SQL
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
UNION
A SQL operation that combines the results of two or more SELECT statements into a single result set, eliminating duplicate rows.
UNION ALL
A SQL operation similar to UNION, but it includes all rows from the combined result sets, including duplicates.
INTERSECT
A SQL operation that returns only the rows that are present in both of the result sets from two or more SELECT statements.
EXCEPT
A SQL operation that returns all rows from the first result set that are not present in the second result set, effectively subtracting the results of one query from another.
FULL JOIN
A SQL operation that combines rows from two or more tables based on a related column, returning all records when there is a match in either table and filling with NULLs where there is no match.
CAST
A SQL function that converts an expression from one data type to another, allowing for data type compatibility in operations and queries.
CAST( field AS type)
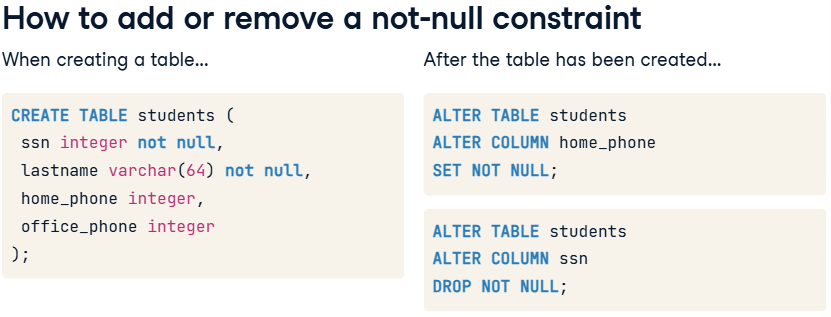
NOT NULL constraint
A SQL constraint that ensures a column cannot have a NULL value, enforcing that every record must contain a value for that column.
ALTER TABLE
A SQL command used to modify the structure of an existing table, allowing for changes such as adding, deleting, or modifying columns and constraints.
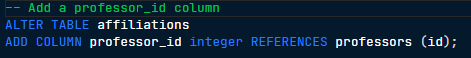
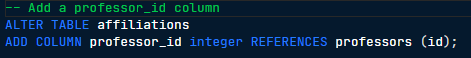
ADD COLUMN
A SQL command used to add a new column to an existing table within a database, specifying the column name and data type.
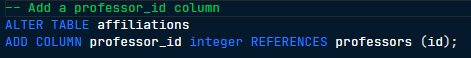
REFERENCES table (column)
A SQL constraint used in defining foreign keys that establishes a link between the current table and a column in another table, ensuring referential integrity.
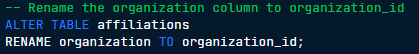
RENAME column to new_column_name
A SQL command used to change the name of an existing column in a table to a new specified name.

ADD CONSTRAINT table1_table2_fkey FOREIGN KEY (id) REFERENCES table (id)A SQL command used to add a foreign key constraint to a table, linking a specified column in the current table to a column in another table, thereby enforcing referential integrity.
UPDATE table_a
SET column_to_update = table_b.column_to_update_from
FROM table_b
WHERE condition1 AND condition2 AND ...;This query does the following:
For each row in
table_a, find the corresponding row intable_bwherecondition1,condition2, etc., are met.Set the value of
column_to_updateto the value ofcolumn_to_update_from(from that corresponding row).
The conditions usually compare other columns of both tables, e.g. table_a.some_column = table_b.some_column. Of course, this query only makes sense if there is only one matching row in table_b.
-- Update professor_id to professors.id where firstname, lastname correspond to rows in professors
UPDATE affiliations
SET professor_id = professors.id
FROM professors
WHERE affiliations.firstname = professors.firstname AND affiliations.lastname = professors.lastname;Example: This SQL command updates the professor_id in the affiliations table to match the id from the professors table, based on matching firstname and lastname values. It also selects the first 10 rows from the affiliations table for review.

Referential Integrity Violation
Occurs when a foreign key constraint is violated, meaning a value in a foreign key column does not match any value in the referenced primary key column of another table.
-- Identify the correct constraint name
SELECT constraint_name, table_name, constraint_type
FROM information_schema.table_constraints
WHERE constraint_type = 'FOREIGN KEY';
-- Drop the right foreign key constraint
ALTER TABLE affiliations
DROP CONSTRAINT affiliations_organization_id_fkey;
-- Add a new foreign key constraint from affiliations to organizations which cascades deletion
ALTER TABLE affiliations
ADD CONSTRAINT affiliations_organization_id_fkey FOREIGN KEY (organization_id) REFERENCES organizations (id) ON DELETE CASCADE;Changing how Referential Integrity Violation is enforced by defining or modifying foreign key constraints between tables to ensure that relationships are maintained.
OLTP
Online Transaction Processing | Purpose: Support day to day operation | Tasks: Update latest customer transaction
OLAP
Online Analytical Processing | Purpose: Support business decision making | Tasks: Find the most loyal customers
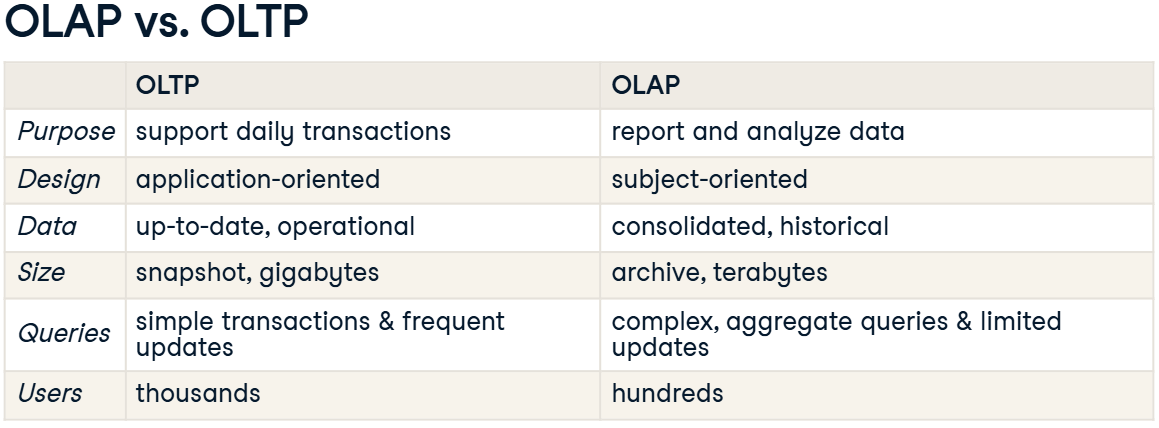
Distinguish the difference between OLTP vs OLAP
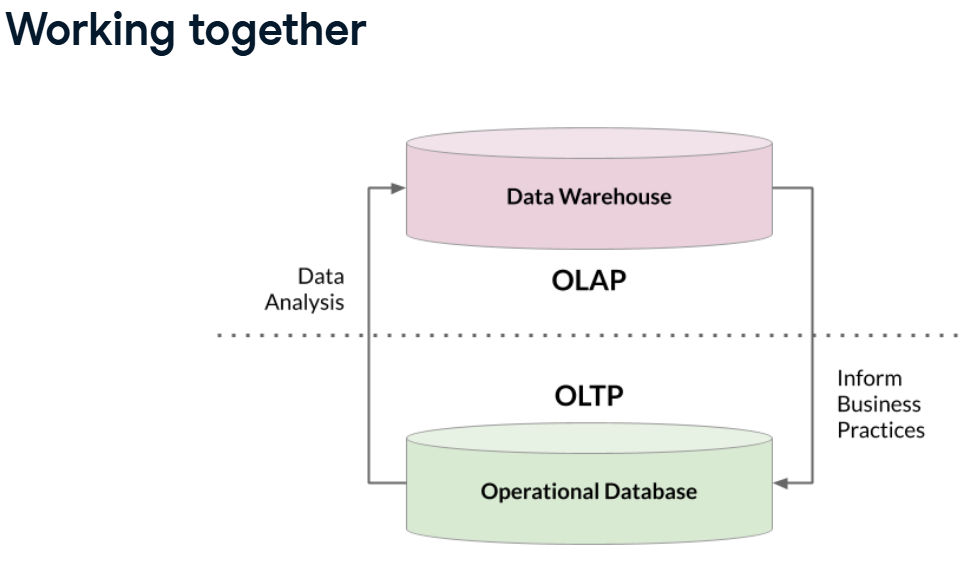
OLTP & OLAP influence on each other
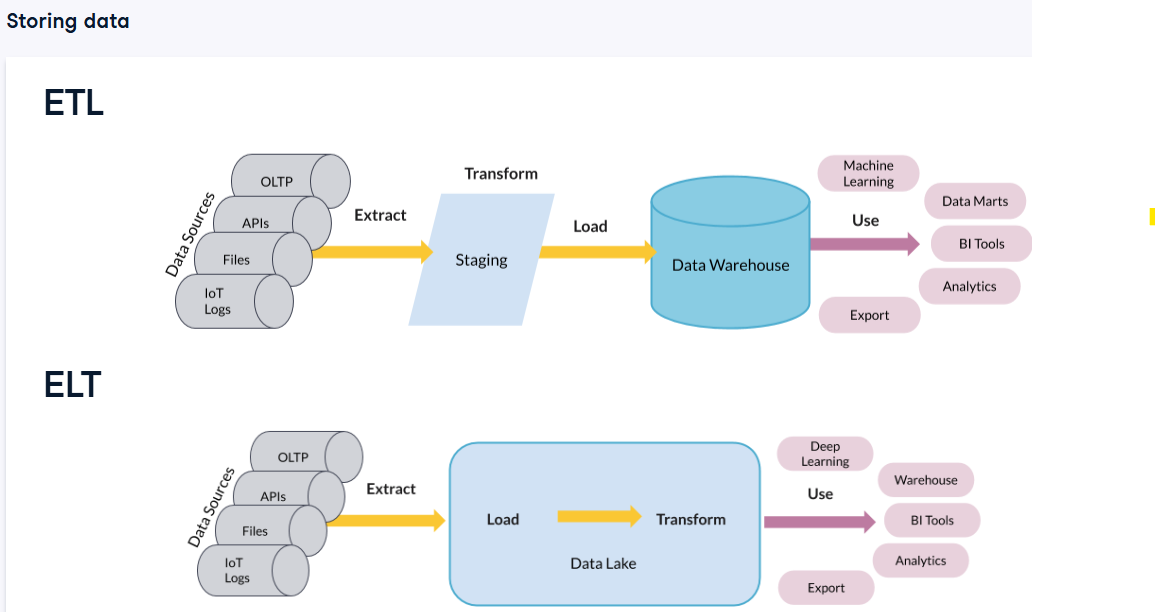
ETL vs ELT visual
Tool | Purpose | Modeling Style | Architect Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
Cogito | Real-time analytics | Minimal, in-memory | Support real-time models, dashboards |
Clarity | Raw data extraction (SQL) | Normalized (3NF) | ETL design, data mapping, integrity |
Caboodle | Enterprise reporting (EDW) | Dimensional modeling | Subject-area modeling, SCDs, performance |
Cogito vs Clarity vs Caboodle
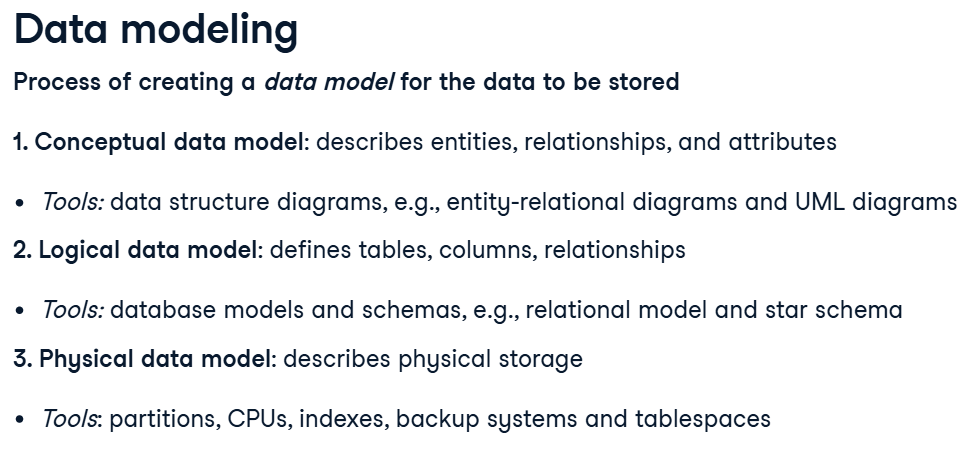
Conceptual vs Logical vs Physical data model
Star Schema
Dimensional modelingapproach used in data warehousing that organizes data into fact and dimension tables for efficient querying.
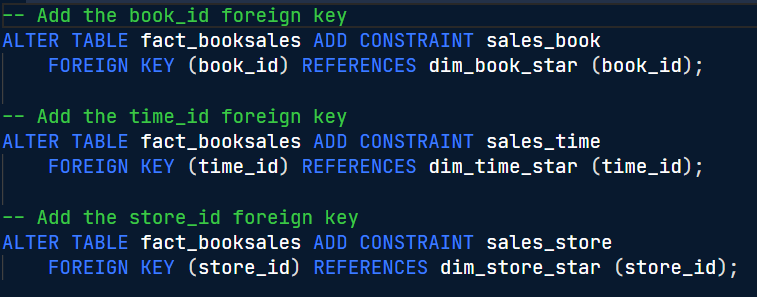
FORIEGN KEY function
-- Create a new table for dim_author with an author column
CREATE TABLE dim_author (
author varchar(256) NOT NULL
);
-- Insert authors
INSERT INTO dim_author
SELECT DISTINCT author FROM dim_book_star;
-- Add a primary key
ALTER TABLE dim_author ADD COLUMN author_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY;
-- Output the new table
SELECT * FROM dim_author;Create a new table. Add a new column. Insert value.
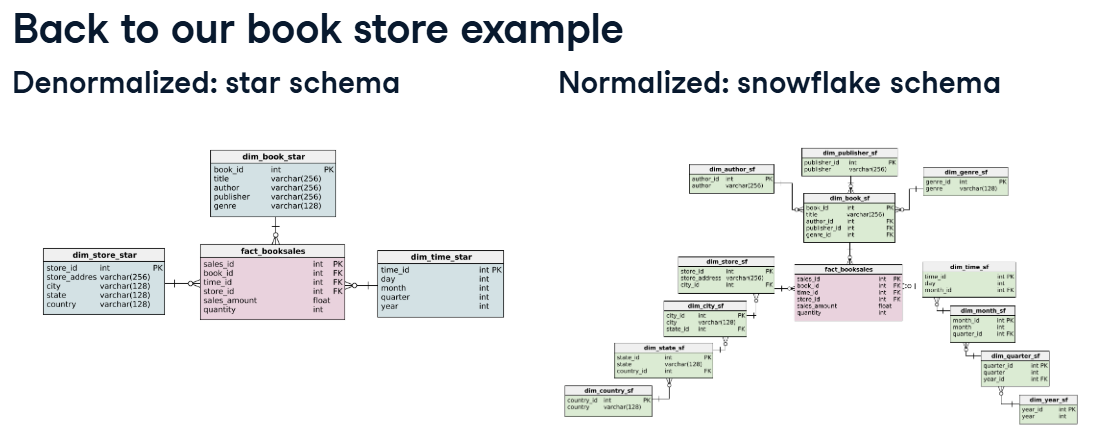
Denormalized = Star Schema. Normalized = Snowflake Schema

Normalization in OLTP vs OLAP

Query for viewing views

Creating view example

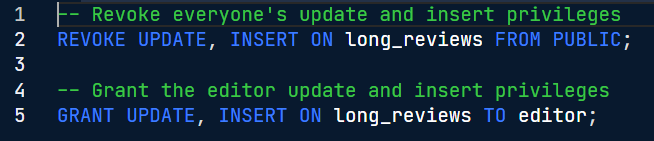
Grant/revoke view access
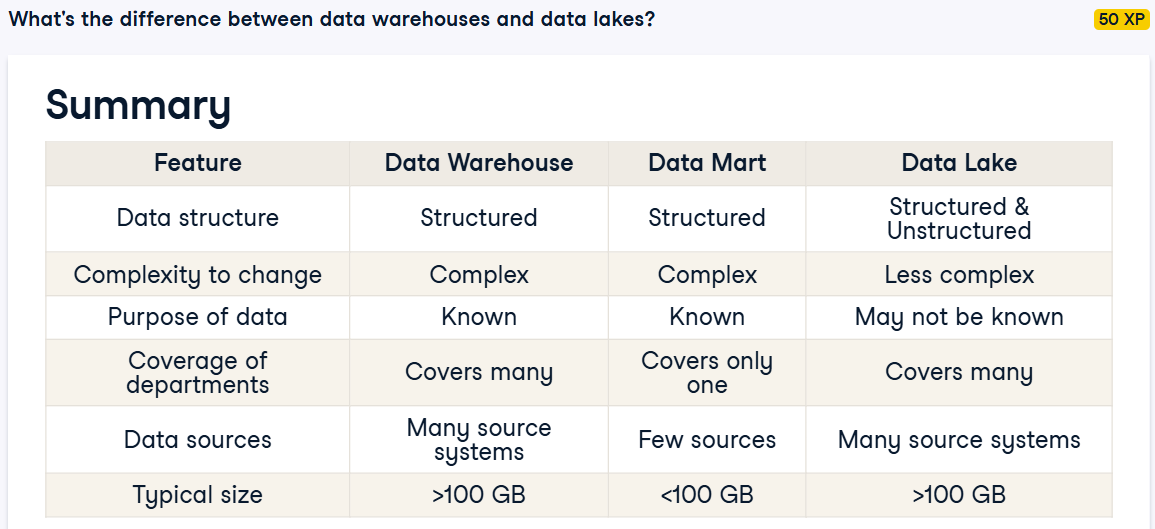
Data Warehouse vs Data Mart vs Data Lake
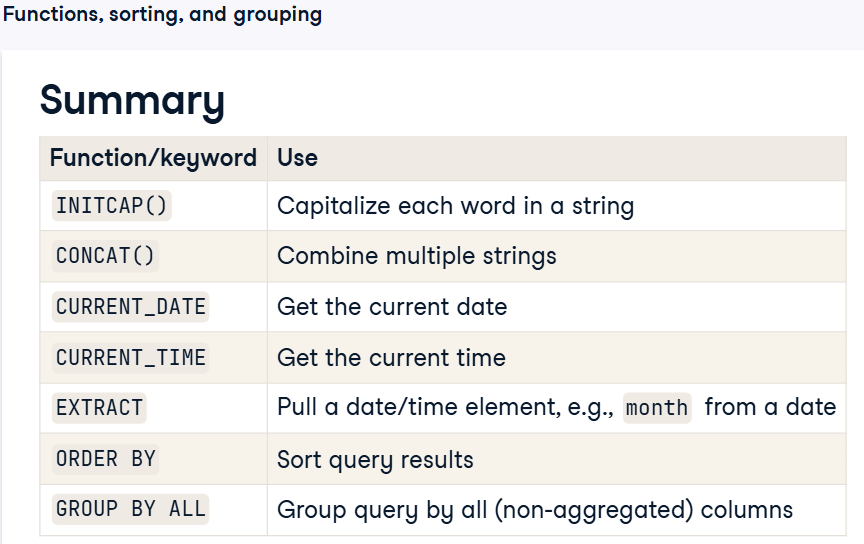
Snowflake SQL functions

Why Lateral instead of regular join

Snowflake SQL query history
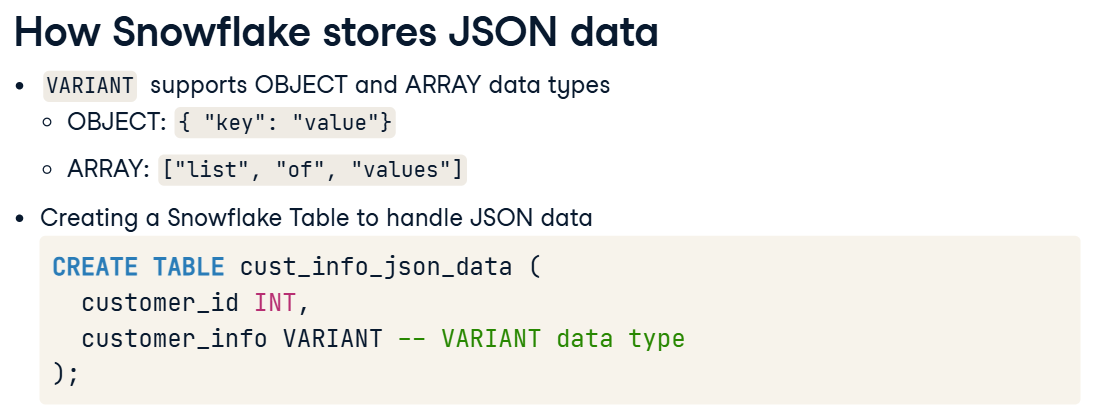
Snowflake SQL storing JSON data
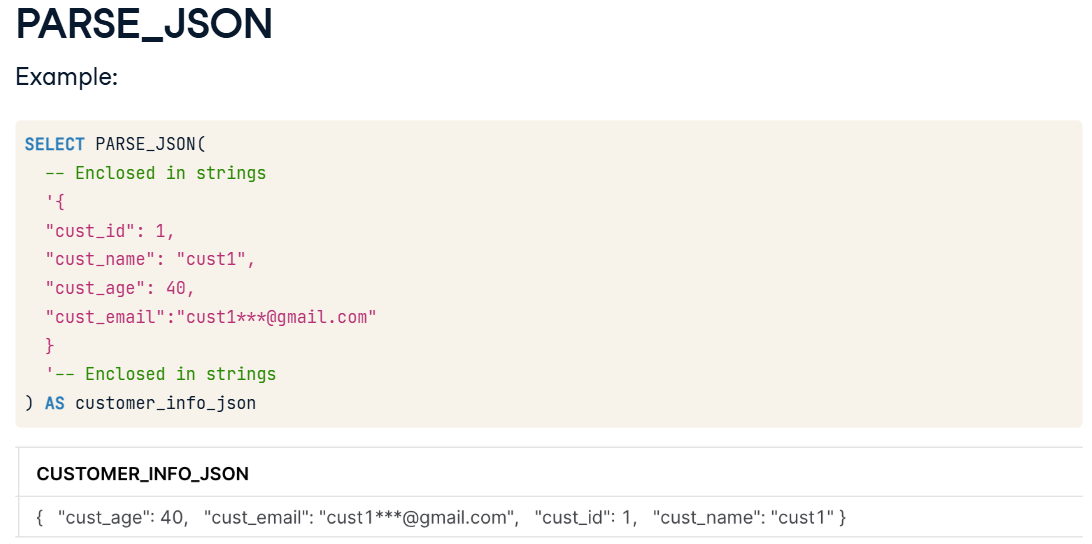
PARSE JSON example

OBJECT CONSTRUCT example
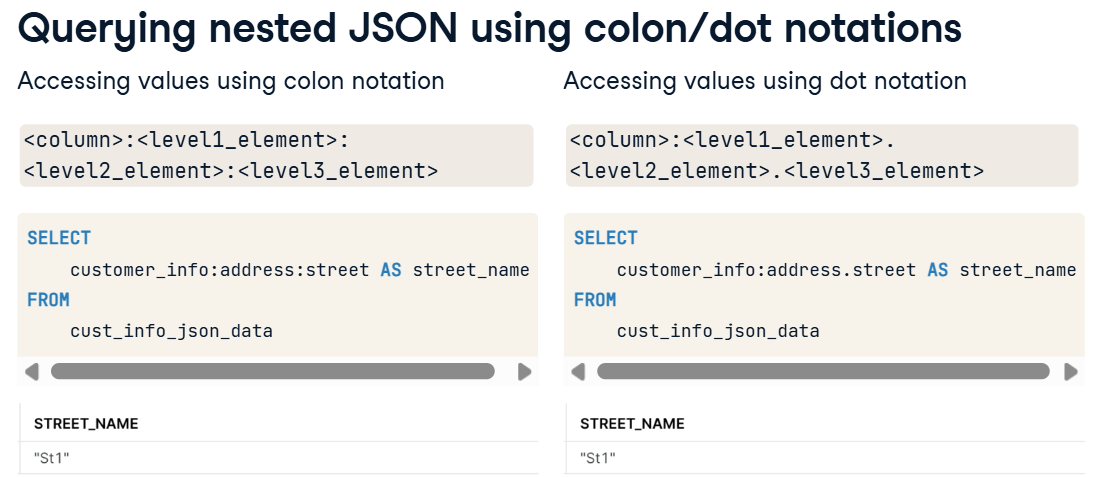
Nested JSON dot vs colon