DATABASE DEVELOPMENT ACTIVITIES During the SYSTEMS DEVELOPMENT LIFE CYCLE (SDLC)
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PPT 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Systems Development Life Cycle
(1) Planning
(2) Analysis
(3) Design
(4) Implementation
(5) Maintenance
Planning’s purpose
develop a preliminary understanding of a business situation and how information systems might help solve a problem or make an opportunity possible
Planning’s deliverable
written request to study the possible changes to an existing system or the development of a new system that addresses an information systems solution to the business problems or opportunities.
Analysis’ purpose
analyze the business situation thoroughly to determine requirements, to structure those requirements, and to select among competing system features
Analysis’ deliverable
functional specifications for a system that meets user requirements and is feasible to develop and implement
Design’s purpose
elicit and structure all information requirements; to develop all technology and organizational specifications
Design’s deliverable
Detailed technical/functional specifications of all data, forms, reports, displays, and processing rules; program and database structures, technology purchases, physical site plans, and organizational redesigns
Implementation’s purpose
write programs, build data files, test and install the new system, train users, and finalize documentation
Implementation’s deliverable
Programs that work accurately and to specifications, documentation, and training materials
Maintenance’s purpose
monitor the operation and usefulness of a system, and to repair and enhance the system
Maintenance’s deliverable
Periodic audits of the system to demonstrate whether the system is accurate and still meets user's needs
Enterprise Modeling (Planning)
- Analyze current data processing
- Analyze the general business functions and their database needs
- Justify need for new data and databases in support of business
Enterprise Data Model (Planning)
establishes the range and general contents of organizational databases
Enterprise Data Model (Planning)
data architectural framework used for integration
Enterprise Data Model (Planning)
enables the identification of shareable data across functional and organizational boundaries
Conceptual Data Modeling (Planning)
- Identify scope of database requirements for proposed information system
- Analyze overall data requirements for business function(s) supported by database
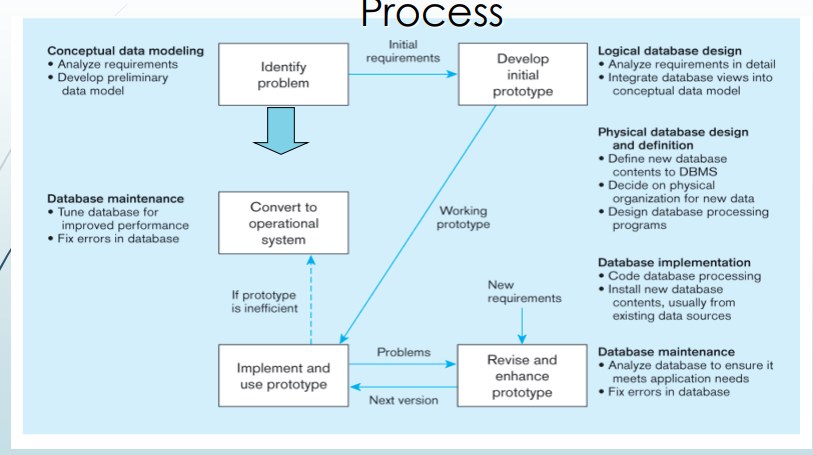
Conceptual Data Modeling (Analysis)
what part of database development activity during SDLC is the ff:
▪ Develop preliminary conceptual data model, including entities and relationships
▪ Compare preliminary conceptual data model with enterprise data model
▪ Develop detailed conceptual data model, including all entities, relationships, attributes, and business rules
▪ Make conceptual data model consistent with other models of information system
▪ Populate repository with all conceptual database specifications
Logical Database Design
what type of database design is the ff:
▪ Analyze in detail the transactions, forms, displays, and inquiries
▪ Integrate database views into conceptual data model
▪ Identify data integrity and security requirements, and populate repository
Physical Database Design
what type of database design is the ff:
▪ Define database to DBMS (often generated from repository)
▪ Decide on physical organization of data
▪ Design database processing programs
Logical Data Model (LDM)
what type of data model has these characteristics:
(1) Includes tables, columns/fields and keys
(2) Uses business names for entities & attributes
(3) independent of technology platform
Physical Data Model (PDM)
what type of data model has these characteristics:
(1) Includes tables, columns, keys, data types, validation rules, database triggers, and access constraints
(2) Uses more defined and less generic specific names for tables and columns
(3) Requires a knowledge of the specific DBMS that will be used to implement the database
Conceptual Data Model (CDM)
what type of data model has these characteristics:
(1) Includes high-level data constructs
(2) Uses non-technical names
(3) Represent data from the viewpoint of the organization, independent of any technology
Database Implementation
what part of database development activity during SDLC is the ff:
▪ Code and test database processing programs
▪ Complete database documentation and training materials
▪ Install database and convert data from prior systems
Database Maintenance
what part of database development activity during SDLC is the ff:
▪ Analyze database and database applications to ensure that evolving information requirements are met
▪ Tune database for improved performance
▪ Fix errors in database and database applications and recover database when it is contaminated
Waterfall
What type of approach to SDLC is the ff:
-The outcome of one phase acts as the input for the next phase.
-Documentation intensive
-Detailed, well-planned development process
Rapid Application Development (RAD)
What type of approach to SDLC is the ff:
Iterative process of rapidly repeating analysis, design, and implementation steps until they converge on the system the user wants
Prototyping
-Popular RAD method
-Repeat implementation and maintenance
activities with new prototype versions
Agile Software Development
Examples are Scrum, Lean, Kanban, and XP
5 Key Principles of Agile Methods
(1) Satisfying customers is of foremost
importance
(2) Develop projects with inspired contributors
(3) Interactions are best when done in person
(4) Software that works is a measure of progress
(5) Reflect and adapt on an ongoing basis
4 Core values of Agile
(1) Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
(2) Working software over comprehensive
documentation
(3) Customer collaboration over contract
negotiation
(4) Responding to change over following a plan
▪ When a project involves changing requirements
▪ When most of the necessary database structures already exist
RAD or Agile Software Development should be considered when: (2 situation)
Prototyping Database Methodology and the Database Development Process