11ECON Chapter 10 - Unemployment
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Labour market
. Refers to the supply and demand for labour/employment:
• Supply: willingness of people to be hired for their labour by firms
• Demand: willingness of employers to hire labour
. Regarding the state of jobs, it is dependent on the total number of jobs available, and on the number of people competing for them

Labour force
. The combination of people that are employed and unemployed (employed + unemployed)
—> including the people who are unemployed, employed part time and employed full time
—> includes people who are either working or seeking work
. At July 2025, Australia’s labour force is 15 308 900 people
. Not all people work for various reasons
—> EG:
• Below the minimum age of employment
• Retirees
• Just choosing not to seek paid employment
—> THEREFORE
. The labour force (or work force) is the term for people who are either working or seeking work
. This means that those that are not seeking employment, for whatever reason, are not in the labour force
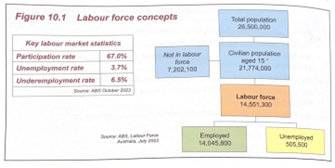
Participation rate
. the proportion of the working age population that is in the labour force (currently employed or currently seeking employment)
. Participation rate = (Labour force/working-age population) x 100
Current data:
. In Sept 2025, participation rate was 67%, having increased from 66.9% in August 2025 à cost of living rises have forced people to find work
Recent Significant data:
. was 65.5% in March 2020, then fell to 62.2% in May 2020, then rose to 65.9% in June 2021, then fell to 64.4% in September 2021 to rise to 66.2% in April 2022, then continuing the pre-covid trend of a steady increase
Male Participation rate
• Fallen from 76% in 1990 to 71% in 2023
—> why:
• Higher education retention rates
• Changing social attitudes
. Males are retiring earlier
Female participation rate
• Risen from 53% in 1990 to 63% in 2023
—> why:
• Higher levels of education
• Changing attitudes towards gender roles
• Falling fertility rates
• Improved access to childcare
• Flexible working arrangements
Target for participation rate
. as high as possible
Business cycle and participation rate fluctuations
. Some fluctuations in the participation rate are to be expected over the course of the business cycle, because the apparent number of job opportunities influences people’s decisions to seek work
• Contraction:
. Job seekers may become discouraged if they feel they have limited prospects of attaining employment
• Expansion:
. Encourage people to enter the job market due to better prospects of being able to obtain employment
. The rate might rise or fall about 1-1.5% over the course of the cycle
How can changes in labour force participation affect monthly employment data
EG: an increase in economic activity after a period of slow growth might not translate into shorter waits for employment.
—> This is because the more people that seek employment, the larger the participation rate and, subsequently, an increase in unemployment if new participating people do not have a job
Unemployment rate
. Proportion of the labour force who are willing and able to work, but are not in paid work for at least 1 hour a week
. Target = full employment (~4% where everyone who wants a job can find one)
Unemployment rate data
Unemployment
• Occurs when people who are willing and able to work (in the labour force) cannot find paid work for at least one hour per week à this is the unemployment rate
Conditions to be unemployed: an individual is
1. Part of the working age population (15-65) and NOT a full-time student
2. Not working 1+ hour paid work per week (or 5+ hours per week in family business)
3. Actively seeking work (been actively seeking work in the month prior to survey + carried out specific tasks to suggest they were actively seeking work like contacting employment services, responding to job advertisements and sending their resume to employers)