Types and Relative Percentages of Leukocytes in Normal Blood
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
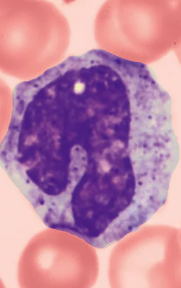
Neutrophils
A type of White blood cell (Leukocytes)
Granulocytes
Most numerous WBCs 50-70% of WBCs
Granules contain either hydrolytic enzymes or antimicrobial proteins “brew“ called defensins (spears)
Very phagocytic
a cell that is highly capable of phagocytosis, meaning it can efficiently engulf and destroy foreign particles, such as bacteria, fungi, and cellular debris. referred to as “bacteria slayers”
Defensis granules merge with phagosome(vesicle)
Form “spears“ that piece holes in membrane of ingested microbe
Characteristics:
Multilobed nucleus
Lilac color cytoplasm, due to pale red and blue cytoplasmic granules
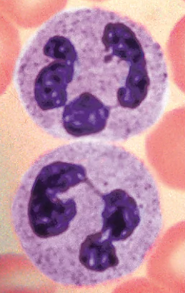
Eosinophils
A type of White blood cell (Leukocytes)
Granulocytes
2-4% of all WBCs
Red-staining granules contain digestive enzymes
Release enzymes onto large parasitic worms, digesting their surface
Also play a role in allergies and asthma, as well as immune response modulation
Lack enzymes that specifically digest bacteria
Reside in loose tissues
Characteristics:
Bilobed nucleus, connected by a broad band (thick)
red cytoplasmic granules
Large coarse granules
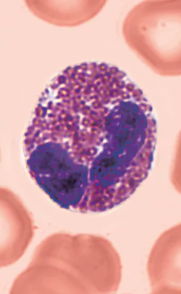
Basophils
A type of White blood cell (Leukocytes)
Granulocytes
Rarest WBCs, make up only 0.5-1%
Large, purplish-black granules contain histamine
Histamine is a inflammatory chemical that acts as a vasodilator (makes blood vessels dilate) amd attracts other WBCs to the inflamed site.
Characteristics:
Bilobed nucleus
Purplish-black cytoplasmic granules
Nucleus deep purple with one to two constrictions, U or S shaped and a little hard to see
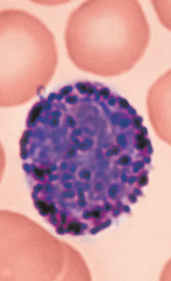
Lymphocytes
A type of White blood cell (Leukocytes)
Agranulocytes
Second most abundant WBC, make up 25% of leukocytes
Few are found in blood, mostly found in Lymphoid tissue (ex: lymph nodes, spleen, etc.)
Crucial to immunity
Two types:
T lymphocytes (T cells): act against virus-infected cells and tumor cells
B lymphocytes (B cells): give rise to plasma cells, which produce antibodies
Characteristics:
Large dark purple nucleus that takes up most of the cell volume; spherical or might have a slight indent
Pale blue cytoplasm around nucleus
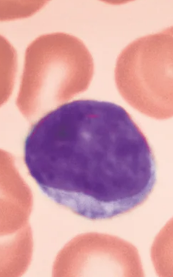
Monocytes
A type of White blood cell (Leukocytes)
Agranulocytes
3-8% of leukocytes
The largest leukocytes
Leave circulation, enter tissues, and differentiate into macrophages with prodigious appetites
macrophages are actively phagocytic cells, crucial against viruses, intracellular bacterial parasites, and chronic infections.
macrophages can activate lymphocytes to mount an immune response
Characteristics:
U-ish, Kidney-shaped nucleus
Abundant pale blue cytoplasm
darkly stained purple nucleus