Antibacterials
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What are some differences between gram positive and gram negative bacteria?
Gram-positive bacteria:
Thick peptidoglycan layer
Contains acids
Gram-negative bacteria:
Thin peptidoglycan layer
Two cell membranes
Outer membrane with lipopolysaccharides
More resistant to antibiotics than gram-positive bacteria
How to test for gram negative/positive bacteria
the Gram Test
heteraromatic purple stain (yrstal violet) sticks to the outer membrane
decolourise with an organic solvent
-ve cells are red/pink (E. coli)
+ve cells are purple
Describe the appearance of:
Staphylococcus aureus
Streptococcus sp.
E. coli
round clusters of cells
chains
isolated round cells
What was dangerous about the first antibacterial agents?
Contained arsenic which could easily lead to poisoning
What is an example of a Sulfonamide and how do they work?
The prodrug prontosil
In the body, it turns into sulfanilamide, the active antibacterial compound.
It inhibits enzymes essential for bacteria growth
What is a prodrug
A compound that is metabolised in vivo into the active form of the drug
e.g. protosol is reduced to sulfonamide
How can you improve the Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) in a drug
Can only modify non-essential parts of the drug
R group can be replaced to create a drug that is more water-soluble, or causes less kidney damage
What is the site of action of sulfonamide drugs?
Inhibit the enzyme dihydropterate synthetase, which helps synthesise folic acid in bacteria.
Folic acid is used for DNA synthesis in bacteria so without it they die.
Describe the biosynthesis of folic acid
dihydropterate synthase catalyses SN2 reaction
diphosphate group is a good leaving group
DHFR (anti-microbial dihydrofolate reductase) reduces imine bonds using NADH (nature's NaBH4)
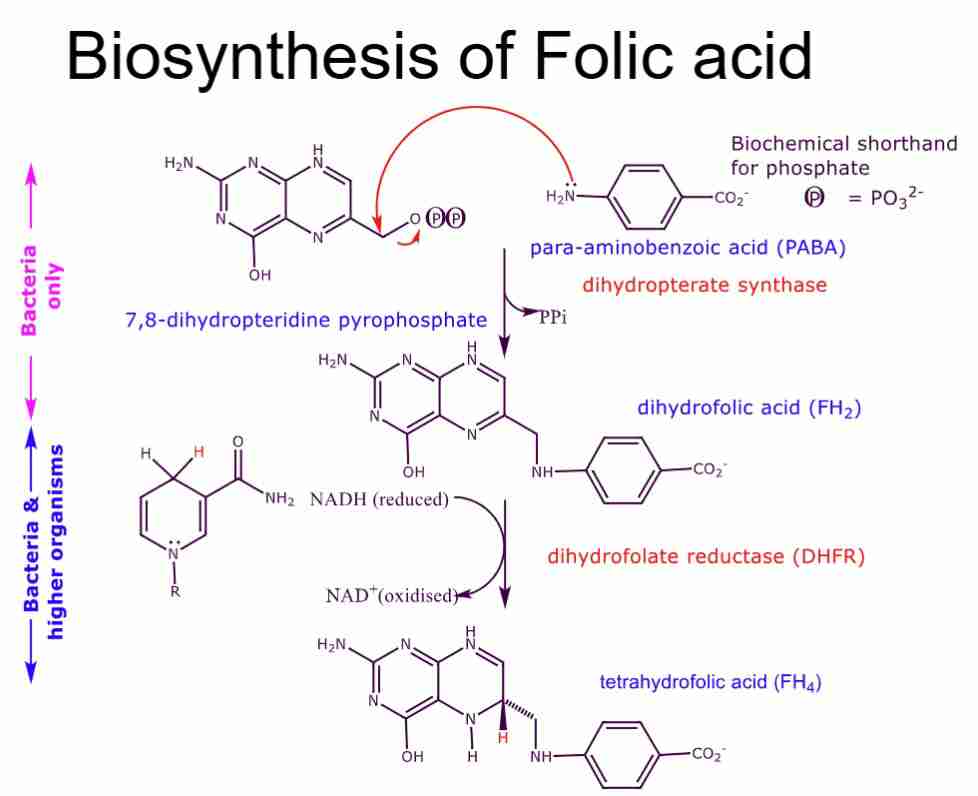
What type of inhibitors are sulfa drugs
reversible competitive inhibitors (binds to active site of dihydropterate synthase)
What is DHFR
Dihydrofolate reductase
Acts as a reducing agent in the bacterial folic acid synthesis pathway (nature’s NaBH4)
What is a drug that inhibits DHFR
Trimethorpin - antibacterial agent
What is Septrin
Mixture of Trimethoprin and sulfamethoxazole which counteracts resistance to one of the drugs.
The sum of the two drugs together is more powerful than the effect of the two separately
What are Trimethoprin and sulfamethoxazole examples of
Anti-metabolites - compounds that block metabolic enzymes
Bacteriostatic drugs - compounds that inhibit growth and replication, not kill directly