Pharmacology II Exam I: Multimodal
1/192
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
193 Terms
What is the International Association for study of pain definition of pain?
An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual ot potential tissue damage described in terms of such patient
___________ = normally nonharmful stimulus that is perceived as painful
allodynia
______=Increased sensitivity to pain
Algesia
____=Pain producing
Alogenic
______________ = absence of pain in the presence of a normally painful stimulus
analgesia
_________________ = unpleasant painful abnormal sensation whether evoked or spontaneous
dysesthesia
_______________ = heightened response to normally painful stimulus
hyperalgesia
_______________ = pain in the distribution of peripheral nerves
neuralgia
________________ = abnormal distrubance in the fx of a nerve
neuropathy
______________ = abnormal sensation whether spontaneous or evoked
paresthesia
T/F: poorly controlled acute pain may lead to chronic pain states
true
acute pain is _____________, and lasts ____________
self-limited; 1-14 days
Chronic pain lasts longer than ___ months and is maintained OR beyond the course of healing
3 months
Malignant chronic pain can be related to
and/or cancer treatment
Non malignant chronic pain can be? (5)
1. Neuropathic
2. Inflammatory
3. Musculoskeletal
4. Idiopathic
5. Combination of any/all
_______________ & ______________ are types of nociceptive pain
somatic and visceral
How is nociceptive pain treated?
Opiods and NSAIDS
somatic pain comes from tissue damage --> activation of _____________ fibers
a delta; C fibers
_________________ pain is described as well localized and sharp
somatic (nociceptive)
_________________ pain is described as dull, cramping, squeezing, vague, and poorly localized
visceral (nociceptive)
what type of pain is often accompanied by ANS reflexes like N/V/D, HR, BP increase
visceral (nociceptive)
____________ pain is caused by damage to CNS or PNS nerves and is due to dysfunction of the CNS (spontaneous excition) --> abnormal processing of painful stimuli that leads to spontaneous excitation of chronic pain states
neuropathic
what pain is described as burning, tingling, shocklike
neuropathic
what are the non-nociceptive pains
neuropathic
idiopathic
T/F: chronic pain often exhibits more than 1 type of pain classification
true
T/F: Idiopathic pain is associated with chronic pain states, pain with no apparent cause and psychological symptoms
True
T/F: opioids normally manage neuropathic pain really well?
What else should they use?
false; normally does not work on neuropathic pain
steroids, anti-convulsants, cannabis- anything to calm down the nerves
what are the four processes of somatic nociceptive pain
1. transduction
2. transmission
3. modulation
4. perception
_______________ = transformation of a noxious stimuli (chemical, mechanical, or thermal) into an action potential
transduction
In transduction, Noxious stimuli is detected by________whoch conduct a noxious stimuli to the dorsal horn of the spinal cord
nociceptors
Large and myelinated fibers are what kind? what pain is sensed?
A delta fibers
fast sharp pain- withdrawal mechanism
Smaller non myelinated fibers are what kind? What pain is sensed?
C fibers
dull, burning, throbbing, aching
T/F: During transduction, there is a release of chemical mediators from inflammatory response and release of neurotransmitters, as well as stimulation of peripheral nociceptors and action potential
True
______________ = process by which an action potential is conducted from the periphery to the CNS
transmission
The ______tract carries signals from the trunk and the lower extremeties
spinothalamic
The primary afferent neurons ( a delta and c fibers) are located where?
dorsal root ganglia of SC
What are the two types of 2nd order neurons?
1. Nociceptive neurons- receive input solely from primary afferents
2. Wide range neurons- input from nociceptive ( a delta and c fibers) efferent fibers and non nocicpetive fibers
2nd order neurons are generated in the ________ , cross the midline of the ________, through the anterior _______, and ascend in the anterolateral pathway to the _____ to synapse with 3rd order neuron
rex laminae I,II, & V
spinal cord
commissure
thalamus
3rd order neurons reside in the lateral _______& intralaminar nuclei and send the action potential to the cerebral cortex for interpretation
thalamus
________________ = the recognition of pain signal from various areas of the brain
perception
Perception happens when recognized by various areas of brain including (4)?
amygdala
somatosensory
hypothalamus
anterior cingulate cortex
________________ = brains response to action potential, alteration of neural afferent activity along the pain pathway (suppresses/enhances pain signals)
modulation
In modulation, the descending axons travel via the ______(DLF) and synapse with the brain and spinal cord
DORSOLATERAL FUNICULUS
Action potentials travel down to the __________via the dorsolateral funiculus and activate the __________releasing hormones
substantia gelatinosa
enkephalin
Enkephalin then binds to opiate receptors ...either presynaptic_____order or postsynaptic ______order
first
second
Enkephalin causes decreased _______(excitatory neurotransmitter) which suppresses the ascending pain transmission
substance P
Inhibitory neurotransmitters released via descending pathway (5)
Glycine
GABA
Enkephalin
Serotonin
Norepinephrine
what is the primary treatment for pain
reducing transduction through inhibiting neurochemical mediators
what areas of the brain are responsible for perception of pain
1. amygdala
2. somatosensory area of cortex
3. hypothalamus
4. anterior cingulate cortex
describe the process of transduction
1. noxious stimuli detected by primary afferent nociceptors (a-delta and C fibers)
2. release of chemical mediators and neurotransmitters
3. stimulate periperpheral nociceptors: depol = Na influx; K efflux = repol
4. AP travels up to dorsal root of spinal cord & pain impulse generated
what is the peptide found and released from the peripheral afferent (sensory) nociceptor C fibers and
involved with slower than other nerve fibers, chronic, pain
Substance P
what receptors does substance P work on? What does this result in?
Acts via the G-protein linked neurokinin-1, neurokin 2
results in vasodilation, extravasation of plasma proteins, degranulation of mast cells, and sensitization of the stimulated sensory nerve
What major excitatory neurotransmitter is released in the CNS and from the Aδ & C primary afferent nerve fibers
and effects are instantaneous = initial, fast, sharp pain
Glutamate
what receptors does glutamate work on
NMDA, AMPA, kainite, mGluR
what are your excitatory neurotransmitters with pain
1. substance P
2. glutamate
What peptide is released during the inflammatory process and is algesic (causing pain) and has direct stimulating effect on peripheral nociceptors via specific bradykinin receptors (B1 & B2)
Bradykinin
What amine is released from mast cell granules, basophils, and platelets via Substance P
and reacts with various receptors to produce edema and vasodilation
Histamine
What amine stored and released from platelets after tissue injury
and reacts with multiple receptor subtypes and exhibits analgesic effects on peripheral nociceptors
•Can potentiate bradykinin induced pain
Serotonin
What receptor does serotonin work on?
5-HT
What is a metabolite of arachidonic acid that is Synthesized from COX-1 and COX-2, Associated with chronic pain and Sensitize peripheral nociceptors causing hyperalgesia
Prostaglandins: (PGE)
What is released
in response to to tissue injury by a variety of immune and nonimmune cells via the inflammatory response- Include interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α
Cytokines
what are your inhibitory neurotransmitters with pain
1. glycine - chloride linked (GlyR)
2. GABA ( GABA a, GABA b, GABA c)
3. enkephalin
4. serotonin
5. norepi (a2 adrenergic)
inhibitory neurotransmitters are released via the ________________ pain pathway
descending
_________________ pain is acute pain on top of chronic pain
breakthrough pain
what are some mechanisms at which acute pain transitions to chronic
1. initiated by either periperhal or central mechanisms (peripheral or central sensitization)
2. hyperexcitable nerve endings (change from direct nerve injury, or sprouting of new nerve endings)
3. neuroma formation
4. damaged nerves have lower pain threshold so respond to non-noxious stimuli
_______________________ hyperalgesia occurs at the original site of injury, enhanced pain from heat and mechanical stimuli
primary
_______________ hyperalgesia occurs in uninjured tissues surrounding the injury, enhanced pain response to mechanical stimuli
secondary
SNS response can depend on what? (4)
1. size of surgical field
2. number of nerve pain receptors in area
3. bleeding, infection
4. coexisting disease
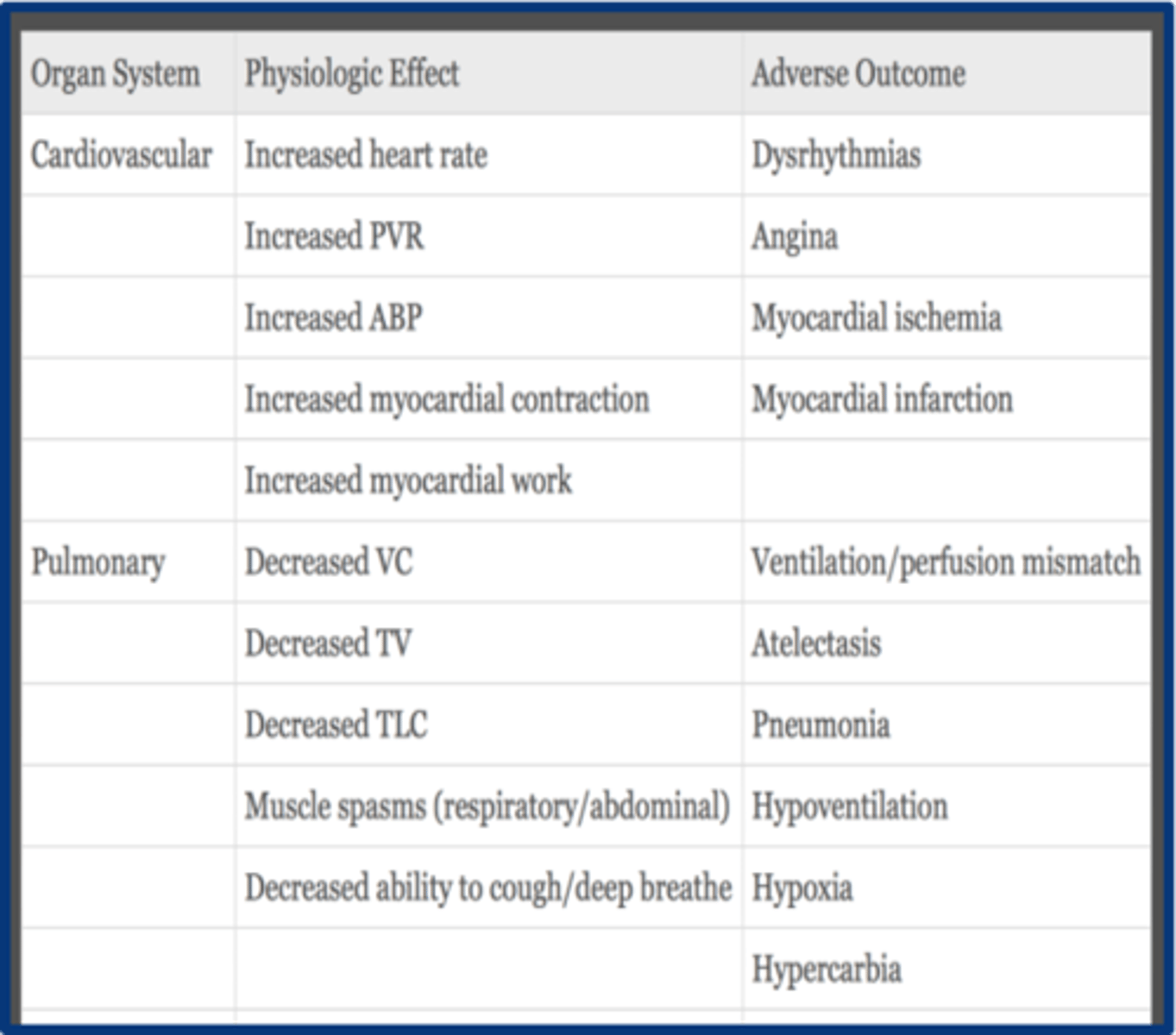
CV physiologic effects of acute pain
1. increased catecholamines
2. increased cortisol --> increased HR, increased vascular resistance, increased myocardial activity, and increased ABP
3. increased myocardial O2 demand & consumption
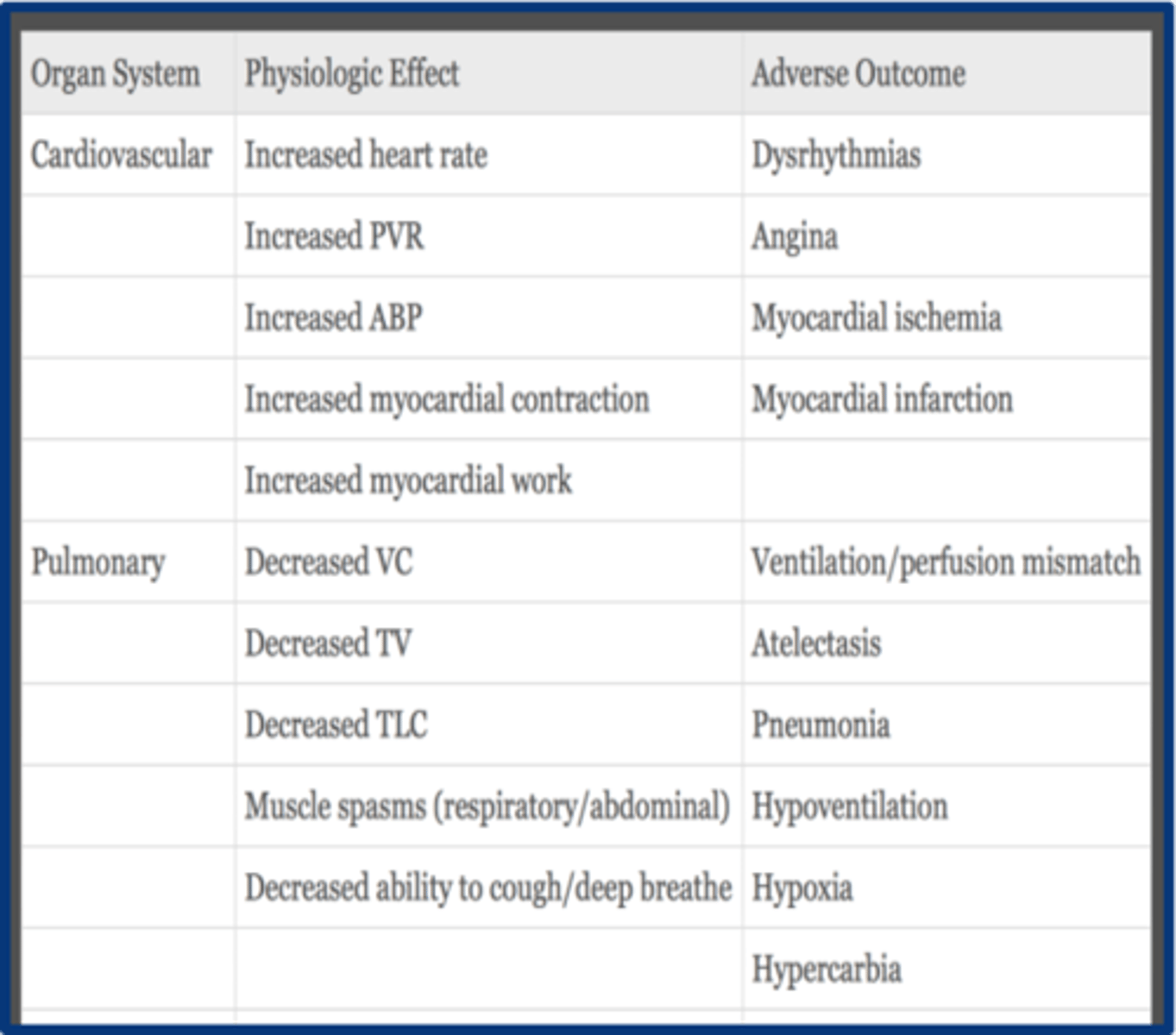
aggressive pain management is essential to preventing _________________
post-op cardiac complications
respiratory physiologic effects of acute pain
1. decreased TV due to decreased movement
2. muscle spasms = decreased/limited respiratory movement (lose breath)
3. poor cough --> atelectasis and PNA
4. decreased VC, IC & TLC
*Worse in pts with pre-existing pulm dysfunction (Asthma, COPD) or ⬇FRC at baseline (morbidly obese, elderly)*
GI physiologic effects of acute pain
1. decreased gastric emptying
2. decreased intestinal motility
3. increased smooth muscle sphincter tone
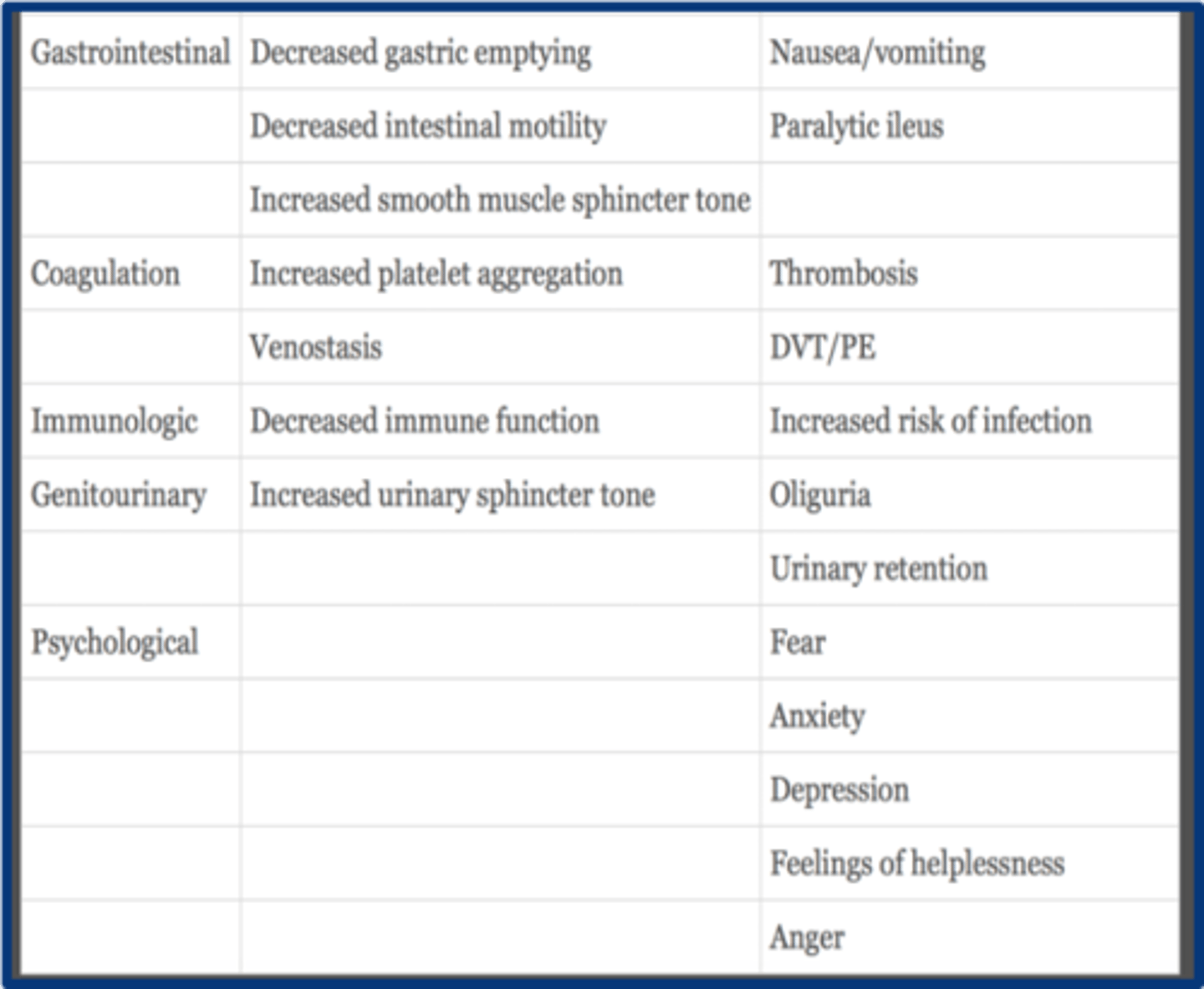
what are the coagulation effects of acute pain
1. increasd plt aggregation
2. venostasis
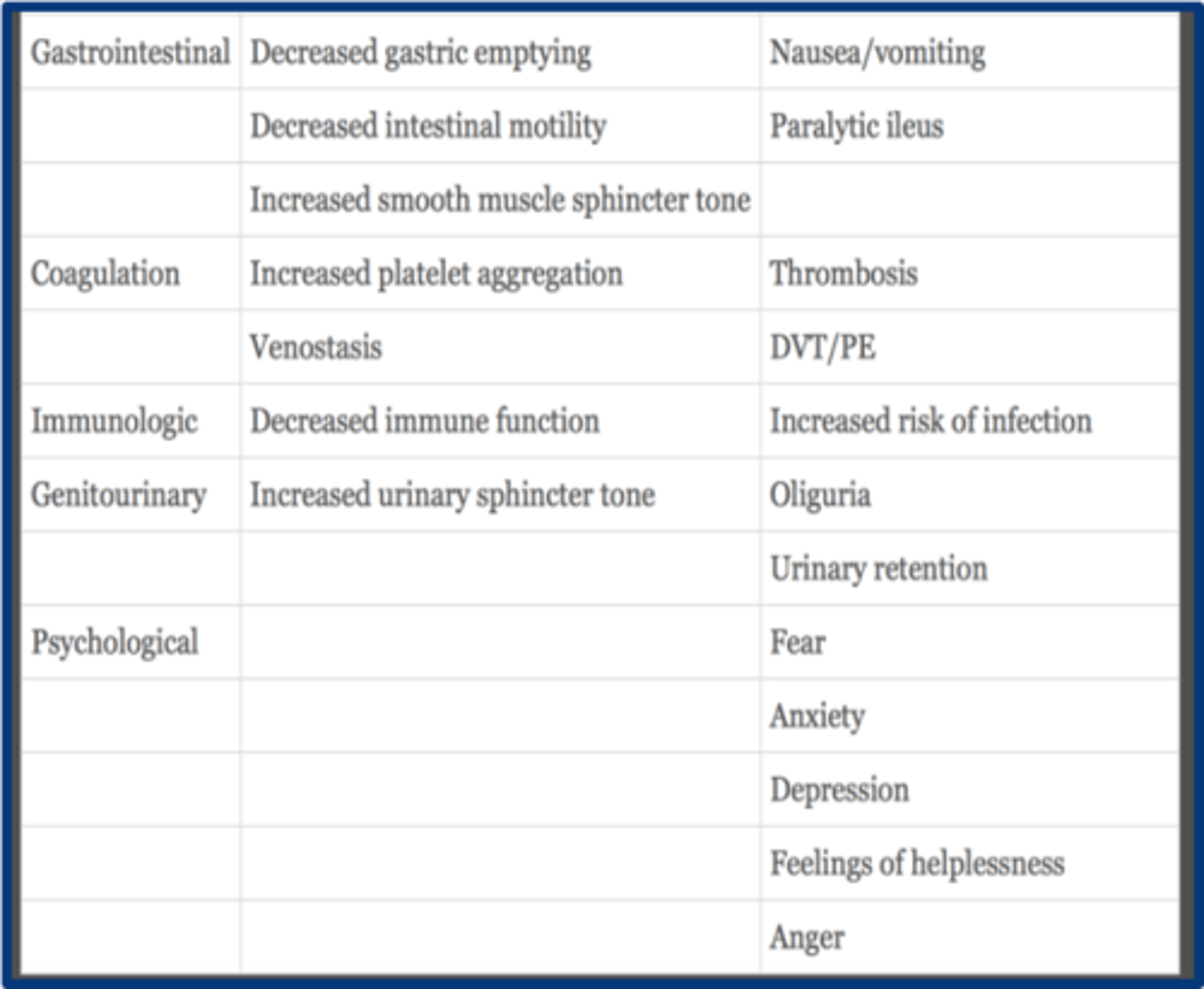
with acute pain immunologic function is ______________
decreased
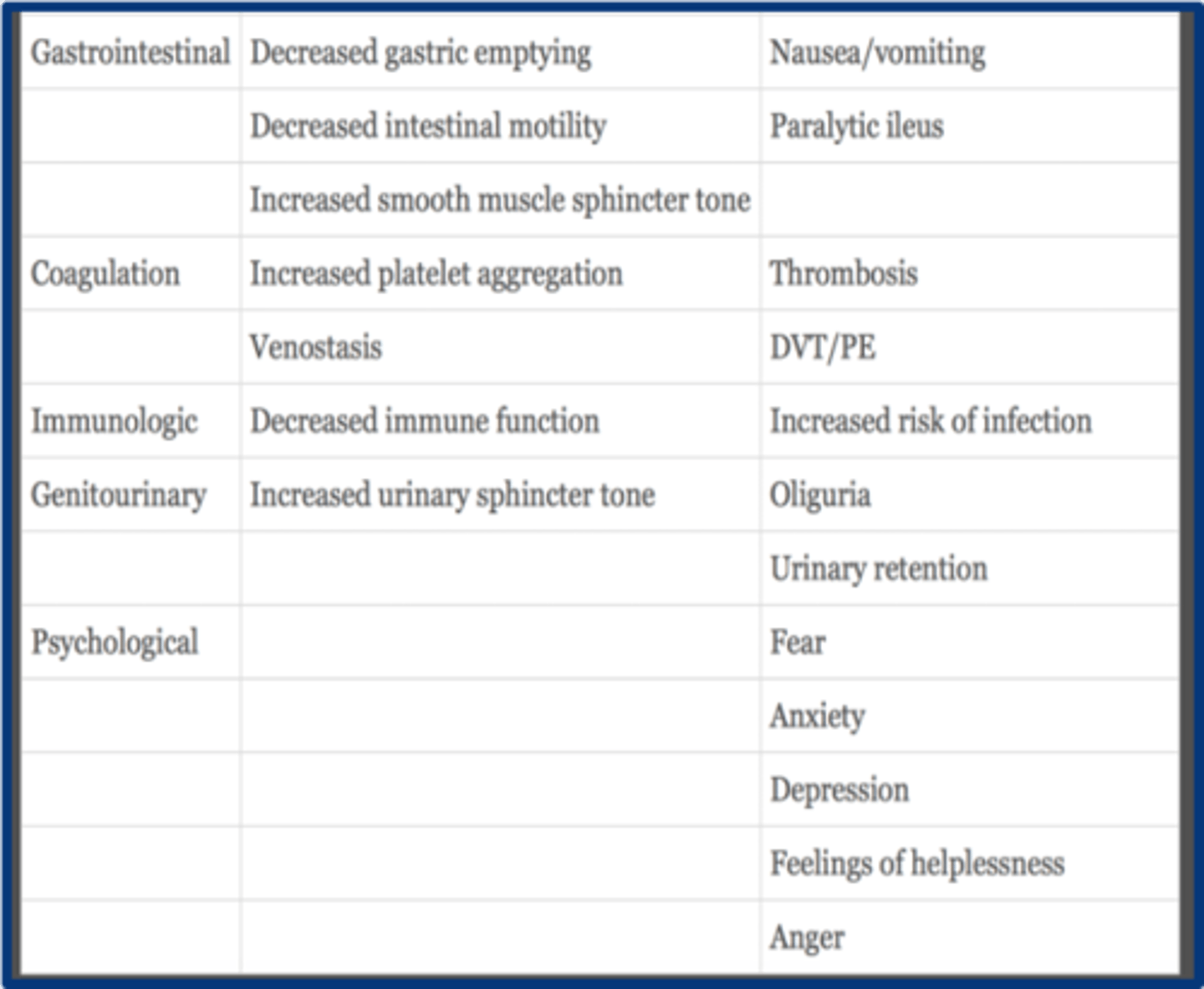
GU effects of acute pain
increased urinary sphicter tone --> oliguria and urinary retention
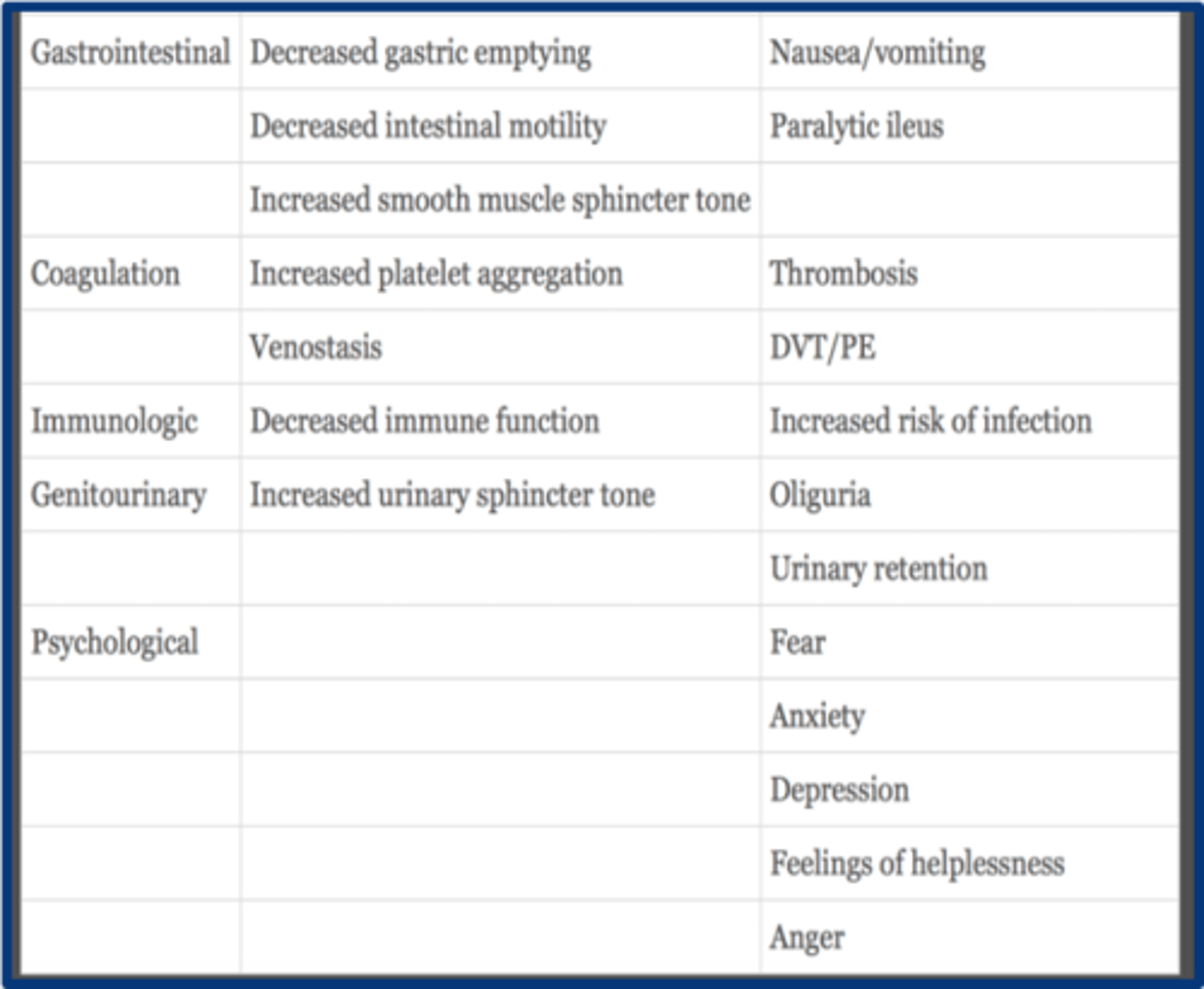
psychological effects of acute pain
1. fear
2. anxiety
3. depression
4. helplessness
5. anger
Central sensitization pain
Alteration of central nervous system processing of sensation leading to amplification of pain signals; lower threshold for non painful stimuli
Ex: fibromyalgia
In central sensitization, pain modulation is_________, d/t neuroplastic changes of ______. Repetitive stimuli to injured nerves alters the________levels. This is associated with _______pain states.
enhanced
CNS
neurotransmitter
chronic
T/F: Peripheral sensitization is environmental chemical changes of peripheral nerves
Release of algogenic substances and neurotransmitters
leads to enhanced excitability of nerves- firing and twitchy
which reduces nociceptive thresholds
High-threshold nerve endings become responsive to non-noxious stimuli
True
In the Wind up phenomenon there is sensitization of the ______Neurons, and increased release of neurotransmitters ( esp. glutamate), leading to sustained stimulation of ______fibers--> longer sustained depolarization (basically a repeated stimulus send up an exaggerated response)
WDR
c fibers
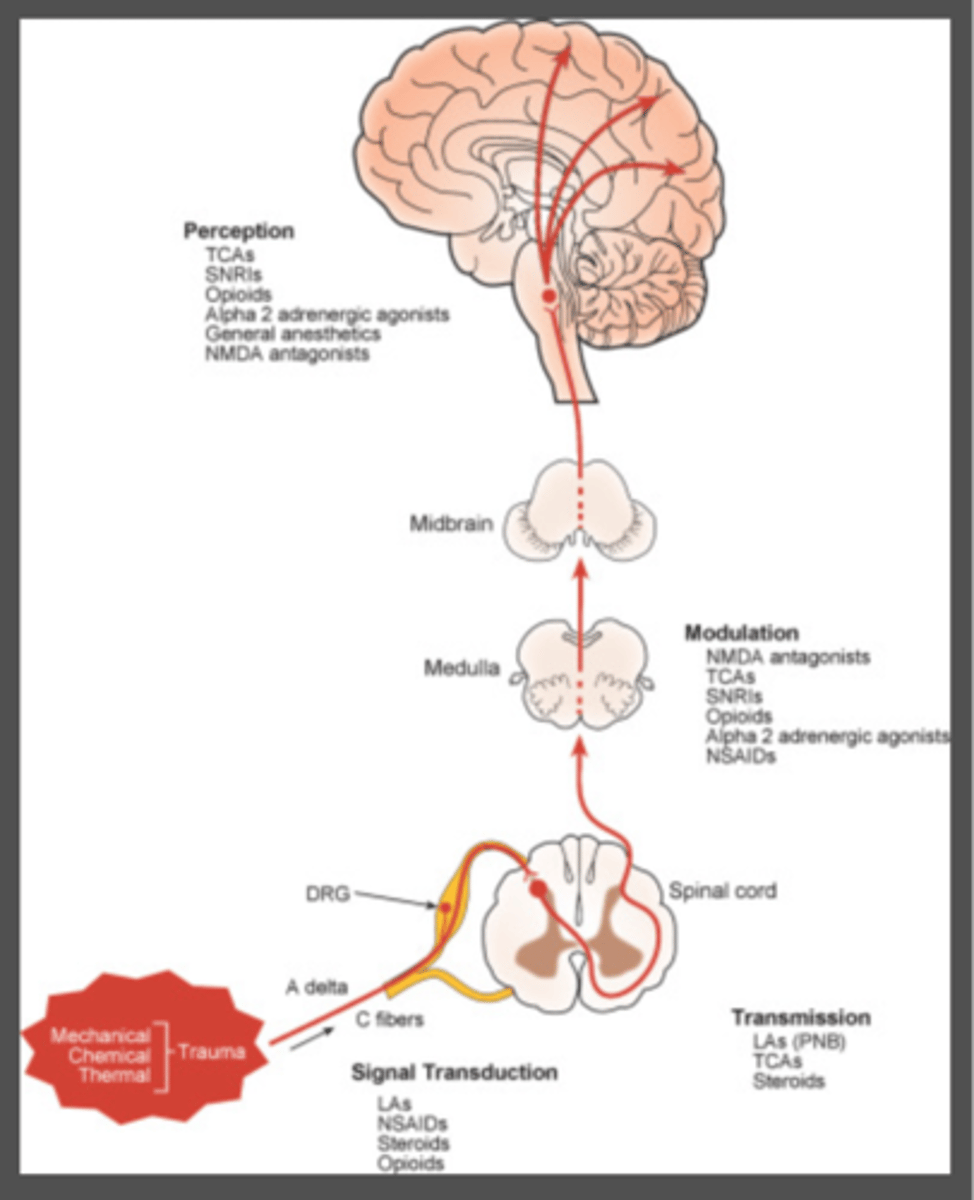
what medications act on transduction of pain signals
1. NSAIDs
2. LA
3. steroids
4. antihistamines
5. opioids
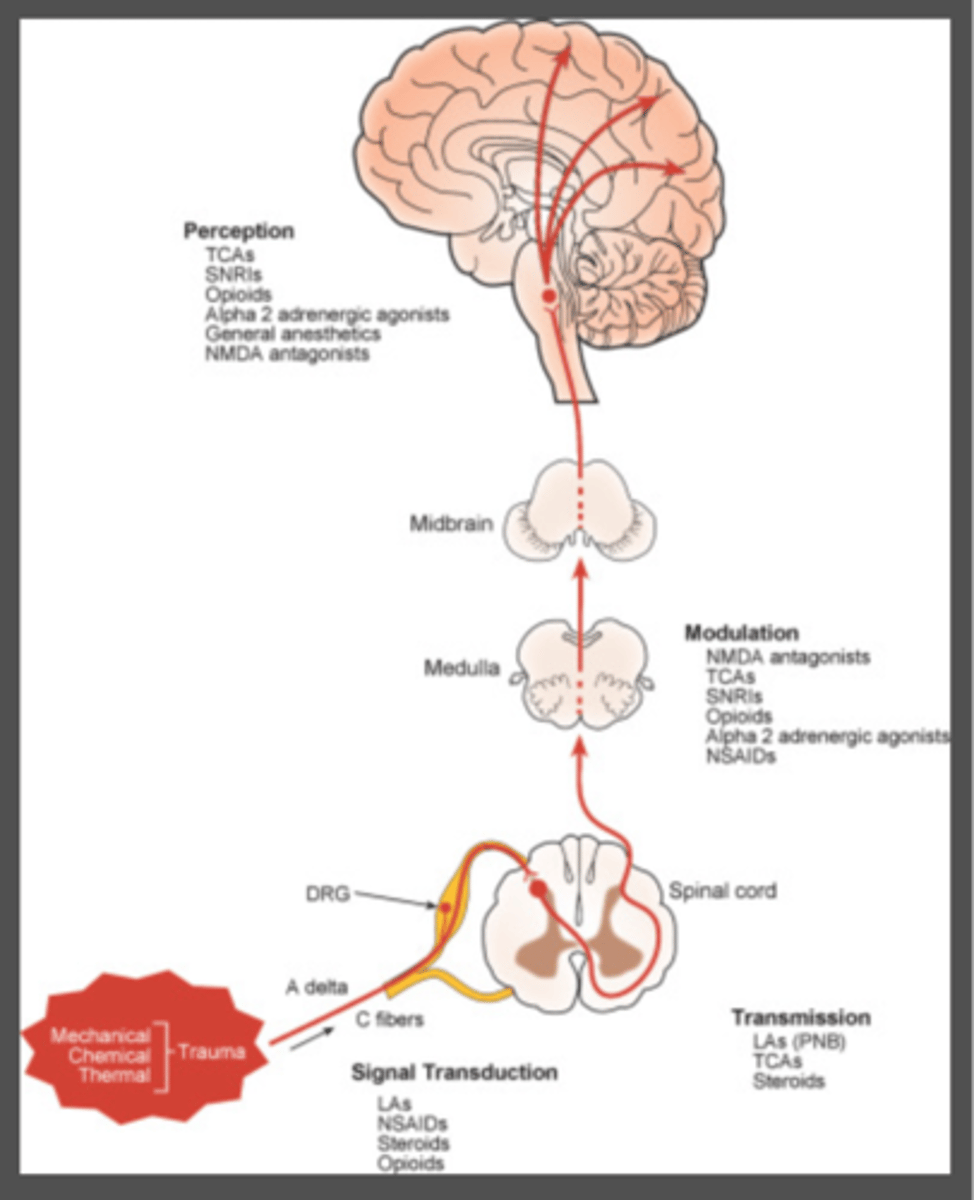
what medications act on transmission of pain signals
LA
TCA
Steroids
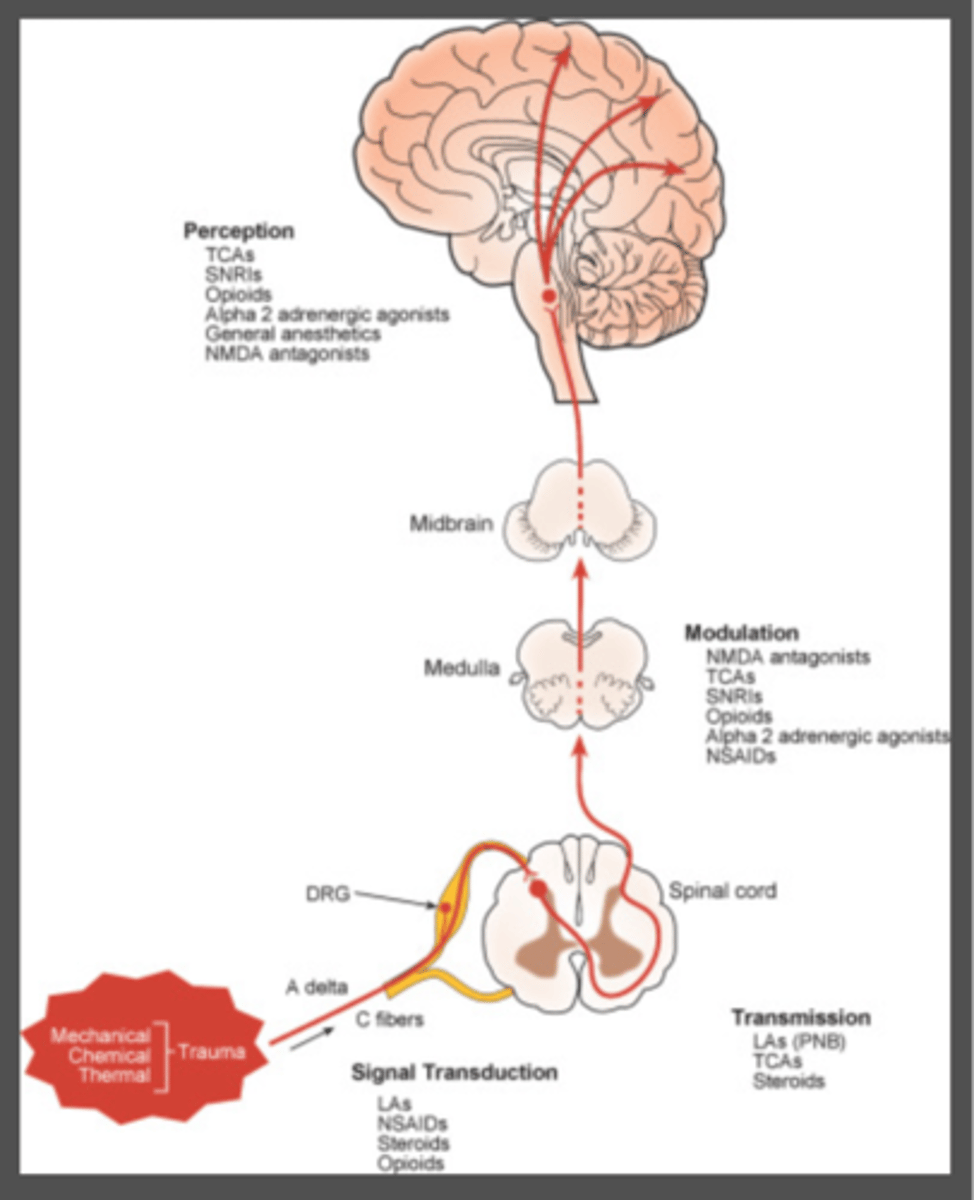
what mediations act on modulation of pain signals
1. neuraxial opioids
2. NMDA antagonists
3. alpha 2 agonists
4. AChE inhibitors
5. SSRIs
6. SNRIs
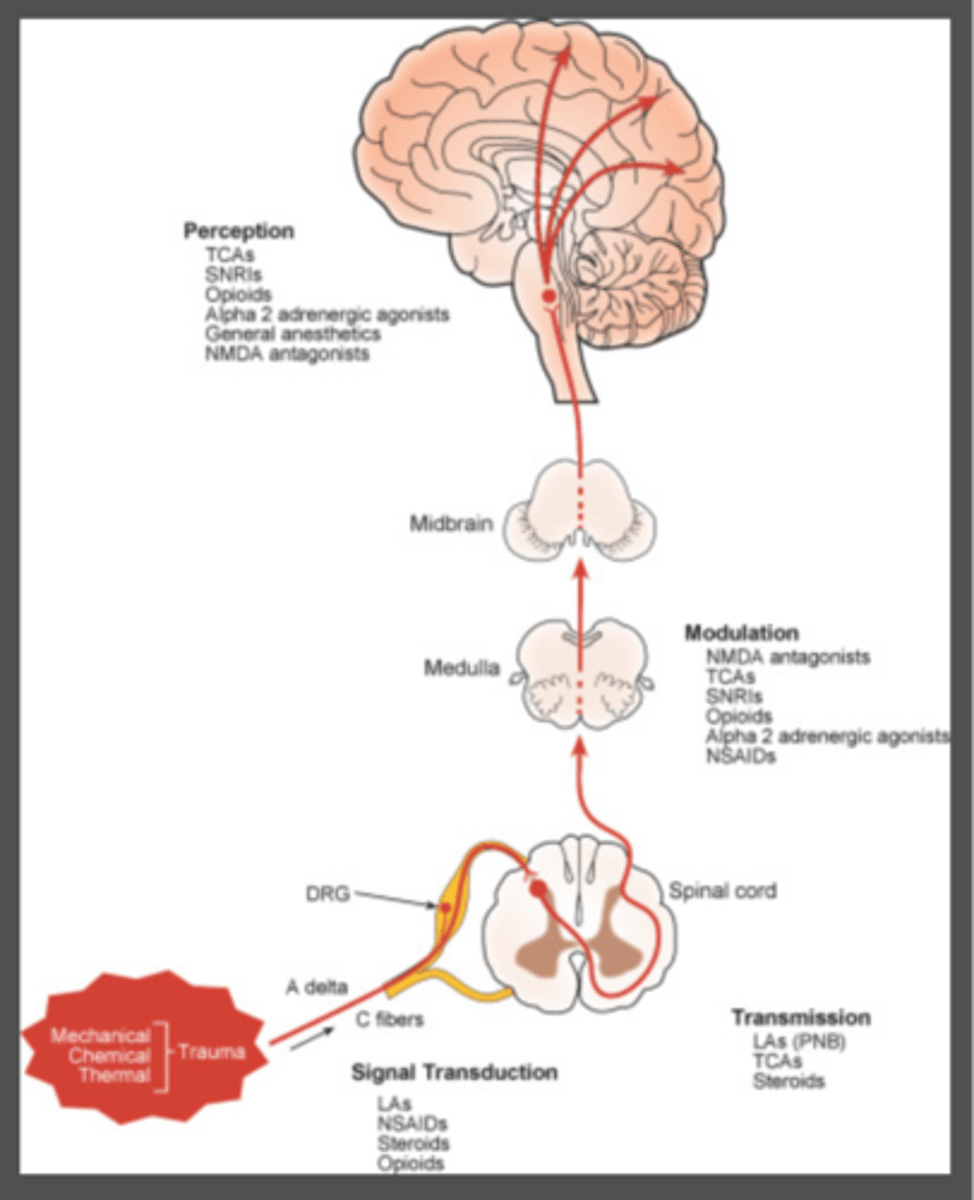
what medications act on perception of pain signals
1. GA
2. opioids
3. alpha 2 agonists
What are the groups of NSAIDS (5) and examples
Acetic acid- toradol
Oxicam - mobic
Propionic- Ibuprofen, naproxen
salicylate- aspirin
cox 2 selective- celebrex
MOA of NSAIDs
blocks COX-1 and 2 --> decreased prostaglandin synthesis from arachidonic acid --> decreased nociception and tissue damage/inflammation
The 3 main properties of NSAIDS
antipyretic
analgesic
anti inflammatory
what type of pain responds to NSAIDs the best
nociceptive
NSAIDs are mostly metabolized in the _______________ with excretion into __________________
liver; urine/bile
responsibilities of COX- 1
1. plt aggregation (via thromboxane A2)
2. gasric mucosal integrity
3. renal fx
inhibition of COX-1 -->
1. gastric irritation
2. renal microvascular constriction
3. plt inhibition
COX_____ is widespread throughout the body, necessary for homeostasis and is working all the time
1
______________ is an inducible enzyme that releases prostaglandins in the presence of inflammation, comes into play when theres injury
COX-2
COX _________ mediates pain, fever, and carcinogenesis
2
inhibition of COX2 -->
analgesia
adverse reactions of NSAIDs
1. GI dyspepsia
2. renal dysfx
3. peptic ulcers
4. hepatocellular injury
5. asthma exacerbation
6. allergic reactions
7. tinnitus
8. urticaria
MOA of how NSAIDs --> GI toxicity
decreased prostaglandin synthesis --> decreases in GI blood flow and secretion of mucus
risk factors for GI toxicity with NSAIDs
1. high dose
2. older age
3. H. pylori infection
4. hx of prior ulcer
5. concominant use of low dose ASA, anticoags, or corticosteroids
conventional NSAIDs and COX-1 have what effect of platelets
impairs the ability of the plts to aggregate (i.e. activity)
T/F: COX-2 has no effect on plt aggregation
true