lecture 5 unti 1 cells
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
what does the length constant limit
how far apart the receptive surface can be from the trnsmitting surface
5 properties of action potential
brief reversals in membrane potential (-55 mV to +40 to hyperpolarized -80 within 1-2 ms), only occur when Vm reaches threshold depolarization value, action potentials are the same amplitude for a give axon, they regenerate along the lenght of an axon, followed by two refactory period (absolute refractory period, relative)
absolute refractory period
the period after a neuron generates an action in which it cannot generate another
entirely due to the inactivatoin of voltage-gated Na+ channels (will not reopen until inactiviatoin process is removed)
relative refractory period
period of time after action potential where it is must harder to generate an action potentials, undershoot still occuring and membrane potential is hyperpolarized,
who studied action potentials
huxley and hodgkin
falling phase of action potential
hyperpolarization below resting levels (the under shoot) before it then returns to resting level
how do current behave during an actin potential
they change - early inward current is what depolarizes the membrane, and the outward current hyperpolarizes it
what does a larger depolarization do to action potential
leads to a greater number of action potentials; the spike rate goes up
spike rate
the rate at which neurons generate action potentials
clustering of action pottentaial
where do action potentials regenerate
along the length of an axon
relative refractory period
stronger than usual depolarizatoin is necessary ot bring the mmebrane to threshold
absolute refractory period
period of time after action potential is generated where it cannot generate another. it also goes in one direction - away from the axon initial segment
4 phases of action potential
rising phase (depolariatoin), overshoot (peak depolarization), falling phase (hyperpolarizatoin), undershoot (Vm briefly lower than resting potential)
what is the purpose of the voltage clamp technique?
The voltage clamp technique measures the currents required to hold the membrane potential at a specific level, allowing researchers to study the ionic currents and their dependence on membrane potentia
What role does tetrodotoxin (TTX) play in experiments?
TTX blocks voltage-gated Na⁺ channels, which eliminates the early inward current and confirms that Na⁺ is responsible for this current.
Describe the time-dependence of Na⁺ conductance during an action potential.
Na⁺ conductance increases rapidly when the membrane is depolarized but decreases quickly due to channel inactivation.
What role does tetra-ethyl-ammonium (TEA) play in experiments?
EA blocks voltage-gated K⁺ channels, which eliminates the late outward current and confirms that K⁺ is responsible for this current.
describe the time-dependence of K⁺ conductance during an action potential.
K⁺ conductance increases more slowly than Na⁺ conductance but remains elevated for the duration of the depolarization because K⁺ channels do not inactivate.
what does hyperpolarization do
) It closes the voltage-gated K + channels; 2) It closes the activation
gates of the Na+ channels; 3) It opens the inactivation gates of the Na + channels
T2
conductoin tau
Na⁺ Conductance vs K+
rapid and transient; slower and
What is the purpose of a voltage-clamp experiment?
the voltage clamp technique measures the currents required to hold the membrane potential at a specific level, allowing researchers to study the ionic currents and their dependence on membrane potential.
Describe the time-dependence of Na⁺ conductance during an action potential.
Na⁺ conductance increases rapidly when the membrane is depolarized but decreases quickly due to channel inactivation.
inactivation of channels
after .5 ms of current flow thru voltage gated na+ channels, smth gets in the a
early current
inward flow of na+
when does conductance of na+ increase rapidly
whem membrane is clamped above threshold; at more depolarized membrane potentials bc more voltage gated na+ channels are open
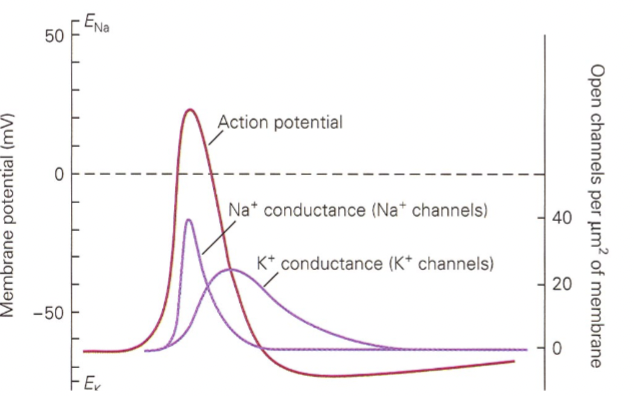
explain
rapid increase of gNa takes mp to peak of action potential, slow rise in gK and rapid decline of gNa (bc of Na+ channel inactivatoni) bring back mp to resting level
why does salatory conduction only occur in myelinated axons
rescrits voltage-gated channels to nodes of ranier
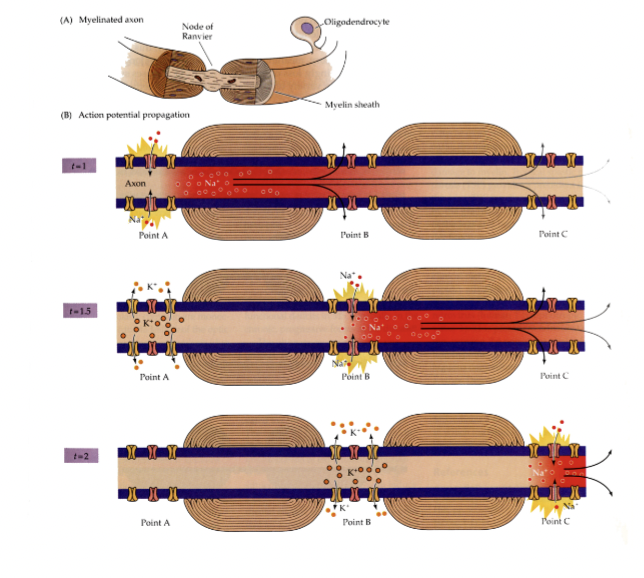
explain
current moves down to reach next node of ranvier
depolarization current opens na+ channels to regenerate ap
then current moves down the next myelin to depolarize next node of ranvier, thus jumping from node to node
t is short —> ap moves faster
what contributes to spped of myelination
time constant, and spacing of nodes
What happens if myelination is lost, as seen in diseases like multiple sclerosis?
Action potentials fail to propagate properly because the current cannot efficiently jump between nodes.
WHERE are voltage gated na+ channels and k+ channels found
Na+ = nodes of ranvier ; K+ = juxta-paranode (on either side of the nodes)
why can the action potential only move one way
na+ channels slowly become inactivated, so
how is an action potential initiated
membrane potential reaches a threshold value