W4: Organisational Structures and Organisational Culture
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
organisational structure
framework in which the organisation defines how tasks are divided, the work of employees and departments coordinated, and authority distributed
organisational affects organisations’ ability to reach their goals
All organisations are perfectly designed to get the results they are now getting. If we want different results, we must change the way we do things
dimensions managers should consider when choosing organisational structures
division of labour, coordination, centralisation
formal organisational design
division of labour (differentiation), coordination mechanisms (integration), distribution of decision rights ((de) centralisation)
division of labour: past: Adam Smith’s Pin Factory
reliance on division of labour
division of labour: scientific thought disadvantages
increases loneliness, reduces autonomy of worker, dehumanisation of work
division of labour: today: “Silo effect” critique
too much specialisation can create silo effects (tunnel vision - losing focus of organisation’s goals + tribalism within departments AND misaligned efforts - misses cross-fertilisation opportunities)
forces for (de)centralisation
degree to which decision-making authority is concentrated at higher levels of organisation
centralisation
organisational crisis, management desire for control, increase consistency
decentralisation
complexity - size, diversity, desire for empowerment, increase flexibility, innovating from within
formalisation
standardisation of workflows (SOPs), specification of design criteria, written documentation of decisions + activities, often in places with high levels of hierarchy (e.g public sector)
formalisation: drawbacks
firms relying on innovation need to be careful of formalisation as it will stifle creativity
organisational structures: military hierarchy
clear chain of command, orders formulated at top and passed down, reports passed up (reporting line), no provisions for coordination or communication between units
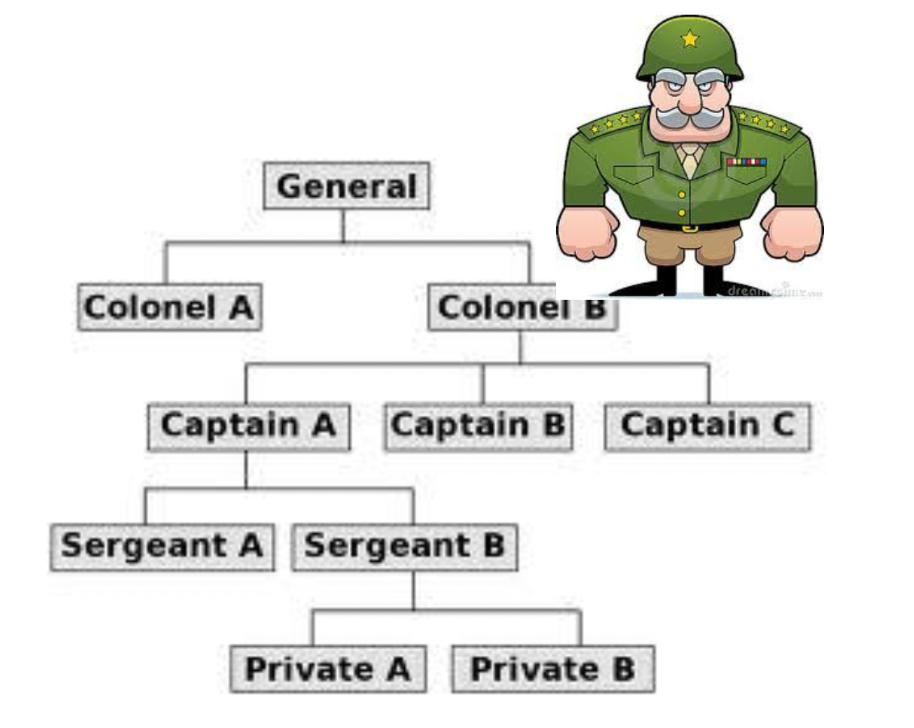
military hierarchy: advantages
clear where accountability lies, clear chain of command
organisational structures: flat organisational structure
large span of management, large number of people reporting to CEO, works when job performed is flat and routine, whatever is produced is tangible, well organised and well understood
flat organisational structure: advantages + disadvantages
quick decision-making, clear view of organisational goals, wide spans of control and centralised authority, few organisational barriers (ensure flexibility), inexpensive
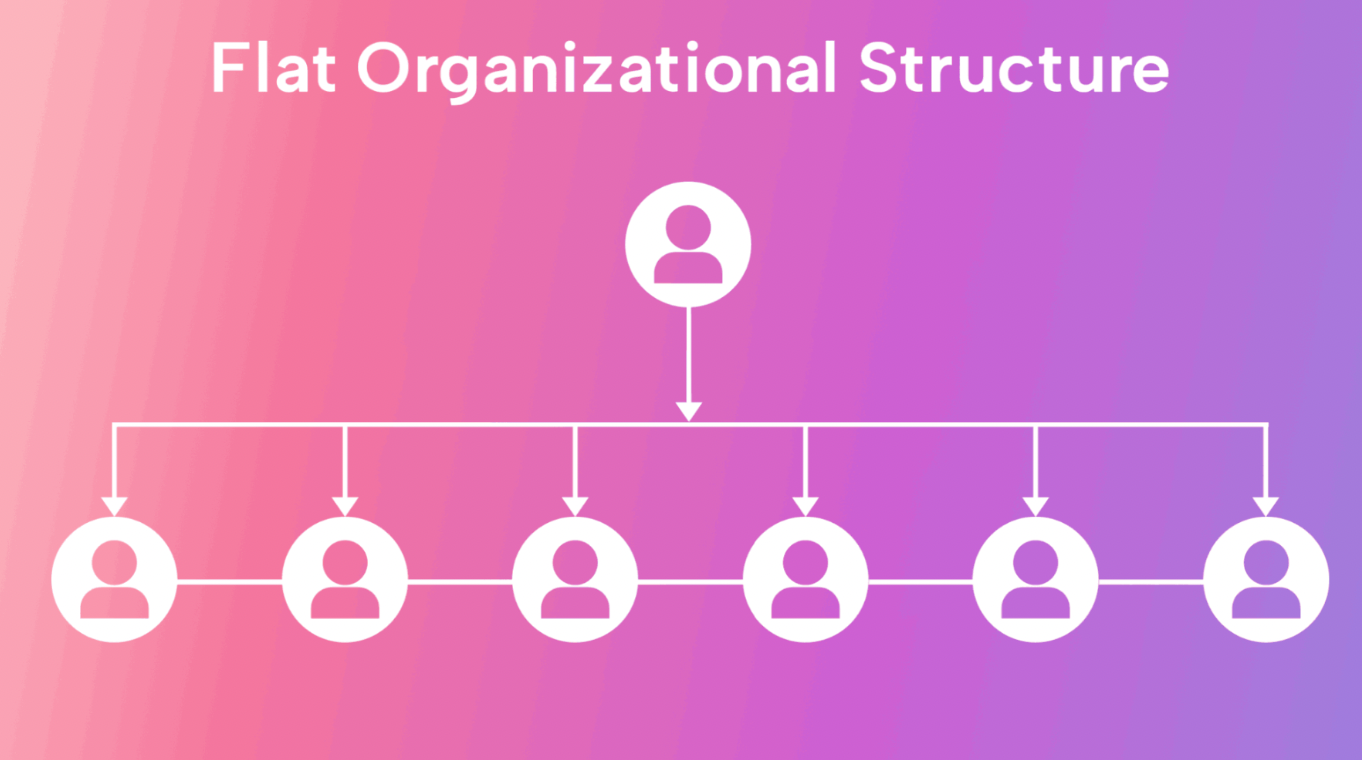
flat organisational structure: disadvantages
not feasible for large complex organisations, depends critically on top management team
organisational structures: functional structure
departmentalisations (people with similar skills and expertise)
functional structure: advantages
clear chain of command, efficiencies with people having common skillsets in each department, coordination within function, in-depth specialisation
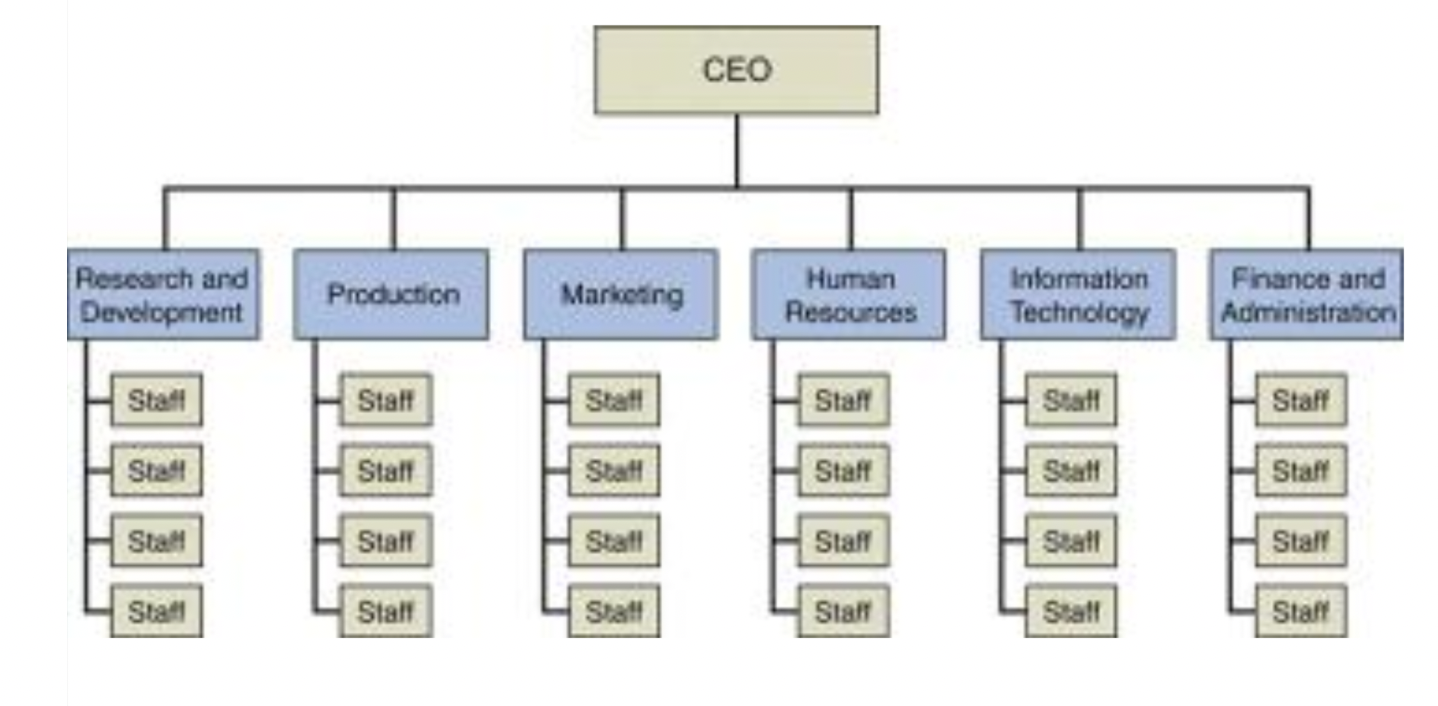
functional structure: disadvantages
silos (risk limited collaboration + info sharing across departments), limited view of org goals
organisational structures: multi-divisional structure
groups based on organisational output rather than function (e.g apple - computers, iPads, watches etc.) - functions within each division
multi-divisional structure: advantage
focuses on specialisation within particular products not functions, greater collaboration across functions, facilitates cross-functional collaboration
multi-divisional structure: disadvantages
miscommunication (chain of command not well defined), support functions replicated in each division, create unwanted rivalries between divisions, limits knowledge sharing in functional areas
organisational structures: matrix (multi-dimensional) structure
organisational outputs, combining lines of authority for function with lines of authority for products
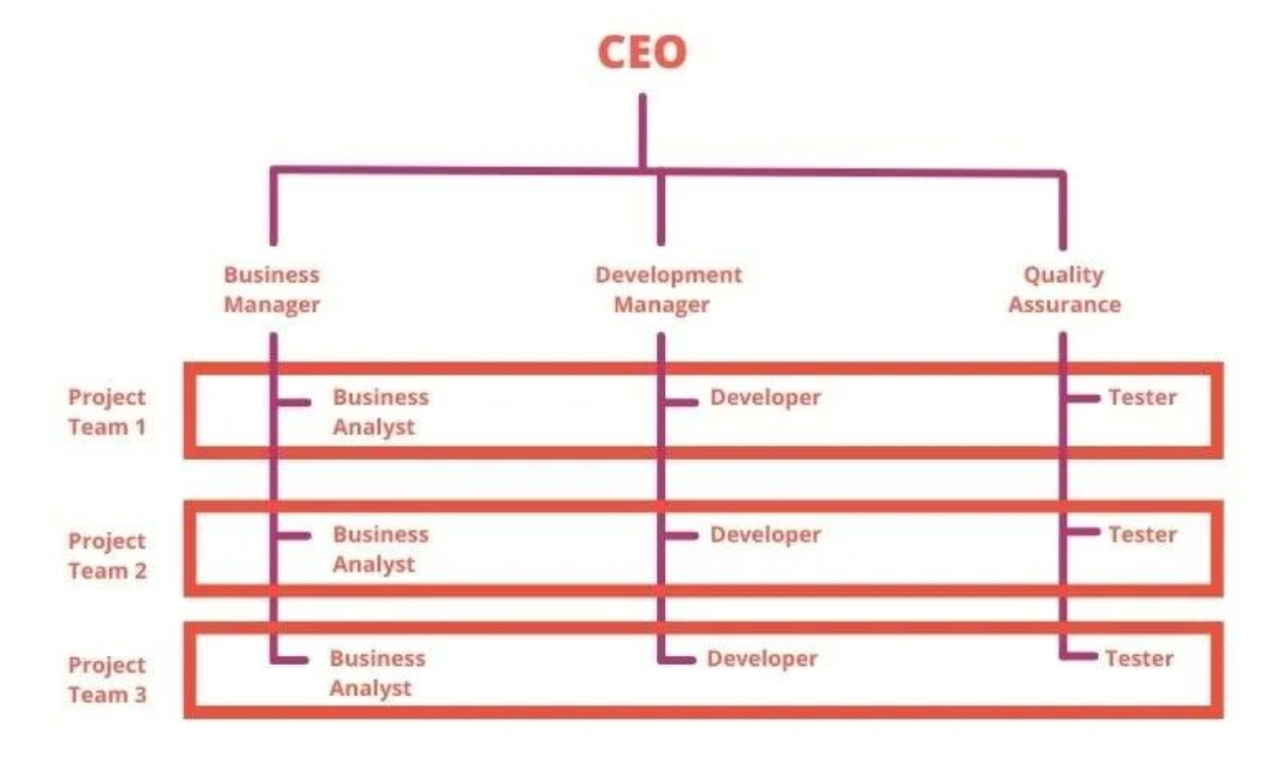
matrix (multi-dimensional) structure: advantages
fluid design that can respond to environmental changes, high information carrying capacity, high degree of coordination, potentially faster decision-making
matrix (multi-dimensional) structure: disadvantages
expensive and complex, dual authority can lead to task and personality conflicts to slow down decision making
organisational structures: contingency factors
strategy, size, technology, environmental uncertainty
low environmental uncertainty
mechanistic structure - rigid and tightly controlled: high specialisation, rigid departmentalisation, clear command chains, narrow control spans, high formalisation, limited info network, high centralisation
high environmental uncertainty
organic structure - highly flexible and adaptable: low specialisation, fluid team-based structure, wide control spans, low formalisation, open comms network, empowered employees
organisational culture
ways of thinking and doing things that is shared by a degree by all members of the organisation which new members must learn and accept in order to b accepted into service
strong culture
provide critical control, motivational and coordination benefits but can also lead to rigidity and be unhealthy
culture: intensity
degree of approval/disapproval attached to cultural values and norms
culture: cyrstallisation
degree of consensus and consistency with which cultural values and norms are shared
culture: visible levels
can be seen at surface level - artefacts (dress, office layout, symbols, slogans, ceremonies)
culture: invisible levels
deeper values and shared understandings held by organisation members - expressed values, underlying assumptions and deep beliefs
organisational culture: attention to detail
degree to which employees are expected to exhibit precision, analysis and attention to detail
organisational culture: outcome orientation
degree to which managers focus on results or outcomes rather than on how they are achieved
organisational culture: people orientation
degree to which management decisions take into account the effects on people in the organisation
organisational culture: team orientation
degree to which work is organised around teams rather than individuals
organisational culture: aggressiveness
degree to which employees are aggressive and competitive rather than cooperative
organisational culture: stability
degree to which organisational decisions and actions emphasise maintaining the status quo
organisational culture: innovation and risk taking
degree to which employees are encouraged to be innovative and to take risk
visible carriers of culture: language + metaphors
used to communicate assumptions, values, ideology
visible carriers of culture: props
used to reinforce values and ideology
visible carriers of culture: stories
used to draw attention to norm and heroes/role models
visible carriers of culture: ceremonies/rituals
build in-group cohesion and morale and reinforce values and norms
visible carriers of culture: dress/uniform
establish positive organisational identity
adaptability culture
values creativity and innovation, encourages individual initiative and autonomy in decision-making, adaptive response to environments that require fast responses
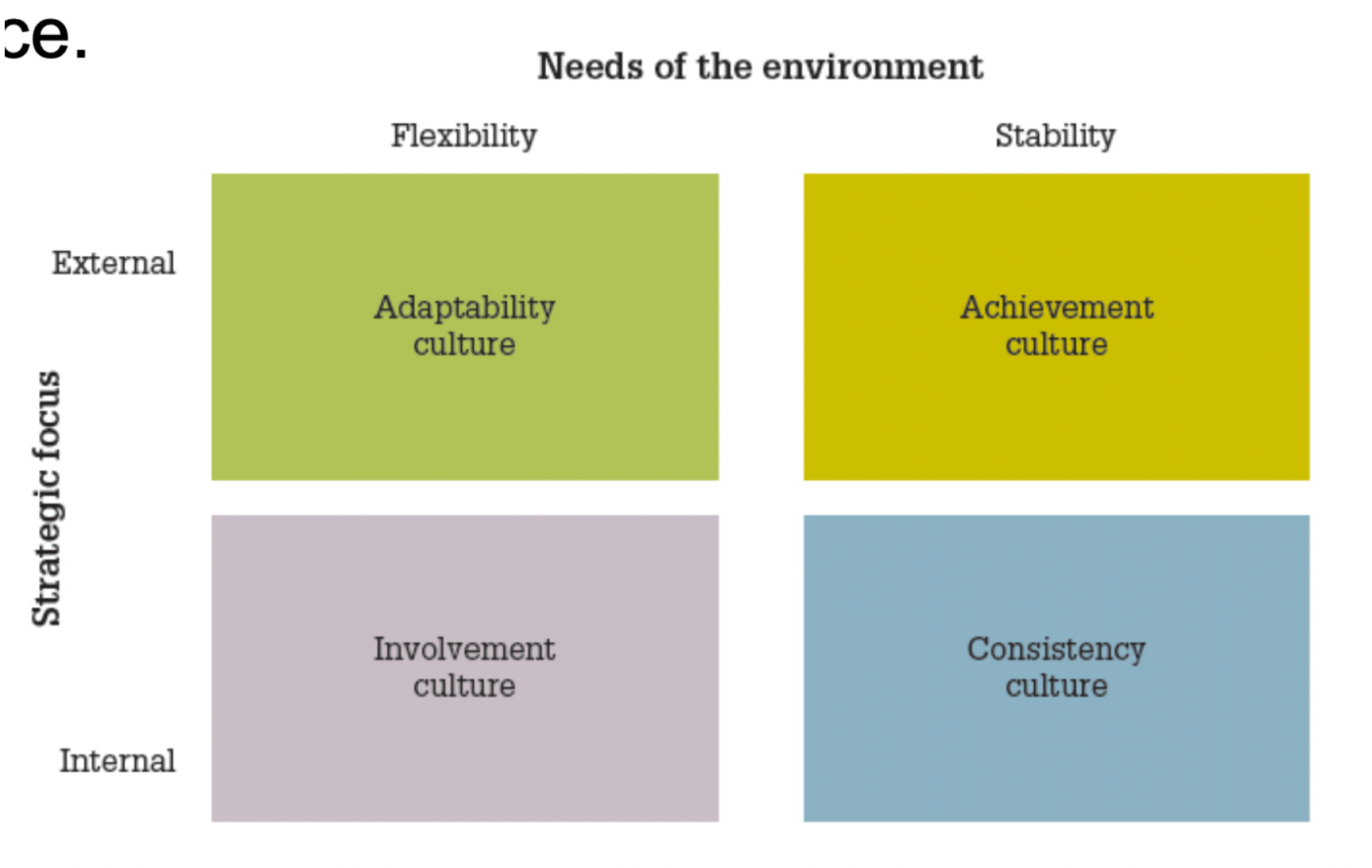
achievement culture
results-oriented, values competitiveness, personal initiative, achievement, cost-cutting, rewards for high performers, suitable for stable environments
involvement culture
high value on getting needs of employees, values cooperation, consideration and equality, characterised by family-like atmosphere
consistency culture
values and rewards standardisation, control and well-defined structure for authority and decision making uses internal focus and consistency orientation, not always suitable for today’s fast changing environment
reinforcing an adaptive organisational culture
consistent info/behaviour, employee selection/socialisation, comprehensive rewards for norm-consistent behaviour, participation
reshaping organisational culture for adaptive response
unsettle existing culture + resettle new culture
unsettle existing culture
create a crisis, highlight non-distinctiveness of culture, inject + support diversity, encourage participation of and give power to minority options
resettle existing culture
over-communication, introduce novel artefacts (new stories, symbols etc.), change reward system