The digestive system
1/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is digestion?
Digestion is the process by which your body breaks down the food you eat into smaller, simpler substances that can be absorbed into the blood and used for energy, growth, and repair.
OR
To convert large insoluble food molecules into smaller soluble ones
Why do we need to?
Small food molecules can pass through the walls of the small intestine and then dissolve into the blood stream. Large food molecules cant do this
Mechanical digestion
Digestion begins in the mouth where food is broken down by the teeth. This is called mechanical breakdown. The small parts of food are mixed with saliva and swallowed
Passage
Mouth
Oesophagus
Stomach
Small intestine
Large intestine
Anus
The stomach
After food is swallowed it enters the stomach which is basically a muscular bag filled with hydrochloric acide. So food enters the stomach from the gullet.
Two things happen to food in the stomach
microbes are destroyed
The chemical breakdown of food begins
The small intestine
From the stomach, food enters the small intestine where digestion is completed and the small digested food molecules are absorbed into the bloodstream
Large intestine
After the small intestine, the remains of any undigested food travel to the large intestine. All that is left of the food is water and waste material. The water is valuable and so it is absorbed into the large intestine into the blood stream.
Waste material
It cannot be digested or used by the body. This undigested waste travels to the rectum where it is stored until leaving the Body through the anus
Digestive enzymes
The chemicals that break large insoluble food molecules into smaller soluble molecules
Different types of digestive enzymes
The chemicals that break large insoluble food molecules into smaller soluble molecules. They are classified by the type of food that they affect, so there are three main types: carbohydrase, protease, lipase
Carbohydrase
Breaks carbohydrate into smaller sugars
Protease
Breaks protein into amino acids
Lipase
Breaks fat into fatty acids and glycerol
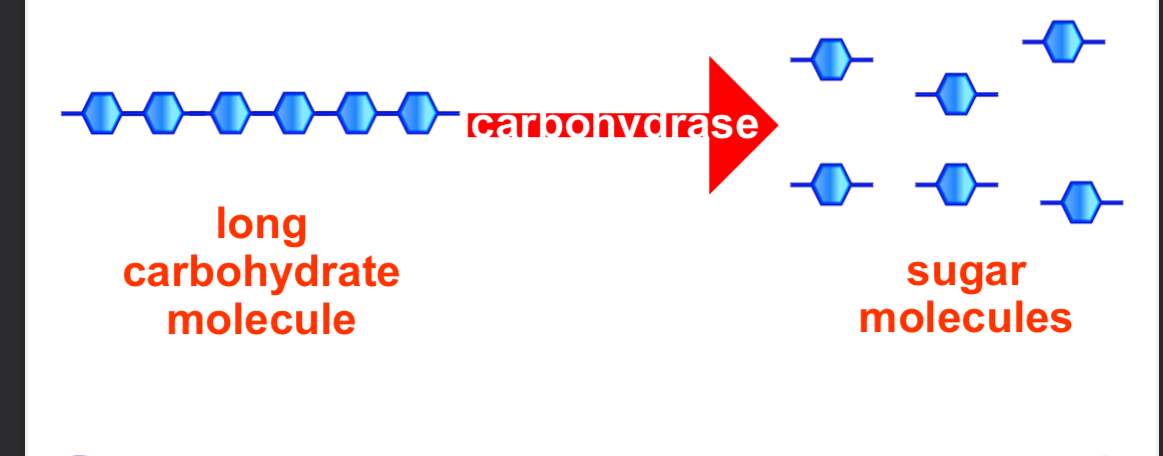
Enzymes and carbohydrate digestion
Carbohydrates are chains of identical sugar molecules.
The digestive enzymes called carbohydrase break the chemical bonds between the individual sugar molecules in each carbohydrate chain
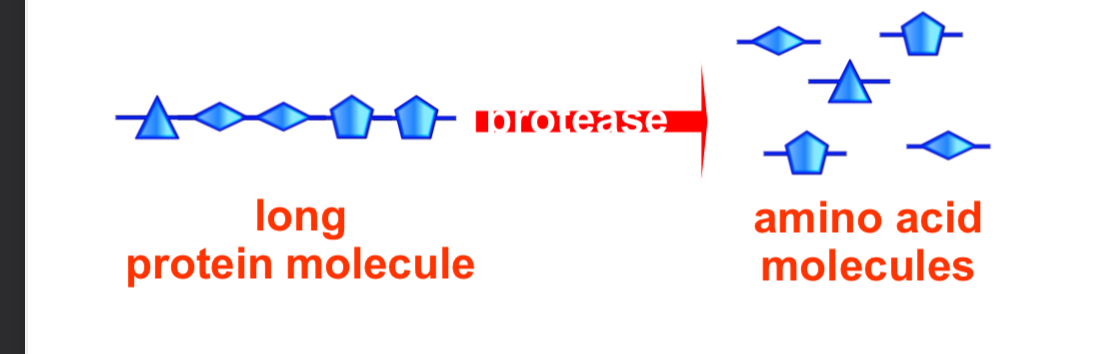
Enzymes and protein digestion
Proteins are made up of amino acids.
Proteins are digested enzymes called proteases. These enzymes work in an acidic environment to break the proteins into smaller amino acids
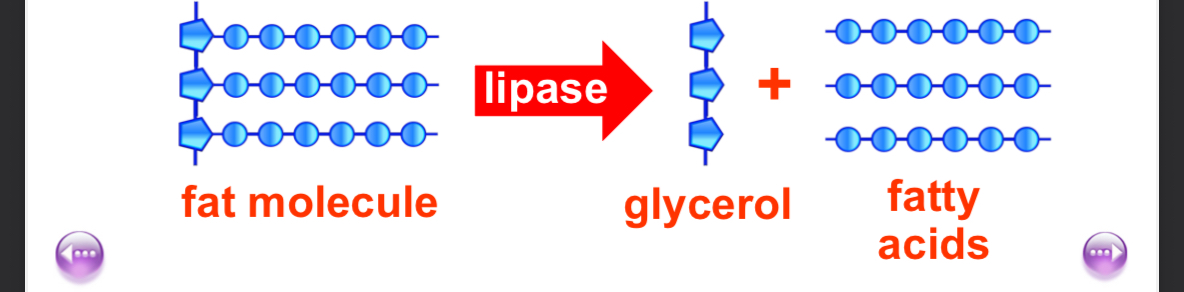
Enzymes and fat digestion
Fats are digested in two stages
Firstly bile (released by the gall bladder) allows the fat to “mix” with water by breaking the fat into smaller droplets. This is called emulsification.
Secondly, the digestive enzyme lipase breaks each fat molecule into the smaller glycerol fatty acid molecules.
Carbohydrate
A nutrient in food that provides energy
Enzyme
A chemical that helps digestion breaking large molecules into smaller ones.
Fat
A nutrient in food that provides a store of energy
Large intestine
The organ where water is removed from undigested food
Minerals
Compounds in food that provides the elements needed in small amounts for a healthy diet
Protein
Needed for growth and repair
Vitamins
Substances found in food that are needed in small amounts for health.
Stomach
– The organ where food is mixed with acid and enzymes.
Small intestine
The organ where digestion is completed and digested food molecules are absorbed.