The Golgi apparatus, Perixsome, Lysosome
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Golgi apparatus structure
several membrane-covered stacked, flattened sacs (or cisternae)
the sacs are disk-like and often slightly curved (convex and concave surfaces )
Vesicles go from cis to trans
Golgi apparatus function
sorting system for proteins coming from the RER
Modifies the proteins by glycosylation
activation of peptides by proteolysis or phosphorylation
synthesis of glycosaminoglycans and mucin
Selection enzymes for lysosome
Destination of proteins synthesize in the RER and passing through the GOLGI
come back to RER
remain in golgi
go to lysosomes
undergo exocytosis
Destination of proteins from the golgi
proteins found in the lumen of Golgi that need to go to RER - have a sequence of amino acid: KDEL - to be recognized by KDEL receptors
Proteins that continue in Golgi - lack signal peptide KDEL - may present other signals to bind to membranes sites
Proteins to be delivered to lysosomes - have specific marker - 6 phosphate mannose
Content leaving golgi can undergo?
constitutive secretion
regulated secretion
Constiutive secretion
vesicles coated by coating proteins (COPs)
not dependent on specific stimulatin
secretion products - immediately secreted
continuous process
Regulated secretion
vesicle coated clathrin proteins - controlled by specific stimulation
Proteins to be secreted are stored into vesicles that accumulate close to plasma membrane fuse with the membrane after specific extraceullular stimulation
Vesicle traficking
ENDOCYTOSIS (IN)
the vesicle originates from the plasma membrane and internalizes extracellular material
EXOCYTOSIS (OUT)
he vesicle originates intra-cellularly and fuses with the plasma membrane, thus releasing its content in the extracellular space
GEMMATION
the vesicle originates from a cell membrane and the whole vesicle (with its content) goes in the extracellular environment (ex: apocrine secretion).
Coating functiono
coating of proteins - favours bending of the membrane during the formation of vesicle
allows selection of components that have to be inserted and transported into a vesicle
Direction and destination - transmembrane protein v-SNARE on vesicles recognizes sequence t-SNARE on the target memrbane
COPs coating
coated by COP 2- move from RER to Golgi
coated by COP 1 - move from Golgi to RER
Veiscles coated by clathrin - move from Golgi to plasma membrane or to endosomes
Types of endocytosis
receptor-mediated endocytosis - after the molecules binded to specific membrane receptors
pinocytosis - very tiny soluble molecules
phagocytosis - particular molecules, bacteria
autophagy - specific type of endocytosis
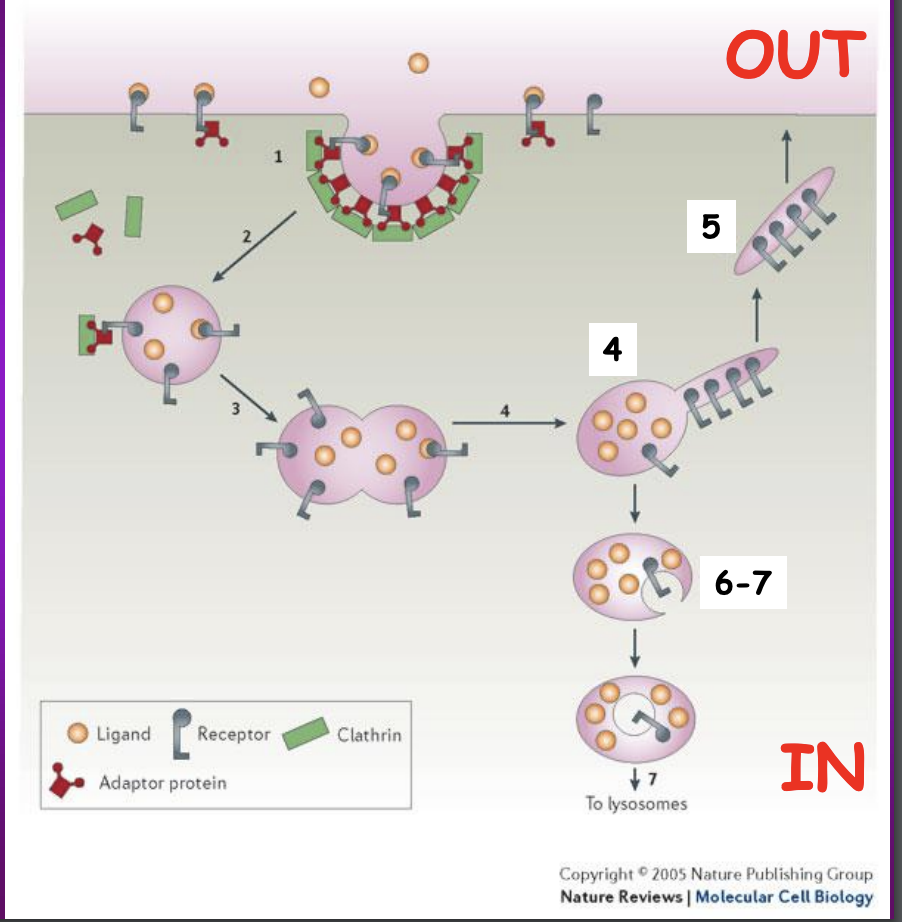
Clathrin-mediated endocytosis process
Extracellular ligands - bound to cell-surface receptors associated with the adaptor protein
bind to clathrin - forms a cage-like pit from the plasma membrane
As the coat grows - the vesicle pinches off - GTPase protein DYNamin forms a spiral collar around the base of vesicle
Following internalization - clathrin coat disassembles
Vesicel fuses with other membranes
In acidic early endosome - ligands are released from receptors - they are sorted away and go to the membrane
Internal vesicles will go to lysosomes
example: Low-Density lipoproteins receptors
Phagocytosis
phagocytes - come from blood - able to destroy bacteria, viruses, damaged cells or dea
PHASES
Recognition and adsorption of the particle to be ingested
Internalization of the particle - digestion in lysosomes
Lysosomes
contain more than 50 lytic enzymes - break down waste material (proteins, nucleic acid, lipids, carbs)
Protein of lysosomes - made in RER and tagged with mannose-6-phosphate
interlinked with - phagocytosis, endocytosis, autophagy
Active hydrolases
active at ph t
inactive if released in the cystol - pH 7.2
Storage of melanin - in form of melanosomes
Lysosomal storage diseases
group of diseases - abnormal accumulation of substances inside lysosomes
cause - defects in lysosomal enzymes - required for metabolism of moleculess
Examples: Tay-Sachs disease, Gaucher disease, Niemann-Pick disease, Hunter syndrome
Children are affected: developmental delay, defects in many organs, movement disorders, dementia, early death.
PEROXISOMES
Heterogeneous group of membrane-bound organelles containing several enzymes acting in different metabolic activities
Originates from the rer
Features
enzyme catalase - 40% of all enzymes - transorms H202 in water and O2
variable shape
number
enzymes - fatty acid and amino acid oxidation - production of H202
detoxification of dangerous substances penetrated into the organism
removal of free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as the superoxide radical, the hydroxyl radicals (OH-) that may damage cell DNA and proteins
Peroxisomes and CNS
Oligodendrocytes (type of Peroxisomes) - role in axonal integrity
Demadge of peroxisomes - axonal loss and demyelination
Formation of Perxomes
come from RER
Microvesicles contain peroxisome proteins - originate from rer
fuse to form peroxisomes