AP Psychology: Topic 3.4 - Cognitive Development Across the Lifespan
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Schema
a concept or framework that helps organiz and interpret information
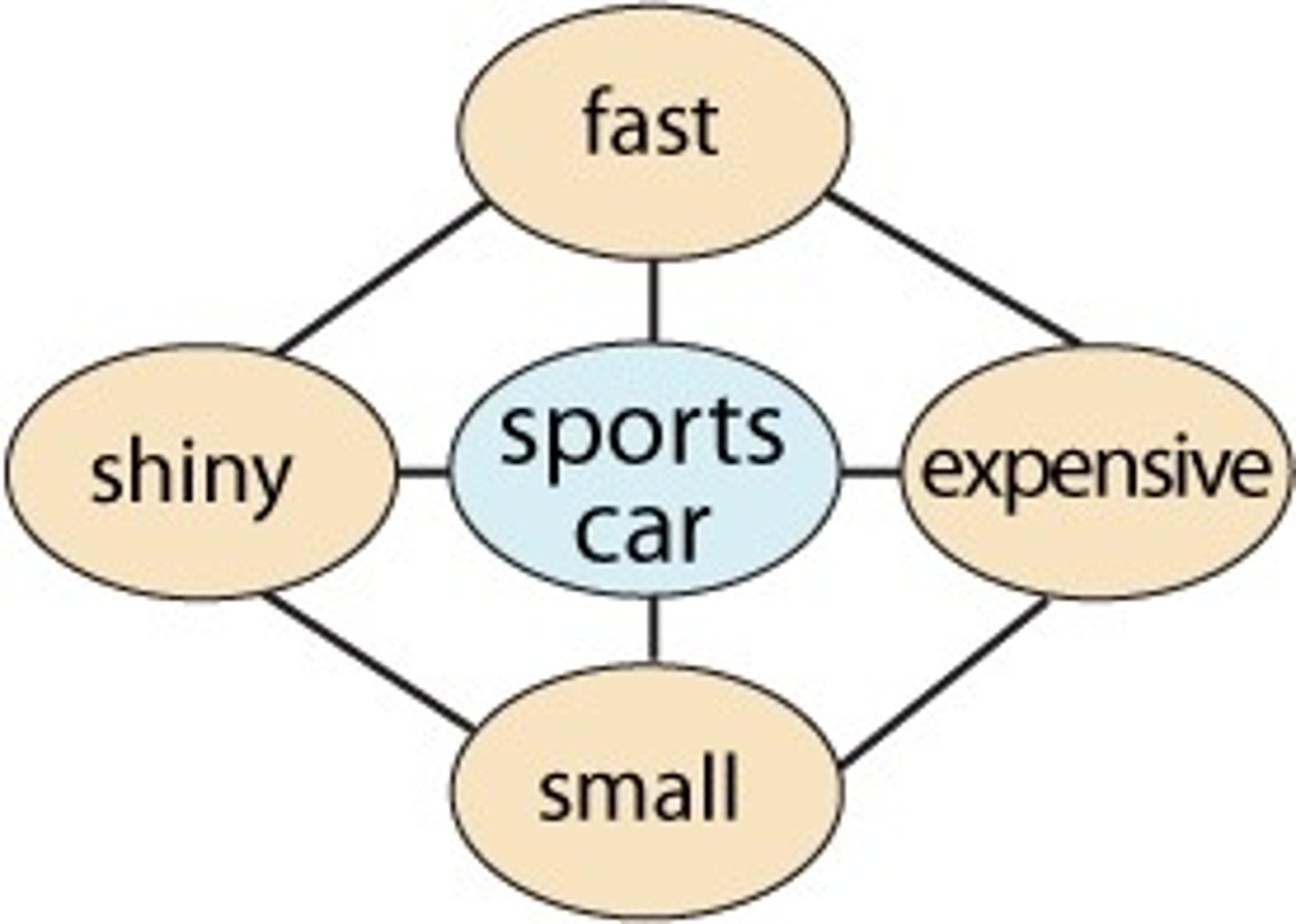
Assimilation
interpreting new experiences according to existing schemas and adapting them into one's collection of schemas

Accommodation
when new information causes a person to modify their current understandings (schemas)

Sensorimotor stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage (from birth to about 2 years of age) during which infants know the world mostly in terms of their sensory impressions and motor activities

Preoperational stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage (from about 2 to 6 or 7 years of age) during which a child learns to use language but does not yet comprehend the mental operations of concrete logic

Concrete operational stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (from about 6 or 7 to 11 years of age) during which children gain the mental operations that enable them to think logically about concrete events

Formal operational stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (normally beginning about age 12) during which people begin to think logically about abstract concepts

Object permanence
the understanding that objects continue to exist even when out of view

Mental symbols
mental concepts that represent real objects

Pretend play
make-believe activities in which children create new symbolic relations, acting as if they were in a situation different from their actual one

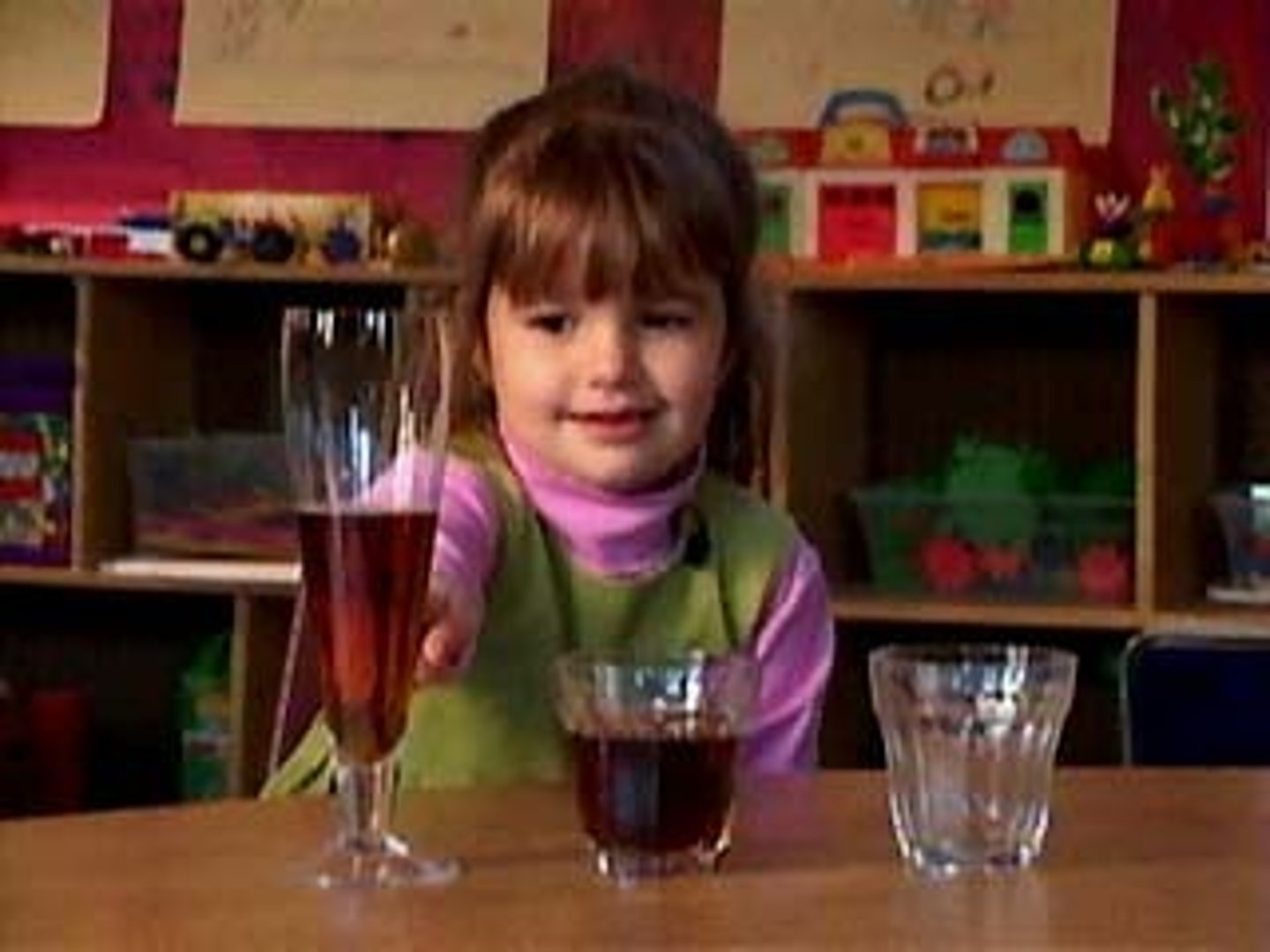
Conservation
a principle of concrete operational reasoning that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in form

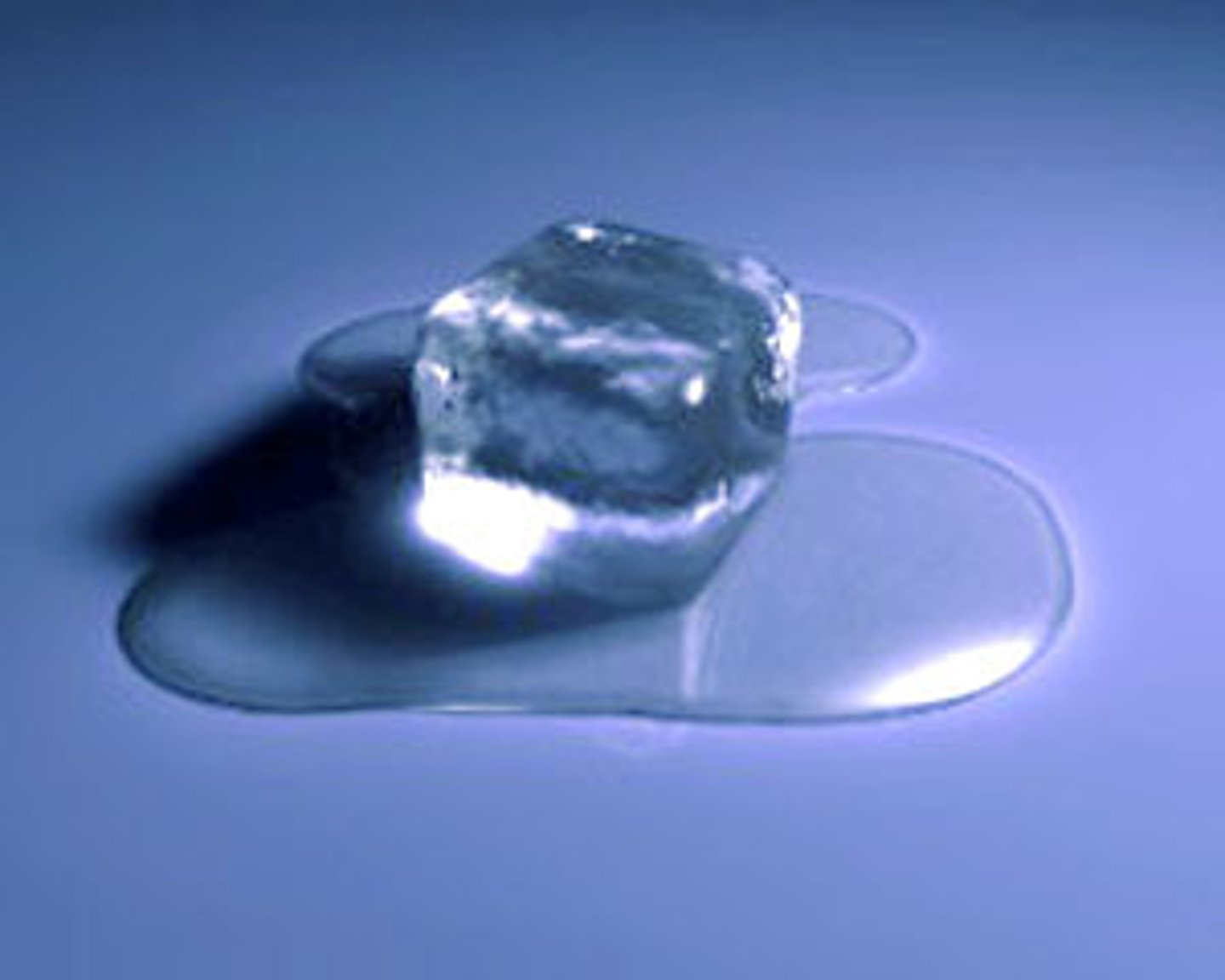
Reversibility
the understanding that some things that have been changed can be returned to their original state (e.g., water → to ice → to water)

Animism
the belief that objects have lifelike qualities and are therefore capable of having feelings, intentions and emotions

Egocentrism
a characteristic of the preoperational stage in which a child has difficulty taking another person's point of view
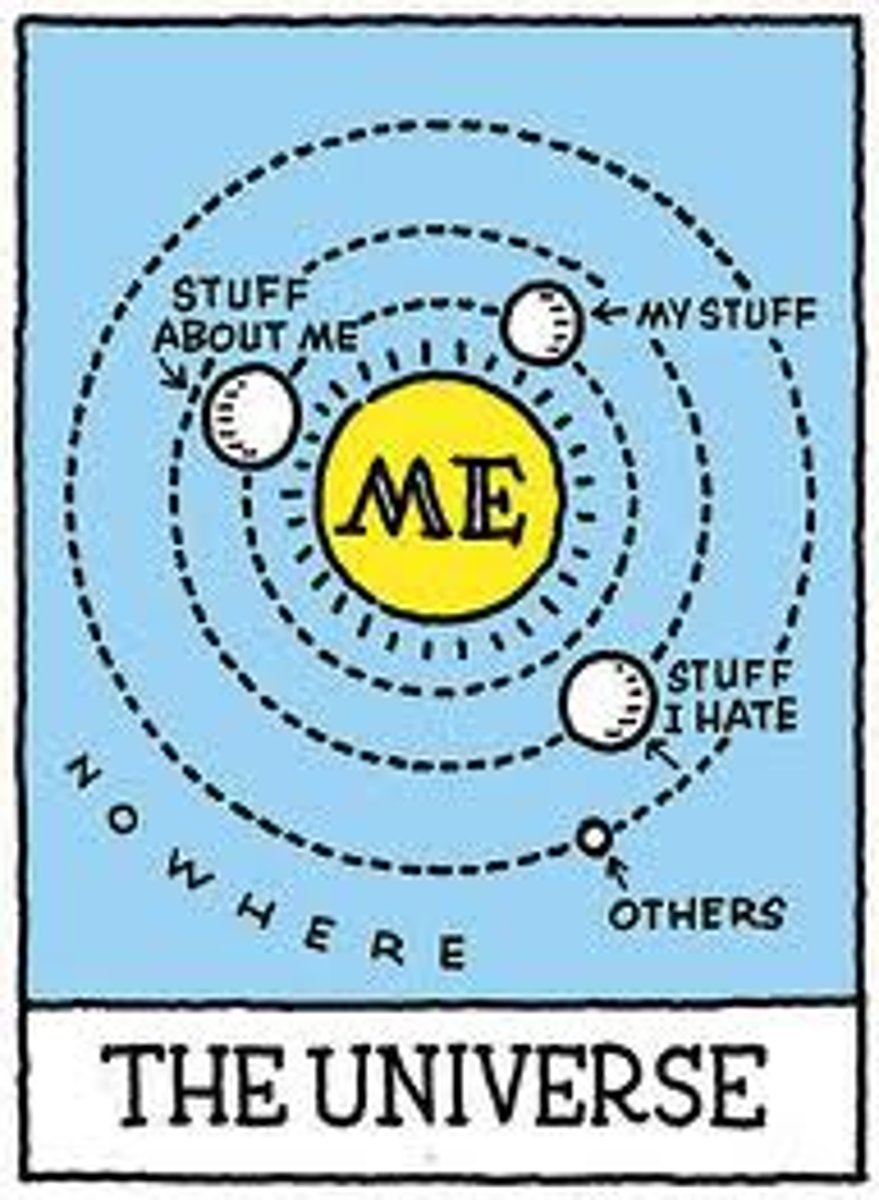
Theory of mind
an awareness that others have mental states such as knowledge, intentions, and beliefs and that these might differ from one's own

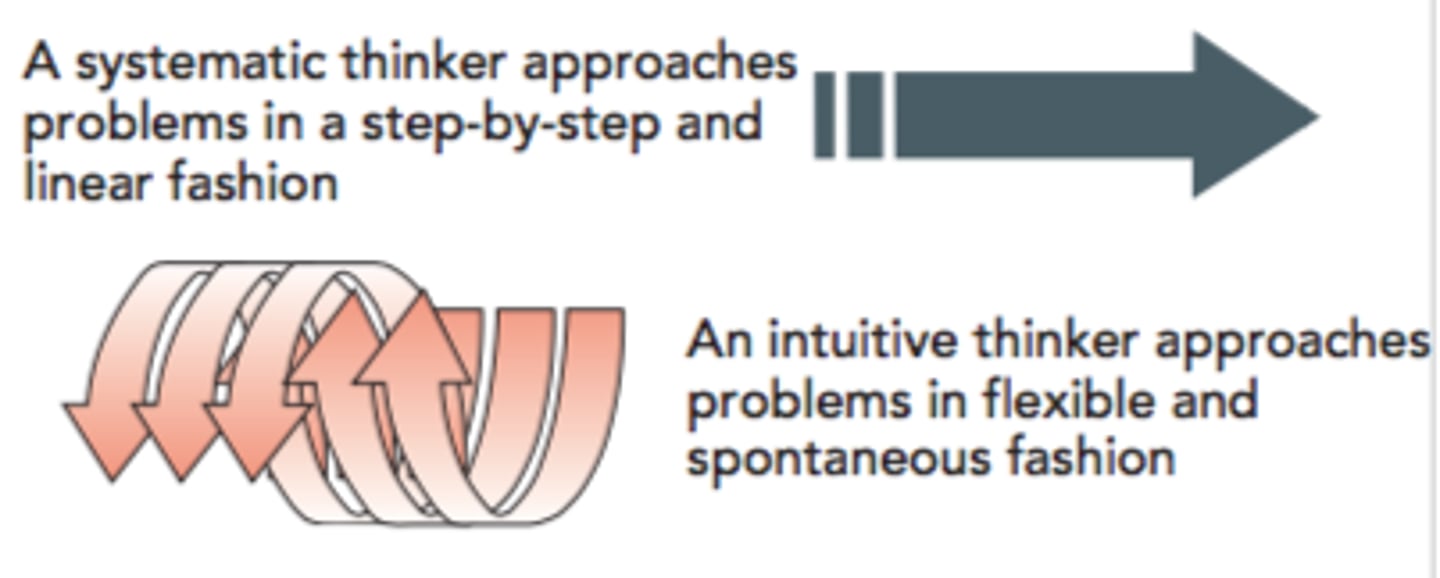
Systematic thinking
approaching problems in a rational, step-by-step, and analytical fashion
Abstract thinking
thinking in terms of symbols, ideas, and concepts
Hypothetical thinking
thinking that is based on what is possible and not just what is real even when this conflicts with what is accepted as true

Scaffolding
support structures used by teachers that help a learner get to the next level (breaking down new information or skills into pieces that are digestible for a learner)

Zone of proximal development
the difference between what a learner can do without help and what they can do with guidance and encouragement from a skilled coach or partner

Crystallized intelligence
a person's general knowledge, vocabulary, and reasoning based on acquired information

Fluid intelligence
reasoning ability and the use of new information for learning and problem solving

Dementia
a slowly progressive decline in cognitive function, including memory, thinking, and judgment, that is often accompanied by personality changes
