Physical Geography Weeks 10+
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Components of the Water Cycle
Consists of
Inputs (Water flowing into the system)
Outputs (Water leaving the system)
Stores (Water staying in the system)
Examples for Stages of Water Cycles
Inputs - Precipitation
Outputs - Snowmelt runoff, groundwater movement to streams, evaporation, transpiration
Stores - Lakes, wetlands, soil and aquifer stores, ice, snow, ocean, atmosphere
Water Cycle Control Volume
A volume of the land surface that water enters, exits, and is stored in over time
aka a watershed, drainage basin, catchment
Watershed, Drainage Basin, Catchment
Area which water funnels into, typically in a valley
Consists of
Drainage Divide
Interfluves
Valleys
Stream Networks in Watersheds
1st Order - no tributaries
2nd Order - confluence of two 1st order streams
3rd Order - confluence of two 2nd order streams
Drainage Patterns
Dendritic, Rectangular, Trellis, Radial/Annular, Parallel, Deranged
Damn, Real Tall Rodents Are Pretty Dope
Dendritic Drainage Pattern
Tree-like
Efficient movement of water as streams lengths are short
Rectangular
Right-angle stream intersections
Formed by jointed/faulty rock terrain
Trellis
Right angles to main rivers, moves down mountain slopes
Valleys, ridges where rocks have different resistance to erosion
Radial/Annular
Water moves down sideways from central area
Created by dome structures (volcanos)
Parallel
Parallel streams associated with steep slopes
Deranged
No clear drainage pattern or stream valley
Ponding created
Drainage Density Formula
Measures efficiency of watershed
Dd = ∑L / AD
Total length of stream divided by area of watershed
AD = an area
∑L = total length of streams draining that area
Dd = Drainage density (Km2)
Drainage Density
Higher drainage density when more precipitation
Higher drainage density in less permeable soils
River Discharge
Rate of flow of water volume, including sediments
Volume length of travel per unit time
m3 s -1
River Discharge Formula
Q = A x V
Q = discharge m3 s -1 ; A = area; V = avg stream velocity
=
W x D x V
W = channel width D = avg channel depth; V = avg stream velocity
Measuring River Discharge
Measure the stream’s width.
Make several segments
Calculate area of each segment: area = width segment × depth.
Calculate discharge of each segment = area × velocity.
Add all segment discharges → total flow.
Causes for Discharge Variation
Size and Shape of the Watershed
Basin geology, permeability of rock type
Differences in vegetation type
Precipitation, type, distribution
Hydrograph
Measure of discharge over time for a specific location
Influence of Basin Size on Streamflow over time
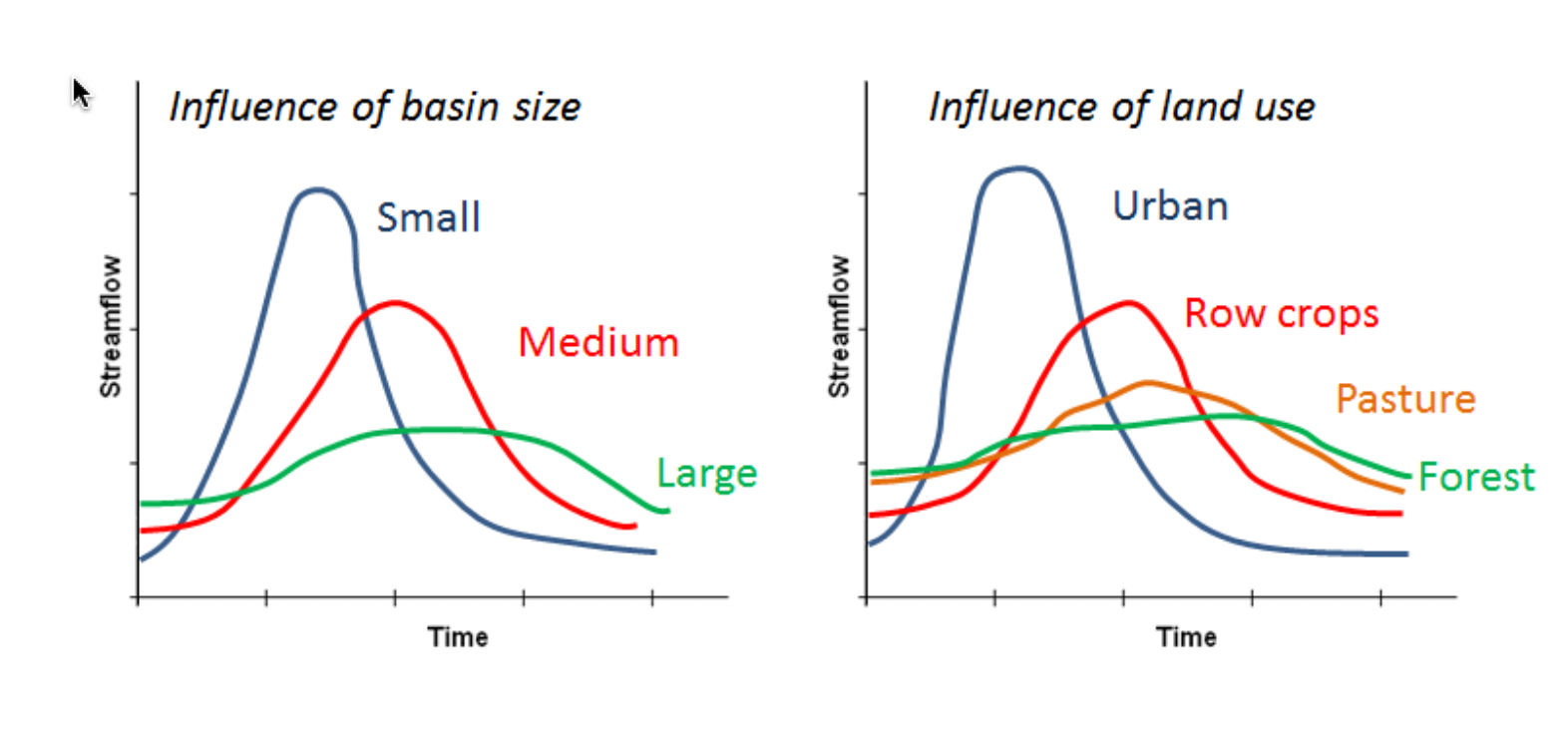
Influence of Land Use on Streamflow over time
Peak flow in urbanization is dramatic as sealed surfaces increase discharge

Different types of inconsistent rivers
Intermittent - flows part of the year, some groundwater
Ephemeral - flows after precipitation
Perennial - Flows all year, fed by rainfall, groundwater, and snowmelt
Why is Discharge + the Hydrograph important?
Water supply - excess precipitation is used by humans
Flood predictions
Water quality - quality is influenced by chemical, biological processes as water flows through channel
Driving Forces that Influence Coastal Environments
External Drivers, like solar energy and lunar cycle which cause….
Wind, weather, tides, and waves, along with human activity which cause….
Erosion, transportation and deposition which shape….
Coastal landforms
The Littoral Zone
Typically the highest point where water reaches from storm surges on land to where the water is too deep to carry sediments
typically 60m depth
Littoral zone naturally shifts and changes
Wave Refraction
Redistribution of Waves
Resistant rock refracts the wave energy, which results in differences in erosion
formation of coves and bays
Wave energy highest in headlands (converging), lowest in coves (diverging) which eventually straightens coasts
Tidal Influences on Coastal Erosion
Occur twice daily, caused more by the pull of the moon and less, but to some extent, by the pull of the sun
Spring tide (new moon and full moon)
Neap Tide (first and third quarter moon)
Spring Tide
Combined gravity of sun and moon
when both are on the same side of earth, or when the moon is on the opposite side of the sun
increased tidal range
Neap Tides
decreased tidal range
sun and moon at right angles relative to earth
Wave Action
Friction between wind and ocean surfaces which causes
Wave Details
Caused by energy transfer from molecule to molecule in a circular form
circular formations get smaller with increasing depth
with depth becoming shallower, waves slow down and space between crest and trough shrinks
height and steepness increases which causes breakers
breakers alter geomorphology
Littoral (Longshore) Current
Water current moving parallel to shore
movement of large amounts of material is called beach drift
Littoral Drift = beach drift + longshore drift
Coastal Deposition by Water
Landforms created by deposition carried out by water
Beaches
Tombolo (island connected to mainland by bar)
Lagoon (shallow water separated by sand or reefs)
Bay Barrier - a spit that goes across a bay
Two Types of Coasts
Erosional
Depositional
Beach locations
Can be found along oceans, seas, lakes, or rivers
Implications of Sea Level Rise
Vulnerable areas
What is the Cryosphere?
All of the frozen parts of the hydrosphere
Sea Ice (Forms, grows, and melts in the ocean)
Ice Sheets (Mass of glacial ice (>50000km)) (Greenland and Antarctica)
Ice Shelves (Permanent floating ice shelves connected to land)
Icebergs (derived from ice formed on land)
Snow
Glaciers
Permafrost (ground that remains frozen for two or more years)
Glacier (definition + how they are formed)
Large mass of ice on land or ocean
Accumulation of snow which gets compacted through mass and freeze-thaw cycles (firn)
compaction and freeze-thaw eventually makes glacial ice (glacial ice)
quicker formation in wet climates (rockies) than dry climates (Antarctica)
Two main types of glaciers
Continental, Alpine
Types of Alpine Glaciers
Valley Glaciers
River of ice in a valley formed by a stream
Cirque Glaciers
Glaciers form in a snowfield of a cirque (bowl)
Formed by accumulation of snow
Piedmont Glaciers
Spill/spread out of a confining valley
Tidewater Glaciers
Glaciers at the edge of the ocean which calve into the sea
Continental Glacier
Continuous mass of ice
Ice Caps
Ice Fields
Ice Cap
Miniature ice sheet with a dome shape
less than 50,000 km2
polar and sub-polar regions
flat, high elevation
Ice Fields
Interconnected glaciers that cover mountainous areas
Glacial Formation
Open systems (inputs of snow, outputs of water, vapour, and ice)
Accumulation zone - part of snowfield where snow collects
Firn - Multi-year snow that turns into ice
Firn/Equilibrium Line - Line indicating where snow stays or melts
Mass Balance
Balance between inputs of snow and outputs of meltwater, water vapour, and ice in glaciers
negative mass balance = size reduction
positive mass balance = size increase
Ablation Zone
Area of glacier melt and sublimation
Plastic Deformation
Glacier movement, comparable to melted plastic moving
coarse warping around landforms
responds to weight, pressure, and gravity
Two Processes of Glacial Movement
Internal Deformation
Most movement occurs within plastic zone beneath the top layer
Brittle zone cracks as plastic zone moves
Basal Sliding
Glacier slides due to meltwater moving through crevasses and acting like a lubricant
Glacial Surge
Rapid, episodic high-speed movement to get rid of excess mass
(~10m/day)
Indications of a surging glacier include
lots of cracking
distorted medial moraines
rapid terminus advancing
Post-glacial landscapes
Polished rock, tarns, U-shaped valleys and fjords, hanging valleys, cirques, horns,
Sorted and Unsorted Glacial Deposits
Sorted = sediment deposits from meltwater
Unsorted = Transport of materials on/within ice
Glacial Drift
Term used for all glacial deposits
Moraines
Lines of rock fragments formed as glacier flows
lateral = on edges
medial = in the middle, as two glaciers merge together
rock deposited on ground = till
Till
Rock deposited on ground from glaciers
Erratics
Large rocks left on landscape from glacial melt and flow
Drumlin
Streamlined, elongated hill formed by glacial drift
shaped like teaspoon bowl
Esker
Long, winding ridge formed by deposited gravel from meltwater flowing on or in a glacier
Soil Makeup
Made of water, air, and particles of minerals and organic matter
Absorbs 10x more CO2 than plants
Filters water
Is a habitat
5 Controls of Soil Development
Parent Material
Climate
Biological Activity
Relief and Topography
Time
Parent Material
Underlying material (bedrock) forms the soil
Imparts its characteristics to the soil
composition, texture, chemistry
Climate
Temperature and moisture characteristics influence soil formation through chemical reactions and breakdown of organic material
Biological Activity
Living organisms which alter the acidity and alkalinity of the soil
Things in and on the soil
Relief and Topography
Slopes that are too steep do not have good soil, as gravity and erosion sweep layers of soil
Flat areas have better soil due to less erosion but can become waterlogged
Slope orientation plays an important role
Time
Rate of soil development depends on parent material characteristics and climate
warm, humid climates = faster soil development
Soil Profile
Vertical section of soil from top to extent of plant roots OR bedrock
Pedon
Smallest unit of soil with soil characteristics in layers
Horizon
Layers of soil, parallel to Earth’s surface
O, A, E, B, SOLUM, C, R
OMA ATE EVERY BROWNIE SO CRAP, RIGHT?
O Horizon
Surface
Organic material with humus (decomposed organic material)
A Horizon
Mineral matter mixed with some humus
E Horizon
Coarse sand with silt
Eluviation
water moves through and carries with it minerals to lower horizons
B Horizon
Where dissolved minerals and nutrients accumulate
Illuviation
Solum
Living Layers
A, E, and B layers
C Horizon
Weathered bedrock and regolith
R Horizon
Bedrock at the bottom of the soil profile
Soil Properties
Important indicator of Soil Fertility
Can Tall Socks Cool My Porcupine?
Colour
Texture
Structure
Consistence
Moisture
Porosity
Soil Colour
Indicates presence of minerals, as well as depth of water table, chemistry, formation
Red = iron oxide
Black = organics
Pale hues = carbonates
Texture
Mixtures of particles of varying sizes
classified using a Soil Texture Triangle
Soil Structure
Size and shape of particles
Ped = smallest cluster of particles, shape of which is used to determine structure
Soil Consistence
Cohesion of particles
related to texture and structure
reflects resistance and breaking with various moisture
Soil Porosity
Spaces holding air, gases, and water between particles
Important for water movement, drainage, and ventilation
High porosity = large spaces
Low porosity = small spaces
Influenced by roots, earthworms, and human activity
Soil Moisture
Moisture within soils
Field Capacity = maximum water available for roots after large pores have drained
Low Field Capacity = wilting plants
Ecosystems
Plants and animals living in their non-living environment
Open systems, no sharp boundaries
Ecology
Study of the relationships between organisms and their environment
Biogeography
Study of the past/present spatial distributions of animals
Population
Group of interacting and interbreeding organisms
Community
Different populations living together and interacting
Biome
Large area of similar vegetation and climate conditions
Biotic and Abiotic Subsystems Which Shape Populations
Biotic
Producers (plants), consumers (animals), decomposers (worms, fungi, bacteria, mites)
Abiotic
Solar radiation, Gas, Water cycles, Mineral cycles
Abiotic Feedback
Abiotic processes influence surrounding environment
sunlight and water influence vegetation growth
Vegetation changes abiotic surroundings
Major Abiotic Factors + Definition
Abiotic Factors influence where species are found as well as how they grow, interact, and die
Air and Soil Temperature
Photoperiod
Amount of Precipitation
Diurnal Processes of Gas Exchange in Photosynthesis
Daytime: Intake CO2 and water, Output O2 and water vapour
Nighttime: Intake O2 and water, Output O2 and water vapour
Stomata
Pores on underside of leaf surface
opening and closing create vacuums which pull water up from roots
CO2 enters, O2 and water leave stomata
Life Zone
Zone of flora and fauna with elevation and latitude from polar regions to tropics
Temperature and Precipitation Influences on Ecosystem
Strong relationship between productivity, sunlight, and precipitation
Highest productivity in warm, wet climates
Limiting Factors and Spatial Distribution
Physical, chemical, and/or biological phenomena which limit the range of a living organism
Ecological Succession
Transition from one biotic community to another when an ecosystem is disturbed and most, or all of its species are eliminated
pioneer species are the first to colonize an area
Facilitation
The presence of a species drives succession by improving conditions for subsequent species
Climax Ecosystem
Final stage of succession
Primary and Secondary Succesion
Primary
invasion and progression from one community to another
Occurs in an area that lacks soil
Secondary
Occurs following disturbance
Plants and animals move into a disturbed area
What do wildfires need to burn?
Fuel, weather, topography