DDS Lecture 3 Content
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Colloid
mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance.
derived from Greek word for glue
ex. smoke from fire, gem stones, milk
Pharmaceutical examples of colloids
hydrogels
micro-particles
emulsions
suspensions
liposomes
nanoparticles
nanocrystals
Blood as a complex dispersion
dispersion medium: plasma (90% water)
dispersed phase: peptides, cells, proteins
Attractive forces
cause molecule to cohere
repulsive forces
prevent molecular interpenetration
Molecular Dispersions
particles less than 1nm
invisible in EM
pass through ultra filter and semipermeable membrane
rapid diffusion
ex. Oxygen molecules, ordinary ions, glucose in water
Colloidal dispersions
particles 1nm-0.5 mcm
detected by ultra EM
pass through filter paper
do not pass semipermeable membrane
diffuse very slowly
ex. colloidal silver solutions, polymers, jelly, milk, paint, shaving cream
Coarse dispersions
particles greater than 1 mcm
visible under microscope
do no dialyze through semipermeable membrane
do not diffuse
ex. most pharmaceutical emulsions/suspensions
red blood cells
Dialysis
uses semi-permeable membrane to separate and obtain sub-colloidal material and free from colloidal contamination
when kidneys fail, dialysis removes colloidal material from blood
keeps body in balance by removing waste, salt, and extra water from building up in body
keeps safe level of potassium, sodium, and bicarbonate in blood
help control blood pressure
Ultrafiltration
separate and purify colloidal material
pressure-driven barrier for suspended solids, bacteria, viruses, endotoxins, and other pathogens
produces water with high purity and low silt density
variety of membrane filters in which hydrostatic pressure forces liquid against semi-permeable membrane
Electrodialysis
movement of ions is aided by electric field applied across semi-permeable membrane
driving force: electrical potential (positive charge attracted to negative charge)
Reverse Electrodialysis
driving force: concentration difference
movement of ions based on concentration gradient
Shapes of Colloidal Particles
spheres and globules
short rods and prolate ellipsoids
oblate ellipsoids and flakes
long rods and threads
loosely coiled threads
branched threads
Colloidal particle behavior
in friendly environment, unrolls and exposes maximum surface area
under adverse conditions, rolls up and reduces exposed area
Properties of colloidal particles affect
flow
sedimentation
osmotic pressure
pharmacological action
Environment of colloidal particle dictates the shape and form of the colloidal particle. This physical property is important for the stability of the pharamaceutical drug. However, the efficacy of pharmacological activity is not directly dependent on the physical nature. (T/F)
Flase
Solid sol
solid in solid colloid
ex. pearls, opals
Solid emulsion
liquid in solid colloid
ex. cheese, butter
solid foam
gas in solid colloid
ex. pumice, marshmallow
sol, gel
solid in liquid colloid
ex. jelly, paint
emulsion
liquid in liquid colloid
ex. milk, mayonnaise
foam
gas in liquid colloid
ex. whipped cream, shaving cream
solid aerosols
solid in gas colloid
ex. smoke, dust
liquid aerosols
liquid in gas colloid
ex. clouds, mist, fog
Can gas in gas form colloid?
No, gas-in-gas always produces solution
Lyophilic Collloids
systems containing particles that interact to an appreciable extent with the dispersion medium
solvent loving
ex. dissolution of acacia or gelatin in water = sol formation
dispersed phase consists of large organic molecules lying within colloidal size range
molecules of dispersed phase are solvated
molecules disperse spontaneously to form colloidal systems
viscosity of the dispersion medium is increased greatly by presence of dispersed phase
dispersion is stable in presence of electrolytes
may be salted out by high concentration of soluble electrolytes
Solvation
attachment of solvent molecules to the molecules of dispersed phase
Lyophobic colloids
materials have no attraction for dispersed medium
solvent-hating colloids
ex. inorganic particles in water (silver, gold, sulfur
preparation methods:
coarse particles reduced in size
aggregates into particles of colloidal range (condensation)
dispersed phase consists of inorganic particles
little interaction between particles and dispersion medium
material does not disperse spontaneously
viscosity of dispersion medium is not greatly increased by the presence of lyophoic colloidal particles
unstable in presence of electrolytes
Amphiphilic
association colloids
amphiphiles/surface active agents have 2 distict regions of opposing solution affinities
can be anionic, cationic, nonionic, or ampholytic
dispersed phase consists of aggregates (micelles) of small organic molecule (below colloidal range)
colloidal aggregates formed spontaneously when concentration of amphiphile excess critical micelle conc
viscosity of system increases as conc of amphiphile increases as micelles increase in number and become asymmetric
in aqueous system, critical micelle con reduced by addition of salt (salting out)
Faraday Tyndall Effect
when strong beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution, a visible cone, rsesulting from the scattering of light by colloidal particles, is formed
optical property of light depends on:
size, shape, and molecular weight of colloids
Kinetic Properties of Colloids
brownian motion
diffusion
osmotic pressure
sedimentation
viscosity
Brownian Motion
random movement of colloidal particles
velocity of particle decreases with particle size
increase in viscosity of medium decreases Brownian movement
Diffusion
Fick’s law of diffusion
particles diffuse from region of higher concentration to lower concentration until system is uniform
direct result of Brownian motion
Osmotic Pressure (pi)
Osmotic pressure of dilute colloidal solution is described by van’t Hoff equation
pi=cRT
c= molar concentration of solute
R=gas constant
T=temperature
Sedimentation
velocity of sedimentation of spherical particle having density p in medium p0 and viscosity no is given my stoke’s law
g= acceleration due to gravity
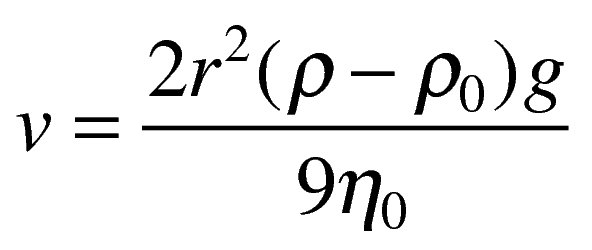
Donnan Membrane Equilibrium
equilibrium that exists between two solutions that are separated by a membrane
membrane constructed so that it allows passage of certain charged components of solution
the presence of a charged impermeant ion (for example, a protein) on one side of a membrane will result in an asymmetric distribution of permeant charged ions.
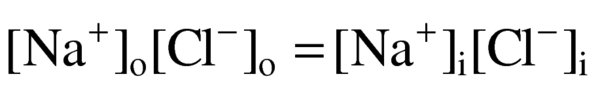
Pharmaceutical Applications of Colloids
extensively used for modifying properties of pharmaceutical agents
most commonly affect solubility of drug
colloidal forms exhibit different properties than traditional forms
used as drug deliversy systems
Advantages of Colloidal formulations/State
some medications found to possess unusual or increased therapeutic property
colloidal silver chloride, silver iodide, silver protein are effective germicides without irritation
colloidal copper used for cancer tratment
colloidal gold as diagnostic agent
colloidal sulfur has higher potency than coarse powder
Hydrogels
colloid
dispersion medium=water
dispersed phase= solid
natural and synthetic gels used for wound healing, scaffolds for tissue engineering, sustained release delivery systems
Disadvantages of Hydrogels
designing useful environmentally sensitive hydrogels
slow repsonse time
limited biocompatibility
biodegradability
Microparticles
0.2-5 mcm loaded microspheres of natural of synthetic polymers
developed as carriers for vaccines and anticancer drugs
increase efficacy and release profiles, drug targeting
non-traditional routes of drug administration
can be used to use mucosal route of administrationg for immunzation
Emulsions/Micro-emulsions
excellent potential drug delivery systems
improved drug solubilization
long shelf life
easy to prepare and administer
3 distinct types: oil external, water external, middle phase used for drug delivery depending on drug and site of action
Microemulsion: used for controlled release and targeted delivery
ex. oligonucleotides
Liposomes
easily utilized by cells
hydrophilic head and lipophilic tail
liquid compartment inside bilayer
uses:
antibodies, proteins, sugars (drug targeting)
chelation therapy for heavy metal poisoning
enzyme replacement
diagnostic imaging (tumors)
cosmetics
Micelles
biocompatible
delivers poorly soluble hydrophobic drugs
similar to liposomes but without liquid core (no bilayer)
uses:
low molecular mass drugs
polypeptides
DNA
polycation based gene drug delivery (polyplexes)
Nanoparticles
submicroscopic colloidal drug carrier systems
composed of oily or aquaeous core surrounded by thine polymer membrane
used for non-viral gene delivery systems
Nano-crystals
inorganic nanostructures
size <10nm
use of semiconductor quantum dots as fluorescent labeling
targeted delivery to blood vessels and lung tissues
The major difference between liposomal drug delivery and Micelles is that one form contains liquid core and the other does not (T/F)
True, Liposomes have liquid core
Interfacial tension
the force causing each liquid to resist breaking up into smaller particles when the liquid is in contact with a second liquid in which it is insoluble and immiscible
Gibbs Free Energy
W=ΔG=ΔAγ
Δ is the size of change in G and A
A is the total surface area of dispersed particles
γ is the surface interfacial tension
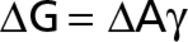
Dimensions of Surface Tension
γ=ΔG/ΔA = erg/cm2 = dyne/cm
Affect of agitation on liquid-liquid systems
distributes dispersed phase throughout dispersion medium
when agitation is stopped, the drive to reduce interfacial free energy results in dispersed phase forming spheres which coalesce
Molecular forces in interface
molecules in bulk exposed to symmetrical force field
molecules in interface pulled into bulk to minimize interfacial area
To stabilize emulsions…
reduce free energy by reducing interfacial tension
Cohesion
The attraction between molecules or atoms of the same substance.
WC=γL+γL=2γL
Adhesion
The attraction between molecules of different chemical substances
For solid-liquid systems:
WA=γL+γS-γLS
Spreading of a liquid on a solid
occurs when work of adhesion exceeds work of cohesion
S= spreading coefficient
S= WA-WC
S=γS-γL-γLS
Molecular Forces in the Liquid/Vapor Interface
dispersion force interactions across interface are possible
low density of gas means few molecules are close enough to interact
Molecular Forces in liquid/liquid interface
dispersion force interactions across interface possible
higher density of liquids means molecules are close enough to interact
diminished pull of interfacial molecules into bulk of each phase
Why does surfactant lower surface tension?
amphiphilic
locate preferentially at interface, decreasing difference between two phases
less tension because polar heads interact with polar phase, nonpolar region interact with nonpolar phase
Wetting
when surface tension (cohesion) is greater than attractive forces on surface, liquid will not wet surface
when attractive forces to surface (adhesion) exceed surface tension, liquid wets surface
Rheology
study of mechanical properties of condensed matter (in particular, complex fluids)
derives from greek “to flow”
concerned with deformation of matter under stress
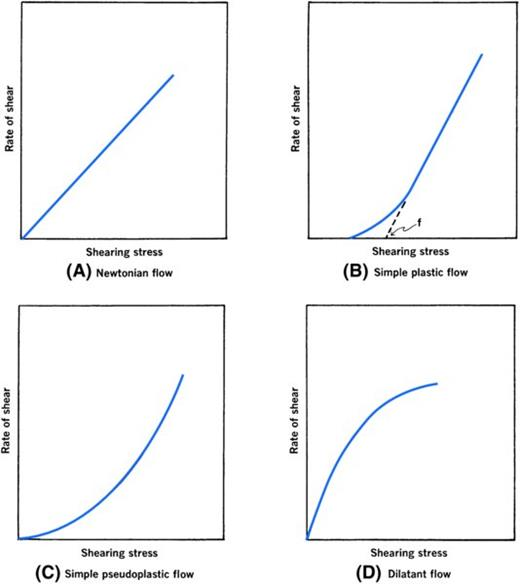
Newtonian liquid
linear relationship between shear rate and stress
constant viscosity
velocity gradient/rate of shear (dv/dr) is difference of velocity dv between two planes of liquid separated by distance dr
force (F’/A) applied to top layer that is required to result in flow (rate of shear, G) is called shearing stress (F)
plot of F vs G = rheogram
newtonion fluid rheogram will be straight line with slope of line being viscosity
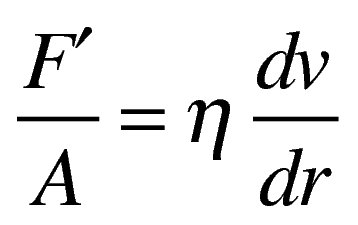
Non-Newtonian liquid
nonlinear relationship between shear rate and stress
change in viscosity with increasing shear rates
plastic, pseudoplastic, dilatant flow
colloidal solutions, emulsions, liquid suspensions, ointments
Viscosity
expression of resistance of a fluid to flow
higher viscosity=higher resistance
η
unit = poise
most convinient unit = centipoise (cP)
1 cP = 1 mPa*s
PA=kg*m/s²=N/m²
Plastic Flow
substances that exhibit plastic flow are called Bingham bodies
flow does not begin until shearing stress corresponding to certain yield value is exceeded
Materials are elastic below yield value
ηP= (F-f)/G
f= yield point

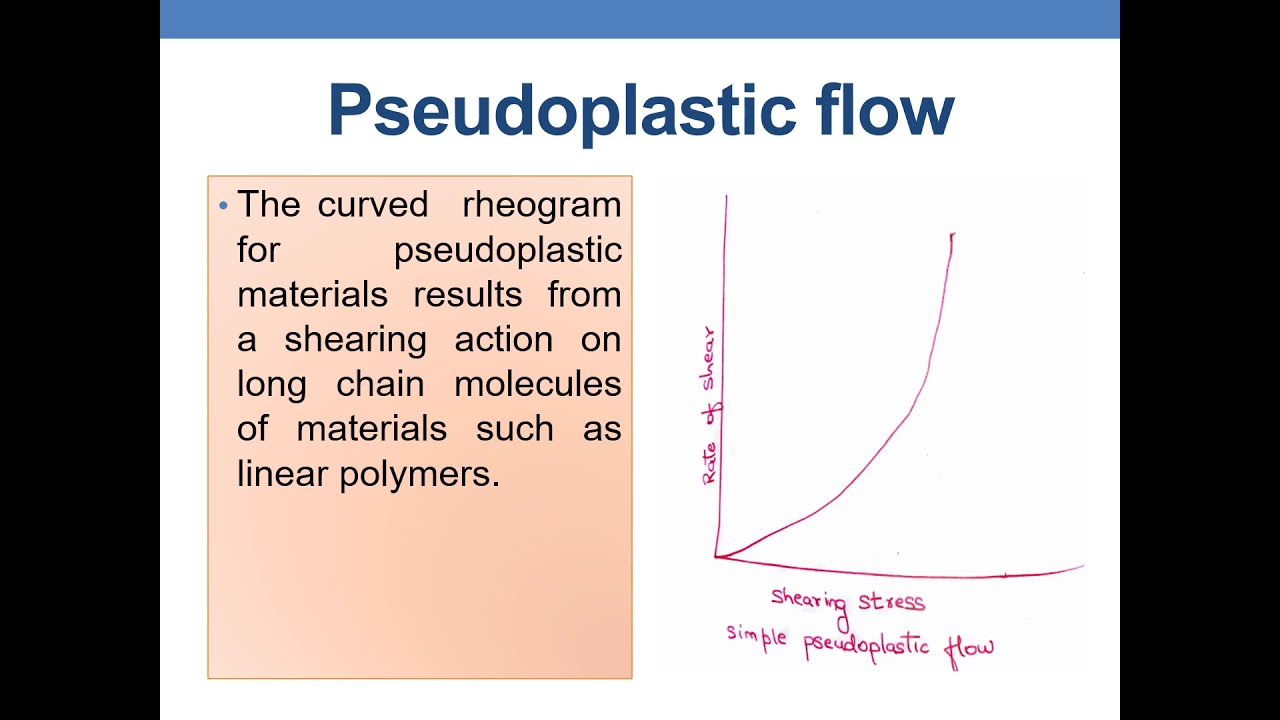
Pseudoplastic flow
begin flow when shearing stress is applied
rate of shear increases with increasing shearing stress
shear-thinning systems
viscosity decreases with added force
polymers align along long axis with additional force
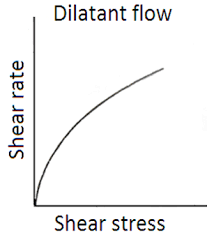
Dilatant Flow
increase in volume when sheared
viscosity increases with increasing shear rate
shear-thickening systems
high percentage of solids in formulation
particles must expand to get past each other
Thixotropic flow
used in some pharmaceutical formulations
reversible gel-sol transformation
upon setting, network gel forms and provides rigid matrix that will stabilize suspensions and gels
when stressed (shook), the matrix relaxes and forms a sol with the characteristics of a liquid dosage form for ease of use
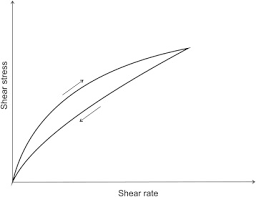
Anti-Thixotropic
Rheopectic
liquids or gases whose viscosity increases with stress over time
increases upon increasing shear stress
ex. some gypsum pastes, lubricants
Viscosity and Formulation
higher viscosity = higher stability
slower settling
higher viscosity = more difficult to dispense
Importance of viscosity in fluids
mixing
particle size reduction of disperse systems with shear
passage through orifices
fluid transfer
physical stability
Important of viscosity in semi-solids
emulsions, pastes, suppositories, tablet coatings can flow/deform
spreading and adherence on skin
removal from jars or extrusion from tubes
capacity of solids to mix with immiscible liquids
release of the drug from the base
Importance of viscosity in processing
production capacity and power requirements of equipment
manufacturing equipment fitted with strain gauges to permit monitoring of torque measurements
Viscosity measurements
cone and plate for semisolids
viscometer for liquids