Nursing TEAS: Science Section
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/271
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 6:38 PM on 9/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
272 Terms
1
New cards
Cell Parts/Organelles
Ribosomes; Golgi apparatus; Mitochondria; Nucleus
2
New cards
Call Parts/Organelles Function
process energy & excrete waste
3
New cards
Ribosomes
protein synthesis and give rough ER it's rough characteristics
4
New cards
Golgi apparatus
modifies & packages proteins
5
New cards
Mitochondria
convert energy
6
New cards
Nucleus
stores DNA
7
New cards
Cells
smallest unit of life
8
New cards
Organ
self-contained part of organism that performs a specific function
9
New cards
Organ Systems
functional groups of organs that work together within the body
10
New cards
Sagittal Plane
divides into left and right parts
11
New cards
Frontal Plane
divides into front and back parts
12
New cards
Transverse Plane
divides into top and bottom parts
13
New cards
Superior
top
14
New cards
Inferior
bottom
15
New cards
Medial
middle
16
New cards
Lateral
to the side
17
New cards
Posterior
back
18
New cards
Anterior
front
19
New cards
Dorsal
top part of hand and foot
20
New cards
Palmar
palm/bottom side of hand and foot
21
New cards
Proximal
closer to starting of a limb
22
New cards
Distal
closer to ending of a limb
23
New cards
Respiratory System Diagram
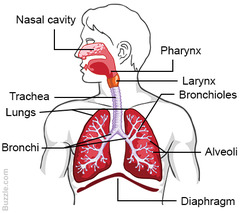
24
New cards
Alveoli
tiny air sacs in lungs where gas exchange occurs
25
New cards
Asthma
lung disease characterized by inflamed, narrowed airways and difficulty breathing
26
New cards
Bronchi
main passageways directly attached to lungs
27
New cards
Bronchioles
small passageways in the lungs that connect bronchi to alveoli
28
New cards
Cystic Fibrosis
genetic disorder that affects the lungs; characterized by difficulty breathing, coughing up mucus, and lung infections
29
New cards
Perfusion
passage of fluid to an organ or tissue
30
New cards
Pleura
membrane around the lungs and inside chest cavity
31
New cards
Surfactant
fluid secreted by alveoli and found in lungs
32
New cards
Tidal Volume (TV)
amount of air breathed in
33
New cards
Trachea
"windpipe"; connects larynx to lungs; made up of "C" shaped hyaline cartilage rings
34
New cards
Ventilation
movement of air in and out of body via inhalation and exhalation
35
New cards
Lungs are also referred to as ....
pleural cavity
36
New cards
Bronchi --> ??? --> ???
Bronchi --> Bronchioles --> Alveoli
37
New cards
Gas exchange in lungs occurs by ....
diffusion
38
New cards
Influenza
common flu
39
New cards
Tuberculosis (TB)
infectious bacterial lung disease
40
New cards
Pneumonia
infection that inflames air sacs with fluid
41
New cards
Arteries
thicker walls; blood vessels that deliver blood from heart to rest of the body
42
New cards
Veins
thinner walls; blood vessels that carry blood to the heart
43
New cards
Capillaries
small blood vessels that connect arterioles and venules
44
New cards
Diastole
cardiac cycle part that refills blood in the heart
45
New cards
Systole
cardiac cycle part that expels blood throughout the body
46
New cards
Heart
muscle that pumps blood throughout the body
47
New cards
Hemoglobin
protein in red blood cells that carries O2 to the rest of the body
48
New cards
Leukocyte
white blood cells that protect the body from disease
49
New cards
Lymphocyte
subtype of a white blood cell
50
New cards
Plasma
yellow part of blood that carries both blood cell types and platelets throughout the body
51
New cards
Heart Attack
blockage of blood flow to heart
52
New cards
Stroke
damage to brain from lack of blood supply to brain
53
New cards
Aneurysm
ballooned and weakened area in an artery
54
New cards
Atherosclerosis
plaque buildup in arteries
55
New cards
Arrhythmias
improper heart-beat
56
New cards
Hypertension
force of blood against artery wall is too high; high blood pressure
57
New cards
Closed Circulatory Loop
Pulmonary Loop and Systemic Loop
58
New cards
Pulmonary Loop
CO2 blood in right ventricle in lungs --> O2 blood in left atrium
59
New cards
Systemic Loop
O2 blood from left ventricle --> body --> CO2 blood from body --> right atrium
60
New cards
The ______ System and _______ System work together to regulate blood and gas exchange.
Circulatory; Respiratory
61
New cards
Pacemaker (SA Node)
sets rhyme for heart contractions
62
New cards
Open Lymphatic System
circulates and filters interstitial fluid between cells
63
New cards
Lymph Nodes
filter interstitial fluid in lymphatic system; found in oral, nasal, and genital regions
64
New cards
Gastrointestinal System
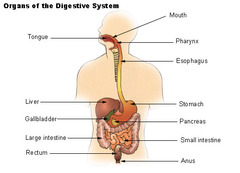
65
New cards
Anus
opening in rectum that expels solid waste
66
New cards
Bolus
partially chewed and swallowed food
67
New cards
Chyme
semifluid in partially digested food
68
New cards
Enzymatic Digestion
breakdown of food by enzymes for absorption
69
New cards
Gallbladder
organ that store bile
70
New cards
Large Intestine
vitamins and H2O are absorbed b4 feces is eliminated; "colon"
71
New cards
Liver
produces bile and regulates glycogen storage
72
New cards
Mouth
oral cavity for entry of food
73
New cards
Pancreas
produces insulin and secretes pancreatic juices
74
New cards
Peristalsis
muscle contractions that move food through digestive tract
75
New cards
Rectum
last part of large intestine and anus
76
New cards
Saliva
"spit" in mouth
77
New cards
Small Intestine
duodenum, jejunum, ans ileum; where digestion and absorption of food occurs
78
New cards
Stomach
digestion occurs mechanically by contractions of smooth muscle and chemically by stomach acids and bile
79
New cards
Mouth Enzymes
Salivary amylase and lipase
80
New cards
Stomach Enzymes
Gastric lipase; Pepsin; HCl
81
New cards
Stomach Hormones
Gastrin; Ghrelin
82
New cards
Liver Enzymes
Bile
83
New cards
Pancreas Enzymes
Pancreatic juices; Trypsin
84
New cards
Pancreas Hormones
Secretion; Glucagon; Insulin
85
New cards
Small Intestine Enzymes
Proteases; Lactase; Disaccharides
86
New cards
Small Intestine Hormones
Secretin; Motilin
87
New cards
Digestion Process
mechanical and chemical digestion in mouth --> food goes through pharynx to stomach --> mechanical and chemical digestion in stomach --> food goes through duodenum to small intestine --> cecum to large intestine --> rectum to anus
88
New cards
Ghrelin
hormone that induces hunger
89
New cards
Leptin
hormone that induces sensation of thirst
90
New cards
Insulin
hormone that induces cellular uptake of glucose
91
New cards
Glucagon
hormone that stimulates the breakdown of stored glycogen
92
New cards
Nerve Structure
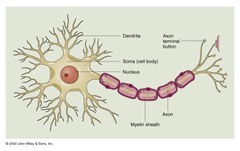
93
New cards
Electrical Current Flow
axon --> myelin sheath --> synapse
94
New cards
Involuntary Nervous System
autonomic nervous system; cardiac and smooth muscles like heart, digestion, and breathing
95
New cards
Voluntary Nervous System
skeletal muscles like walking and throwing
96
New cards
Nerve
bundle of nerve fibers that transmits electrical signals towards and away from brain and spinal cord
97
New cards
Sensory Nerves
sends messages to the CNS; afferent nerves
98
New cards
Motor Nerves
send messages out to muscles' efferent nerves
99
New cards
Skeletal muscles move by contraction of _____ and _____ filaments.
actin and myosin
100
New cards
What is the primary component of muscles?
protein