Chapter 7: Vitamins and New Nutrients
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Vitamins
= organic compounds that
are not insufficiently produced in the body
are naturally present in foods
are necessary in small amounts to maintain normal functioning
lead to specific deficiency symptoms when absent from the diet
Vitamins: Remarks
Are essential FA and AA vitamins?
Endogenous synthesis by microbial flora
Synthesis capacity differs
according to animal species
according to conditions
Relation trace element - vitamin
Deficiency: difficult to detect and variable
Vitamins: General characteristics
= co-enzymes
Bonding to enzyme
covalently bound as substrate
strongly but non-covalently bound as substrate
Holo (with cofactor) vs apo (without cofactor)
weakly bound as substrate
Holo (with cofactor) vs apo (without cofactor)
Utilisation
vitamins need to be converted into active form so that they can be absorbed
Groups
group | vitamins |
vitaminers | E |
pro-vitamins | carotenoids and A |
water soluble | B,C |
fat soluble | A, D, E, K |
Vitamins: General characteristics: Groups according to function
group | vitamins |
involved in mono carbon transfer reactions | folate (M), B12, K and biotin |
hormones | A and D |
energy metabolism | B1, B2, B3, B5 |
anti-oxidants | C and E |
Vitamins: General characteristics: Deficiencies
Vitamin | Deficiency |
A | xerophtalmia |
B1 | beri-beri (dry and wet) → can be destructed by technology |
B12 and folate | megaloblastic anemia → inhibited DNA and RNA synthesis |
B3 | pellagra → in parts of body that are exposed to the sun |
C | scurvy |
K | flora or fat disturbance, infants |
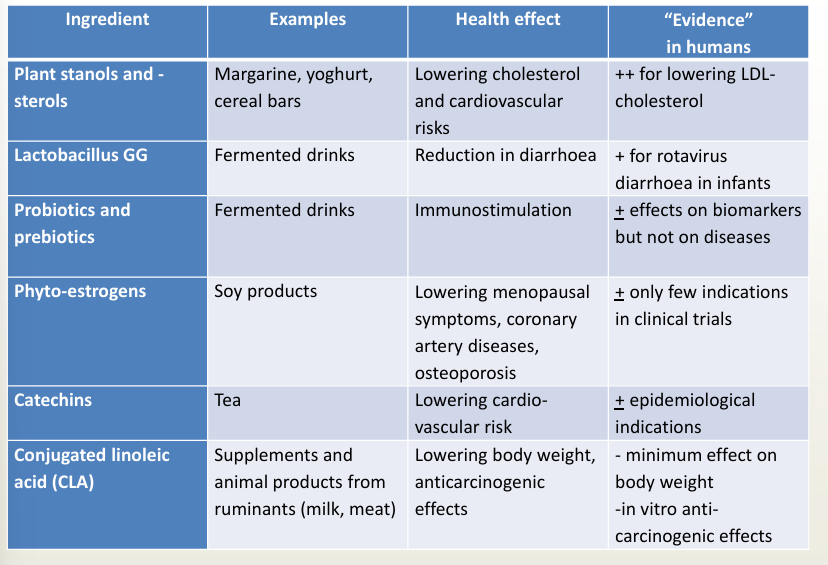
Vitamin A (!)
Source
Animal | Plant |
retinyl palmitate in liver and fatty fish | carotenoids in green and yellow-red vegetables |
high bioavailability | Low bioavailability Conversion beta-carotene into retinol beta-carotene → retinal → retinol 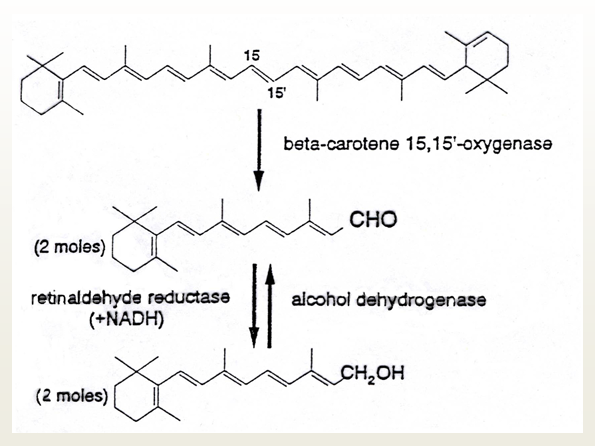 |
Absorbation form
= retinol
Transport and storage of retinol
1) retinol is bound to cellular retinol binding protein (c-RBP) and esterified
2) Esterified form is transported in chylomicrons (CM) to the liver (stellate cells in liver)
3) Retinol is mobilised from the liver after release by a retinyl ester hydrolase (low during protein malnutrition and inhibited by vitamin E and vitamin K)
4) Retinol binds as trans isomer to the plasma retinol binding protein (p-RBP) → secreted by the liver with regulation by estrogens and Zn
5) Retinol binds in target organ (eye, testes, uterus) to specific c-RBP
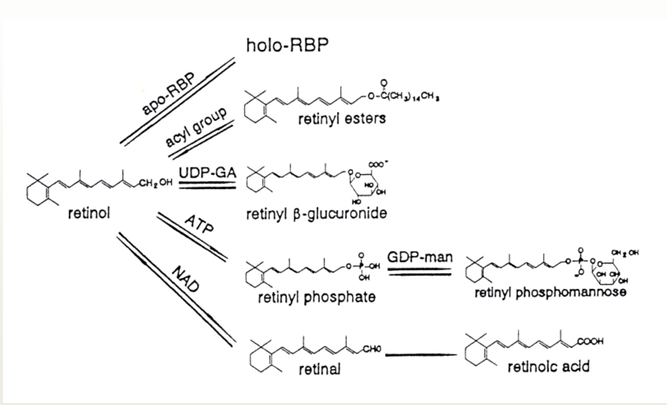
Metabolism of retinol
What | From … to … | Function + (location) |
Binding to a protein | retinol < - > holo-RBP | transport vitamin A (blood) |
Esterification | retinol < - > retinyl esters | storage vitamin A (liver) |
Conjugation | retinol < - > retinyl b-glucuronide | detoxification = only way to remove vitamin A when overdosis (bile / urine) |
Fosforylation | retinol < - > retinyl phosphate | lipid-carrier for sugar rests |
Glycosylation | retinyl phosphate < - > retinyl phosphomannose | glycoprotein synthesis (ephithelium) |
Reversible oxidation | retinol < - > retinal | sight (eye) |
Irreversible Isomerisation | retinal → retinoic acid | light sensitivity of eye |
Functions of vitamin A
Vision
Immune function
Cell growth and differentiation
Skin and epithelial health
Anti-oxidant (beta-carotene)
Toxicity vitamin A
Too much →
pregnancy dangers
eye dangers
neurological dangers
Vitamin D (source, metabolism, role in body, target groups, toxicity)
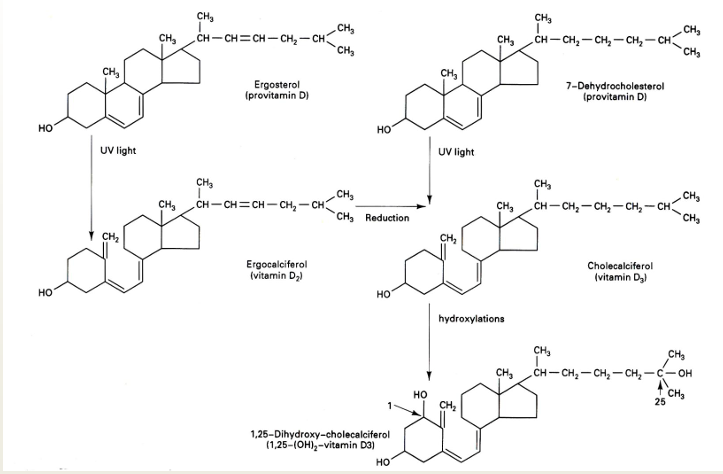
Source
vitamin D’s are not abundant in nature, but their pro-vitamins ergosterol and 7-dehydrocholesterol are present in vegetable and animal food
Metabolism
UV-light needed to form vitamins out of provitamins !!
1,25-diOH - cholecalciferol binds to vitamin D receptor protein in nucleus
Role in body
in Ca-P homeokinesis
plasma concentration of Ca | pathway |
Hypocalcaemia = low Ca-levels | PTH↑ → P diuresis + 25-OH-D hydroxylase ↑ → absorption Ca ↑ → bone mobilization Ca and P ↑ |
Hypercalcaemia = high Ca-levels | calcitonine in thyroid gland ↑ → Ca diuresis + 25-OH-D hydroxylase ↓ → absorption Ca ↓ → bone mobilisation Ca and P ↓ |
Target groups
Breastfed > bottlefed infants
Toxicity
excessive vitamin D → high 25-OH-D concentrations → bone weakening
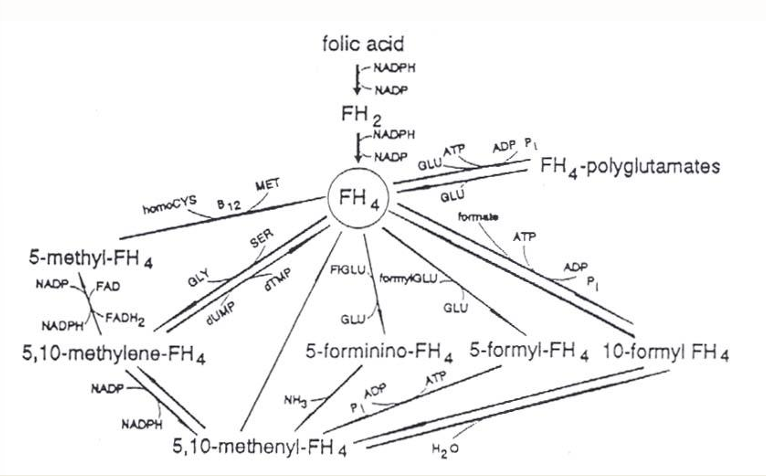
Vitamin B9 (source, metabolism, risk-benefit)
= folic acid = folate
= M
Source
in plants and animals as polyglutamyl derivates of tetrahydrofolic acid (FH4)
Bioavailability dependent of vitamin C, Fe, conjugase inhibitors
Metabolism
Further oxidation to 5-methyl-FH4 (methionine)
B12 brings 5-methyl-FH4 back to FH4 so that FH4 is not stuck in 5-methyl-FH4

Risk-benefit
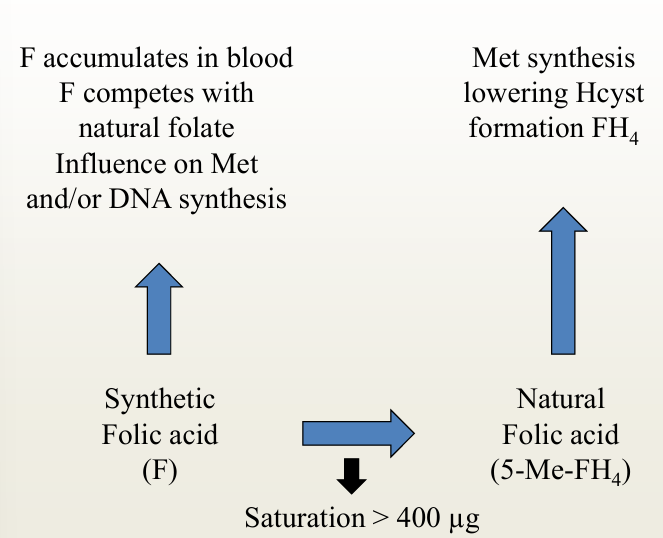
High intake of synthetic folic acid (>400 µg) can lead to accumulation of unmetabolized folic acid in the blood, competition with natural folates, and masking of vitamin B12 deficiency.
Toxicity
masking of vitamin B12 shortage
Normally shortage of B12
Anemia (shortage of B9) + nerve complaints
Shortage of B12 + high B9
No anemia + nerve complaints → more difficult to see that this is a problem of B12
interactions B9 and B12
= from 5-methyl-FH4 to tetrahydrolate (FH4)
= donates methylgroup
Vitamin B12 (source, metabolism, role in body, target groups, toxicity)
= cyanocobalamin
Co+ in center !!
Source
only by microbial synthesis
Metabolism
uptake via active transport in ileum with IF (requires calcium)
transport of adenosyl-B12 (animal) or methyl-B12 (human) via transcobalamines
Role in body
Adenosyl-B12 → cofactor of Me-malonyl-CoA mutase
Methyl-B12 → cofactor methionine synthase
Toxicity
not toxic
Deficiency
nerve problems
antioxidant vitamins
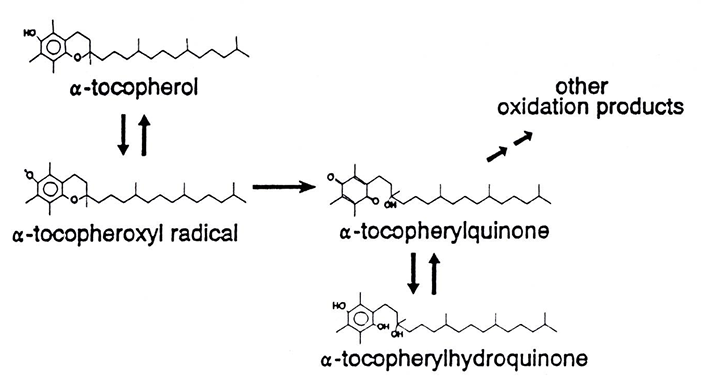
Vitamin E
Vitamin C
Antioxidant vitamins: vitamin E
toxicity !!
antioxidant vitamins: vitamin C
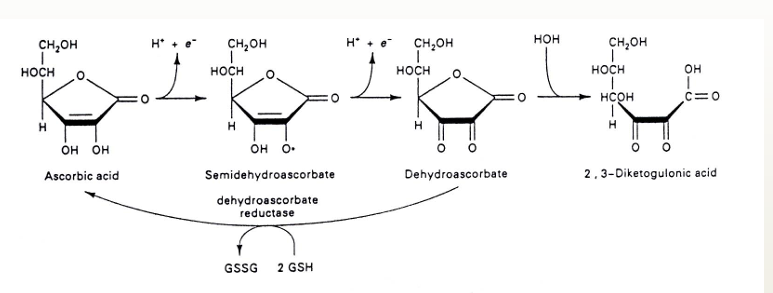
toxicity because it becomes pro-oxidative!! → interferes with synthesis of collagen
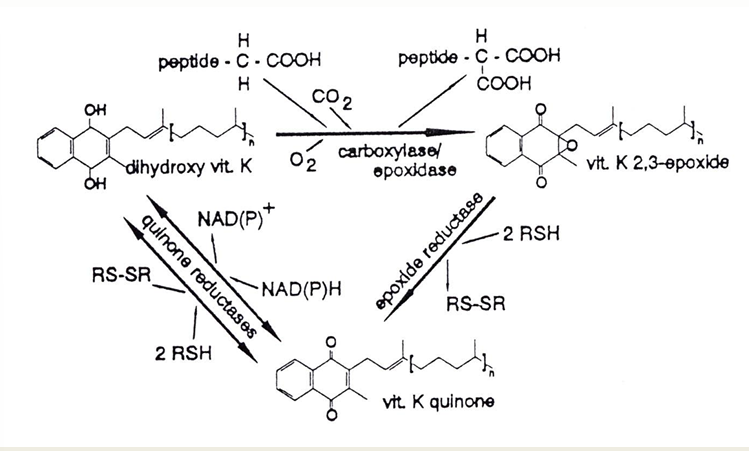
Vitamin K
source
plant: phylloquinones
bacteria: menaquinones
synthetic: menadion
Function
prothrombin = role in blood clotting
osteocalcin = skeleton
carboxylation glu-residues increases Ca-binding properties
New nutrients