DSA Week 3:
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
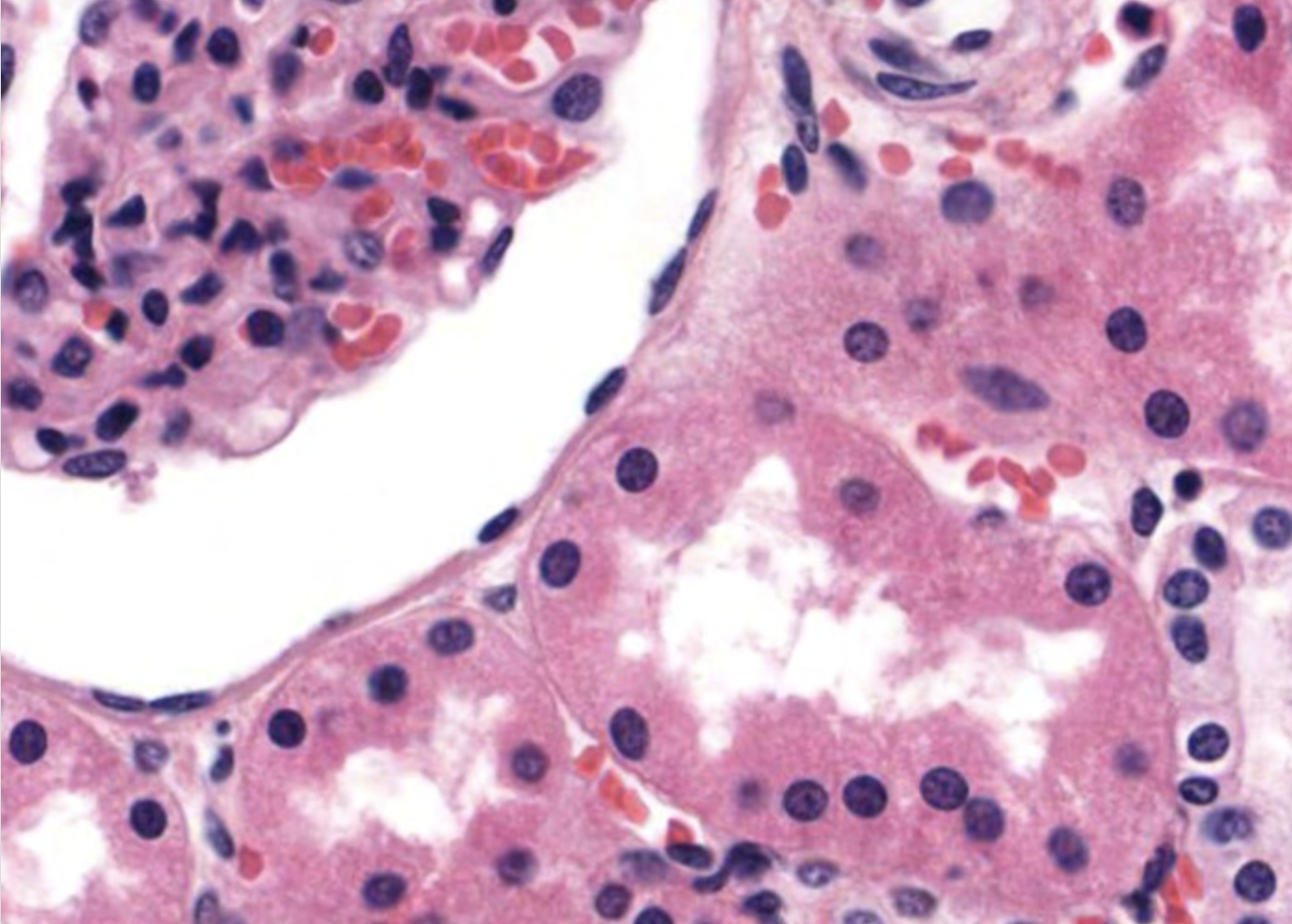
Simple Squamous Epithelial
absorbtion, secretion, filtration in alveoli, glomeruli
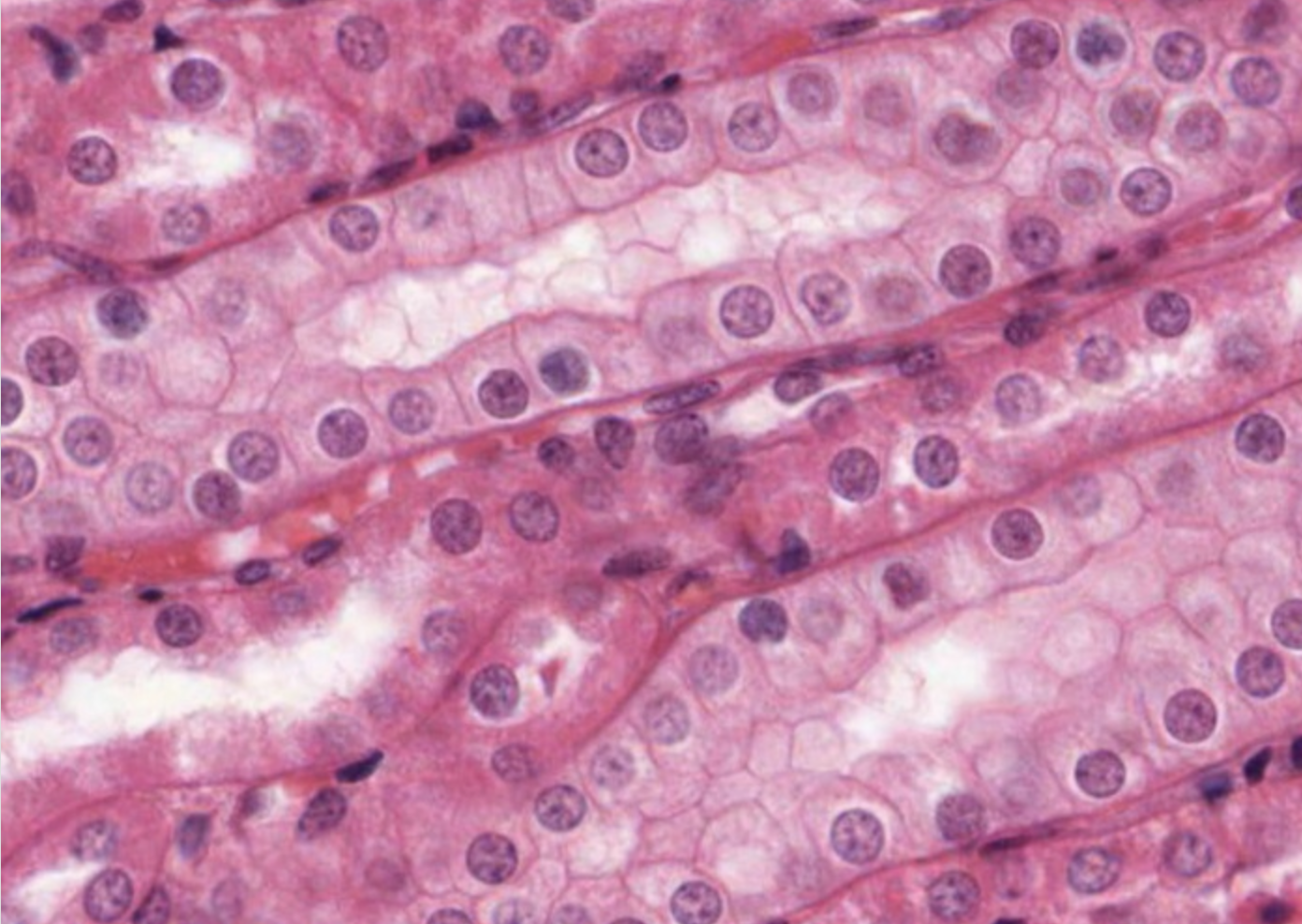
Simple Cuboidal Epithelial
Function: absorbtion, secretion
Location: glands, ureters
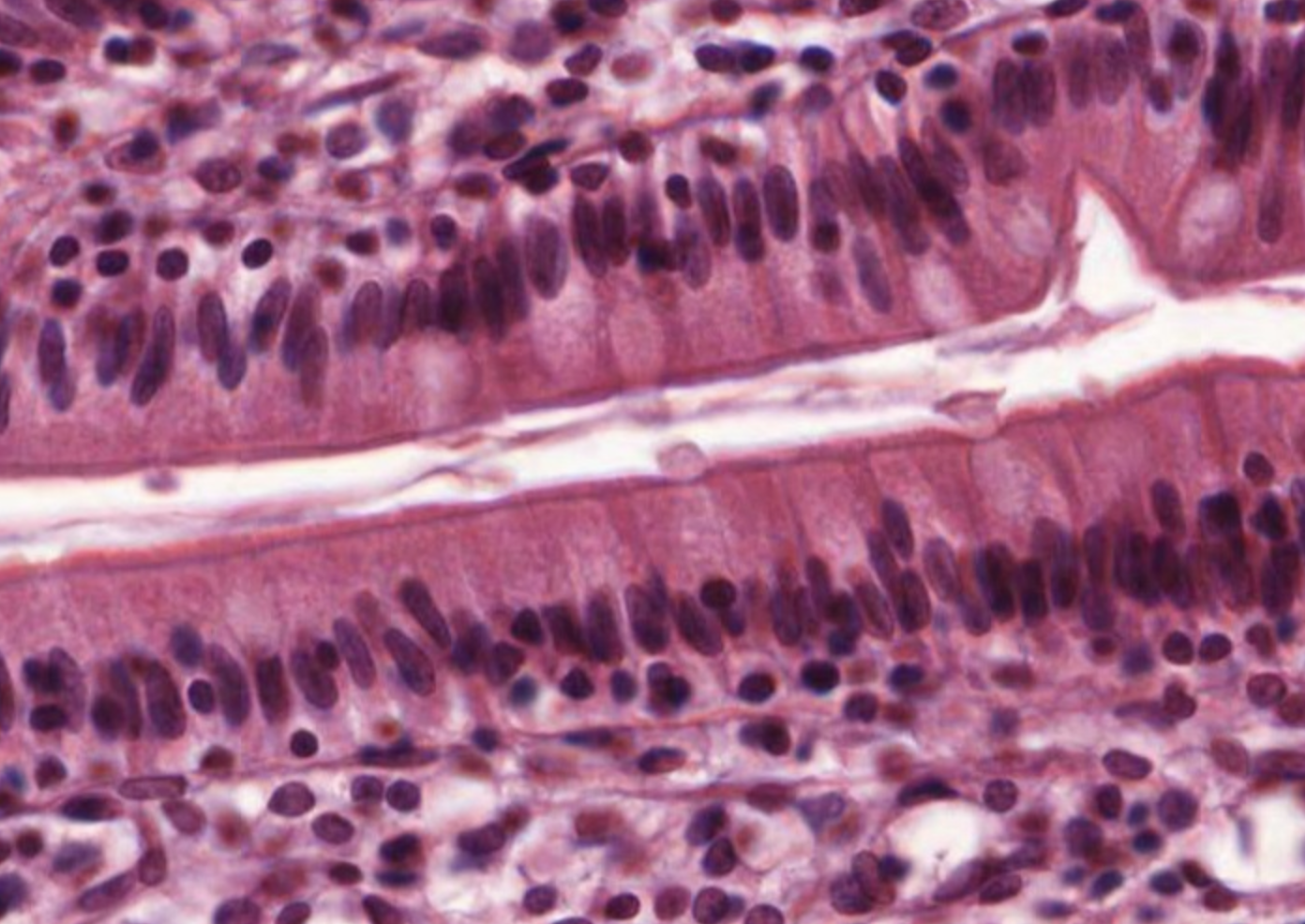
Simple Columnar Epithelial
Function: absorbtion, secretion, associated with mucus-secreting cells
Location: Digestive tract
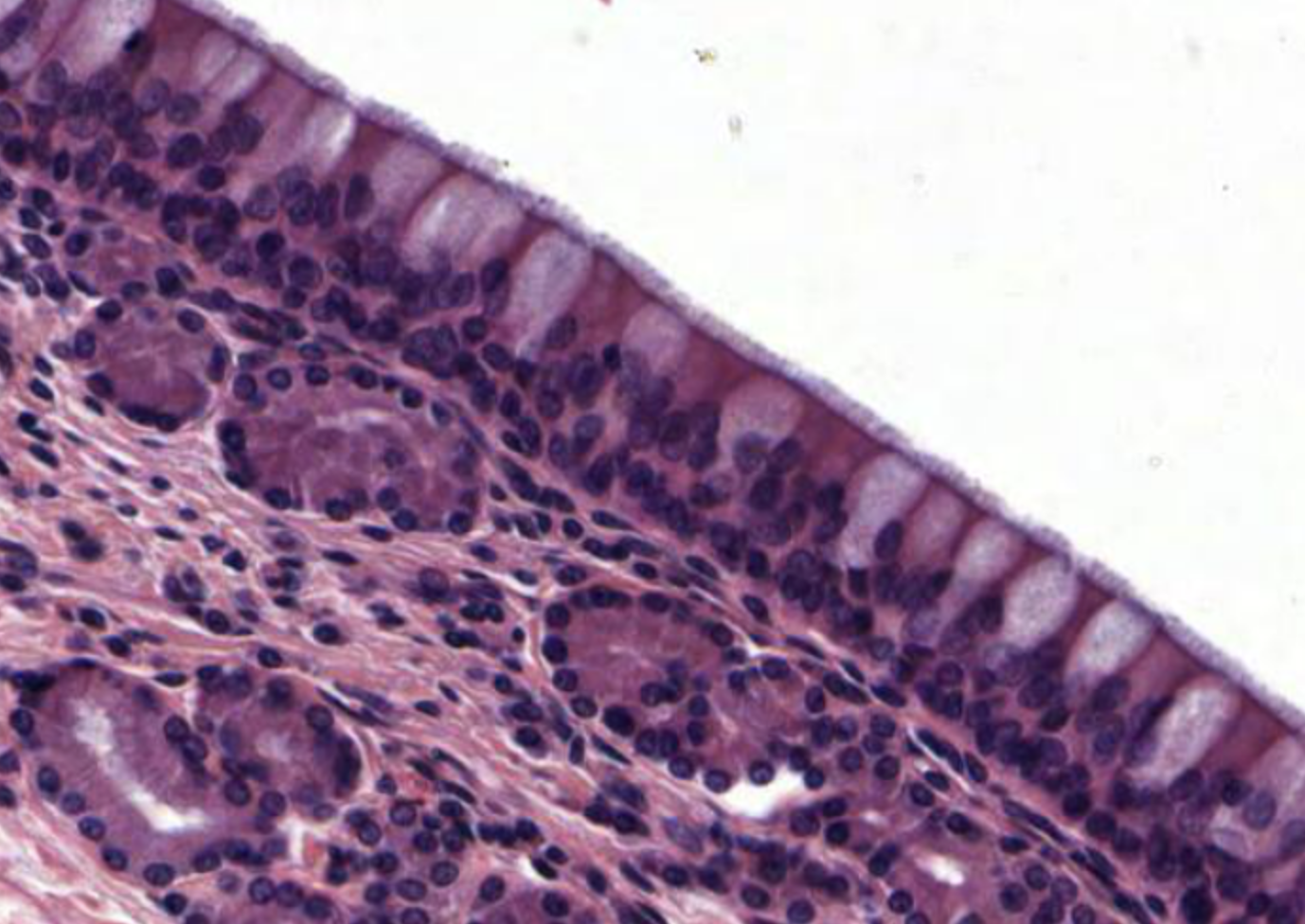
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelial
Function: secretion, propulsion
Location: respiratory tract
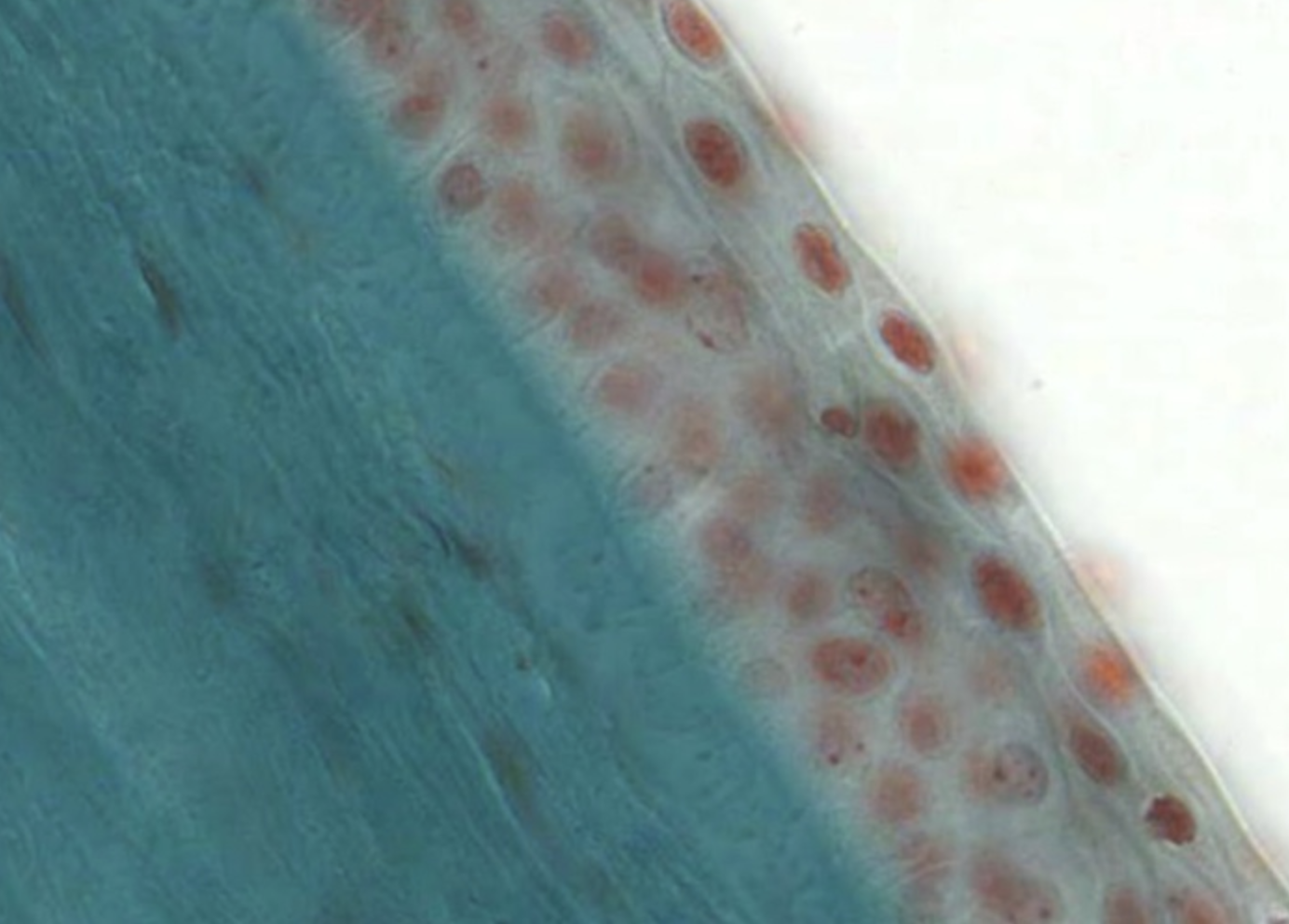
Stratified Squamous Epithelial
Function: protection
Location: outside of skin
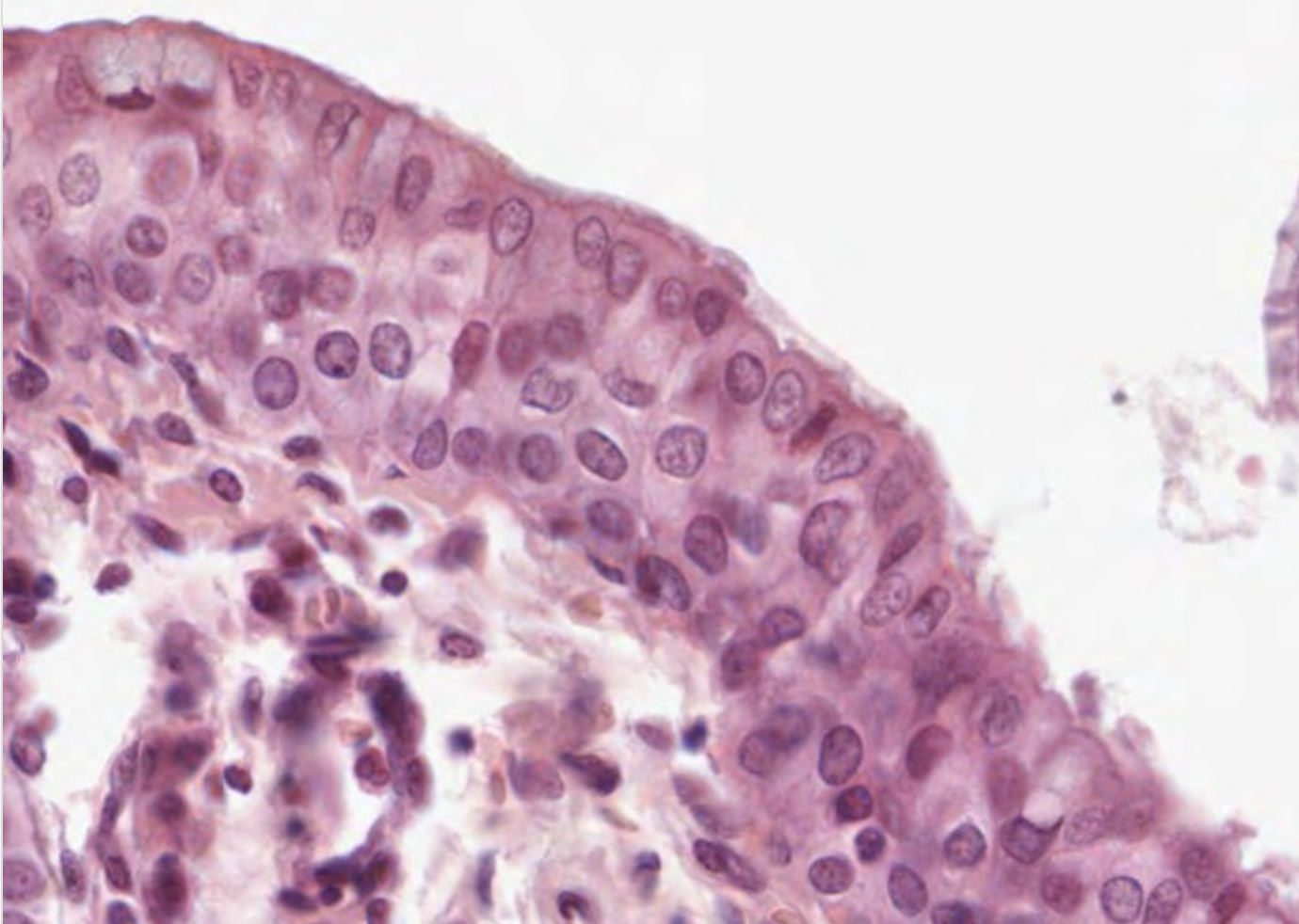
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelial
Function: protection, secretion
Location: ducts of glands
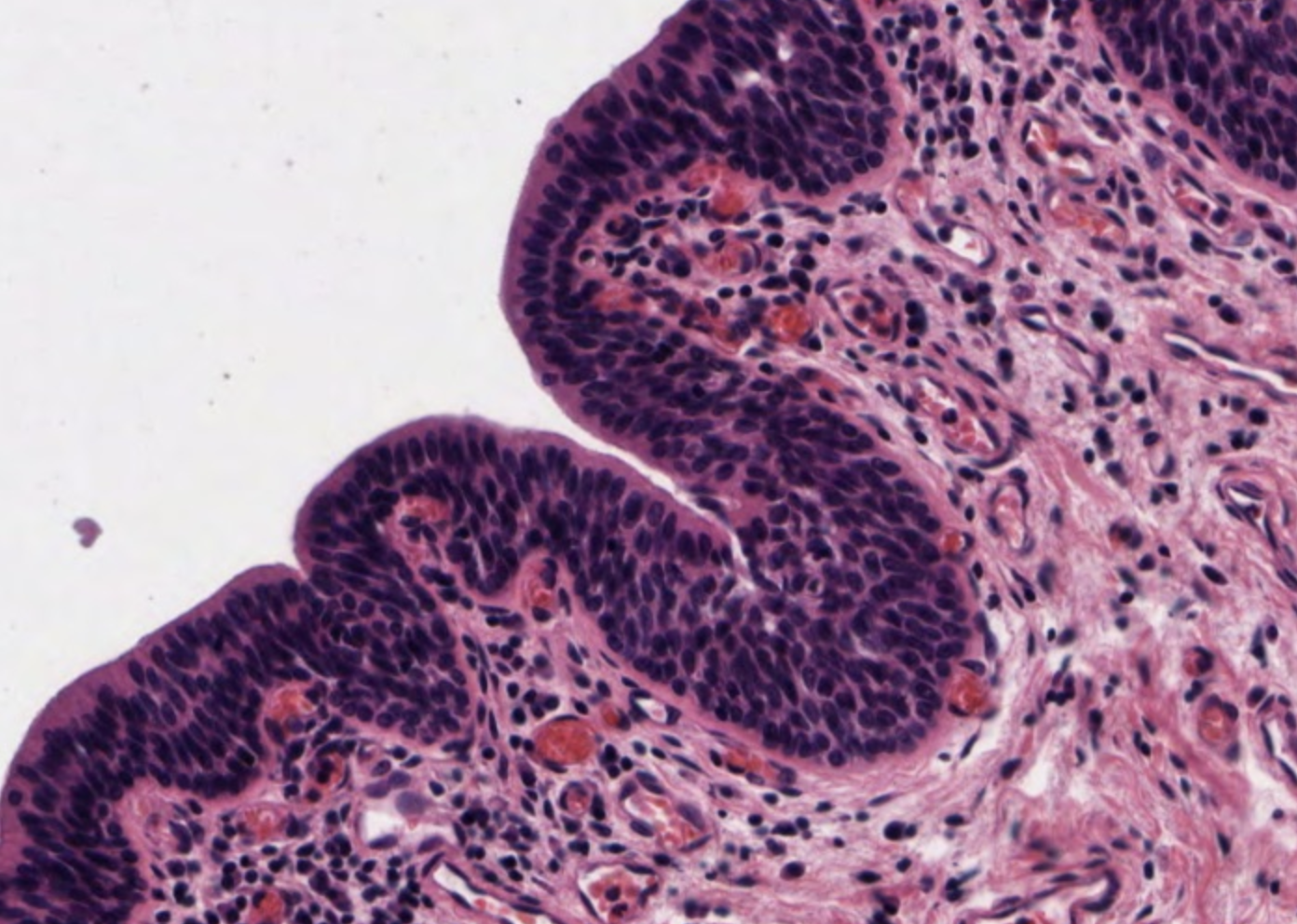
Stratified Columnar Epithelial
Function: protection, secretion
Location: pharynx, urethra, glandular ducts, transition areas or junctions
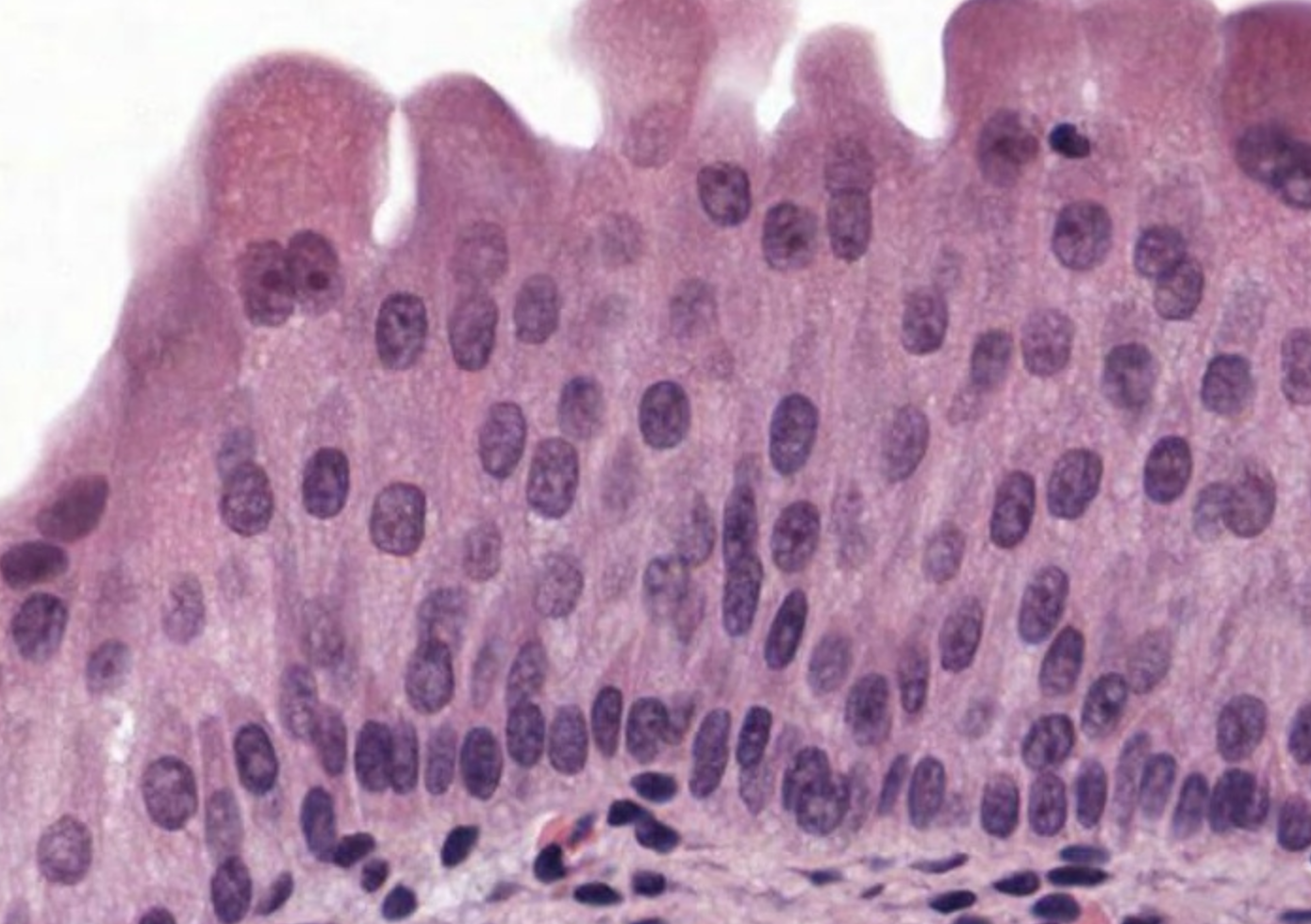
Transitional Epithelial
Function: stretches
Location: lining of hollow urinary organs
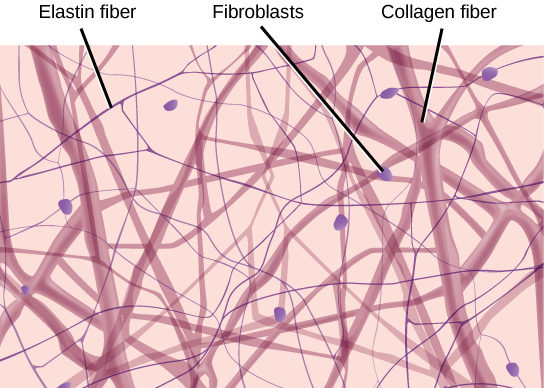
Areolar Connective
universal packing material
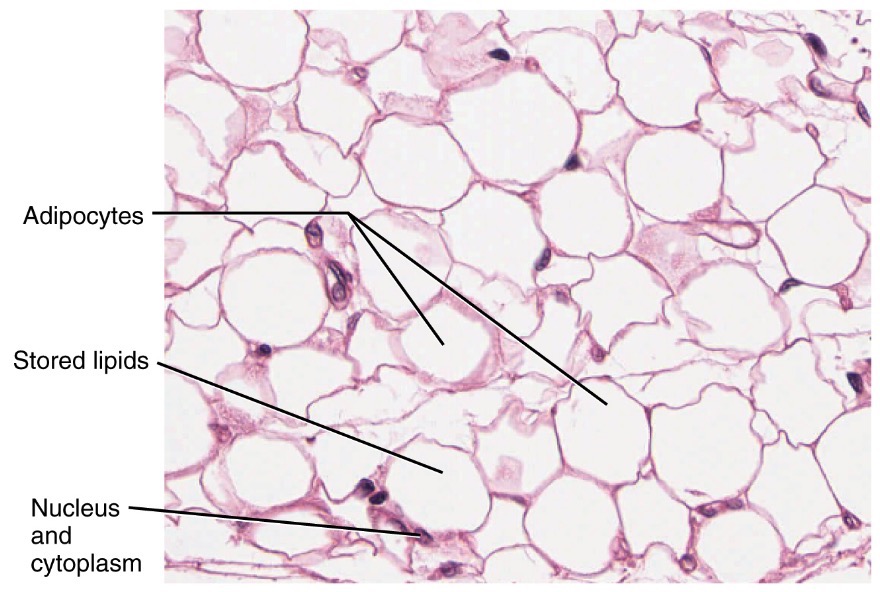
Adipose Connective
stores energy, insulates the body
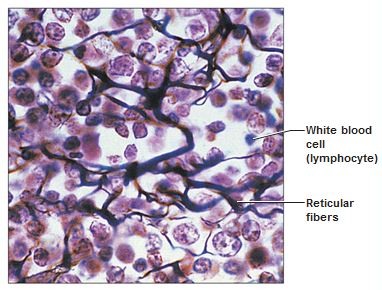
Reticular Connective
internal framework that supports immune cells
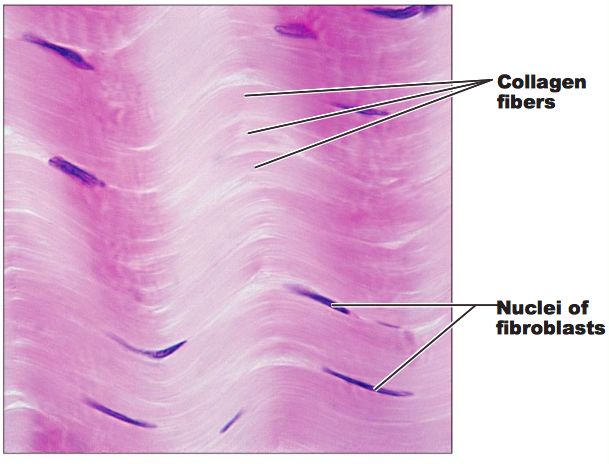
Dense Regular Connective
makes up tendons that attach muscles to bone
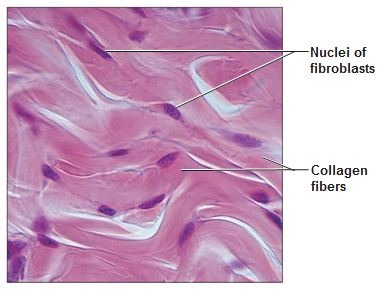
Dense Irregular Connective
providing strength and flexibility in multiple directions, found in the dermis of the skin and organ capsules
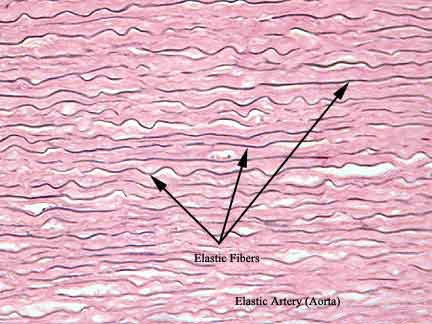
Elastic Connective
allows the tissues to recoil after stretching, found around vertebrate, blood vessel walls and bronchial tubes
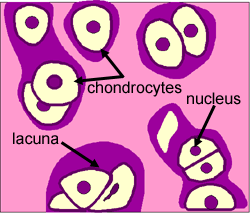
Hyaline Cartilage
Function: strong support and shock absorbtion
Location: tip of the nose, connects the ribs to the sternum
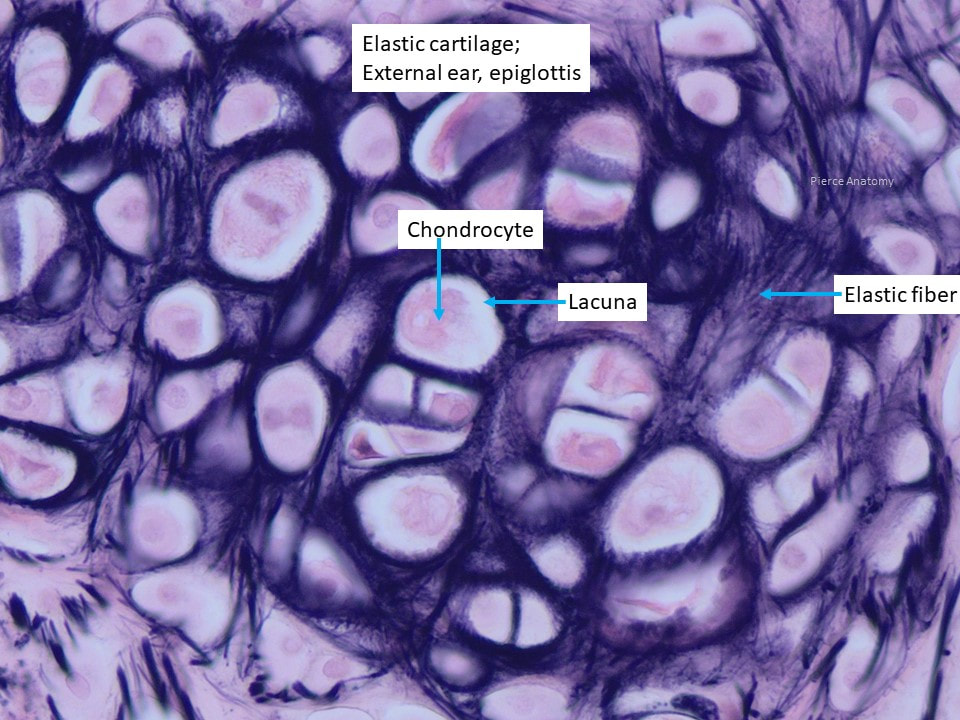
Elastic Cartilage
Function: maintains structure and allows flexibility
Location: outer ear and epiglottis
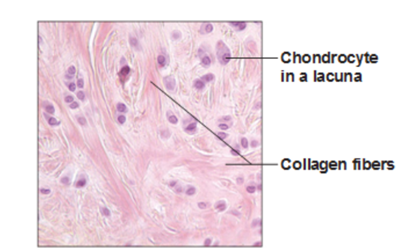
Fibrocartilage
Function: compressible and resists tension
Location: intervertebral discs and knee
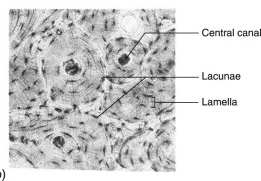
Osseous
supports the body structure, stores calcium and fat, marrow inside bone makes blood cells
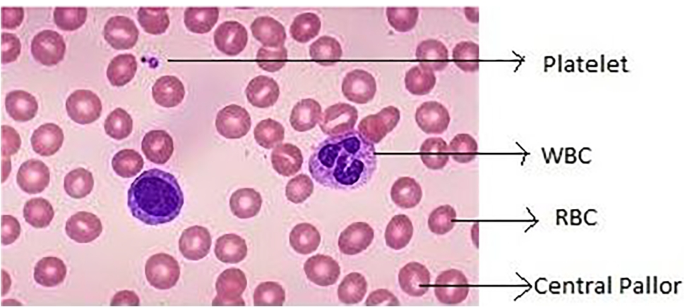
Blood
Function: transports stuff in and out
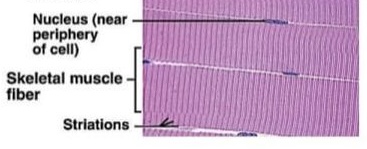
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
multinucleated, striated muscle fibres, voluntary movement
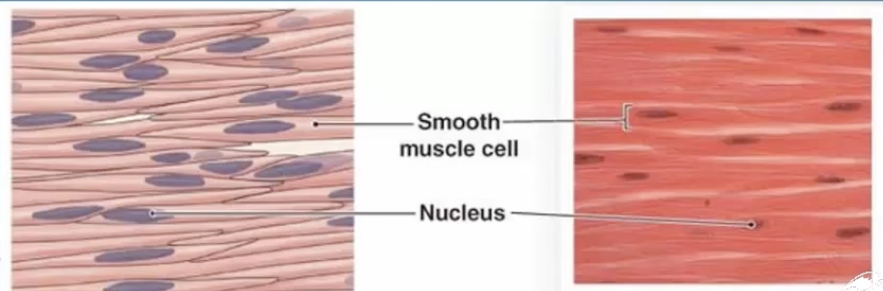
Smooth Muscle Tissue
spindle-shaped, no striation, uni-nucleated, involuntary movement
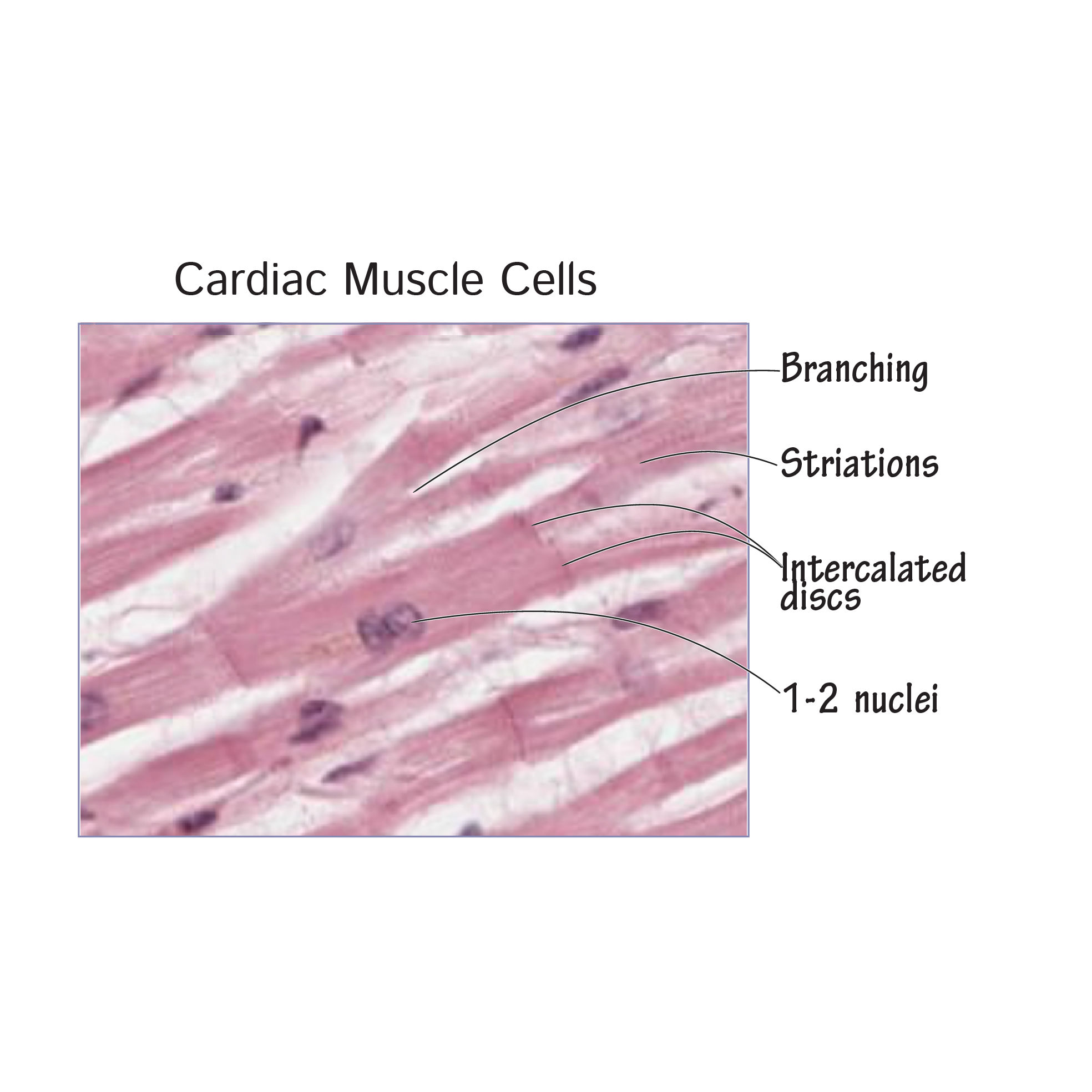
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
branched and striated muscle fibres, electrically couple via intercalated discs, pumps blood
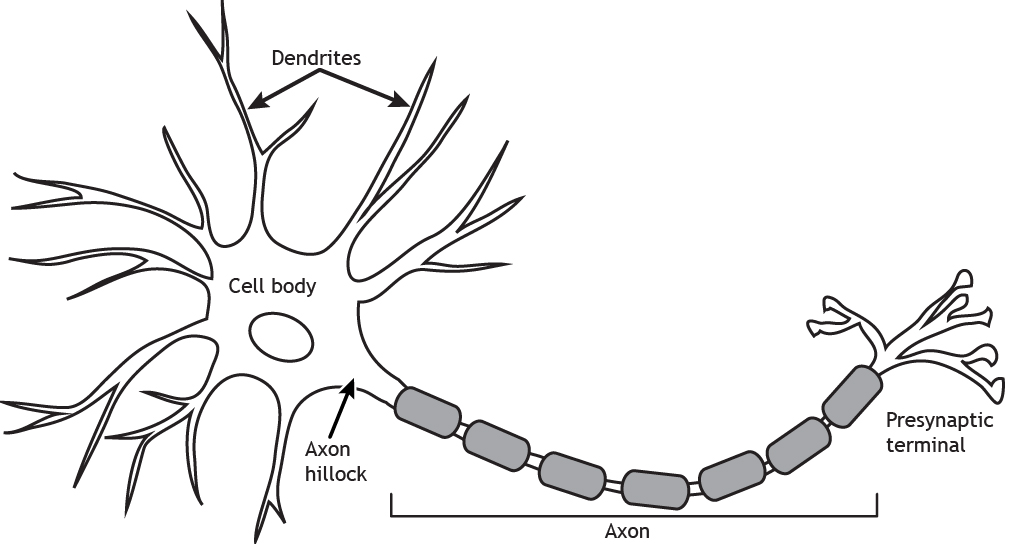
Neurons
basic unit of nervous tissue, sense stimuli and transmit impulses around the body
Neuroglial Cells
support nerve cells: supply nutrients to neurons, removes excess neurotransmitters, maintains electrolyte balance, nervous system repair, protection against microorganisms
Astrocytes
Function: form a blood brain barrier
Location: brain + spinal chord
Schwann Cells
Function: forms the myelin sheath
Repair
proliferation of cells + tissue + scar tissue (function not fully restored)
Restoration
proliferation of cells and tissue (complete restoration of lost structure)