Optic Nerve Evaluation
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
scleral ring
rim size & position
retinal & disc hemorrhages
regions of peripapillary atrophy
RNFL
what are the 5 Rs in optic disc/RNFL evaluation?
vertical
do we care more about the vertical or horizontal disc diameter for glaucoma?
1.8, 1.7
the average vertical disc diameter is ___mm & horizontal disc diameter is ___mm
<1.5
a small disc has an average vertical diameter of _____mm
>2.2
a large disc has an average vertical diameter of ____mm
larger
African Americans have ______ optic discs
large
large discs will have _____ cups
small
small discs will have _____ cups
2
a physiological cup of 0.7 or greater occurs in ___% of normals
larger
in normal eyes, C/Ds are _____ horizontally than vertically
vertical
in glaucoma, ______ C/D increases faster than horizontal
F (more cause for concern but can be completely normal)
T/F: asymmetrical C/Ds always indicates glaucoma
inferior, superior, nasal, temporal
list the areas of the rim in order from thickest to thinnest in a normal eye
temporal rim tissue is = or greater than the vertical poles (superior or inferior)
when should rim tissue changes warrant concern for glaucoma?
notching
focal/local areas of axon loss resulting in little to no remaining rim tissue
3x more
an inferior notch is _________ common than a superior notch
30
notching may occur in ___% of pts
87
notching is ____% specific for glaucoma
inferotemporal or superotemporal
where does rim loss most often occur in early glaucoma?
nasal
with advanced rim loss from glaucoma, the _____ region is the last remnant
inferotemporal → superotemporal → temporal horizontal → nasal inferior → nasal superior
describe the progression of optic nerve damage
progression of field loss
rim tissue loss corresponds with what?
increases
a pale rim ______ the likelihood for a non-glaucomatous optic neuropathy
striations, brightness, visibility of parapapillary retinal vessels
what 3 things should you pay attention to when looking at the RNFL?
red-free light
what is RNFL examination best preformed under?
diffuse loss of striate pattern
increased visibility of retinal vessel borders (sharp wall of small retinal vessels is apparent, vessels are not covered by RNFL & are visualized clearly)
mottled appearance of RPE
fundus appears darker
describe the appearance of diffuse RNFL loss
wedge shaped dark area
describe the appearance of a localized RNFL loss
alpha zone
irregular hypo & hyperpigmentation
thinning of chorioretinal tissue
outer side is retina
inner side is beta zone
pigment irregularities of RPE
present in normal eyes
corresponds to a relative scotoma
beta zone
marked atrophy of the RPE & choriocapillaris
large choroidal vessels become visible
thinning of chorioretinal tissues
more common in glaucomatous eyes but can be in normal eyes
width inversely correlates w/ rim width at the same area
progression associated w/ progressive glaucoma
corresponds to an absolute scotoma
thinner
a larger beta zone → _____ rim
absolute
beta zone atrophy will result in _______ scotoma
relative
alpha zone atrophy will result in _______ scotoma
OAG
PPA is more common & greater in ______
T
T/F: the degree of PPA correlates w/ optic disc damage
T
T/F: the location of PPA correlates w/ the location of optic disc damage
T
T/F: location of PPA correlates w/ the location of VF defects
F
T/F: optic disc hemorrhages are not indicative of glaucoma progression
2-6mo
what is the timeline for an optic disc hemorrhage to resolve?
0-1, PVD
an optic disc hemorrhage is seen in ____% of the normal population due to what?
4-10
optic disc hemorrhages are found in ____% of eyes with glaucoma
20-25
optic disc hemorrhages are found in _____% of eyes with normal tension glaucoma
4-8
optic disc hemorrhages are found in ____% of eyes with high pressure glaucoma
5
____% of optic disc hemorrhages are bilateral
NTG
in what type of glaucoma are optic disc hemorrhages most common?
edge of NFL defect
where are optic disc hemorrhages most commonly seen?
F
T/F: an optic disc hemorrhage can occur in an area with no NFL tissue
no
are optic disc hemorrhages seen in advanced glaucoma?
unknown
what is the etiology of optic disc hemorrhages?
inferotemporal (or superotemporal)
where are optic disc hemorrhages most commonly seen?
20-25
______% of optic disc hemorrhages are on the nasal side of the optic nerve
20-60
____% of optic disc hemorrhages recur
myopic disc
cup asymmetry

inferior temporal notch
superior temporal rim loss

notch
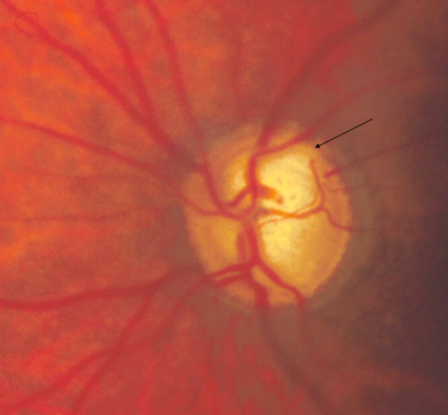
inferior focal notch
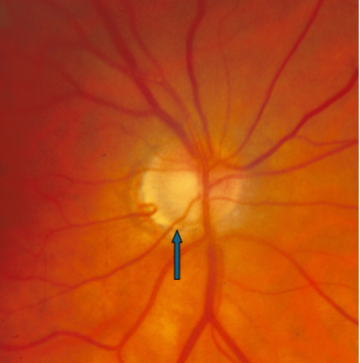
inferior notching
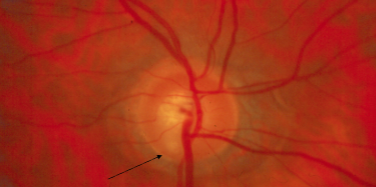
inferior notching
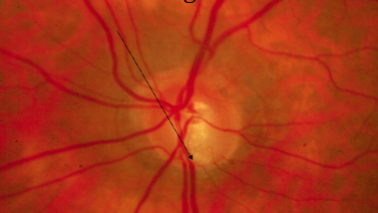
diffuse loss of striations
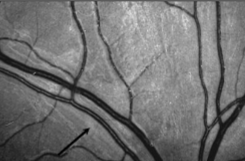
diffuse RNFL loss
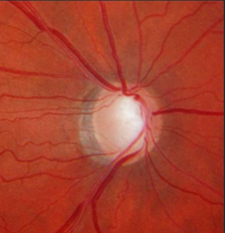
localized RNFL defect
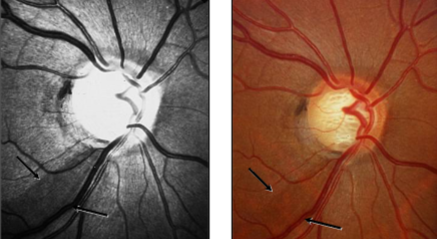
inferior diffuse NFL loss
inferior diffuse NFL loss

superior wedge NFL defect
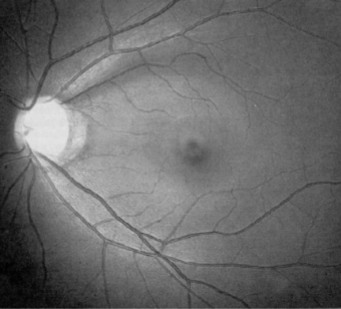
wedge NFL defect
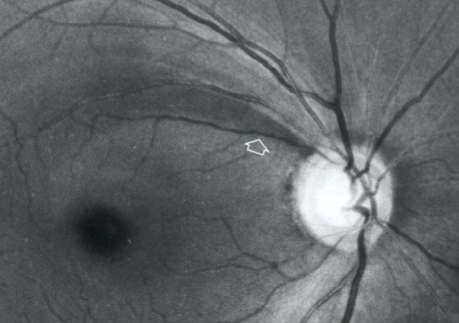
notching of rim & NFL loss
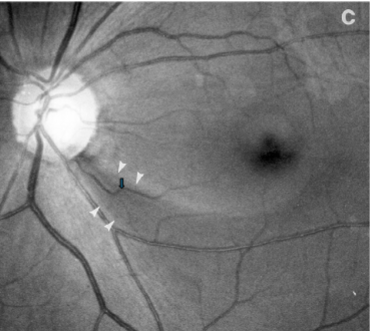
drance heme
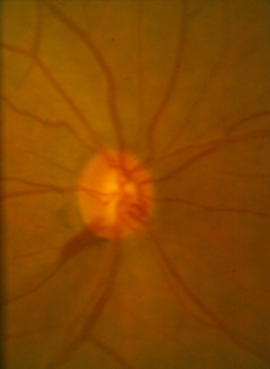
disc hemorrhage
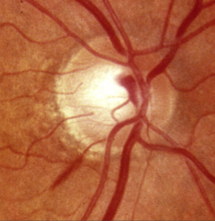
disc hemorrhage
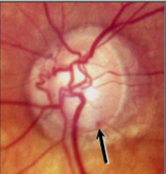
disc hemorrhage
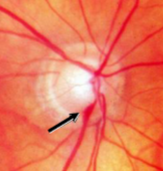
disc hemorrhage
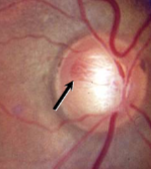
drance hemorrhage
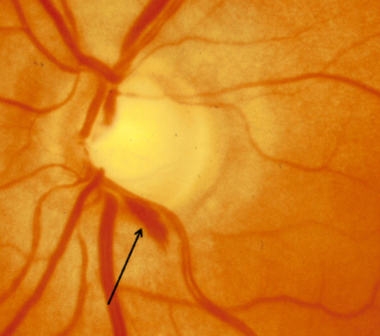
drance hemorrhage
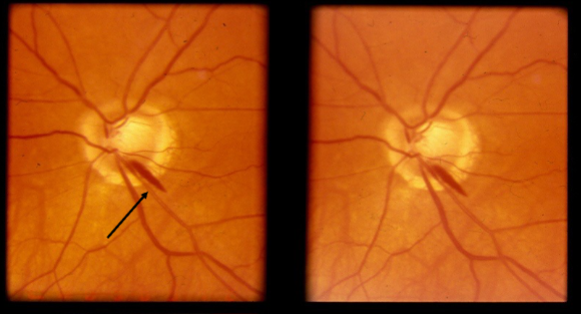
disc hemorrhage
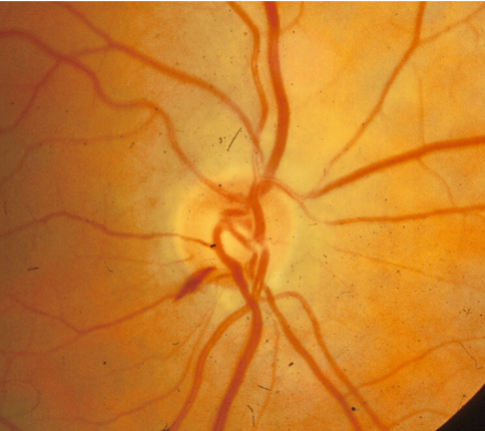
disc hemorrhage
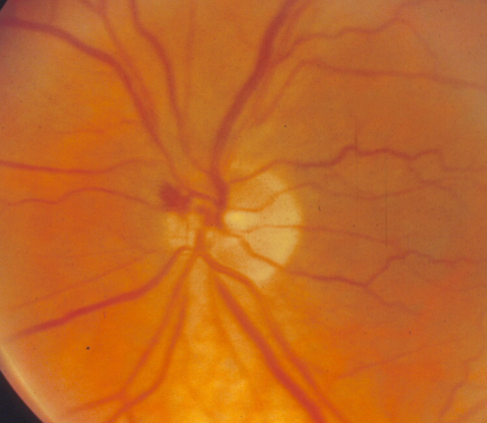
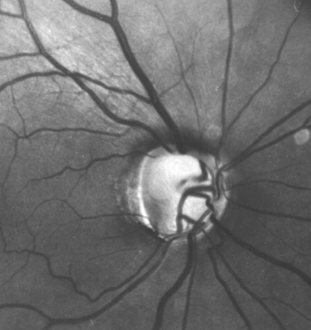
advanced cupping w/ laminar dots
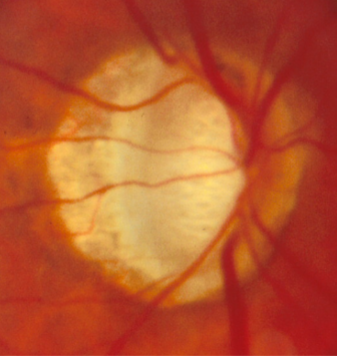
lamina visible & total erosion to the trim

baring of circumlinear vessel
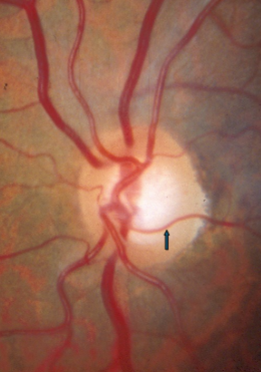
baring of circumlinear vessel
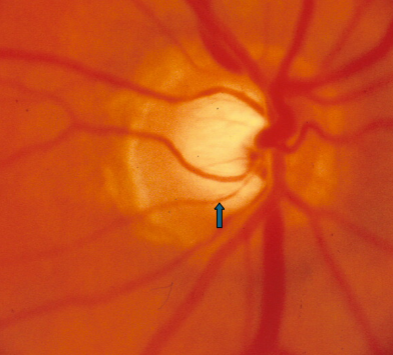
bean pot cup
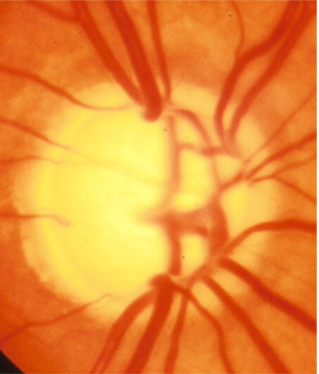
bayonetting of retinal vessels
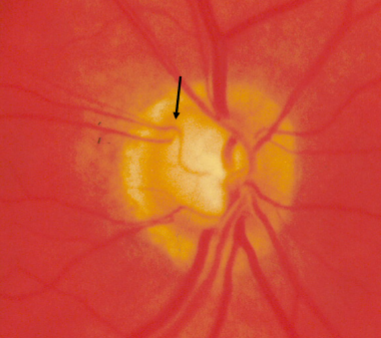
advanced glaucoma cupping