L5 Conjunctival Signs & Degenerations
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Jessica
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
PMN stands for
PMN stands for polymorphonuclear neutrophil
PTG stands for
pterygium
the conjunctival is made up of mucous membrane extending from the __________ junction to the ______ limbus
mucocutaneous
corneoscleral
1. free rotation of the globe
2. aids in normal eyelid function
3. protective barrier
4. production to tear film
5. ocular surface immunity
6. limbal stem cell maintenance
All are functions of
the conjunctiva
what 3 parts make up the conjunctiva
palpebral, bulbar and fornix
what are the two layers of the conjunctiva
epithelium and stroma
epithelium layer of the conjunctiva contains (3)
goblet cells, langerhan cells and dendritic melanocytes
t/f the conjunctival stroma is highly vascularized. contains nonstriated muscle, nerves, & fatty tissue
true
is the vascularization on the conjunctiva fenestrated? yes or no
yes
the palpebral conjunctiva shares common arterial blood supply as the ____ which are terminal branches of the _______ artery
lids
ophthalmic
t/f bulbar conjunctiva supply branches from the anterior ciliary artery form superficial plexus anastomose with vessels from palpebral conj
true
the junction between the conjunctiva and the cornea is known as the
corneoscleral limbus
conjuctival epithelium is continuous with ______ epithelium; although it is a different structure
corneal
where are the limbal stem cells stores
corneoscleral limbus
is the conjunctiva more or less organized than the cornea
less
cornea is more organized
what is the purpose of the limbal stem cells
renew and regenerative parts of the corneal epithelium
t/f the limbal stem cells act as barrier between conjunctiva and cornea
true. bc the difference in structure
if the stem cells are not working or injured how does that effect the cornea
poor epithelization or conjunctivalization of the cornea
conjunctival injections vessels are derived from anterior ciliary artery and ______ arteries
palpebral
1. superficial bright red blood vessels
2. fade towards corneoscelral limbus
3. easily moved
4. blanches with phenylephrine
all describe
conjunctival injection
1. no accompanying exudation or cellular infiltration
2. may be caused by smoke, fog, UV radiation, vasoconstrictor rebound
all describe
hyperemia
an acculumation of fluid within or beneath the conjunctiva is termed as
chemosis
the pathophysiology of chemosis begins with conjunctival capillaries ______ plasma proteins faster than fluid can pass between ______ cells
leak
epithelial
chemosis
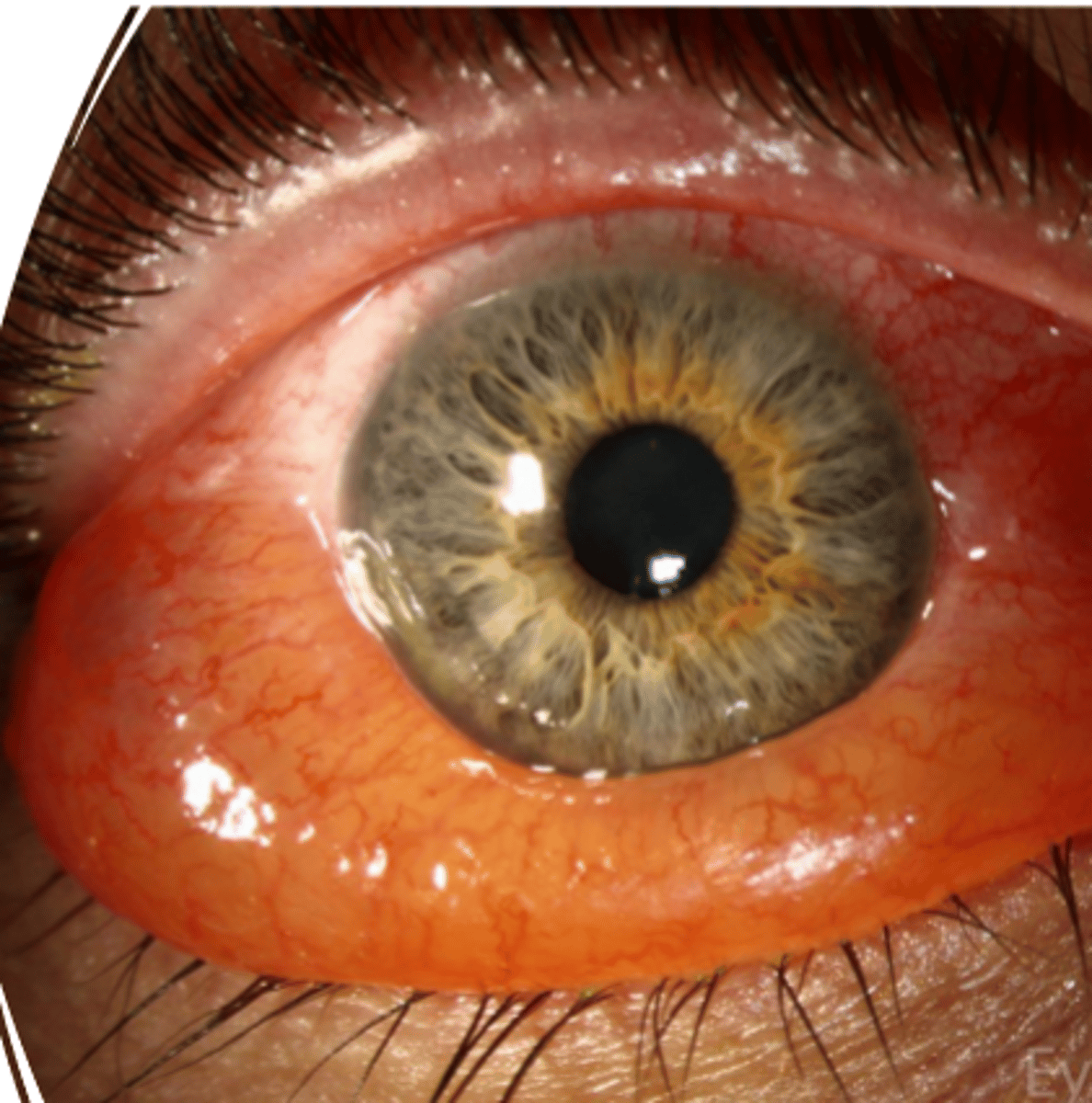
papillae is a _____-mediated vascular reaction
histamine
papillae has nonspecific sign of inflammation resulting from ____ and ____ cell infiltration
edema , PMN
when papillae is found on upper tarsal what is its shape
flat topped
if papillae is found on the limbus, what is its shape
dome shaped
a patient who likes to we CL wants to keep wearing them. during bio microscopy the palpebral conjunctiva looks like it have flattened top with central fibrovascular core and the lower lid has similar but with a dome shape. what is that
papillae
giant papillary conjuctivitis is usually seen in what other conditions(3)
vernal conjunctivitis
atopic keratoconjunctivitis
foreign body reaction
how do giant papillary conjunctivitis occur
results from the breakdown of anchoring septae
where is GPC usually seen upper or lower tarsal conj
upper tarsal conj
usually GPC is greater than __mm in diameter
1mm
is GPC seen in immune or mechanical trauma. yes or no
yes
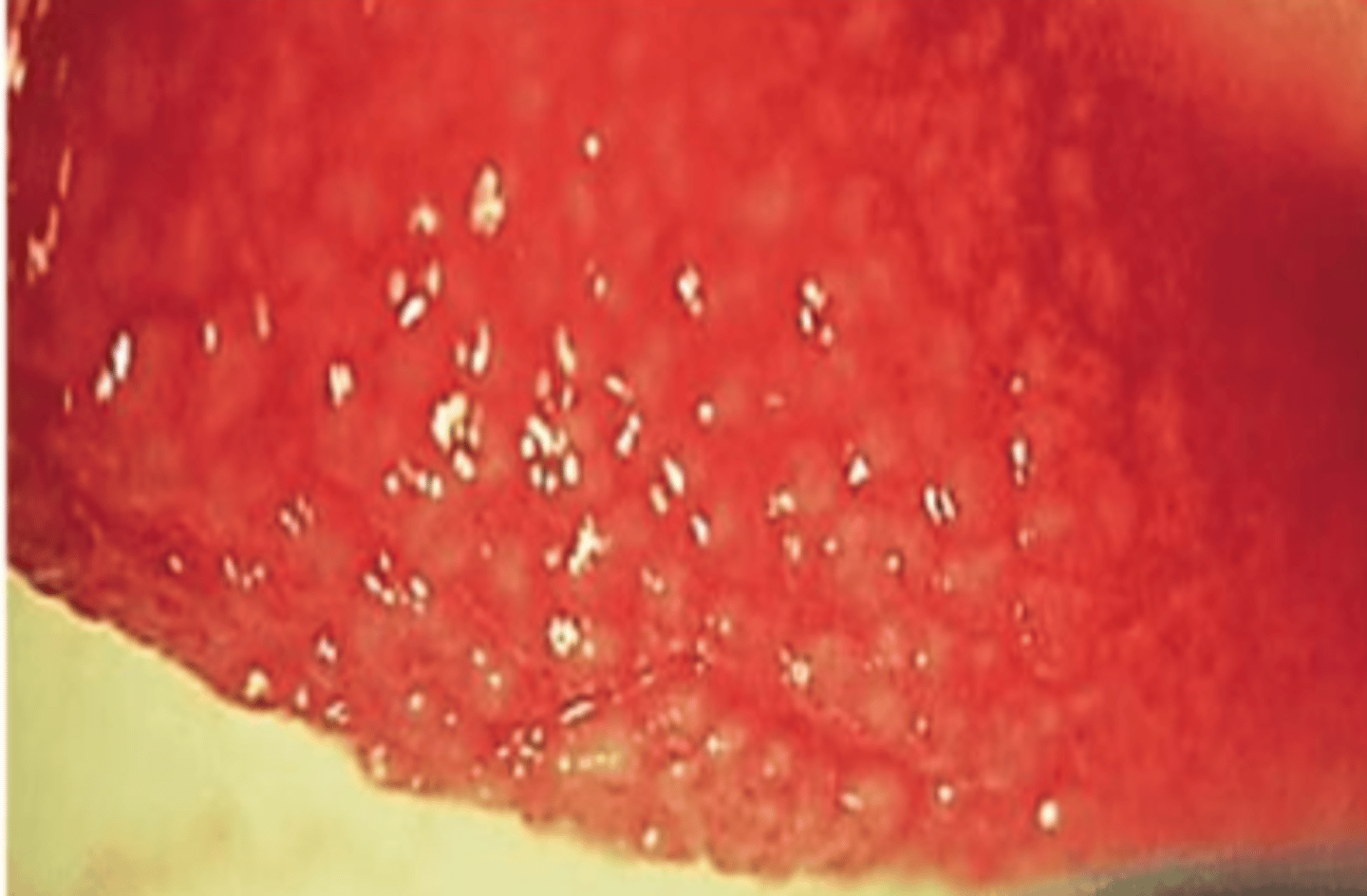
_____ have
1. yellowish white, discrete, round elevations of the conjunctiva
2. central portion is avascular, with BV going up over convexity from base
3.seen at limbus
4. 0.5-2mm diameter
follicles
what is the pathophysiology of follicles
a lymphocytic response with lymphoid germinal centers & central fibroblast
are follicles a non specific or specific inflammatory response
specific
follicles of childhood stay throughout adulthood
no, they go away with age
t/f folliculosis of childhood more prominent in fornix and fade towards lid margin
true
can follicular conjunctivitis been seen conditions like chlamydia, toxicity viruses such as herpes, adenovirus?
yes (CHAT)
when understanding if it papillae or follicle what aspect matters?
location
papillae
follicle
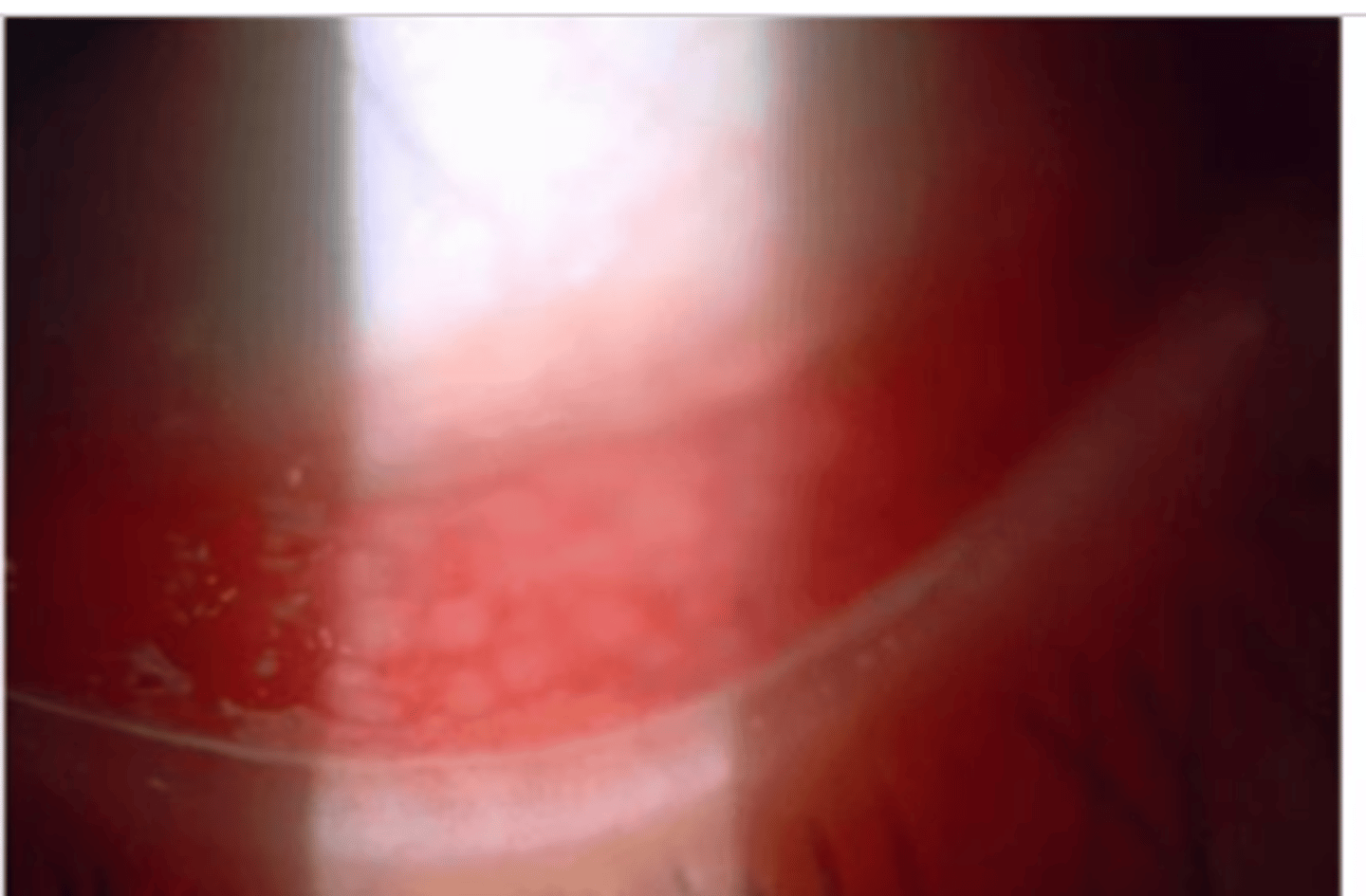
pathophysiology begins with fibrin that has attached to ______ epithelium
conjunctival
what is the different between true vs pseudomembranes
true: leaves raw surface * causes bleeding when peeled
pseudo: superficial little to no growth into conjunctival epithelium
a patient comes for a routine exam. they tell you they been diagnosed herpes simplex virus. later on you look into their eye and notice a white thick line on inferior palpebral conjunctiva. what is that
membrane
what is the number one cause of membranes
adenovirus
besides HSV and adenovirus what are other causes of membranes (3)
corynebacterium diptheriase, b-hemolytic streptococci & candida
membrane
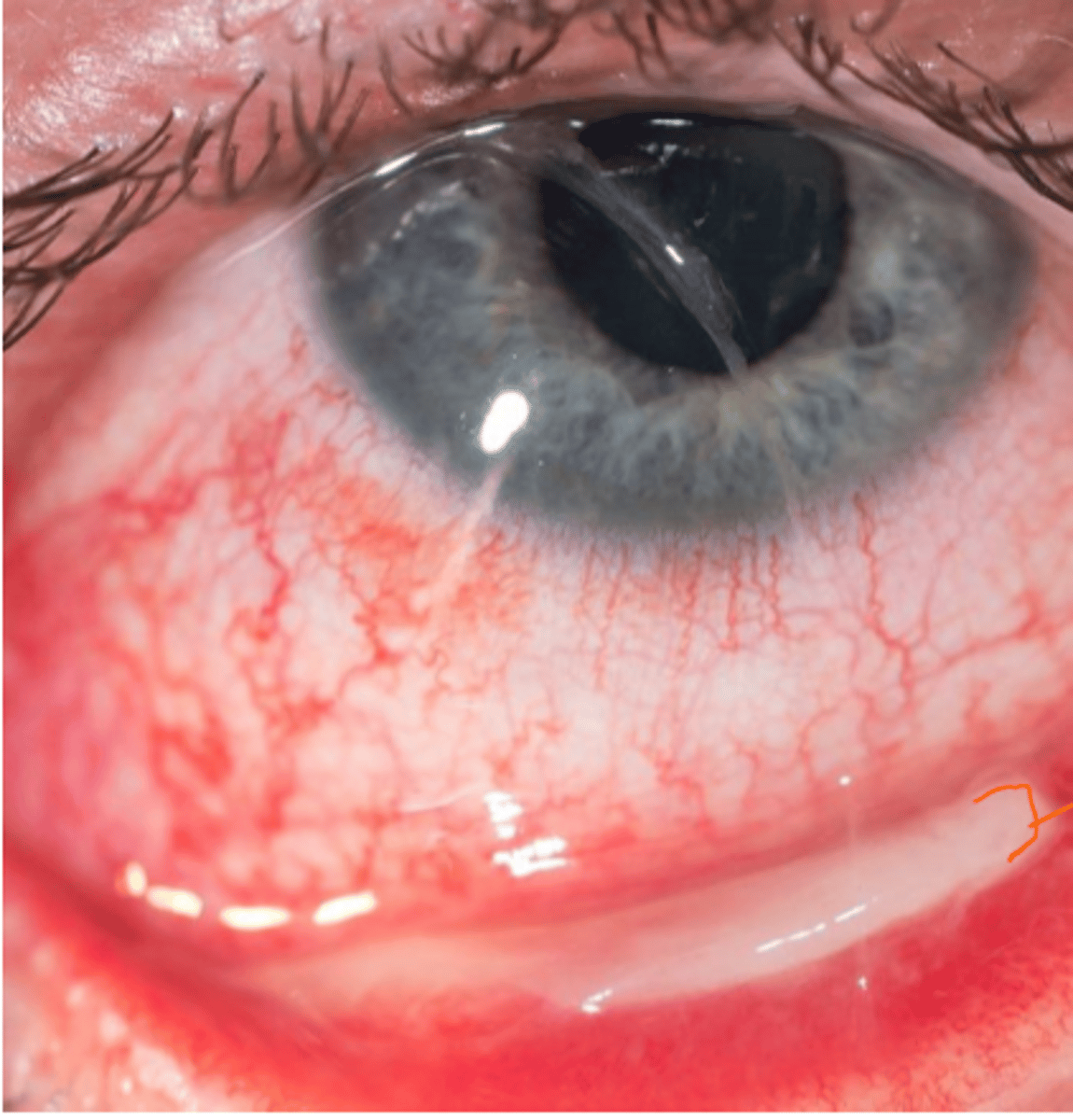
____ are associated with
1. vernal conjunctivitis
2. inclusion conjunctivitis
3. ligneous conjunctivitis
4. steven johnson syndrome--> toxic epidermal necrolysis
membranes
t/f membranes can lead to
conjunctival scarring
goblet cell loss
entropion
trichiasis
limbal stem cell failure
true
ankyloblpeharon
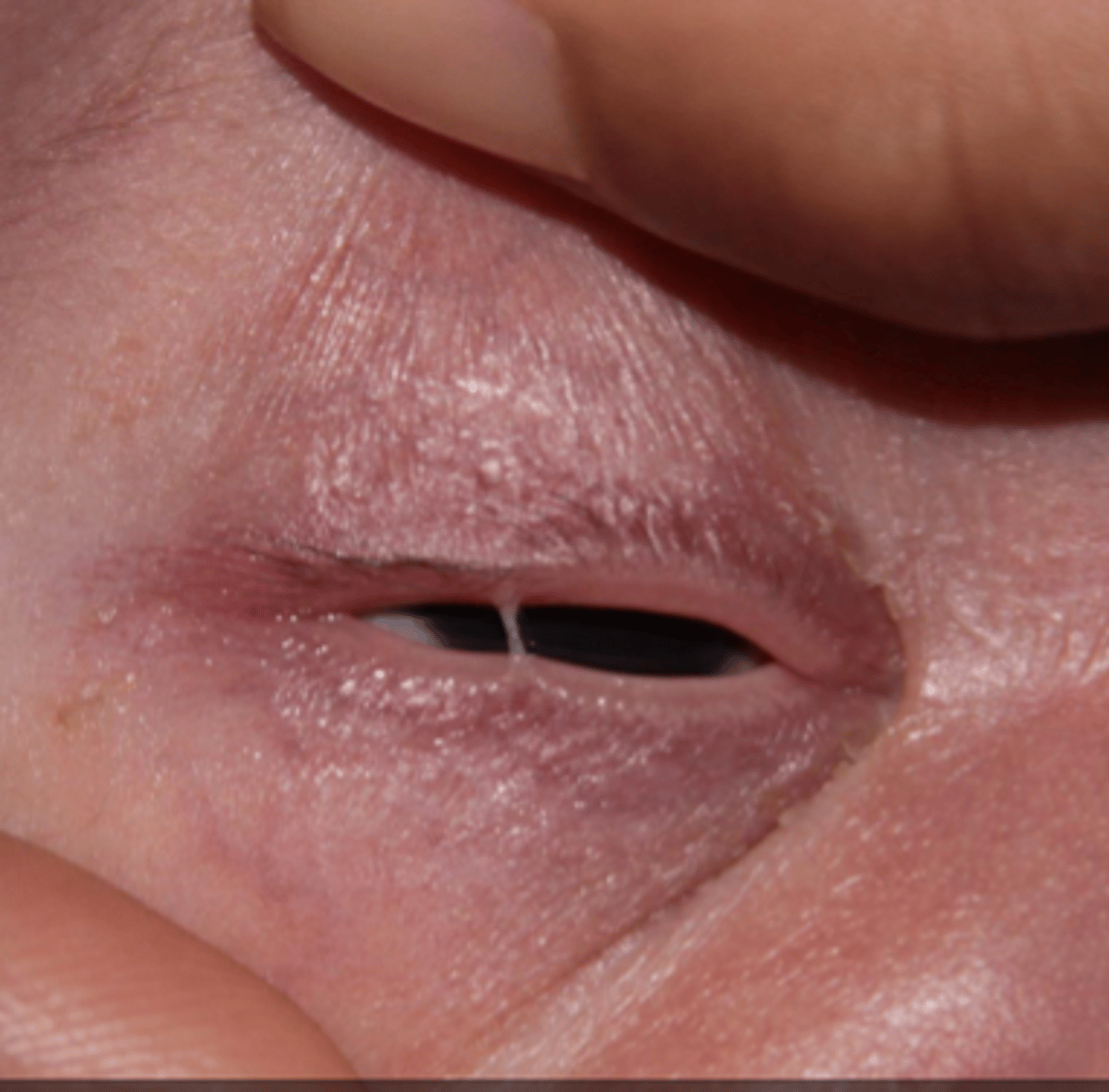
symblepharon
______ is the scar formation secondary to desctruction of stromal tissue
cicatrization
it first starts as shortening of the fornix, stellate fibrosis
later it progresses to symblepharon
the end stage is obliteration of fornix, keratinization of epithelium AKA ankyloblepharon
what is it
ciciatrization
what condition is associated with cicatrization
ocular mucous membrane pemphigoid
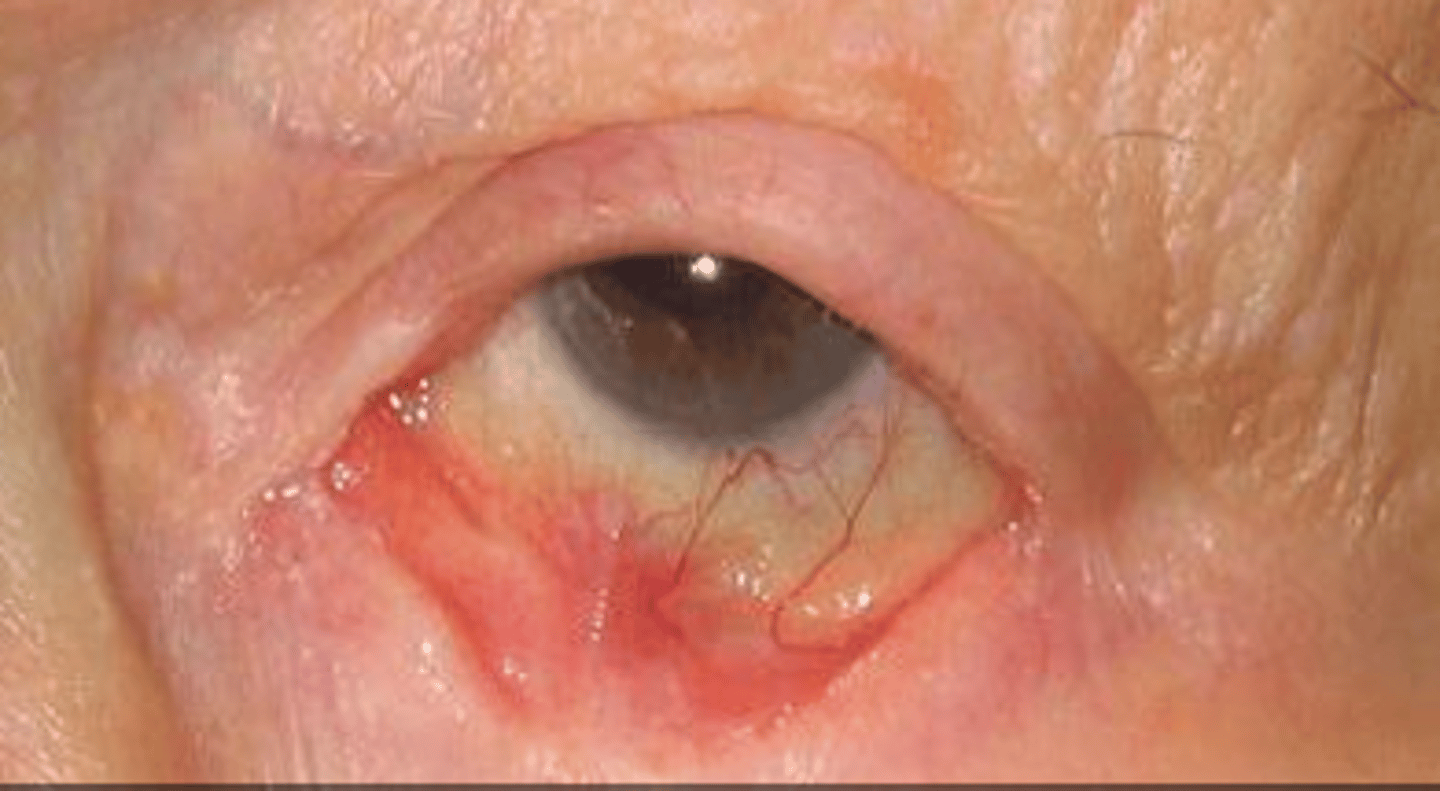
granulomas
granuloma is:
cluster of immune cells nd other material secondary to inflammation
granuloma always affects the
stroma
t/f granulomas may be due to infectious or inflammatory eitology
true
t/f granulomas can be flat or evelated
true
granulomas have infectious causes such as (4)
parinaud oculoglandular syndrome
tularemia
TB
syphilis
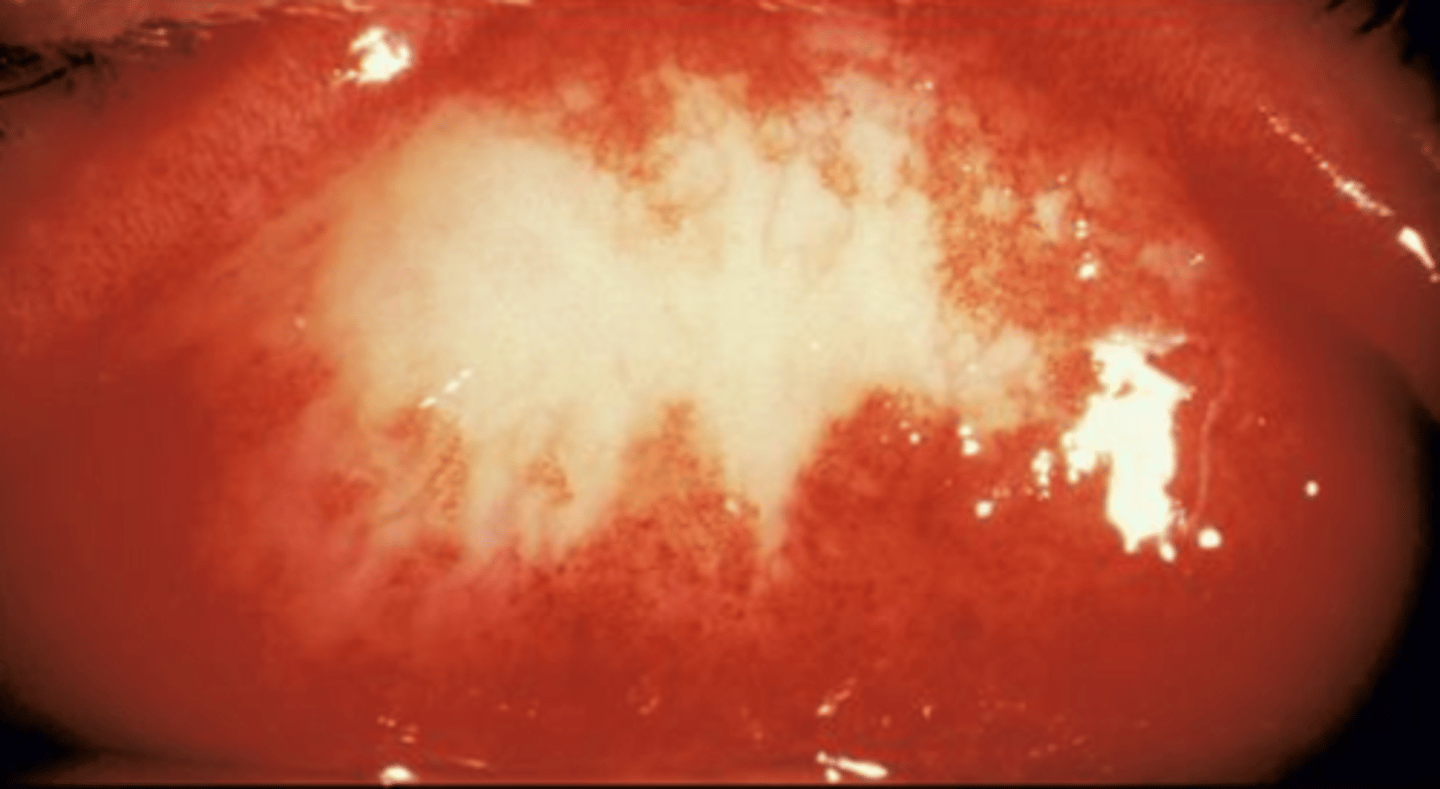
exudate
what 3 classifications do exudate fall under
1. purulent or hyperactue
gono or meningitidis
2. mucopurulent (bacterial/chlamydial)
3. water (allergic/viral)
for the lymph nodes medially they drain into
submandiubular nodes
for lymph nodes laterally they drain into
preauricular nodes
lymphadenodopathy can occur in conjunctivitis.. which is more common viral or bacterial?
viral, usually ipsilateral
____ is a elevated, horizontally oriented area of bulbar conjunctival thickening within the palpebral fissure
pinguecla
pinguecula tend appear white to yellow fatty appearance unless ______ occurs
keratinazation
for pinguecula is the cornea involved? yes or no
no
are pinguecula unilateral or bilateral
bilateral
are pinguecula seen more commonly on nasal or temporal side
nasal
what two things increases chances of pinguecula
age & UV exposure
when looking at a pinguecula, what are other differentials (3)
ocular surface squamous neoplasia (OSSN)
limbal dermoid
other conjunctival tumors
if a pinguecula is inflamed its called
pingueculitis
if the pingueculitis is mild what is the best tx option
artificial tears
if the pingueculitis is moderate to severe what is the tx option
topical steroid= FML 0.1% or FML acetate 0.1% or loteprednol 0.2% 1gtt
or NSAID= ketorolac 0.4-0.5% QID
or
anti-histamine +/- bepotastine, ketotifen, olopatadine
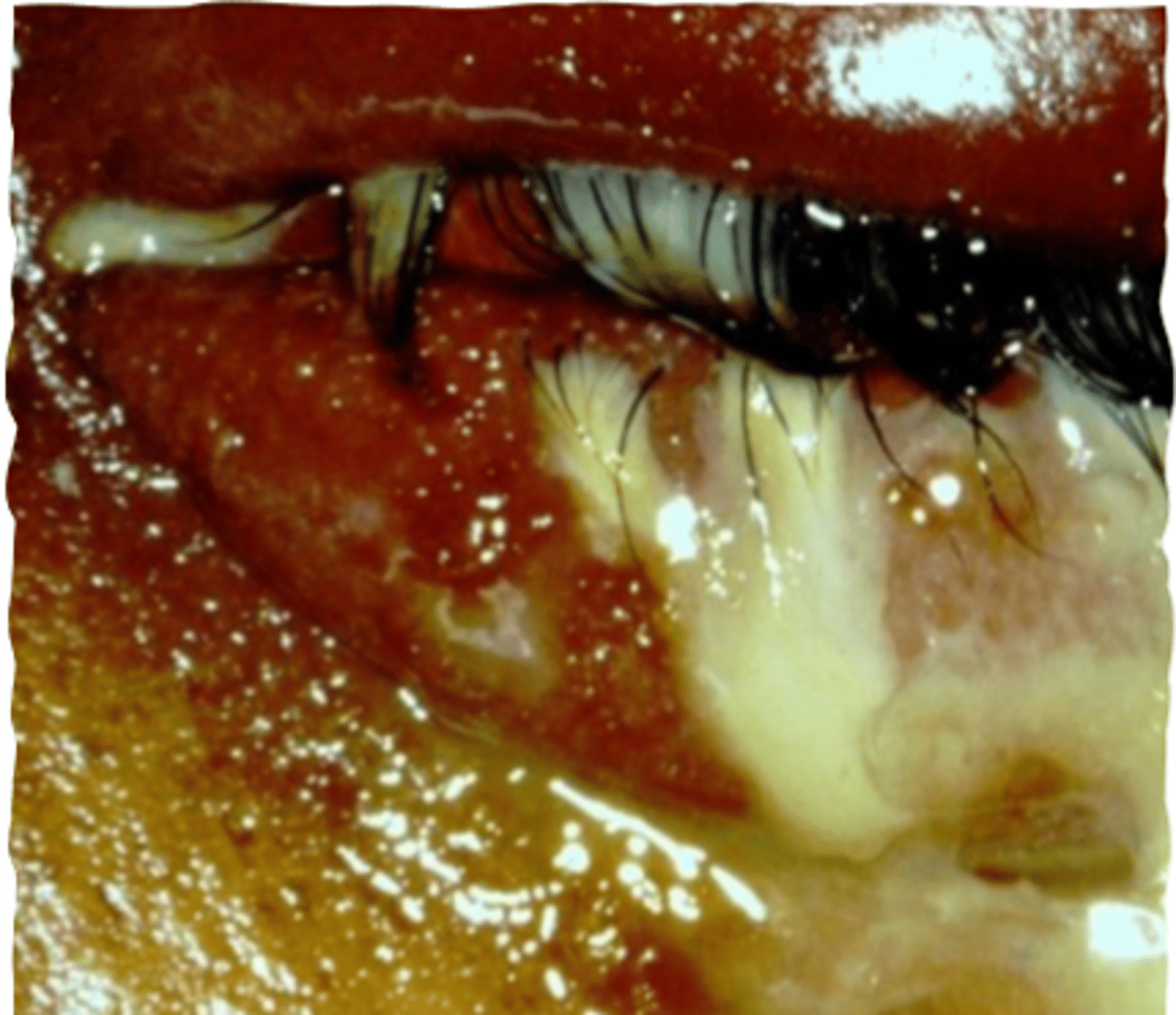
_____ is a growth of fibrovascular tissue on the cornea and conjunctiva in palpebral fissure
does pterygium seen on nasal or temporal side
nasal
islets of vogt and stocker line are associated findings with
ptergyium
what are islets of vogt
elevated whitish opacities
what is stocker line
iron deposition line delineating head of pterygium
what is the pathogenesis of pterygium
damage to limbal stem cells by UV light & activation of matrix metalloproteinases
the difference between ptergium and pinguecuela is that pterygium is (2)
PTG is vascularized
PTG disrupts bowman membrane in the cornea
what are two causes of PTG (pterygium)
Uv light exposure
outdoor work
a patient comes to you complain about eyes being dry and vision is distorted. In the other eye its vision is gone. what could be diagnosis after bio microscopy?
pterygium
if diagnosing pterygium and one of the eyes of pt is occluded or gone. why is that
pterygium has reached the visual axis
OSSN/ CIN
pseudo pterygium
pinguecula
pannus
are ddx for_____
pterygium
pseudo pterygium
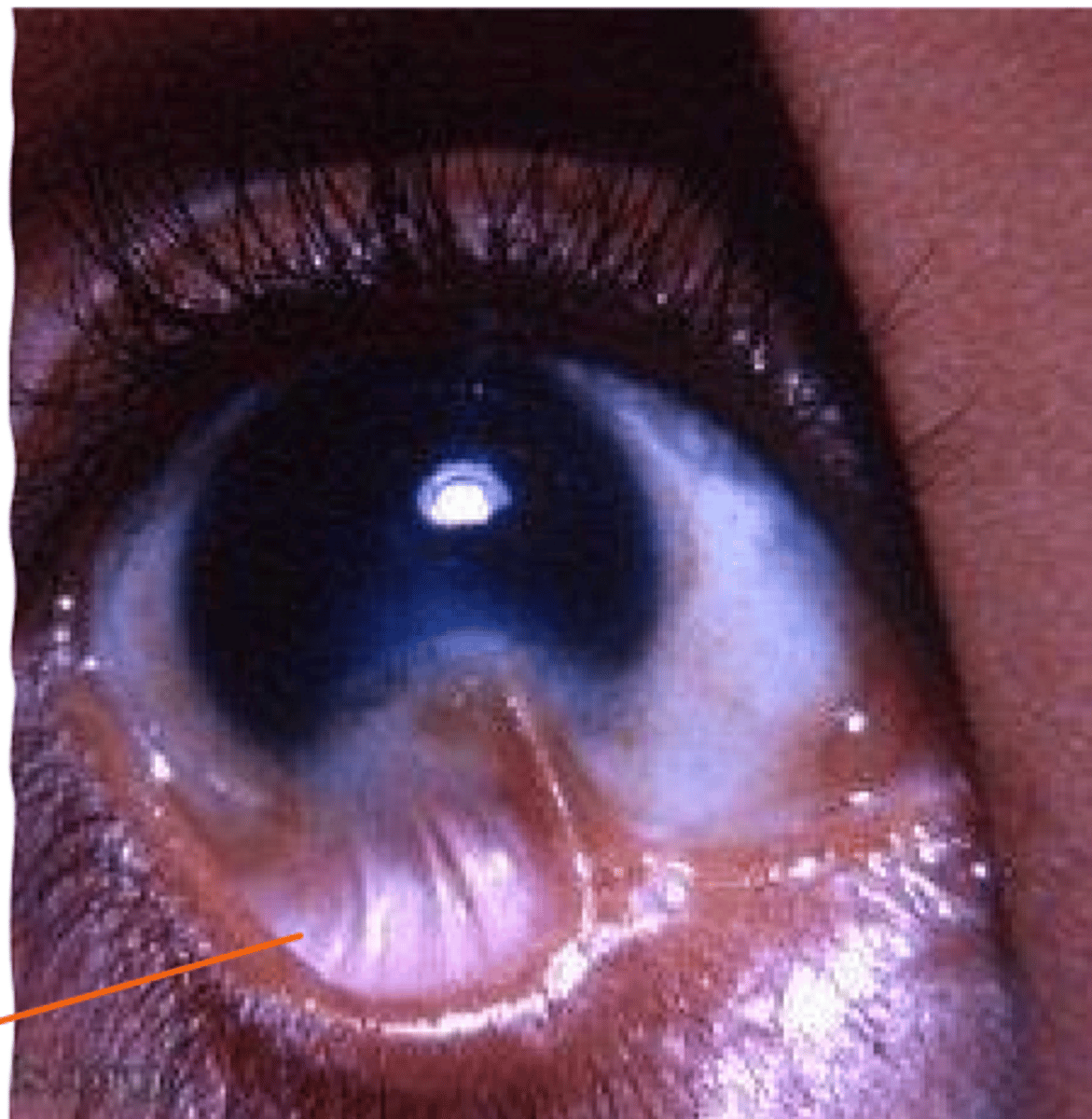
pannus
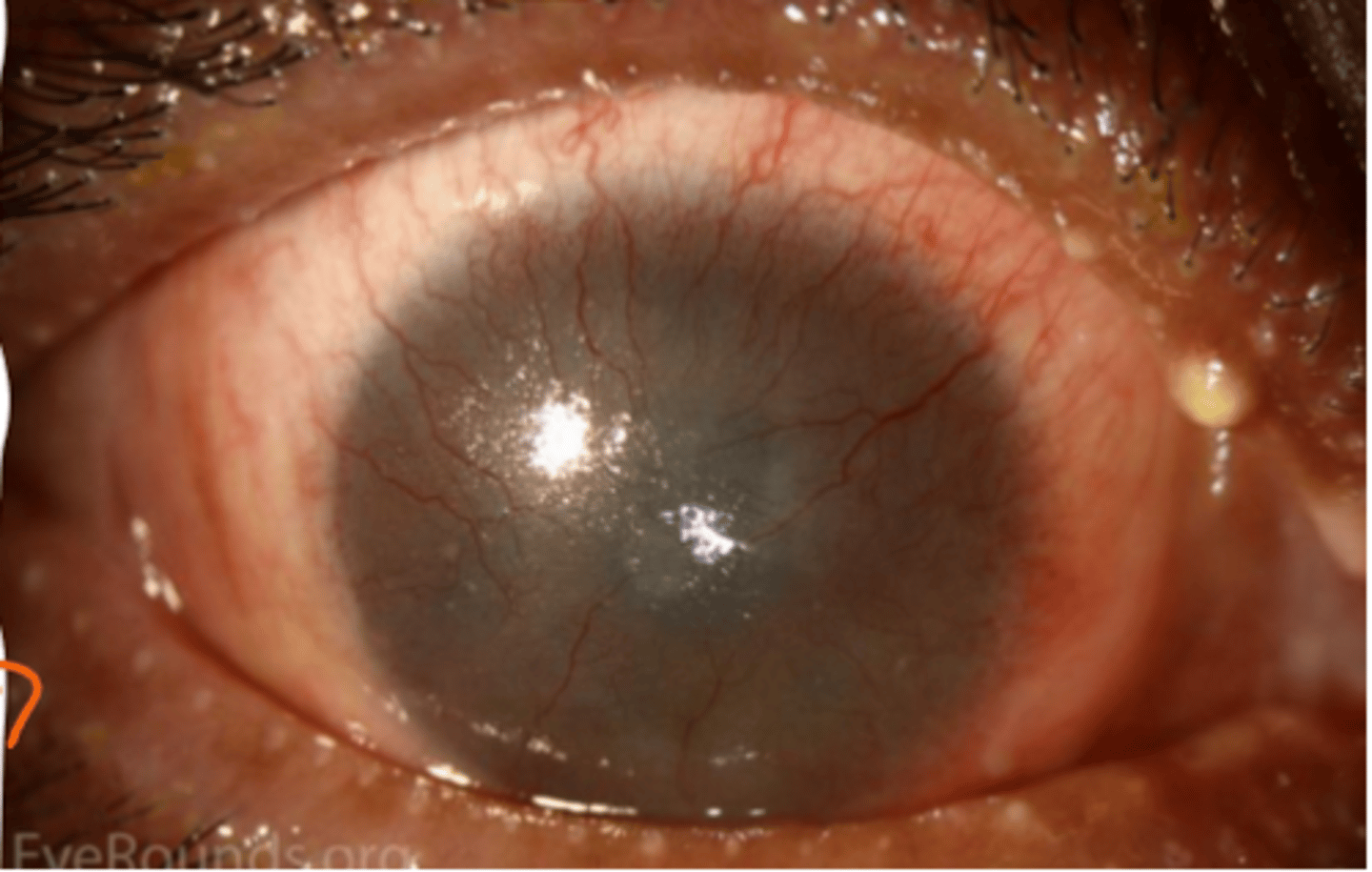
____ is the spectrum of squamos epithelial malignancies
OSSN
what is the most common nonpigmented conjunctival malignancy
OSSN
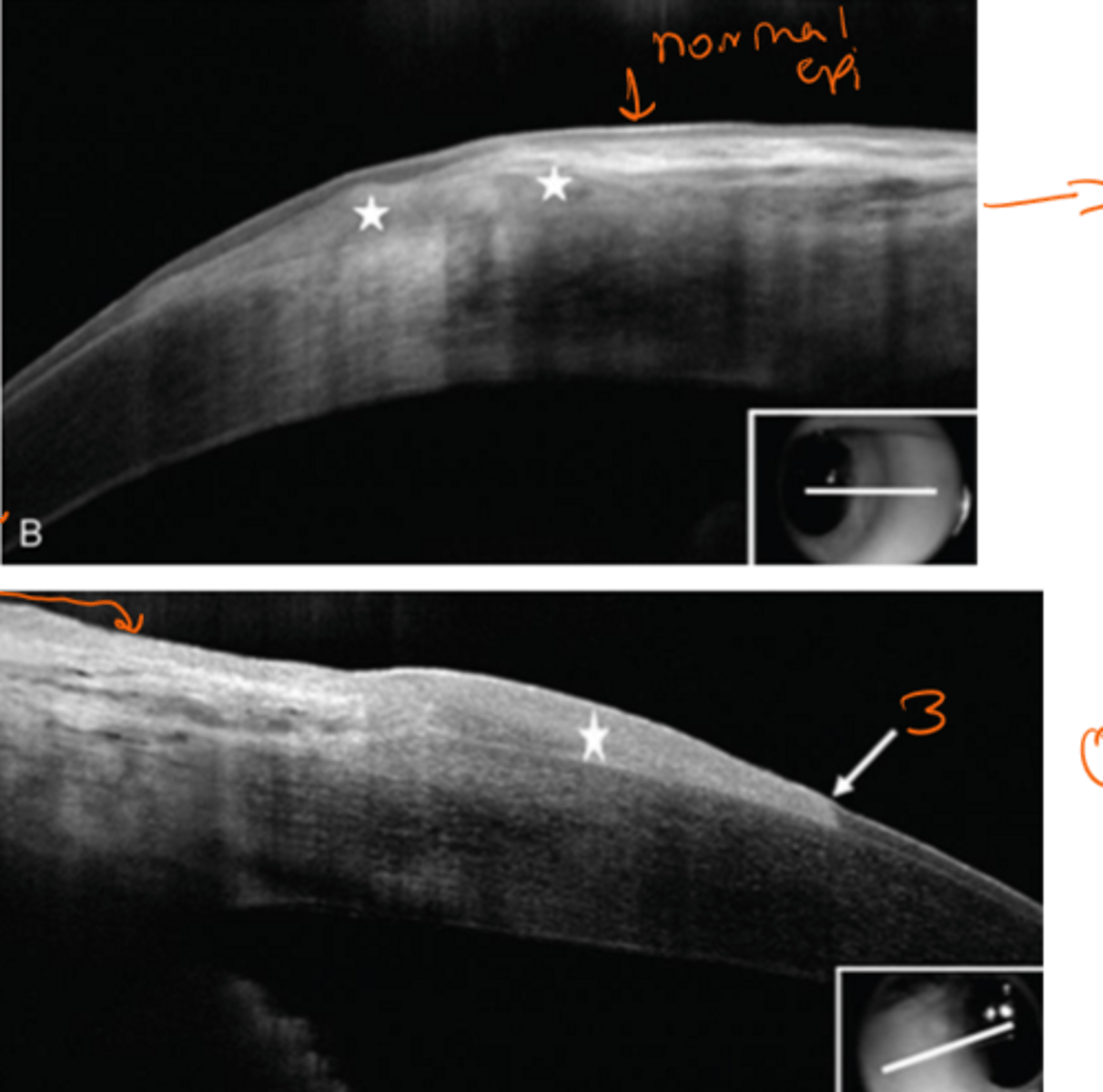
on the OCT, the _____ 3 distinction from it and pterygium
1. thickened epithelium
2. hyperreflective epithelium
3. abrupt transition from normal to abnormal epithelium
OSSN
top ptyergium
bottom OSSN
you should tx pterygium when its causing (5)
discomfort
encroachment of visual axis
significant astigmatism
cosmesis
should u tx a pterygium before cataract sx?
yes bc it induces unexpected astigmatism
how to tx pterygium mild cases (2)
artficial tears or UV exposure
how to tx moderate to severe pterygium (1)
surgical incision with conj autografting is "gold standard"
*common for it to come back
________________ is yellow, gray or black vertical bands anterior to insertion of MR or LR
senile scleral plaques
senile scleral plaques appear in the _____ but can be mistaken for degen or deposition
sclera