W3 LECTURE 7: The Cambrian explosion
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Multicellularity
Many different cell types
Colonial
Many cells (one cell type)
What forces drive evolution of multicellularity
Evolution of colonial form (benefit of size)
Evolution of division of labour (Genetic similarity of a ball of cells, cooperation, evolution of interdependent cells)
Evolution of colonial form
Cells divide but they don't separate
Cells stick together
Benefit: Cells are then freed from predation
Division of labour
Specialisation leads to increased efficiency
Each cell has a specific job
Specialisation in nature (Volvox)
2 different cell types: reproduction, fast division
Different cells with different roles help with fast reproduction
Proterozoic
Former earlier life (pre-cambrian)
Phanerozoic
Visible life (post-cambrian)
Cambrian explosion
Diversification of multicellular animal life in the oceans
High diversity and animals not seen today
Main animal taxa phylogeny
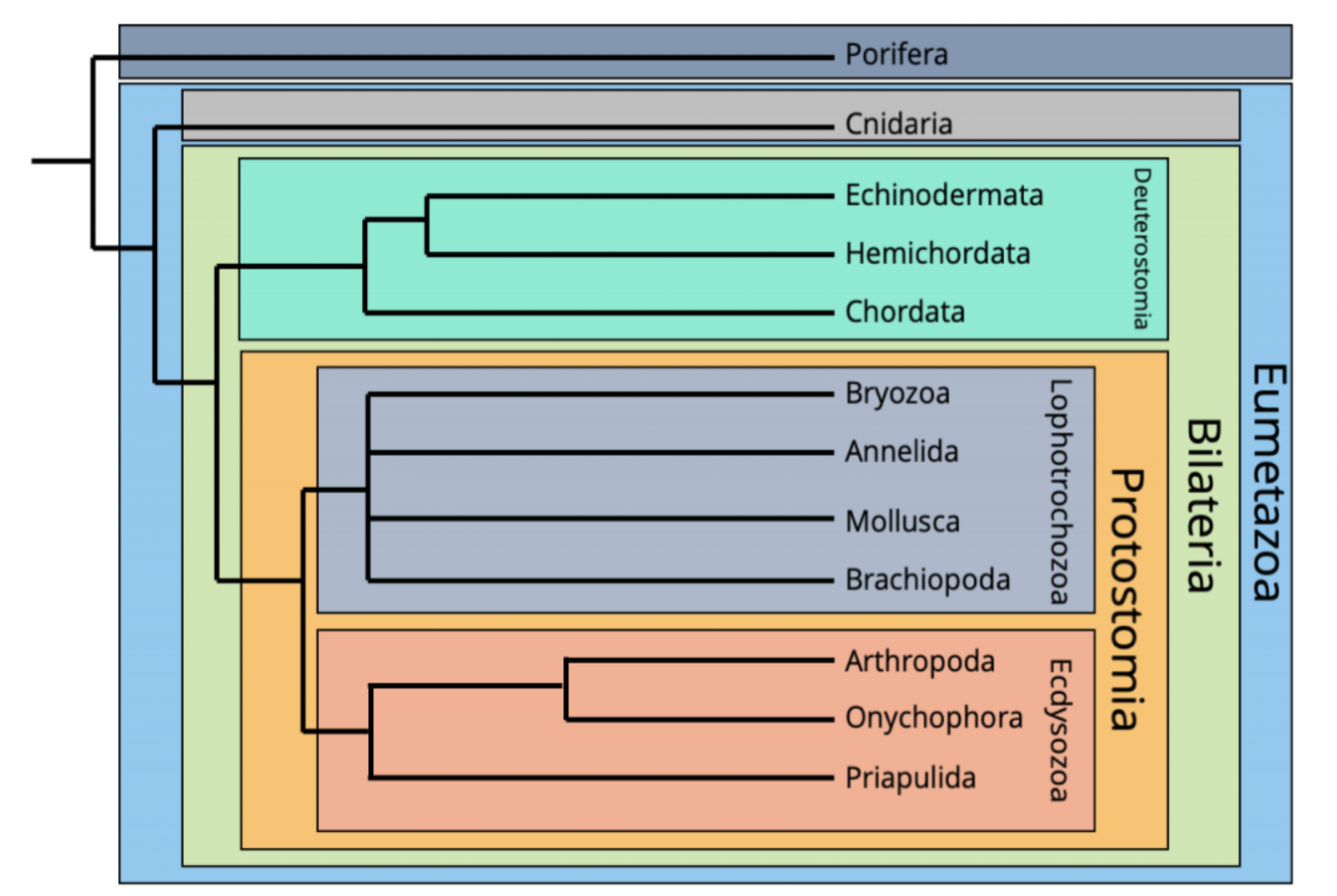
Porifera
Sponges
Asymmetrical
Tissue absent
3/4 cell types
Placozoa
Blob like aggregation of cells
6 cell types - no tissue
Undifferentiated
Ciliary movement, engulf food
Divide by fission, fragmentation
Cnidaria
E.g. jellyfish
Radial symmetry
Tissue
2 cell layers - diploblast
No gut no head
O2 via diffusion , no respiratory system
Asexual reproduction
Predatory via stinging
Decentralised nervous system (no brain)
Bilateria
Bilateral symmetry
Triploblastic - endoderm (inside), mesoderm(middle), ectoderm(outside)
Gut - flow through feeding/digestion (mouth to gut)
Development of head (sensory and mechanical functions of feeding)
Stages of multicellularity in animals
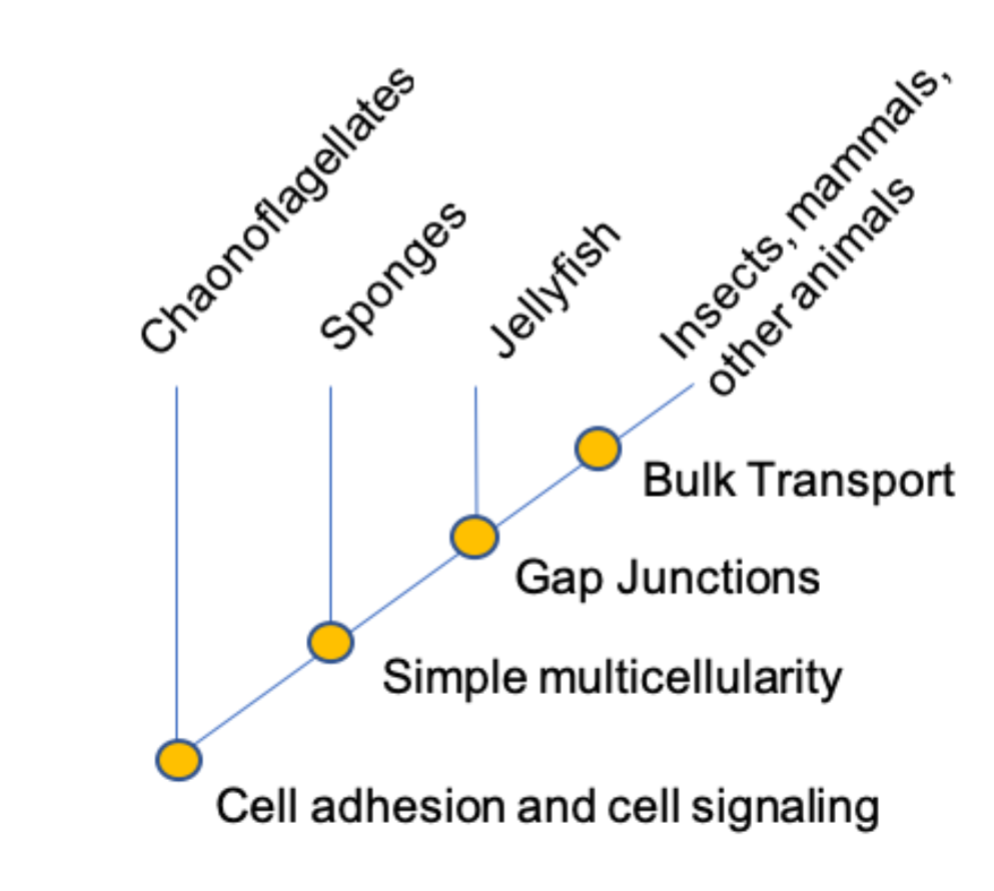
Protostome and Deuterostome split
Proto - Forms mouth first
Deutero - Forms anus first
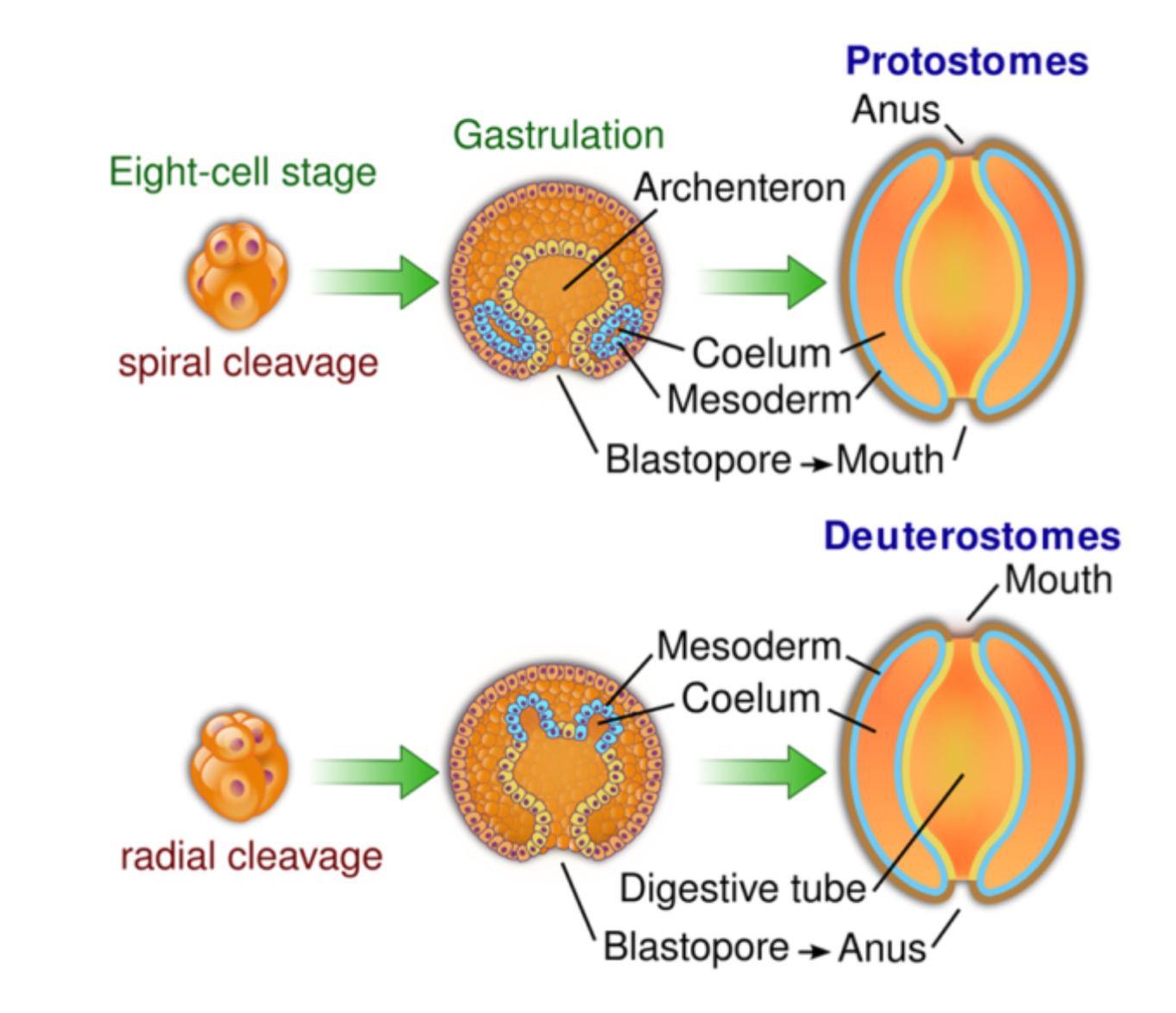
Lophotrochozoa
Protostome development
Spiral cleavage
Larval stage
E.g. Molluscs, Cephalopods, Platyhelminths, Annelids
Molluscs
Diverse: marine ,fresh water, land
Sedentary, mobile
Mostly muscle
High complexity cognition
Shells
Cephalopods
Octopus, squid
High complex cognition
Largest brain size for a body of an invertebrate
Platyhelminths
Flatworms
Disease causing in mammals - parasites e.g. Tapeworm
No body cavity (no gut)
Digestive cavity (mouth = anus)
Annelids
Segmented worms
Marine, fresh water, land
Collagen cuticle
Important in soil
Ecdysozoa
Exoskeleton
Growing and Moulting
Segmented animal
Many legs, paired appendages
May adopt head
Arthropods
Chelicerata: arachnids, mites
Myriapods: millipedes and centipedes
PanCrustacea: Crustacea, Ostracods and Copepods, Insecta/Hexapoda
Nematodes and Nematomorphs
Nematodes:
Unsegmented
‘Roundworms’ like C. Elegans
Bacteriovores
Micro predators
Detritivores: important in soil and in marine sediments
Plant and animal Parasites
Pests and disease causing
Biocontrol agent (e.g. Control of soil stage of insects)
Nematomorphs: Horse Hair worms - parasites
Tardigrades
Waterbears
Segmented
Marine and fresh water
Live on algae
Environmentally resistant
Other ecdysozians
Priapulids:
Penis worm
Marine
22 species now but hyperdiverse in the Cambrian -carnivores, detritivores, filter feeders
Onychophorans:
Velvet worms
Segmented but no exoskeleton
Nocturnal
Ambush predators in terrestrial humid tropics
Echinoderms
Invertebrates
Marine aquatic
Bilateral symmetry
Mesodermal skeleton
No CNS
Water based coelom circulation
Regenerative
Hemichordates
Invertebrates
Sister to Echinoderms
Tripartite body
Some shared characteristics with chordates
Branched gill slits
Stomochord 0 rod that runs down body providing support
Dorsal nerve cord
Chordates
Notochord - Rod down the back
Dorsal nerve chord (spinal chord)
Gill slits - Pharyngeal
Post anal tail
Vertebrates are derived Chordates
Dorsal nerve chord => vertebral column
Cephalochordates
Lancelets, marine
Tunicates
Sea squirts
Marine
Filter feeders
Colonial adults
Vertebrates
Agnatha (jawless fish)
Hagfish
Lampreys
Gnathostomata
Jawed vertebrates
Deep animal diversity defined by
Number of generative layers – one, two (diploblasty), three (triploblasty)
Early development – blastopore fate (deuterostome vs protostome)
Within protostome, Ecdysis presence (Ecdysozoa vs Lophotrochozoa)
What promoted the cambrian explosion
Global temperature changes
Global oxygen changes
Global temperature change
Snowball earth – ended shortly before Ediacarian
Period of extreme cold with high glaciation
- Glacial deposits in near tropical areas
- Low photosynthetic accumulation
Reflectance of light/heat reinforce initial conditions -> long period
Ended by volcanic activity/CO2 input => warming?
Higher oxygen enables multicellular animal function
Physiologically: Diffusion cannot sustain aerobic processes at large size and low o2
Low o2 limits size of aerobic molecules
Higher oxygen enables more trophic levels
Pyramid of biomass - loss of energy stored through trophic levels
Hox genes code transcription factors
Define position
Alter expression of other genes
>development of complex form
Individual Hox genes are found widely in eukaryotes
Animals have an array of them – and number of copies and organismal complexity linked
Enabled bilaterian complexity