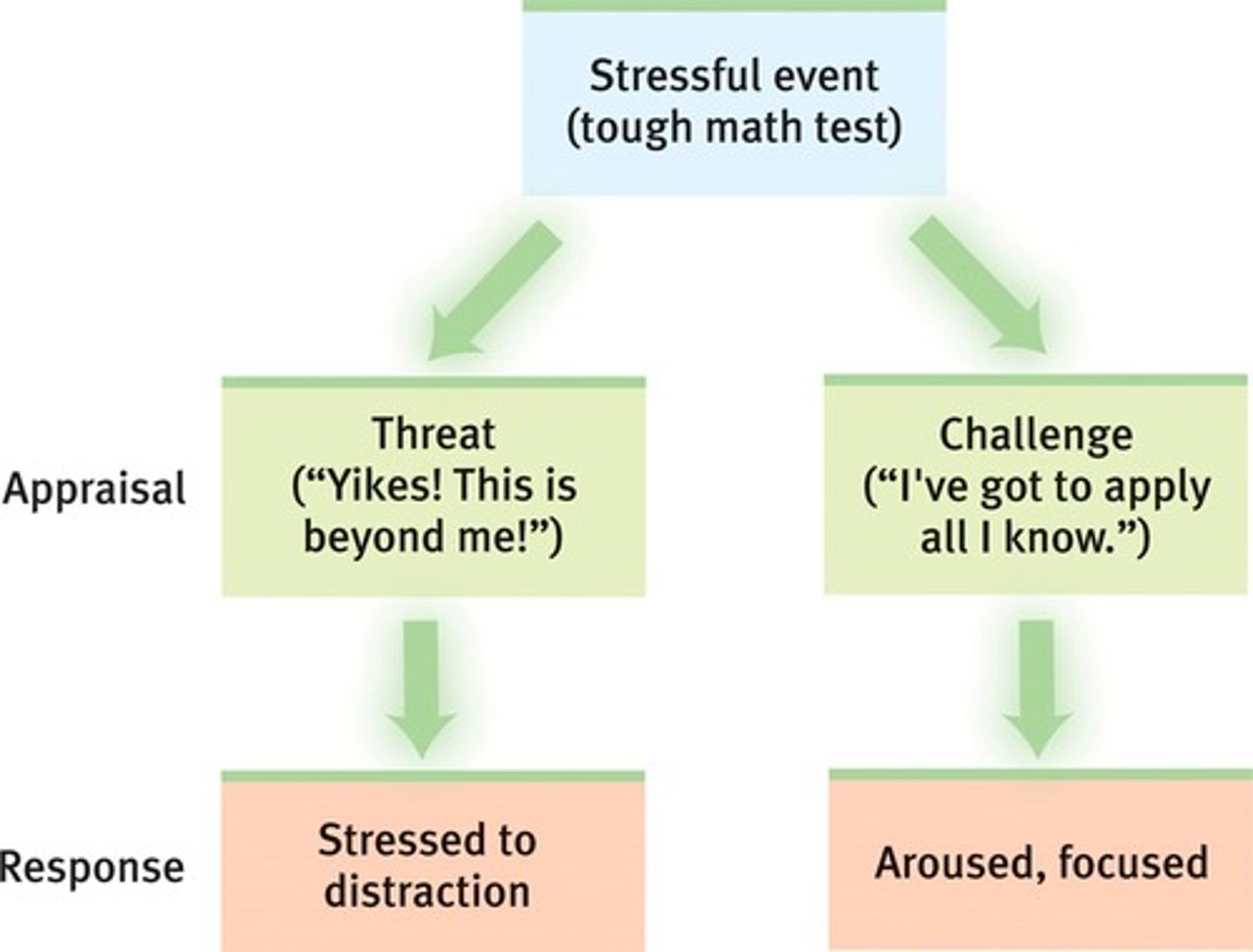
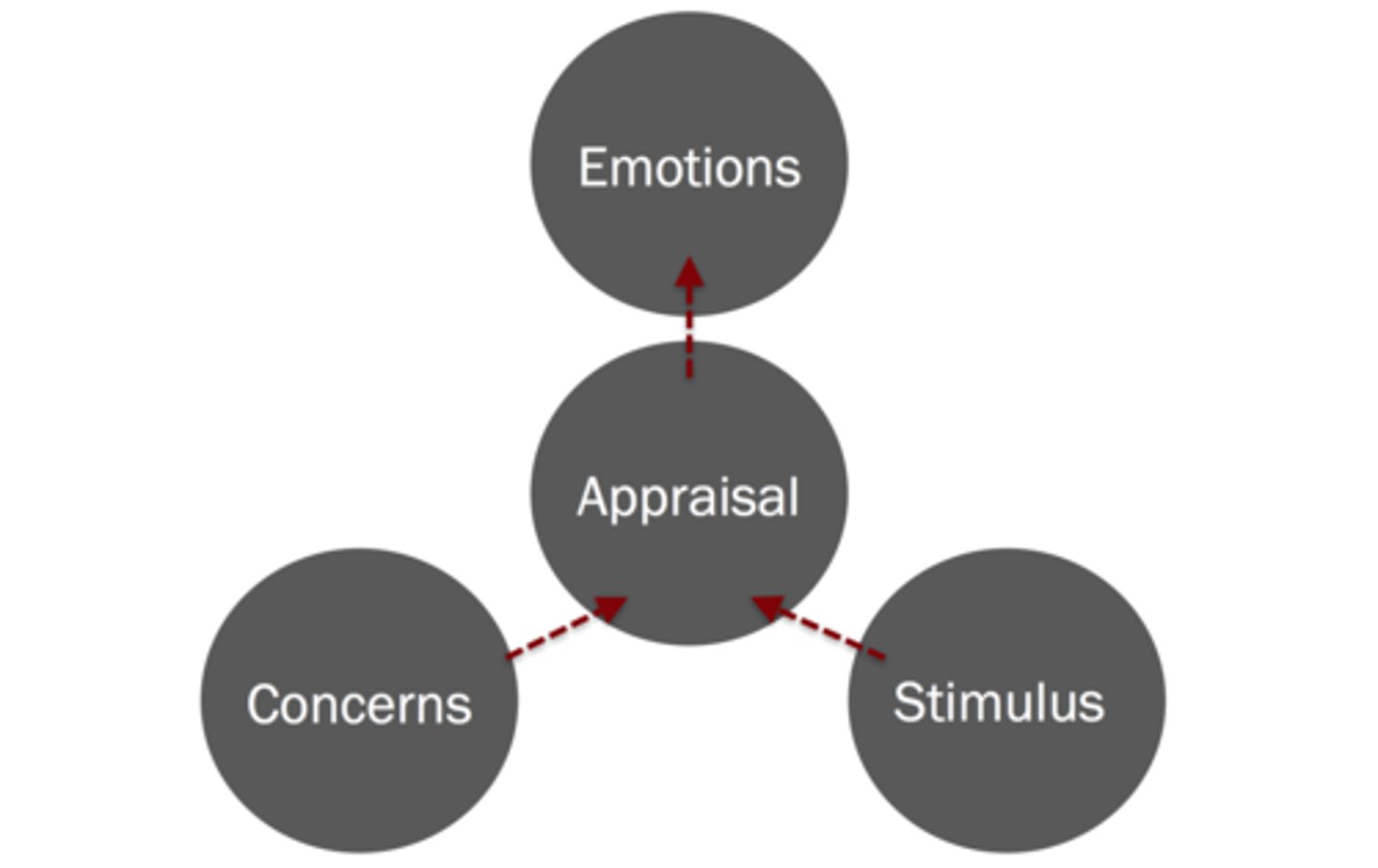
Cognitive appraisal
the process of interpreting an event, which leads to an emotional response (i.e., emotions are directly tied to how a person evaluates a situation)
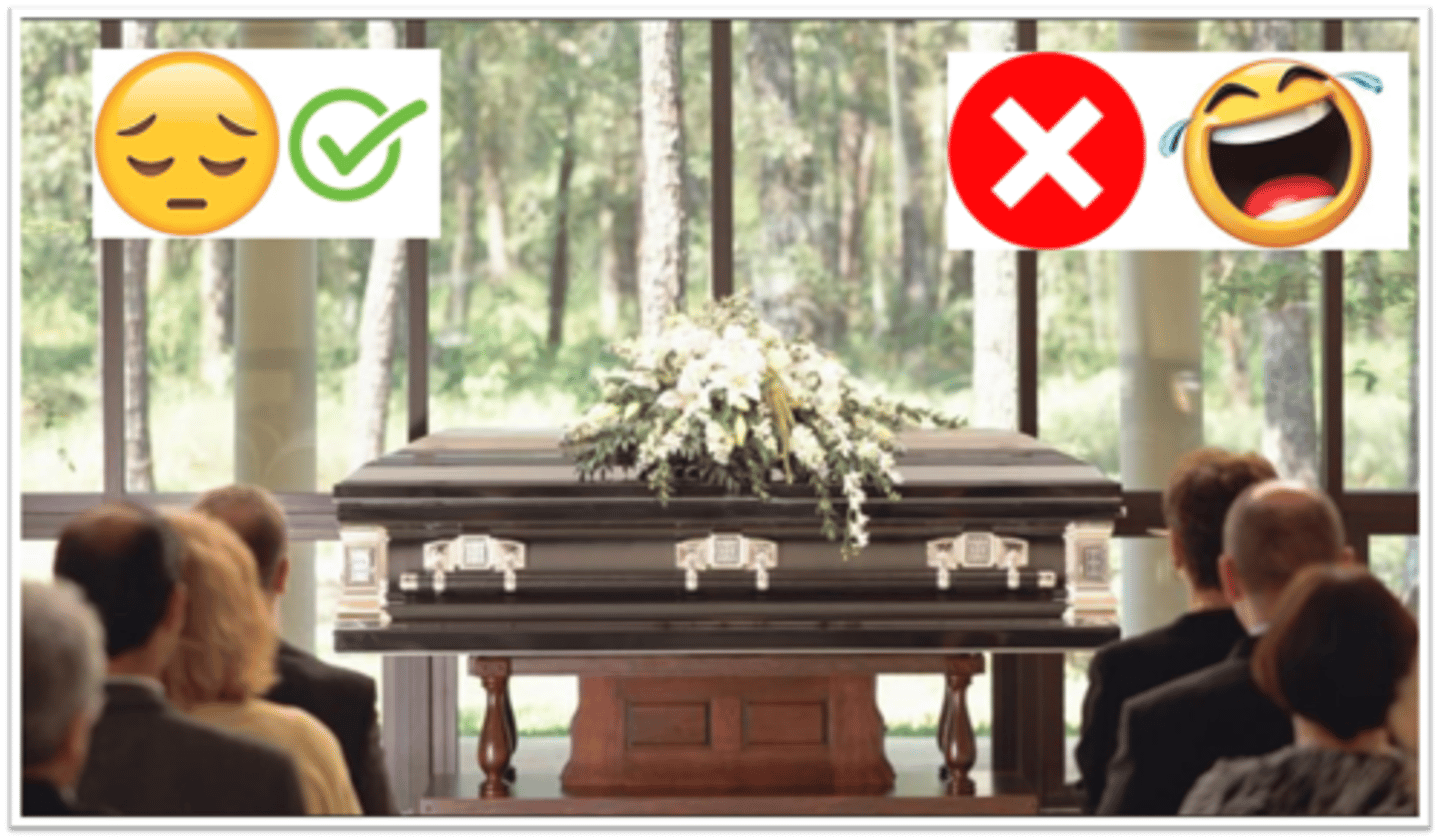
Display rules
culturally determined rules about which nonverbal behaviors are appropriate as emotional responses

Emotional elicitors
facial expressions that can trigger a response similar to other emotional stimuli that have the same valence (e.g., a disgusted face can elicit a similar response to a dirty toilet)
Broaden-and-build theory of emotion
states that positive emotion leads people to explore and develop new skills and resources, which in turn lead to more positive emotions and better health