HECOL 268 - Chapter 11 - the romantic period (1820-1850) and part 2 - the early victorian
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
what is and kind of reaction was the romantic period (1837-1850)?
artistic, literary and intellectual
reaction against the age of enlightenment and its classical focus on reason
what did romanticism emphasis on and what interest in history did they have?
emphasis on emotion and sentiment, imagination was more important than reason
interest in history: middle ages, renaissance and a focus on orientalism
what was tailoring like and what was introduced to make things easier?
Tailoring changed to a mathematical systems
2nds quarter of the 19th century: tape measure introduced and generally accepted
what was dyeing clothing like and what major contributions were made?
Diderot's alchemical charts of affinities (1778)
created Current chemical elements of the period element
what was photography like?
From the 1840s on, photography documented the way people dressed - chemical photography in the past
discovered by louis daguerre - 1839
<<Not just elite allowed to commission a portrait but also normal people>>
true or false: the industrial revolution had a major impact on textile manufacturing, making it easier for the general population to acquire fabrics for clothing at a reasonable cost
true
what machines were produced during this era?
sewing machines: develop in substantial ways in the 1830s and 1840s
knitting frame: 1840s development of a power-driven knitting frame could make seamless hosiery
lace machine: by 1840s most lace patterns could be made by machine
what simulated the slave trade in america during this time?
the need for labor growing and harvesting cotton to feed the textile mills
what did all these technological advances in clothing construction and production lead to?
large immigrant work force
more women working outside the home
transformation in how and where clothing was produced
end of 19th c. = much ready-made clothing was available
what culture transformation happened during this era?
1830s = first american fashion magazines are published latest styles from the center of fashion, paris, to women of various classes
godeys ladys book (magazine)
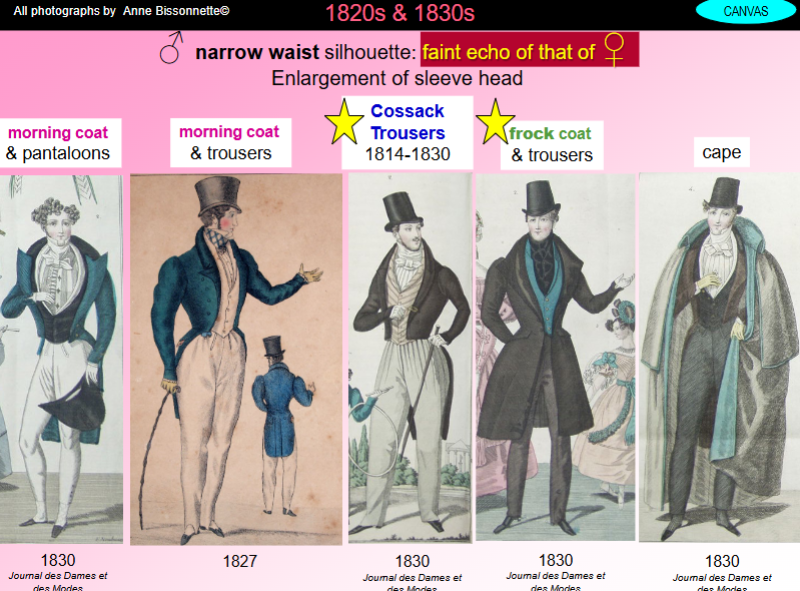
how were menswear (1820s and 1830s)?
Mens narrow waist silhouette: faint echo of that of a womenswear - hourglass silhouette
Enlargement of sleeve head (shoulder)
Cossack trousers
Frock coat with flared skirts (fully skirted coat)
Frock coat and fancy dress
Decorative waistcoats
Fad for plaid
how were generally the womenswear (1820s and 1830s)
‘A’ line with greater volume at sleeve and skirt
Waist moves back to normal level
Waist lowers
Horizontal necklines
Sleeve grows (head 1st)
Wider hem volume

what were Romantic period (1820-50) - women's undergarments?
Drawers or pantalettes
Chemise
Corset
Sleeve pads
Bustle pad (if need be)
Multiple petticoats (starched corded or quilted) (single petticoat is rare)
how were the sleeves for womenswear?
Great variety of sleeves
Volume migrating from head to sleeve to wrist
Leg-of mutton/ gigot sleeve (wide shoulder)

how was the hair for womenswear?
Transition from close-to the-head naturalistic hairstyles with side curls and chignon(bun), to hair “en coques” with hair extensions to create large volumes, hair combs
Heads also treated to exotic and historic styles
Coils of hair in ringlets = 17th century/ or over the ears = medieval

what additional accessories existed for womenswear?
Dress often included embroidered fine white cotton collars and caps, including a cape-like garment called a pelerine
The return of the ferroniere
Ruff (ruffles around the neck like elizabeth) and boa (feathers as a scarf)
what popular outdoor items?
overcoat, pelisse/coat dress (seen in image)
more practical attire as active wear
mantles/capes
orientalism (burnous)

what major event happened in Britain 1837?
a Queen ascended the throne, a young woman named victoria, whose reign was to continue until 1901
<victorian era fashion is more after queen victorias reign, victoria did not bring fashion but she followed fashion (ex. Hairstyle from classical revival)
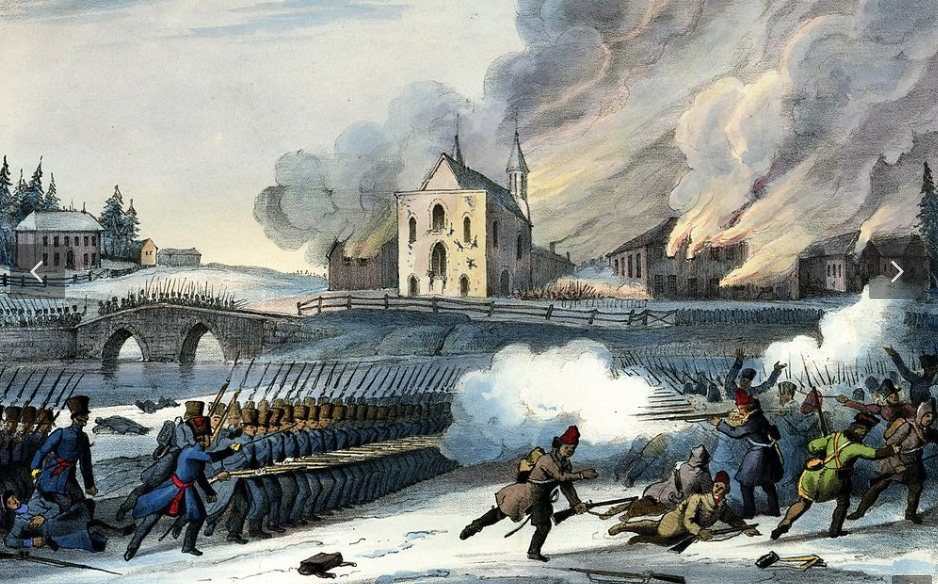
what was the lower canada rebellion?
1837-38, armed conflict, activists in lower canada (quebec) began to work for reform of the economic disenfranchisement of the french speaking majority and working-class english-speaking citizens
red cap of liberty and capote (coat of wool trade blankets)
discrimination against french people, french people had to change their last name to a british last name to get a job

what major science and technology events happened in the victorian era
<< 1838 - first photograph of a human we know of that doesn't take hours and only about 15 min >>
From the 1840s on, photography documented the way people dressed
Frederick douglas: anti-slavery reformer who was a former slave
Kate mcdougall
what major cultural movements happened (specifically for women)
Mid-19th century campaigns for voting rights for women
1792 - mary wollstonecraft fought for women to be considered as full citizens did not succeed however they started a process rolling
1848 - elizabeth cady stanton and susan b anthony comes together to organize a wave of feminism, very white :(
Sojourners truths “aint I a women?, 1851
Cyril jessop member of the legislative assembly of alberta 1921-26
what happened during the california gold rush (1848-1855)
Levi’s jeans originated during the California Gold Rush in 1848 when miners needed durable pants for their work
Tailor Jacob Davis added rivets to reinforce the pockets, and Levi Strauss, a fabric supplier, patented the design. Over time, Levi’s jeans evolved, with key developments including the addition of a double arc design on the pockets in 1873, a leather patch in 1886, belt loops in 1922, and a red tab trademark in 1936. Zippers were added in 1954
Levi’s jeans became a staple for workers and later a popular fashion item.
1820s-1840s menswear
Outdoor mens wore capes for more formal occasions (<< evening occasions>>)
Indoor mens continued to wear dressing gowns and banyans at home
Late 1830s-1840s dress
Late 1830s: elbow volume for women but soon sleeve is tight all over; facial hair for men: sideburns reach enormous proportions
Mens styles, like womens, became more subdued in the last decade of the romantic period
Exoticism in undress for men (<, garments and accessories)

1840s dress and what are the negative effects of it
Sleeve: usually narrows and waist often pointed in front
Skirt: long and voluminous
Subdued (dim)
<< instead of light, garments start to be dark, black satin etc, some lighter pants but suit then becomes all dark>>
<< men garments are fitted and women garments are voluminous (many petticoats) with tight underneath (corsets)>>
<< start to see garments igniting and they cant get out of the garments fast enough and end up burning, a problem while cooking>>
<< dirts, garments trailing on the floor, uncomfortable, dangerous (igniting) so we start to see dress reform movements and women saying no they will not wear this>

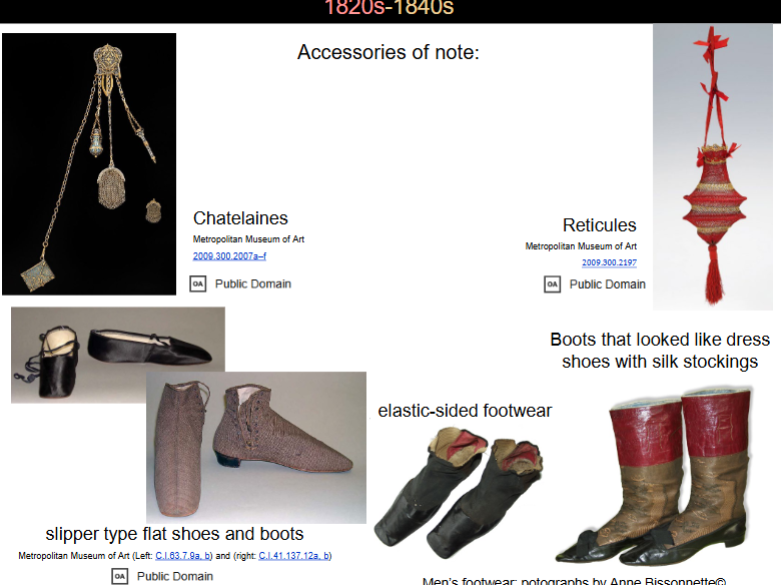
accessories in 1820s-1840s
Chatelaines: return of the medieval style
Reticules: a return of it and more elaborate
Slipper type flat shoes and boots
elastic -sided footwear
Boots that looked like dress shoes with silk stockings
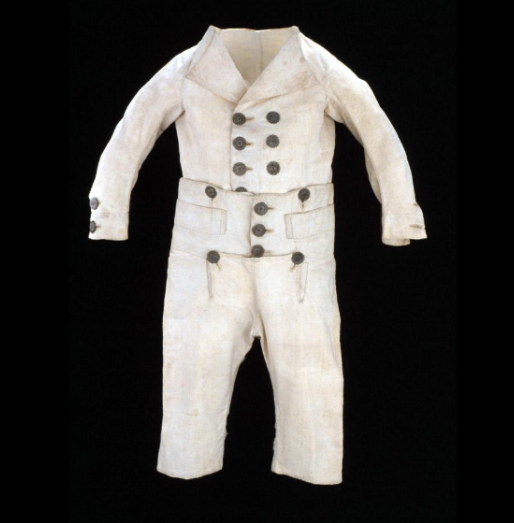
childrenswear
Children were dressed like small adults, except for small boys who wore skeleton suits (1780s until ca. 1830) or skirted garments until age four or five
(skeleton suit, colonial williamsburg)
The clothes of small boys could be very similar to their mothers

true or false: they stopped sexualizing children
false, Late 1830s and 1840s, children were dressed like small adults more and more (idea of a small waist, sexualizing children)