HAP Pages 28-35 (Phase 1 Cell cycle)
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
10/28/25: First batch, 10/29/25: Second batch added
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Cell Division
one cell splits into two daughter cells, including both mitosis and cytokinesis
Centromere
The narrow (center line) that holds the two sister chromatids together where the spindle fibers attach during cell division
Growth
An increase in cell size to prepare it for cell division.
What is mitosis?
process of cell division in which a single cell divides to produce two genetically identical daughter cells (AKA nuclear division)
Interphase
The period before mitosis when the cell grows, does its job, and duplicates its DNA.
What happens in Prophase
Chromatin condense into chromosomes
Metaphase
When chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell.
Anaphase
Where sister chromatids are pulled apart and moved to opposite sides of cell
Telophase
Chromosomes reach the poles, uncoil and form new nuclear membranes
Cytokinesis
When the cell’s cytoplasm divides to make two separate cells.
What is Chromatin
The form DNA takes when it’s wrapped around proteins(Happens in interphase)
Replication
The process of copying DNA so each new cell gets a complete set of genes.
Centriole
A small cylindrical structure in animal cells that helps organize spindle fibers during mitosis.
Spindle
A network of microtubules that attaches to chromosomes and pulls sister chromatids apart
DNA
The molecule that carries an organism’s genetic instructions in a code of bases
Unicellular
organism made of a single cell that performs all life functions on its own.
23
The number of chromosomes in a human gamete (sperm or egg), representing one complete set of chromosomes.
Cell Cycle
The repeating sequence of stages a cell goes through to grow and divide
Chromosomes are made up of what
2 daughter cells held together by a centromere
In Prophase, the _ _ disappears
Nucelar membrane
In Prophase the _ forms
spindle
In Prophase, the _ disappears
nucleus
In Telophase, the_disapears
Chromosomes
In telophase the _ and _ _ reform
nucleoli, nuclear membrane
During Telophase, the _ furrow forms and disappears
cleavage
What are checkpoints?
control mechanisms that ensure proper cell division and DNA integrity.
Cancer is a disease of _?
Mitosis
What has to happen in order for cancer to progress?
Checkpoints are mutated and don’t stop cell reproduction.
Apoptosis is
programmed cell death, (cell suicide)
HeLa cells are named after
Henrietta Lacks
What is so different about HeLa cells?
do not die after a set number of cell divisions.
In a healthy individual, the pH is
around 7.4
A _ mechanism allows the body to maintain a constant blood pH
homeostatic
_ is when the body reaches and acidic state
acidosis
Acids can remove _ _ from blood cells
negative charge
On the pH scale 7 is
neutral
On the pH scale, anything above 7 is
alkaline
On the pH scale, anything below 7 is
acidic
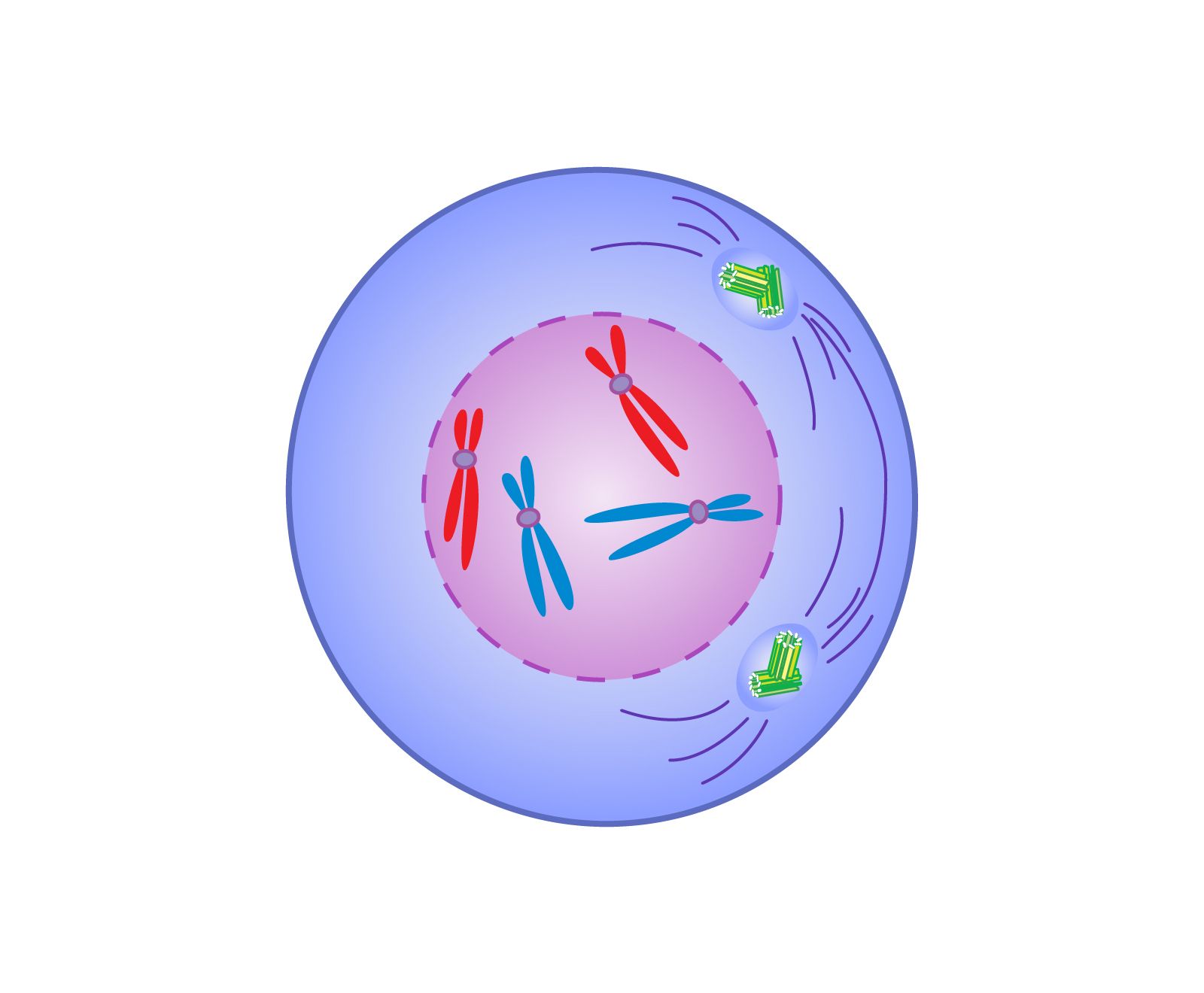
What phase is this?
prophase
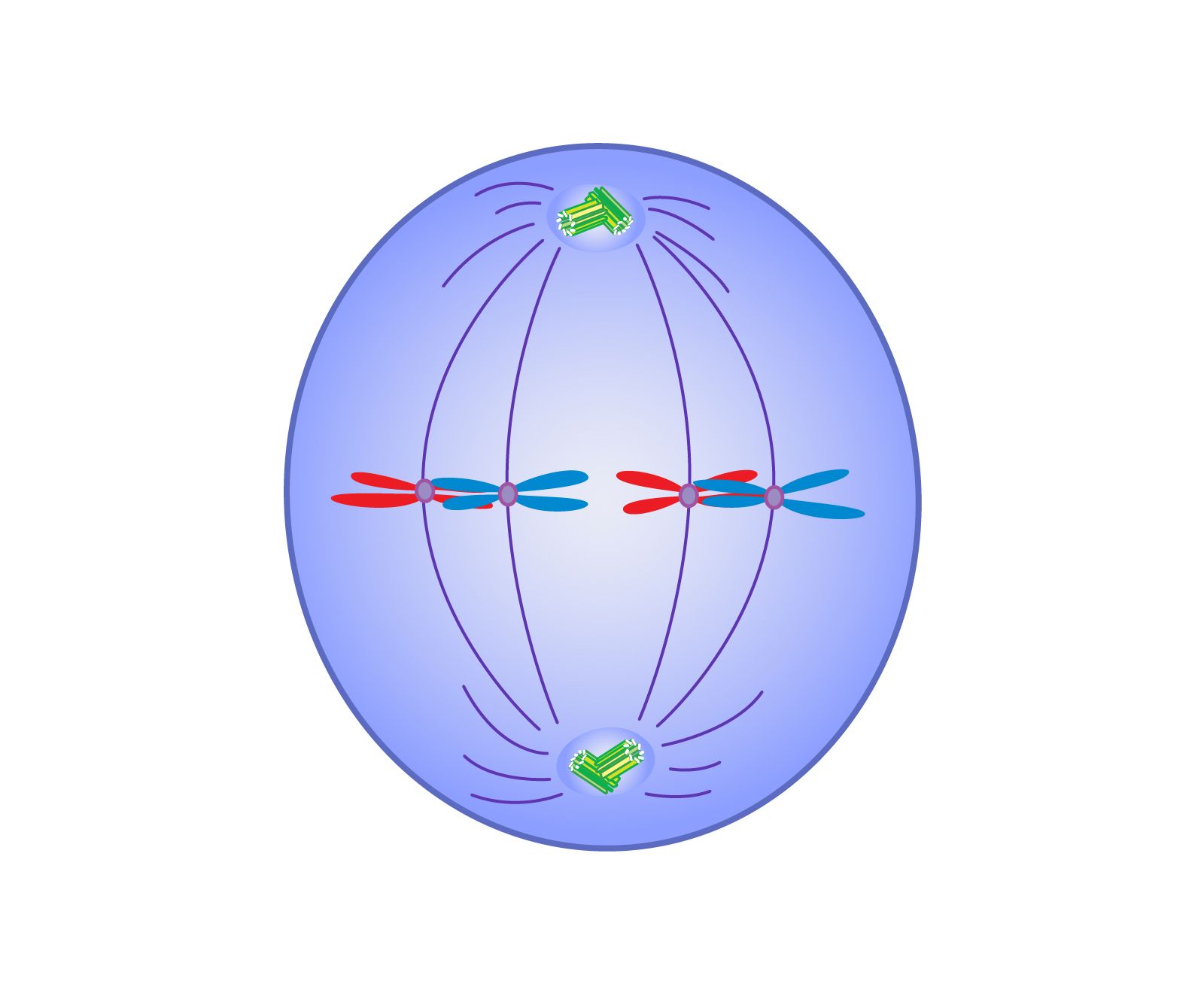
What phase is this?
metaphase
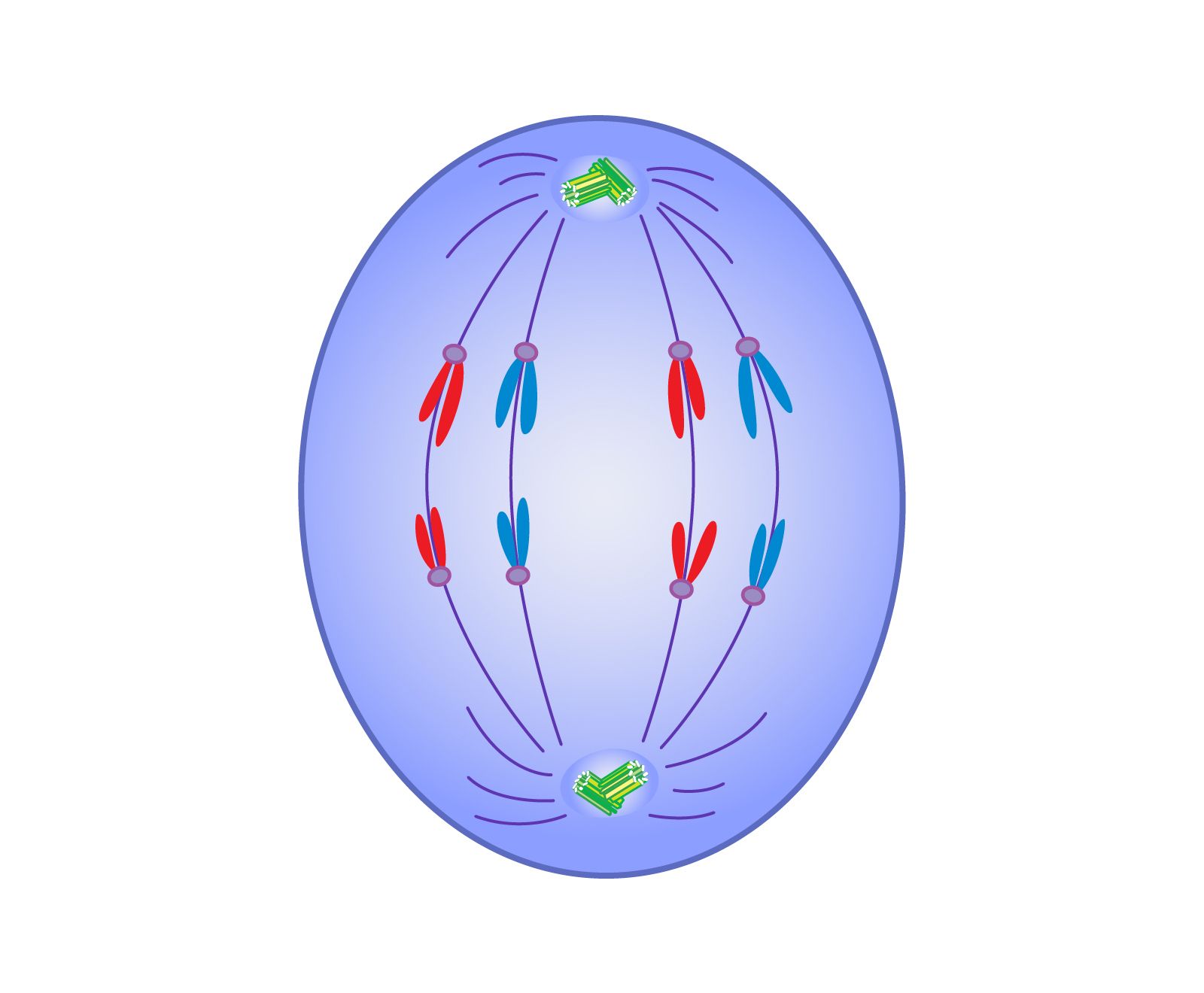
What phase is this?
anaphase
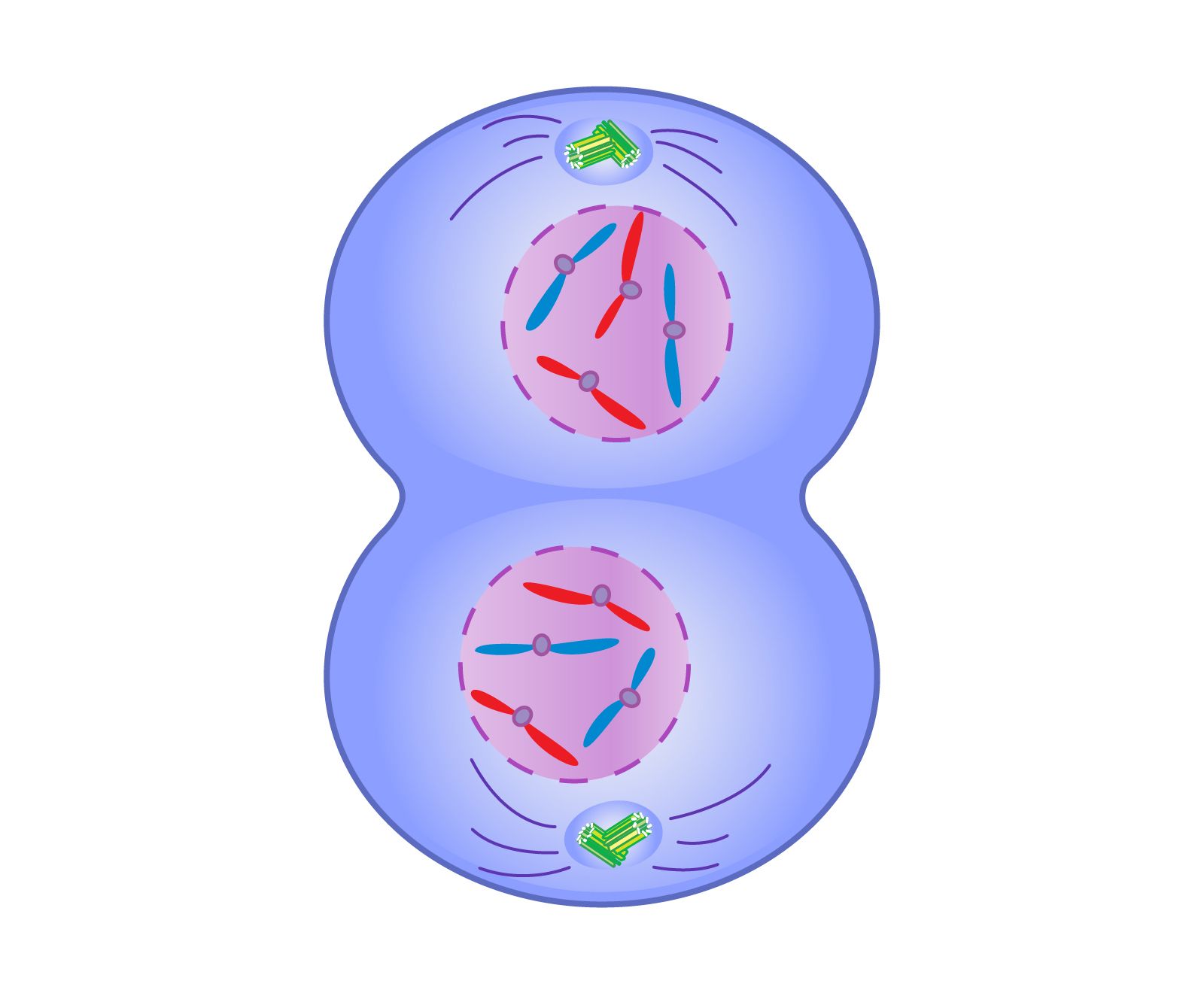
What phase is this?
telophase
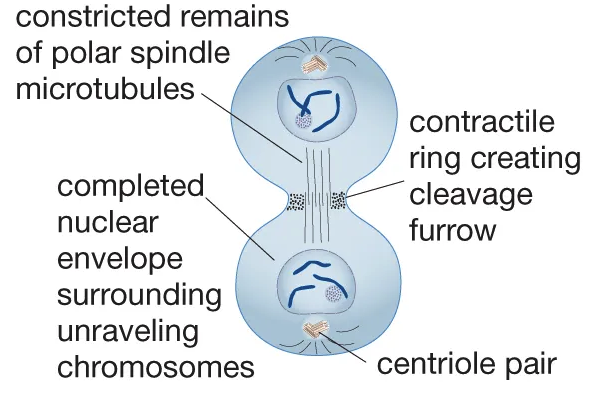
What phase is this?
Cytokinesis
Butterfly children are also known as this disease
Epidermolysis bullosa
What kind of cells are used in gene therapy?
Fibroblasts
What is a vector?
A modified virus used to carry the good gene
What are the 3 main steps of therapy?
1, collection, 2. culture, 3. administer
What is the goal of the gene therapy?
To deliver a working COL7A1 gene into the patient's cells.
What is RDEB?
A severe, recessive type of EB.
What gene is broken in RDEB?
The COL7A1 gene.
What protein is missing in RDEB
Type VII collagen.
What does "ex vivo" mean?
"Outside the body." Cells are treated in a lab, not inside the patient.
Why treat children early?
To prevent bad scarring and contractures (stiff joints).