PHARM Exam2- NeuroP- PNS
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Basic Principles of neuropharm
Divided into:
PNS (peripheral nervous system)
CNS
Drugs Cause: Excitation or suppression (of systems above)
Work to mimic or block neurological body processes
How Neurons send signals
Neuron reaches action potential threshold, sends aciton potential down axon
Releases neurotransmitter at synaptic cleft
Neutoransmitter binds to recepter sight on postsyanptic cell
Sites of action: Axon vs Synapsis
Axonal conduction: NOT selective (local anesthetic)
Some drugs will DECREASE or INCREASE conduction or the amoutn of aciton potential that fire, STOP ALL = NOT SELECTIVE
Synaptic transmission: Drugs that ALTER synaptic transmission, HIGHLY SELECTIVE
Receptor Action: IMPORTANT
Receptor: Ability of neuron to influence the behavior of another cell depends on ability of that neuron to alter receptor activity on target cell
Neuron influence depends on:
Receptor presence
Type
Sensitivity
Distribution
Makes sense just think about
Producing Effects
All neuropharm drugs (other than anesthetics) produce effect by ALTERING RECEPTOR ACTIVITY
May increase or decrease receptor activity
Activated receptor causes incrased likelyhood of postsynaptic neuron to do action potential
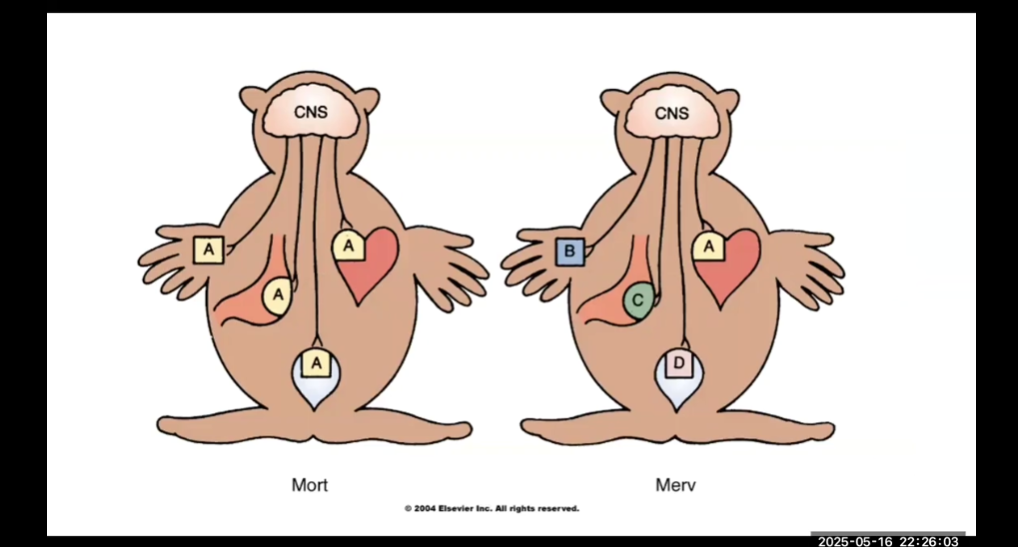
Mort and Merv
Mort- All organs have same type of receptor
Merv- Organs have different receptors
For MORT, drug selective action is NOT possible
More types of different receptors = better ability to have selective affect
Approach to learning about PNS drugs (3 things) + Isoproterenol examples
Type or types of receptors which drug acts on
The normal response to activation of receptors
What the drug in question DOES to the receptor (increase or decrease)
Isoproterenol: Old-school drug for heart problems
Acts on Beta1 and Beta 2 receptors
Normal Response
Beta 1 increase HR + Cardiac Contraction
Beta 2: Bronchial dilation + glucose elevation
What drug does
Cause activation of both receptors
Peripheral Nervous System Division
Somatic motor system: Muscles under voluntary control
Parasympathetic Nervous system/ AUTONOMIC: relaxed/normal body
Sympathetic Nervous system/ AUTONOMIC: Action, F or F
Functions of Parasympathetic: (9)
THINK ABOUT: CHOLINERGIC
Constrict pupils
Stimulate saliva
Slow heartbeat
Constrict airways
Stimulate stomach activity
Inhibit glucose release, stimulate gallbladder
Stimulate intestinal activity
Contract bladder
Promote erection
Overall function:
Digest food
Excrete waste
Control vision
CONSERVE ENERGY
Functions of Sympathetic (10) opposite of parasymp
THINK ABOUT ANDGRENGERIC
Dilate pupils
Inhibit salivation
Increase heartbeat
Relax airway
Inhibit stomach
Stimulate glucose release, inhibit gallbladder
Inhibit intestinal activity
Secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine
Relax bladder
Promote ejaculation and vaginal contraction
Sympathetic main function
Regulate cardiovascular
Regulate body temp
Fight or flight
Overview of autonomic nervous system
Dont have to think about
Regulate heart rate
Regulate secretory glands (salivary, gastric, sweat, bronchial)
Regulate smooth muscles (bronchi, blood vessels, urogenital, GI tract
Sympathetic Homeostatic Objectives
Maintain blood flow to brain
Redistribute blood flow during exercise
Compensate for blood loss, through vasoconstriction
Regulate body temp
Regulate cardiovascular
NOT JUST FOR F OR F
PNS and SNS Innervation
Structures under autonomic control INNERVATED BY BOTH PNS and SNS
Dual innervation = maintain homeostasis
Some times complementary (works together)
PNS cause erection
SNS cause ejaculation
SOME ONLY INNERVATED BY ONE
EX. Blood vessels only innervated by sympathetic (KNOW THIS)
Drugs affect blood vessels ONLY ACT ON SNS
Feedback regulation for single innervation + Baroreceptor reflex
Main elements: Think about thermostat
Sensor
Effector
Neurons connecting sensor to effector
Blood vessel BARORECEPTOR REFLEX (KNOW THIS)
MOST important feedback loop of ANS (regulates BP change)
Located in carotid sinus of aortic arch
If change in BP, detected by baroreceptor and send info to brain
Brain sends impulse along nerve to ANS
Decreased BP = vasoconstriction
Increased BP = vasodilation
Autonomic Tone vs Predominant Tone
Autonomic: Balance between PNS and SNS
Predominant: only one division provides basal control
Most organs predominant = PNS
Vascular system: predominant = SNS
Anatomic Considerations
PNS: 2 neurons in pathway from spinal cord to organ innervated by parasymp nerve
Neurons go from spinal cord to parasymp ganglia = (Pre ganglionic neurons)
Neurons from ganglionic to effector = (post ganglionic neuron)
Same for SNS
Spinal cord -(preganglionic neuron)-parasymp ganglia - (postganglionc neruon)- organ
Somatic Motor System: one neuron in pathway from spinal cord to skeletal muscle innervated by motor neuron (voluntary control)
Ganglion
Junction/Synapse between 2 neurons = GANGLION
Peripheral Nervous System Neurotransmitters
Acetylcholine: Most peripheral NS junctions (present everywhere (PNS, SNS, Somatic motor)
Norepi: released by postganglionic of SNS
Epinephrine: released by adrenal medulla
LOOK at Picture
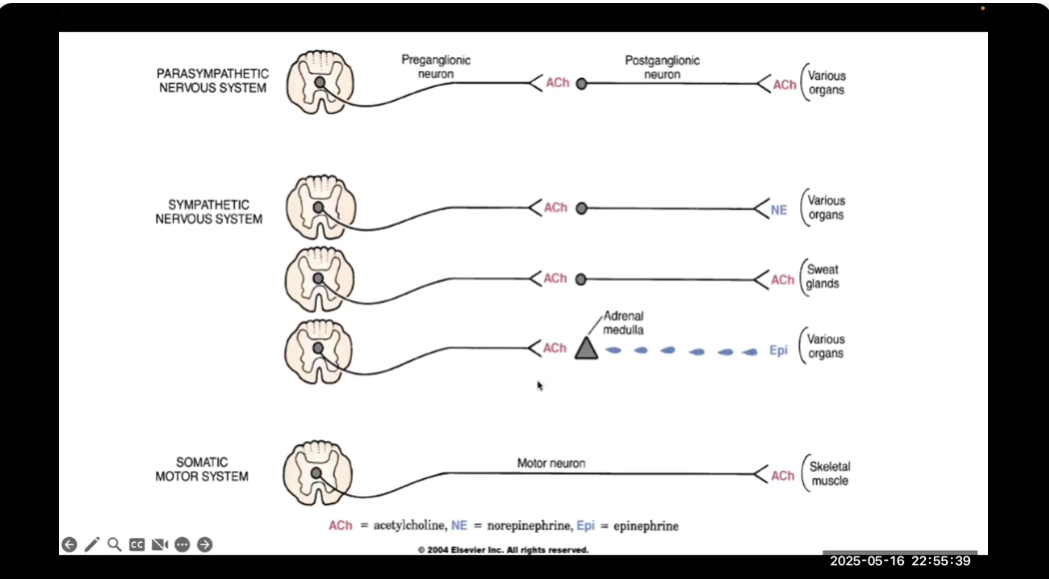
Peripheral NS Transmitters Cntd (picture expalantion) (6 things)
ALL preganglionic neurons of paraS + symp release acetylcholine
ALL postganglionic of parasymp release acetylcholine
Most postganglionic of symp release norepienprhine
Postganglionic of symp for sweat glands release acetylcholine
Epinephrine is principial transmitter released by adrenal medulla
ALL motor neurons to skeletal muscles release acetylcholine
Receptors of Peripheral Nervous
Cholinergic: mediated by acetylcholine
Nicotinic N
Nicotinic M
Muscarinic
Adrenergic: mediated by epinephrine and norepinephrine
Alpha 1
Alpha 2
Beta 1
Beta 2
Dopamine
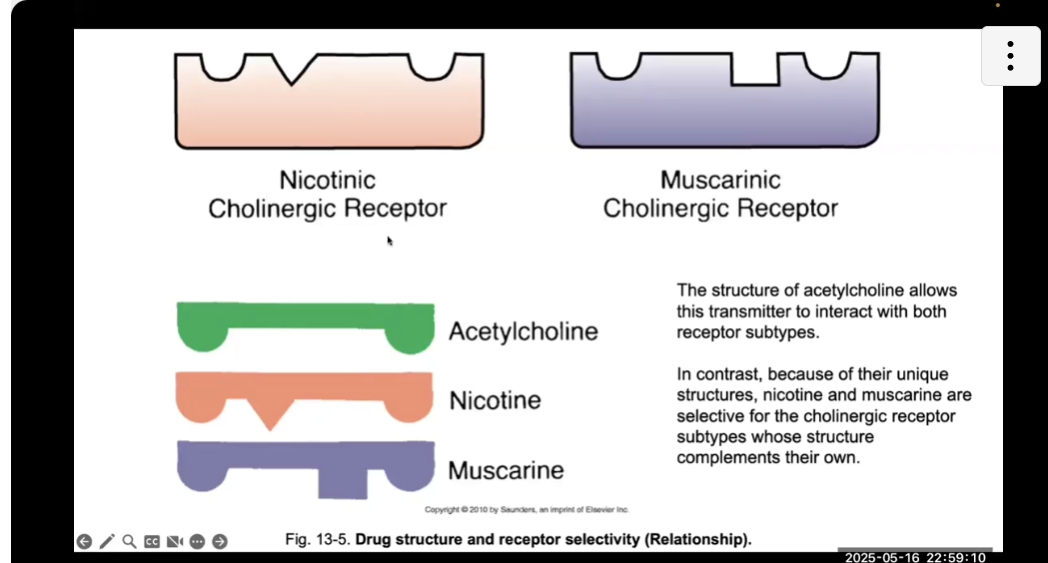
Receptor selectivity
LOOK AT PICTURE, Subtypes of receptors allow for MORE specialization
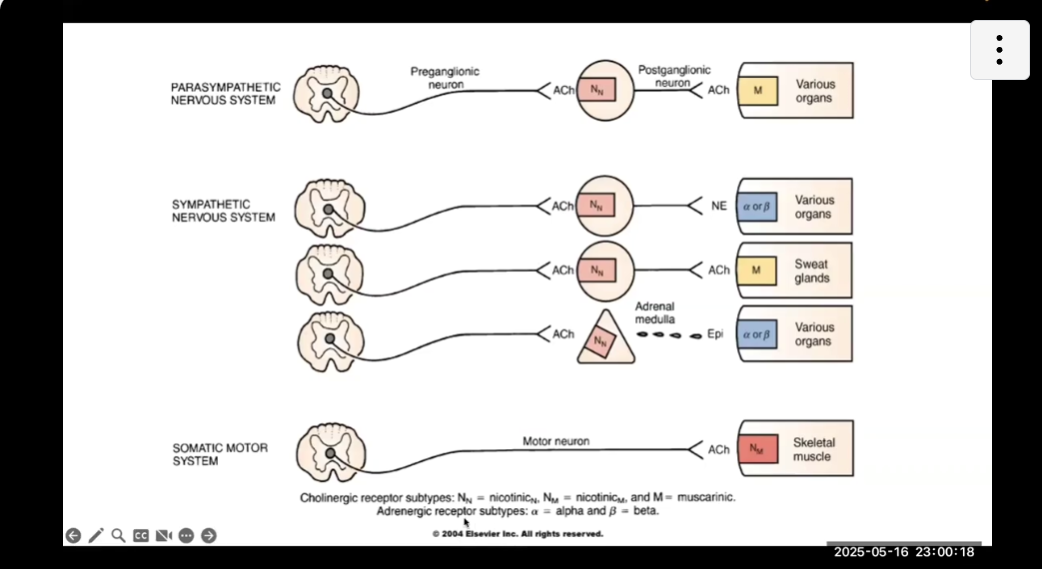
Receptors of Peripheral NS (ALL OF THE ONES IWTH PICTURES = IMPROATN)
Nicotinic N receptors are located on cell bodies of ALL POSTGANGLIONIC NEURONS of parasymp and symp
Nicotinic N also located on ADRENAL MEDULLA cells
Nictonic M located on skeletal muscle
Muscarnic receptors
On ALL ORGANS regulated by parasymp nervous (organs innervated by postganglionic parasymp)
On Sweat glands (think sweaty = musky)
Adrenergic (Alpha, Beta, or both)
Located on ALL ORGANS regulated by SYMPATHETIC (except sweat glands)
ALSO located on organs regualted by epinephrine from adrenal medulla
Functions of Cholinergic Receptor Subtypes
Nicotinic N (neuronal)
Promotes ganglia transmission by producing acetylcholine
Promotes epi release
Nicotinic M (muscle)
Contraction of skeletal muscle
Muscarinic
Activates parasymp NS
Activates sympathetic sweat glands
Andrenergic Receptor Subtypes
Alpha1: (ALL MAJOR SNS Stuff)
Vasoconstriction of arterials: skin, veins, mucous membranes, etc.
Ejaculation
Contraction: bladder + prostate
Pupil dilation
Alpha 2 (less clinically significant)
Located in presynaptic junction
Beta1: (1/2)
HEART
Increase HR, contraction force
Velocity of conduction in AV node
Beta1 (2/2)
KIDNEY
Renin release (to increase blood pressure)
Beta 2
Bronchial dilation
Relax uterine muscle
Vasodilation
Glycogenolysis (glycogen broken down into glucose for energy)
Dopamine
Dilates renal blood vessels
Receptor specificity of Adrenergic neurotransmitters/ CATECHOLAMINES (know this)
Adrenergic neurotransmitter = CATECHOLAMINES
Epinephrine can activate ALL alpha + beta but NOT dopamine
Norepi can activate alpha 1, alpha 2, beta 1, but NOT beta 2 or dop
Dopamine activate alpha 1, beta 1, dopamine
ONLY DOPAMINE CAN ACTIVATE DOPAMINE
Terminology (sympathetic and parasymp)
Sympathetic
Adrenergic
Anticholinergic
Sympathomimetic
Parasympatholytic
Cholinergic Blocker
Parasympathetic
Cholinergic
Antiandrenergic
Sympatholytic
Parasympathomimetic
Adrenergic blocker
Beta adrenergic blocker (beta blocker)
sympathetic inhibitor
Agonist = stimulate
Antagonist = inhibit
Cholinergic/ Parasympatheic NS drugs
Influence cholinergic receptors (most act directly)
Mimic or block acetylcholine
SOME influence cholinesterase (enzyme which breaks down acetylcholine)
Extensive toxicology of cholinergic drugs (nicotine, insecticides, chemical warfare)
Cholinergic vs Anticholinergic drugs
Cholinergic (parasymp)
Mimic acetylcholine
Stimulate cholinergic receptor
Direct stimulation with agonist
Release of acetylcholine
Inhibit acetylcholine breakdown/enzyme
Anticholinergic
Block action of acetylcholine
Cholinergic Drug Types (6)
Direct acting agonists
Indirect acting agonists
Muscarinic antagonist
Nicotinic antagonist
Cholinesterase reactivator
Cholinergic toxicity antidote
Direct Acting Agonist (Cholinergic)
Drug: Bethanechol (muscarinic), Pilocarpine, Cevimeline Nicotine
Receptor: Muscarinic, Nicotinic M and N
Action: Stimulate receptors directly
Uses: Urinary retention, dry mouth(cevimeline), glaucoma(pilocarpine)= increase fluids to eye, GERD (relax lower esophagus), illeus (help stimualte bowel movement)
Side effects: bradycardia, diarrhea, salivation, sweat
Can ALSO BE ADR if impact of these is serious
Contraindications:
Asthma: precipitates bronchospasm (tightening of airway/bronchoconstriction)
Mechanical obstruction in GI or ureters (too much movement can cause perforation)
Nurse implications; WATCH FOR CHOLINERGIC OVERDOSE
Extreme SLUDGE, use atropine as antidote
Indirect Acting Agonist (Cholinergic)// Cholinesterase inhibitors
Drug: Neostigmine (revers), Pyridostigmine (revers), Donepezil
Receptor: Acetylcholinesterase (AChE), inhibit ache allows action of acetylcholine to be prolonged NOT INCREASING ACH, just allowing more to be used
Action Inhibit ACh breakdown, to increase ACH at synapse
Uses: Myasthenia gravis (chronic autoimmune neuromuscular disease), Alzhemier’s for memory, reversal of NMJ block
Other uses: Insecticides, chemical warfare
Side Effects: SLUDGE (salivation, lacrimation, urination, dirrhea, GI upset, emesis) lacrimation = tear flow
Contraindication: patients with bradycardia, urinary or GI obstruction (will make HR TOO slow or cause perforation with obstruciton)
Muscarinic Antagonist (Cholinergic)
Drug: Atropine, Scopolamine(motion sickness), Ipratropium
Receptor: Muscarinic
Action: BLOCK M receptors
Uses: Bradycardia, motion sickness blocks muscarninic in CNS, COPD/Asthma think BRONCHOSPASM, diarrhea,
Side Effects: dry mouth, blurry vision, urinary retention, confusion
Nicotinic Antagonists (Cholinergic)
Drugs: pancuronium, Succinylcholine (M)
Receptor: Nicotinic M and N
Action: BLOCK Nic N and M at NMJ, blocks acetylcholine from binding
Use: Muscle relaxation during surgery, intubation
Does NOT cause patient to lose consciousness/go to sleep just paralysis of muscles
Can STILL FEEL PAIN
Side effects: Respiratory paralysis (that’s why only use with intubation), hyperkalemia (depolarization of muscle receptors = efflux of K)
Reversible: Use anticholinesterase inhibitor (neostigmine, etc.)
Cholinesterase Reactivator (Cholinergic)
Pralidoxime (2PAM)
Receptor: Enzyme- AChE
Action: Reactivate AChe after organophosphate poisoning
Use: Organophosphate toxicity WITH atropine (other antidote drug)
Side effects: hypertension or muscle rigidity
Cholinergic Toxicity Antidote (Cholinergic)
Atropine: ATROPINE IS SYMPOTHETIC AND OPPOSITE TO CHOLINERGIC hence why its an antidote
Receptor: Muscarinic
Action: Competitive antagonist at M receptor
Use: antidote for organophosphate or mushroom poisoning
Side effects: anticholinergic toxidrome if overdosed
Cholinergic Effects: SLUDGE
Salivation
Lacrimation (crying)
Urination
Defecation
GI Distress (cramps)
Emesis (vomiting)
THINK: REST AND DIGEST
Anticholinergic Effects
Flush Skin/ Red skin
Dry mouth,eyes, skin
Dilated pupils
Confusion
Fever
Urinary retention
THINK FIGHT OR FLIGHT
Cant see, cant pee, cant spit, cant shit
Muscarinic Agonists (CHOLINERGIC EFFECTS)
Heart: Bradycardia
Exocrine glands: increase sweat, salivation, bronchial secretion, secretion of gastric acid
Smooth Muscle
Lung contraction
GI tract increase motility
Bladder contraction
Vascular relaxation/dilation
Pupillary constriction (dont need wide view)
Reversible vs irreversible cholinesterase inhibitors/ indirect cholinergic agonists
Irreversible
SAME action as reversible
Longer acting
Used PRIMARILY FOR GLAUCOMA (very low concentration is poisonous in moderate to high dose) because you want it to tstay for a long time DUH
Common in insecticides
Myasthenia Gravis (MG) Treatment
MGL autoimmune disorder leading to weakness of voluntary skeletal muscles
Drug type: acetylcholinesterase inhibitor/ indirect cholinergic agonist
Direct are LESS specific for MG, often activate muscarninc and NOT nicotninc M whihc is necessary here
Drugs: Pyridostigmine
DOSING is INDVIDIUALIZED
Have patient keep record of symptoms and drug affect to determine dose
Do proper assessment after drug: muscle strength, side effects, fatigue onset, etc.
Pt teaching
Overdose (SLUDGE)
Myasthenia crisis
MG ADRs
Cholinergic Crisis: Overdose
Acetylcholine accumulates at all muscarinic and neuromuscular junctions
Skeletal muscle paralysis + respiratory distress due to paralysis
SLUDGE symptoms (due to overstimulation)
Antidote = ATROPINE (anticholinergic)
Myasthenia Crisis: Underdose
Too little medication
EXTREME muscle weakness
Dangerous due to respiratory distress
Antidote: Cholinesterase inhibitor (neostigmine)
Nondepolarizing vs Depolarizing Nicotinic antagonist
Nondepolarizing:
Prevent acetylcholine from binding at NMJ receptors so that no muscle contraction occurs
Depolarizing:
Binds to nicotinic M receptor, mimcs acetylcholine
Depolarizes, causes muscle contractions to depolarize = nerve blockage
Short acting
END RESULT IS SAME FOR BOTH
Nicotinic antagonist Nursing Implications
Patient is STILL ABLE TO FEEL, but cant talk, breathe, or move
Make sure to TALK WITH THE PATIENT
Sympathetic Nervous System Drugs
Mechanism of Adrenergic Receptor Activation
Direct receptor binding
Promotion of NE (norepinephrine) release = more available in synapse
Inhibition of NE reuptake = more available because NOT taken up and removed
Inhibit of NE inactivation = more available
Adrenergic Agonist
Alpha adrenergic: Vasoconstriction
Beta adrenergic
Beta 1: increased heart
Beta 2: bronchodilation of lungs and peripheral blood vessels
Dopaminergic: Dilation of kidney vasculature
Adrenergic Drugs Classes
Direct Acting Agonists
Indirect Acting Agonist
Mixed acting agonist
a1 agonists
a2 agonist
b1 agonist
b2 agonist
Non selective a blocker
Selective a1 blocker
Nonselective b blocker
B1 selective blocker
Mixed a/b blocker
Direct Acting Agonist (Adrenergic)
Drugs: Epinephrine, NE, Dobutamine, Albuterol, Dopamine
Receptor: A or B receptors
EPI = A1,A2,B1,B2
Albuterol = B2
Isoproterenol = B1B2
Action: Directly stimulate adrenergic receptors
Clinical use: anaphylaxis (Epi: blood flow, airway, and heart rate help), cardiac arrest, asthma, shock
Side effects: hypertension, tachycardia, arrythmias, tremors
Indirect Acting Agonists (Adrenergic)
Drugs: Amphetamines, Tyramine, Cocaine
Receptor: Increase NE release or block reuptake
Action: Increase synaptic NE
Uses: ADHD, narcolepsy, nasal decongestion, local anesthesia. adjunct
Side Effects: Anxiety, increased BP/HR, insomnia, addiction (for some)
Mixed Acting Agonist (Adrenergic)
Drug: Ephedrine
Receptor: Direct and indirect
Action: stimulate receptors and promote NE release
Use: Hypotension, nasal congestion
Side effects: Insomnia, tachycardia, CNS stimulation
A1 Agonist (Adrenergic)
Drug: Phenylephrine
Receptor: A1
Action: Vasoconstriction + Increase BP
Use: Nasal decongestion, hypotension, hemostasis (STOP BLEEDING, vasoconstriction at injury sitei)
Side effects: Reflex bradycardia, hypertension
ADR: Necrosis: If IV line is employed with this med and it seeps out it will cause tissue death due to vasoconstriction
Bradycardia
A2 Agonist (Adrenergic) Centrally acting
Drug: Clonidine, Methyldopa
Receptor: A2(central)
Action: Decrease sympathetic outflow from CNS = decrease BP
Uses: Hypertension, ADHD, withdrawal symptoms
Side effects: Sedation, rebound hypertension (if you discontinue drug abruptly blood pressure can skyrocket) , dry mouth
B1 Agonist (Adrenergic)
Drug: Dobutamine
Receptor: B1
Action: Increase heart rate + contractility
Use: Acute heart failure, cardiogenic shock, AV heart block to enhance AV conduction impulse, cardiac arrest
Side effects: Tachycardia, arrythmia, angina, pectoris (increase cardiac oxygen demand
B2 Agonist (Adrenergic)
Drug: Albuterol, Salmeterol
Target: B2
Action: Bronchodilation, smooth muscle relaxation
Use: Asthma, COPD, premature labor (tocolysis), Gluconeogenesis= make glucose
Side Effects: Tremor, tachycardia, hypokalemia, gluconeogenesis = hyperglycemia (BE CAREFUL WITH DIABETICS)
Nonselective A blockers (Adrenergic)
Drugs: Phentolamine, Phenoxybenzamine
Receptor: A1 and A2 (get it, non selective)
Action: Blocks A receptors = vasodilation
Use: Pheochromocytoma, extravasation reversal
Side effects: Orthostatic hypotension, Reflex tachycardia
Selective A1 Blockers (Adrenergic)
Drug: Prazosin, Terazosin
Receptor: A1
Action: Vasodilation of arteries and veins
Use: Hypertension, BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia) = due to dialating ureter allowing for urination, pheochromocytoma (tumor causes hypertension)
Side Effects: First dose + orthostatic hypotension, dizziness, reflex tachycardia, nasal congestion, inhibit ejaculation
B Blockers (Non selective) (Adrenergic)
Drugs: Propranolol, Nadolol
Receptor: B1 and B2
Action: Decrease HR + contractility, bronchoconstriction
Use: Hypertension, angina pectoris, migraine prophylaxis, AFIB (heart rate fast + irregular), stage freight or anxiety (IN LOW DOSES)
Side Effects: Bradycardia, bronchospasm (AVOID WITH ASTHMA), fatigue, high blood sugar due to inhibit of glycogenolysis ? what
NURS IMPL:
Caution with diabetics and asthmatics
Monitor for adverse reactions
Monitor vitals: Cant give when BP and HR is TOO LOW
Can also give orthostatic hypotension
B1 Selective Blockers (Adrenergic) also called CARDIOSELECTIVE
Drug: metoprolol, Atenolol
Receptor: B1
Action: Cardioselectivity: Decrease HR and contractility
Use: Hypertension, heart failure, post MI
Side Effects: Bradycardia, fatigue, masks hypoglycemia symptoms
Mixed A/B Blockers (Adrenergic)
Drugs: Labetalol, Carvedilol
Target: a1, b1, b2 NOT a2 because a2 decreaess SNS form CNS so it would do opopsite
Action: Decrease HR and vasodilation
Use: Hypertensive emergencies, heart failure
Side effects: Hypotension, dizziness, fatigue
Catecholamines
Catecholamines
Norepinephrine and Epinephrine
Do NOT cross the blood brain barrier (unlike Non catecholamines)
B1 Adrenergic Receptor = stimulate cardiac activity
B2 Adrenergic Receptor = Lungs, smooth muscle and bronchial relaxation
THINK: 1 heart, and 2 lungs
Dopamine Receptor Activation: Clinical Consequences
Activation of peripheral dopamine receptors = DILATION OF KIDNEY VASCULATURE
Dopamine
Dopamine receptors: dilates renal blood vessels, increase renal perfusion, prevents renal failure
GIVE DOPAMINE FOR RENAL FAILURE
Urine output SHOULD increase
For SEPSIS/Shock, give higher doses of dopamine to get organs moving and increase HR and BP
Catecholamines vs Non catecholamines
Cat:
CANNOT be used orally, destroyed by MAO and COMT enzymes
Brief active period
CANNOT cross BBB (due to being polar)
Drugs:
Epi
NE
Isoproterenol
Dobutamine
Dopamine
Noncat
CAN be given PO
Metabolized slowly by MAO = longer half life
More able to cross BBB
Drugs:
Ephedrine
Phenylephrine
Albuterol
TAKE A LOOK AT PICTURE
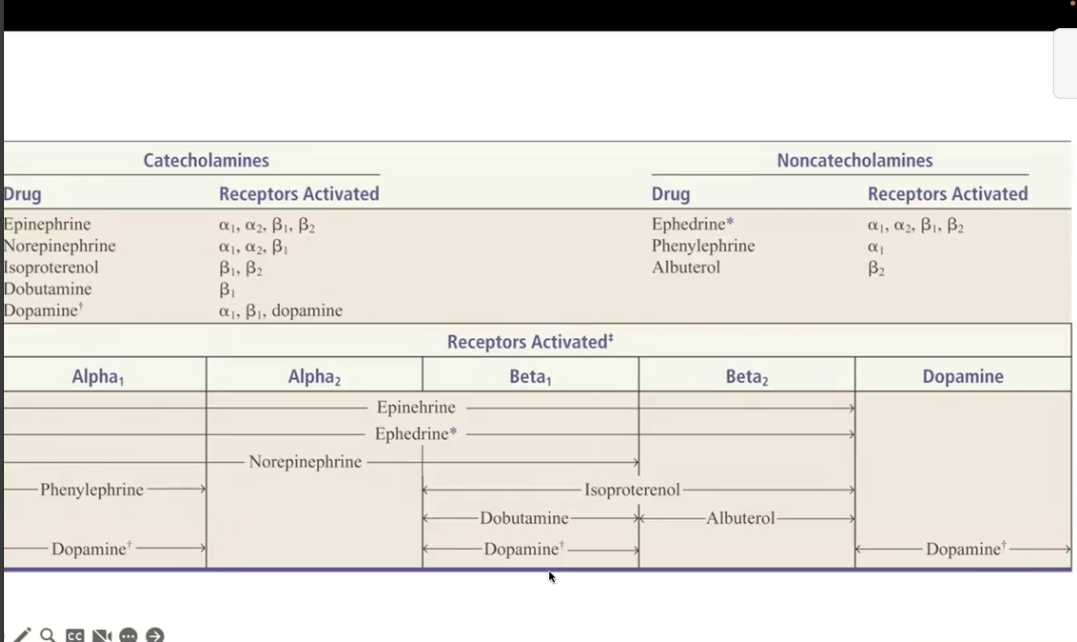
Albuterol Specific (Direct agonist)
Beta 2 receptor acting
NON-CAT
Use; Asthma
Side effects: minimal at therapeutic dose, tachycardia, tremor
Isoproterenol (Direct agonist)
Receptor: B1 and B2
CAT
Use: bradycardia, heart block, asthma (albuterol is better), anesthesia
Side effects: tachy, angina (chest pain due to low blodo to heart), hyperglycemia
Epinephrine: Adrenalin, Epipen (Direct agonist)
ALL ALPHA AND BETA
CAT
Vasoconstriciton
Uss: Asystole/heartblock, anaphylactic shock
Side effects: Hypertensive crisis, dysrhythmia, angina pectoris, necrosis from escaped med, hyperglycemia
Treatment of Anaphylactic Shock
Epinephrine can reverse most sever manifestations
A1 = vasoconstriction
B1 = Increased heart rate
B2 = open airways
DOPAMINE, DOBUTAMINE, EPHEDRINE
Have to look these up?, really just know general class stuff
Adrenergic Antagonist/ Blockers: Selective vs Nonselective
Alpha:
Nonselective: produce A1, A2 blockade
Phentolamine
Selective
Produce a1 blockade + prazosin
Beta:
Nonselective: Blocks B1 and B2
Propranolol
Cardio selective: Blocks B1
Metoprolol
Adrenergic Neuron Blocking Drugs: IS THIS SAME AS Mixed AB block?
Drug: Reserpine
Action: Decrease release of NE from ALL postganglionic sympathetic neurons
Decrease activation of ALL adrenergic receptors: Combo alpha and beta
Use: Hypertension
ADR: Depression, bradycardia, hypotension