Lab 6 (Nitration of Naphthalene)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
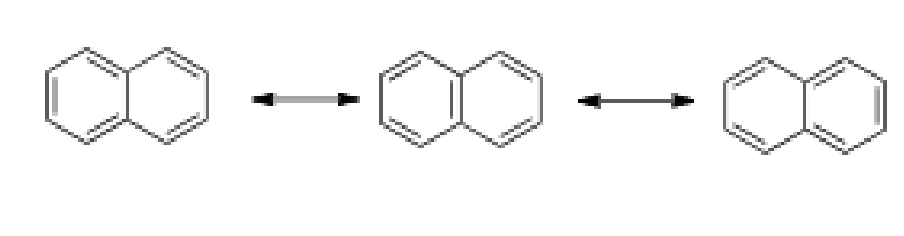
Draw the 3 resonance structures of naphthalene
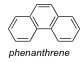
Count π-electrons in phenanthrene. Is phenanthrene aromatic?
14 pi electrons follows (4n + 2) π-electron rule so yes
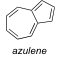
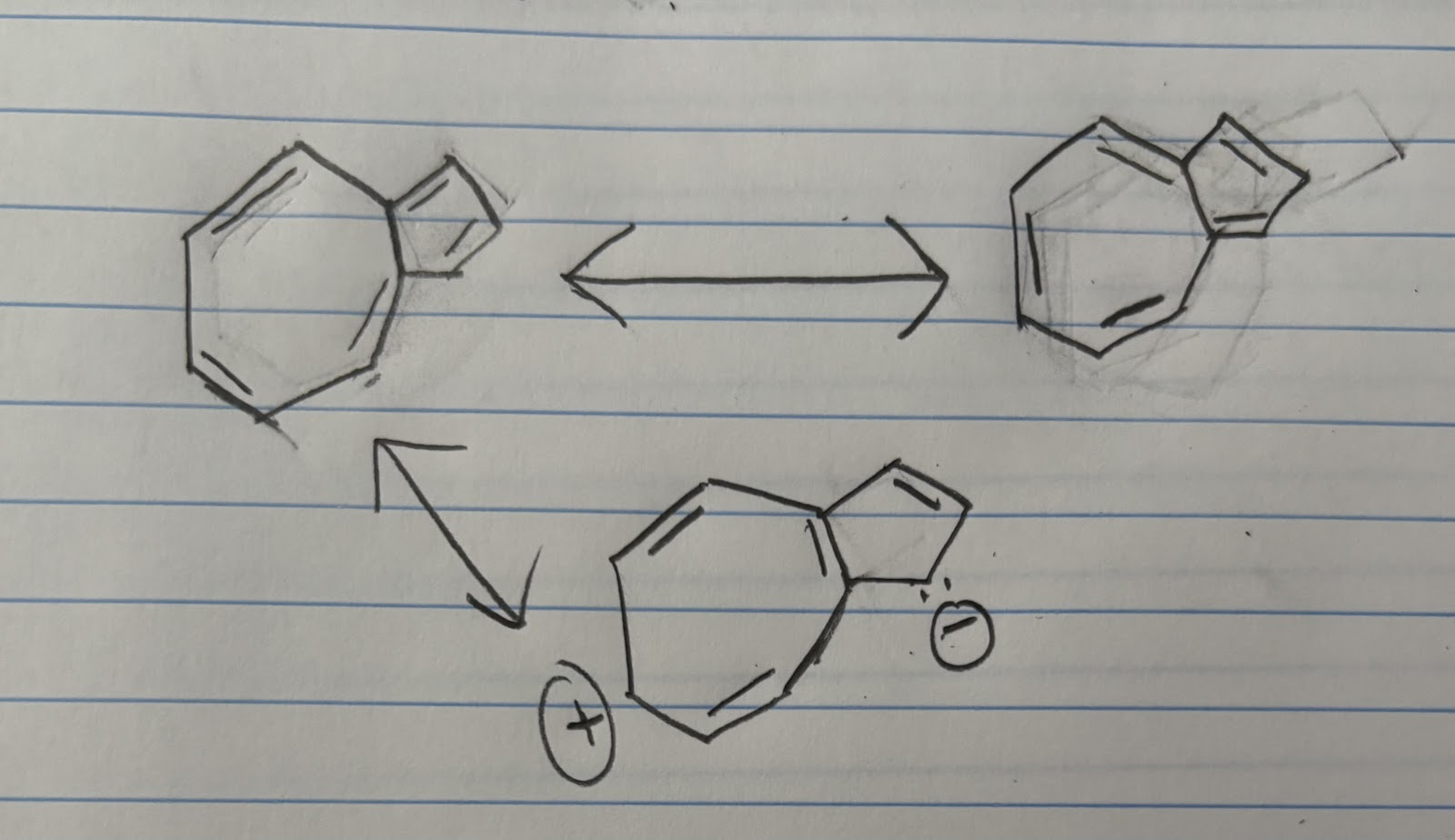
Draw the important resonance structures of azulene. Count -electrons in azulene. Is azulene aromatic?
10 pi electrons, yes
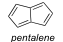
Count π-electrons in pentalene. Is pentalene aromatic?
8 pi electrons, no
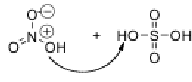
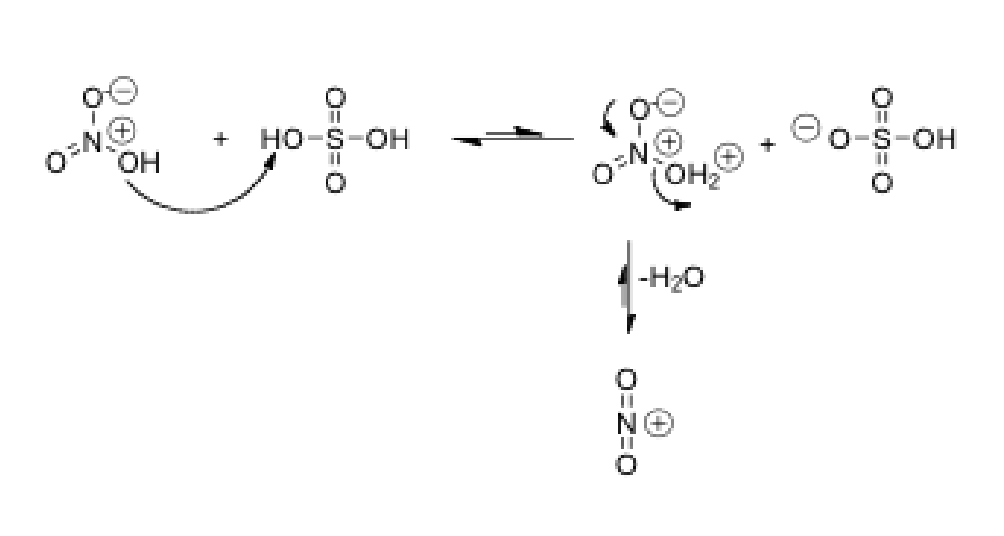
Draw the mechanism of formation of nitronium ions in the mixture of sulfuric acid and nitric acid.
First, OH of nitric acid takes a proton from the sulfuric acid, forming H2O
This H2O group then leaves as water and then just leaves NO2
Electrons from other single bonded Oxygens shift to make 2 oxygens double bonded to the N
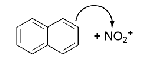
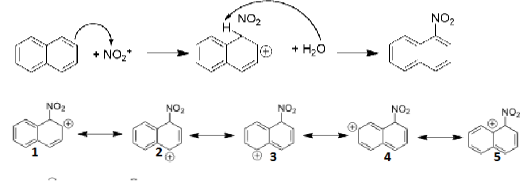
Draw the mechanism of the formation of 1-nitronaphthalene. Show the relevant resonance structures.
Electrons from aromatic compound attack the electrophile
Then water deprotonates the proton, and then the leftover electrons create a pi bond
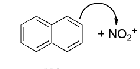
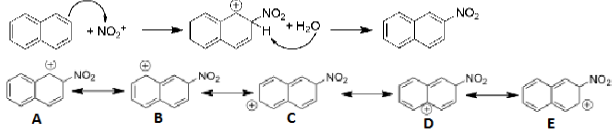
Draw the mechanism of the formation of 2-nitronaphthalene. Show the relevant resonance structures.
Electrons from aromatic compound attack the electrophile
Then water deprotonates the proton, and then the leftover electrons create a pi bond
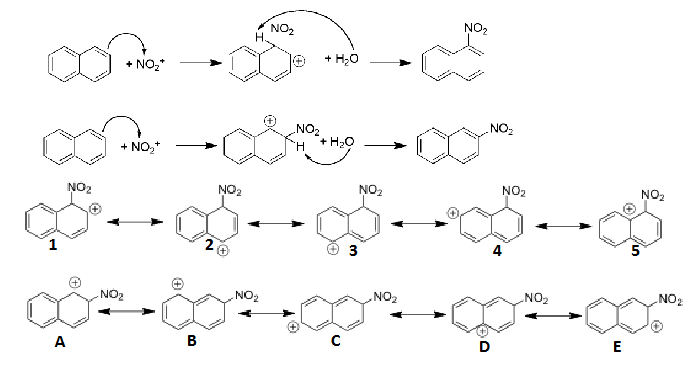
Explain, based on mechanism, which is the main product of nitration naphthalene
Resonance structures of intermediate of 1-nitronaphthalene
Resonance structures 1 and 2 are still aromatic (bc this structure has more aromatic resonance structures it is more stable than 2-nitronaphthalene)
This structure forms faster in the kinetic sense
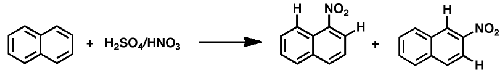
Which product 1-nitronaphthalene or 2-nitronaphthalene should be the thermodynamic product? Why?
2-nitronaphthalene
Kinetic product has more steric hindrance while thermodynamic product has less since the substituent is farther away from the other protons
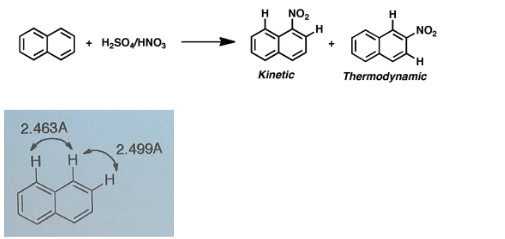
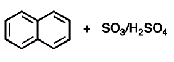
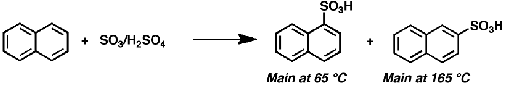
Why does sulfonation of naphthalene, performed at higher temperature, occurs mainly at the 2-position?
Higher temp favors thermodynamic product, thermodynamic product is main product if reaction is reversible
Because sulfonation is reversible it allows it to transition from the kinetic product to the thermodynamic product at high temperatures
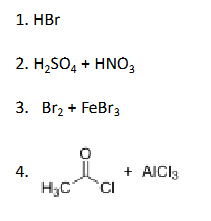
Which of the following reagents will not give a product of electrophilic aromatic substitution with benzene?
HBr
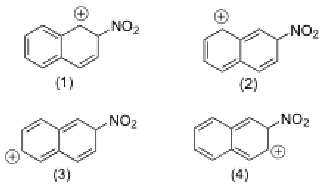
Which resonance structure is the most stable (has lowest energy)?
1, because it is the only one with an aromatic system (conjugated pi bonds)
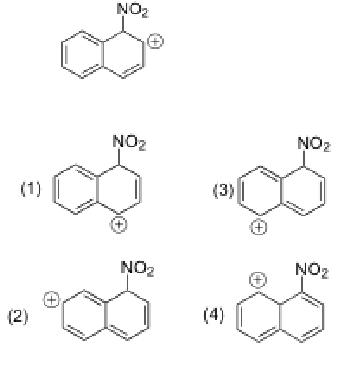
Which structure is not a resonance form of the following intermediate?
4
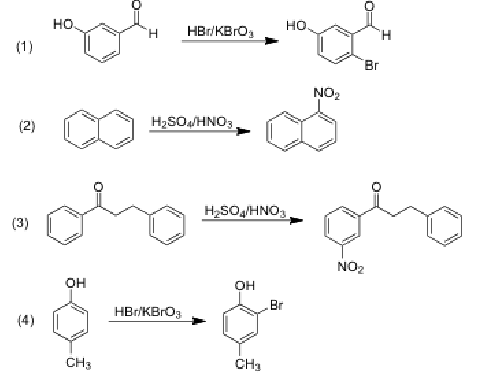
Which equation shows incorrectly the main product of electrophilic aromatic substitution?
3, because the carbonyl compound is deactivating so the substituent would be most likely to be added to the benzene attached to the alkyl group