Ecological Relationships & Population Dynamic
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Population (definition)
Group of individuals of the same species living together in a habitat
Population dynamics (definition)
Study of changes that occur in a population and factors that cause these changes
Why do organisms live in populations?
Safer. Breeding. Habitat provides food and shelter
How is the size of a population controlled? (5)
Competition. Predation. Symbiosis. Parasitism. Emigration
Competition (definition)
When two or more organisms seek a resource that is in short supply in a habitat.
Contest competition (definition)
An active physical confrontation between two organisms in which only one wins the resource.
Scramble competition (definition)
A struggle between organisms for a scarce resource in which each organism gets some of the resource
Adaptation of plants to reduce competition for water or minerals
Different plants take water from different soil depths
Example of plant adaptation to reduce competition
Grass has shorter roots near the surface. Dandelions have long tap roots which get water from deeper soil
Adaptation of animals to reduce competition
Occupy different food niches
Examples of animal adaptation to decrease competition
Caterpillars eat leaves while greenflies eat the sap of roses
Predation (definition)
The act of hunting, killing, and eating prey
Predator (definition)
The organism that hunts, kills and eats its prey
Prey (definition)
The organism that is eaten by the predator
Structural adaptations of predators
Keen eyesight, smell, and hearing
Behavioural adaptations of predators
Catch easiest prey. Live in groups. Change diet and location
Structural prey adaptations
Protective structures (thorns/stings). Camouflage and warning colouration
Behavioural prey adaptations
Stay in large groups
Function of predation in overall scheme of nature
Population control
Draw a graph of a predator and prey relationship
…
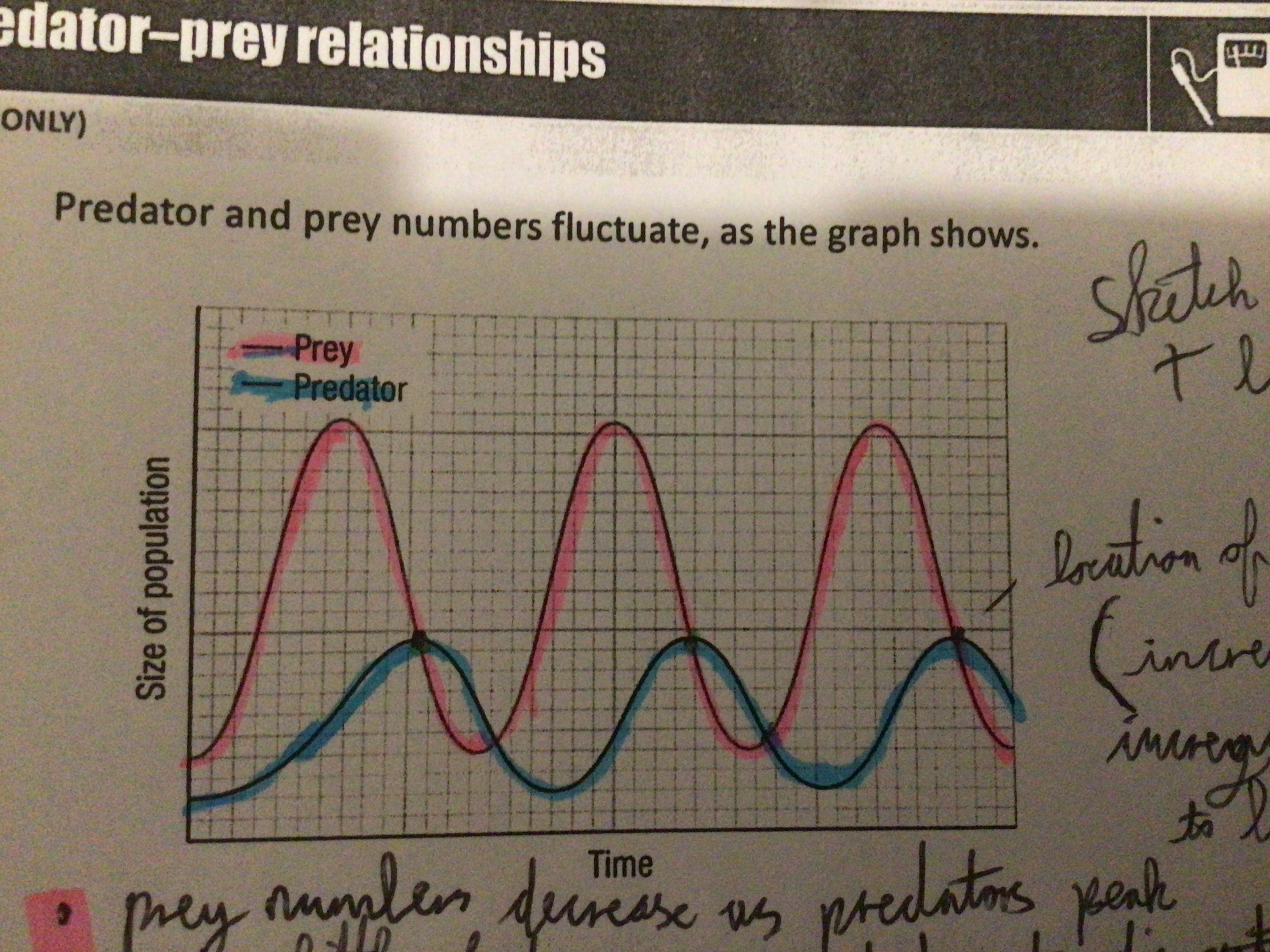
Explain the predator prey graph
Increase in prey due to decrease in predators. Predators increase due to abundant food. Prey numbers decrease. Too little food decreases predators. Prey population increases again.
Why is there a time lag on the graph?
Accounts for the time taken for predators to respond to changes in their prey
Why do predator numbers increase?
Immigration. Abundant food. Mates
Why do predator numbers decrease?
Prey numbers decrease. Disease. Emigration
Symbiosis (definition)
A close relationship between two organisms of different species in which at least one of them benefit
Parasitism (definition)
A relationship between two organisms of different species living together where one benefits and does harm to the other.
Stage 1 of the population curve (lag)
Little increase in population due to adjusting to their habitat
Step 2 of the population curve (log)
Population rapidly increases due to higher breeding because of plentiful resources
Step 3 of population curve (stationary)
Population number no longer increases death rate = birth rate
Step 4 of population curve (decline)
Lack of resources. Death rate > birth rate
Draw a population curve
…
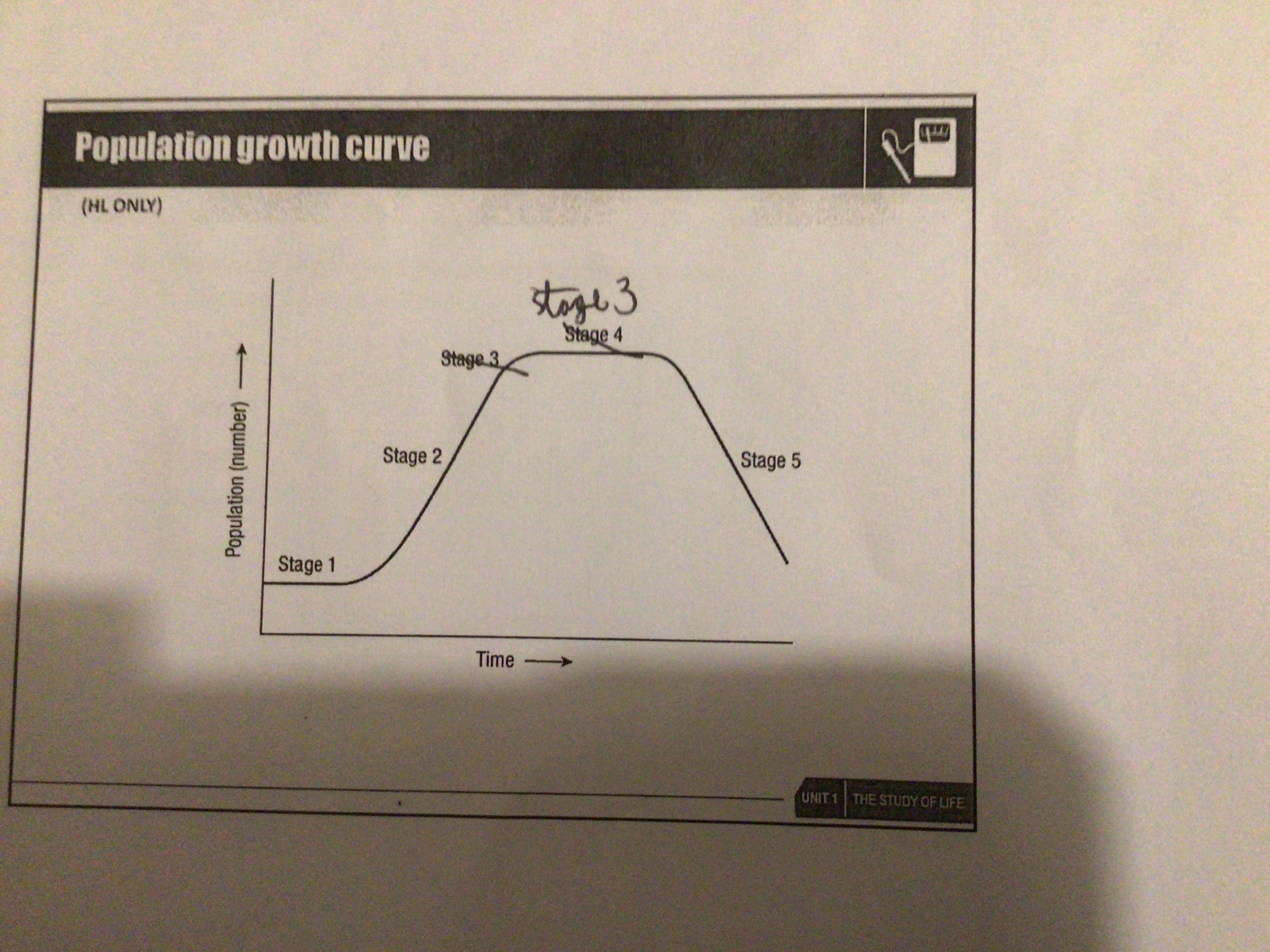
Why does population growth slow down?
Food starts to run out. Not enough room for breeding/overcrowding causes disease. More predators due to higher numbers
What caused the sudden growth in the human population?
Fewer infant deaths. Better sanitation and medicine.
What causes the human population to decrease? (4)
Famine. Disease. War. Contraception
Ectoparasites (definition)
Parasites that live on the outside of the host e.g. lice
Endoparasites (definition)
Lives inside the host e.g. tapeworm