AP Biology Unit 3 Exam
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/46
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
1
New cards
free energy
energy available in system to do work
2
New cards
breaking bonds ______ energy
require
3
New cards
forming bonds _____ energy
release
4
New cards
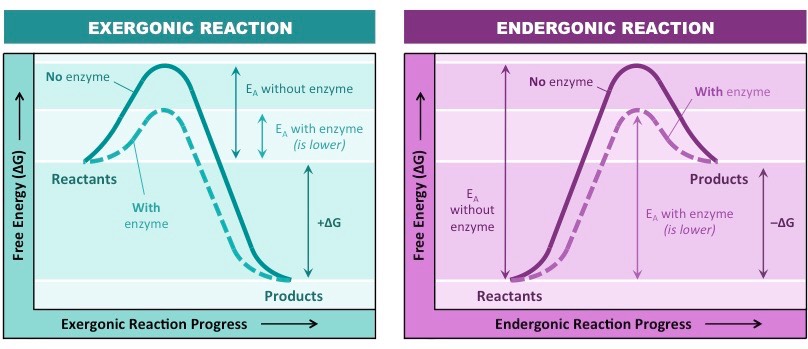
catabolic/exergonic
a polymer is broken down into monomers which increases entropy
5
New cards
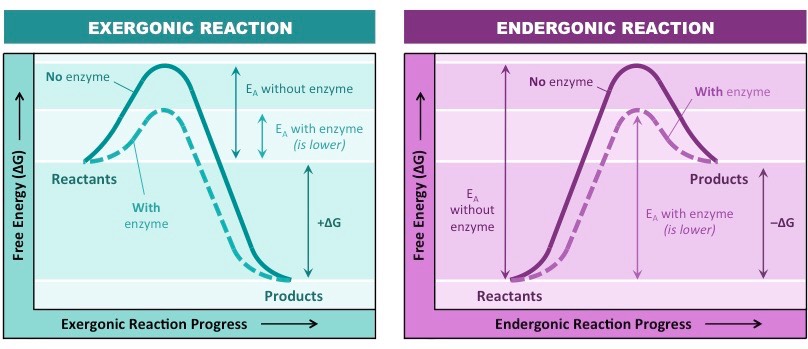
anabolic/endergonic
monomers form a polymer which decreases entropy
6
New cards
entropy
disorder and randomness
7
New cards
enzyme
speeds up reactions and reduces the energy required to carry out reaction without being consumed by the reaction
8
New cards
factors that affect enzymes
pH, heat, cold, competitive inhibitors, and non-competitive inhibitors
9
New cards
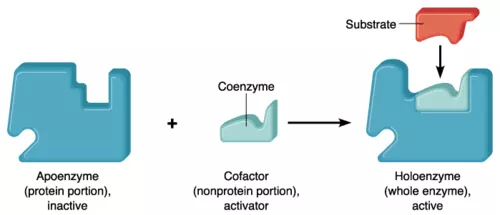
cofactors (inorganic ions) and coenzymes (vitamins)
bind near or at active site to provide appropriate shape or substrate to bind
10
New cards
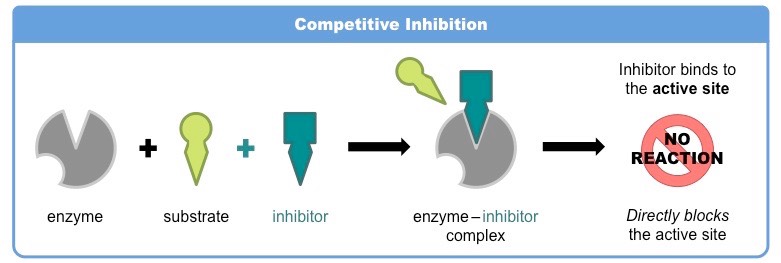
competitive inhibitor
binds to active site to block substrates with binding
11
New cards
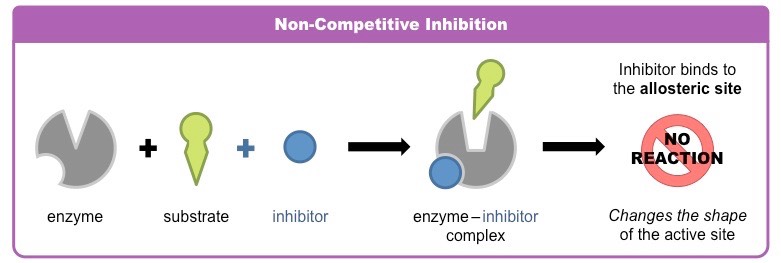
non-competitive inhibitor
binds to allosteric site which alters the shape of the active site, preventing binding of substrate
12
New cards
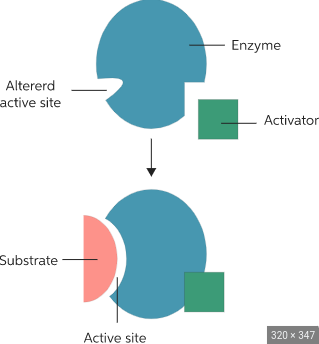
activator
binds to allosteric site to make the active site the appropriate shape to bind with substrate
13
New cards
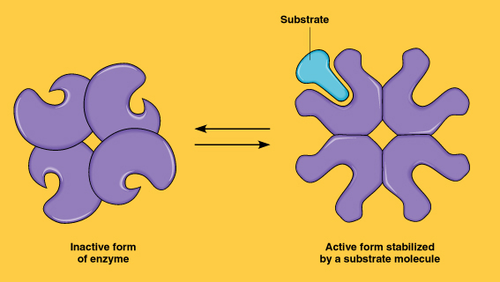
cooperativity
substrate itself is the activator for enzyme with quaternary structure
14
New cards
purpose of cellular respiration
create a usable form of energy for the cell
15
New cards
reactants in cellular respiration
glucose and oxygen
16
New cards
products of cellular respiration
water and carbon dioxide
17
New cards
what happens in glycolysis?
1 glucose molecule is broken down into 2 pyruvate molecules
18
New cards
other than pyruvate, what are the products in glycolysis?
2 ATP and 2 NADH
19
New cards
what is oxidized in glycolysis?
glucose
20
New cards
what is reduced in glycolysis?
NAD+
21
New cards
what is evidence glycolysis was earliest pathway to evolve?
does not require oxygen; Earth’s environment barely had oxygen long ago
22
New cards
what happens in the immediate step in cellular respiration?
the 2 pyruvate (3-carbon) lose a carbon each to produce 2 acetyl-CoA (2-carbon)
23
New cards
when pyruvate is turned into acetyl-CoA, what are the other products created?
2 CO2 and 2 NADH
24
New cards
what happens in the Kreb’s cycle (citric acid cycle)?
acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate form citric acid which then help generate electron carriers, NADH and FADH2 that bring electrons to the ETC
25
New cards
what is released through the Kreb’s cycle?
6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 2 GTP (ATP), and 4 CO2
26
New cards
proton-motive force
H+ concentration gradient; moves from high to low concentration
27
New cards
how is the proton-motive force created in oxidative phosphorylation?
NADH and FADH2 release their electrons into the ETC which helps pump H+ ions from low to high contentration using active transport which builds up H+ ions in the inner membrance space
28
New cards
how is ATP synthesized in oxidative phosphorylation?
H+ moves down concentration gradient through ATP synthase which provides energy for the formation of ATP from ADP and Pi
29
New cards
what is the purpose of photosynthesis?
to produce sugar for cellular respiration
30
New cards
reactants of photosynthesis
carbon dioxide and water
31
New cards
products of photosynthesis
sugar and oxygen
32
New cards
where do light-dependent reactions occur?
thykaloid membrane
33
New cards
what happens in the photosystems?
electrons of the chlorophyll are energized and enter the ETC
34
New cards
which photosystem does sunlight enter first?
photosystem II; once electrons are energized, it allows for the breakdown of water into oxygen and H+
35
New cards
purpose of the first ETC in photosynthesis
pumps H+ from the stroma into the thykaloid space in order to create a proton-motive force which is used in ATP synthesis
36
New cards
why do electrons enter another photosystem in photosynthesis?
electrons enter a second photosystem (photosystem I) to get re-energized by the sunlight and then enter the second ETC
37
New cards
purpose of the second ETC in photosynthesis
provide energy to form NADPH from NADP+ and H+
38
New cards
how do pigments in photosystem II re-generate electrons?
when water is broken down into oxygen and H+, electrons get replaced
39
New cards
why do light-dependent reactions switch to cyclic electron flow periodically?
because ATP is depleted quickly in the next phase (Calvin cycle), a cyclie electron flow quickens the ATP generating process
40
New cards
purpose of the Calvin cycle
use ATP and NADPH to convert CO2 to sugar
41
New cards
where does the Calvin cycle take place?
stroma of a chloroplast
42
New cards
first step of the calvin cycle: carbon fixation
enzyme, rubisco brings together 3 CO2 and 3 RuBP (5-carbon) to form unstable 3 6-carbon compounds which immediately breaks down into 6 3-carbon sugars
43
New cards
second step in the Calvin cycle: reduction
6 ATP phosphorolate (add phosphorus) 6 3-carbon sugars; 6 NADPH then reduce the 6 sugars to create 6 G3P; one G3P is released leaving 5 in the cycle
44
New cards
third and final step in Calvin cycle: regeneration
3 ATP are used to rearrage 5 G3P into 3 RuBP to restart the Calvin cycle again
45
New cards
primary productivity
measures how much solar energy is converted to organic compounds in a period of time
46
New cards
gross primary productivity (GPP)
total amount of oxygen or biomass produced
47
New cards
net primary productivity (NPP)
amount of oxygen or biomass left over after producers perform cellular respiration