BE 450 PPT 8 Chemical and Biological Properties - Exam 2
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
spectroscopy, chromatography
characterization of biomaterial properties relating to the chemical composition can be accomplished through what 2 techniques?
spectroscopy
measure the interaction between light and matter
chromatography
molecules are physically separated on the basis of chemical characteristics (charge or MW)
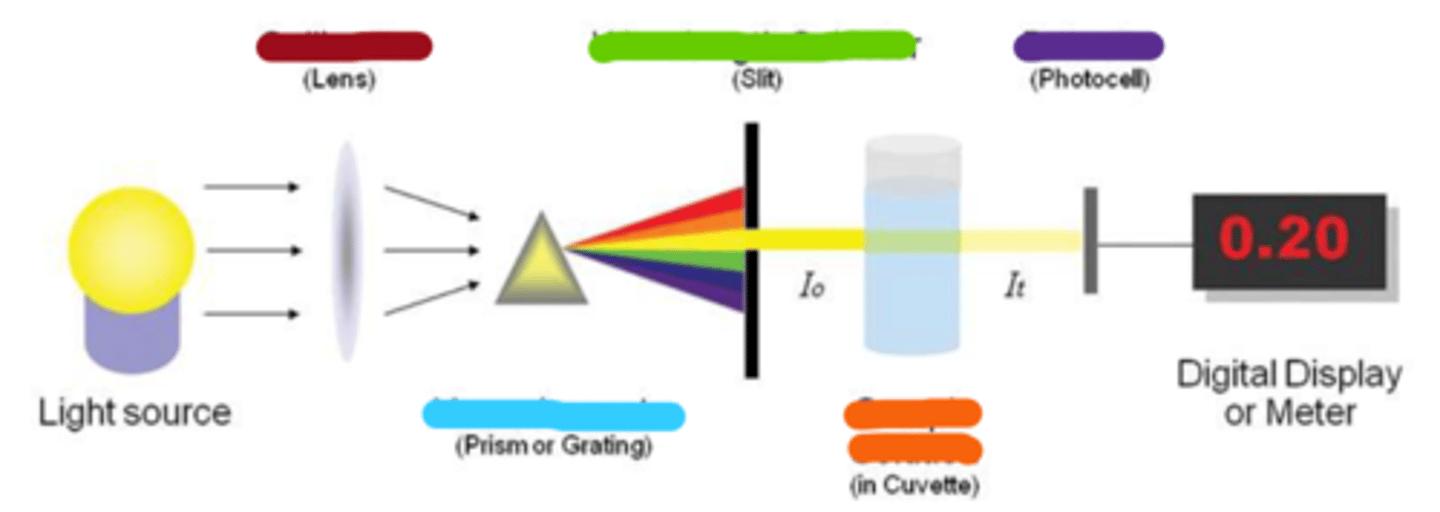
collimator
red
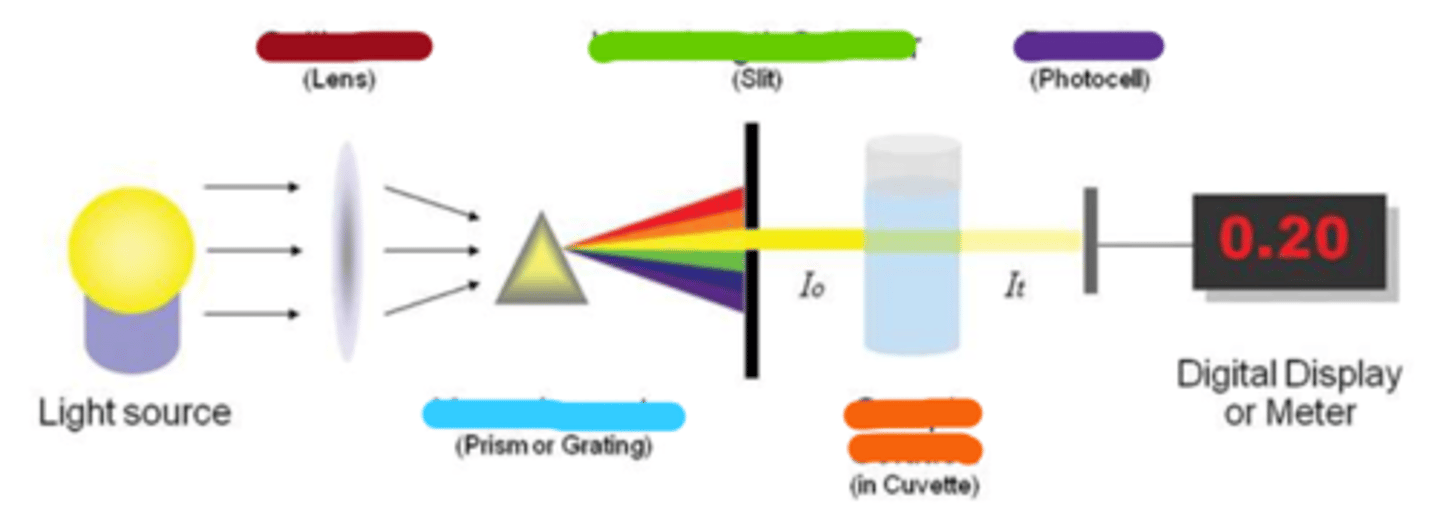
wavelength selector
green
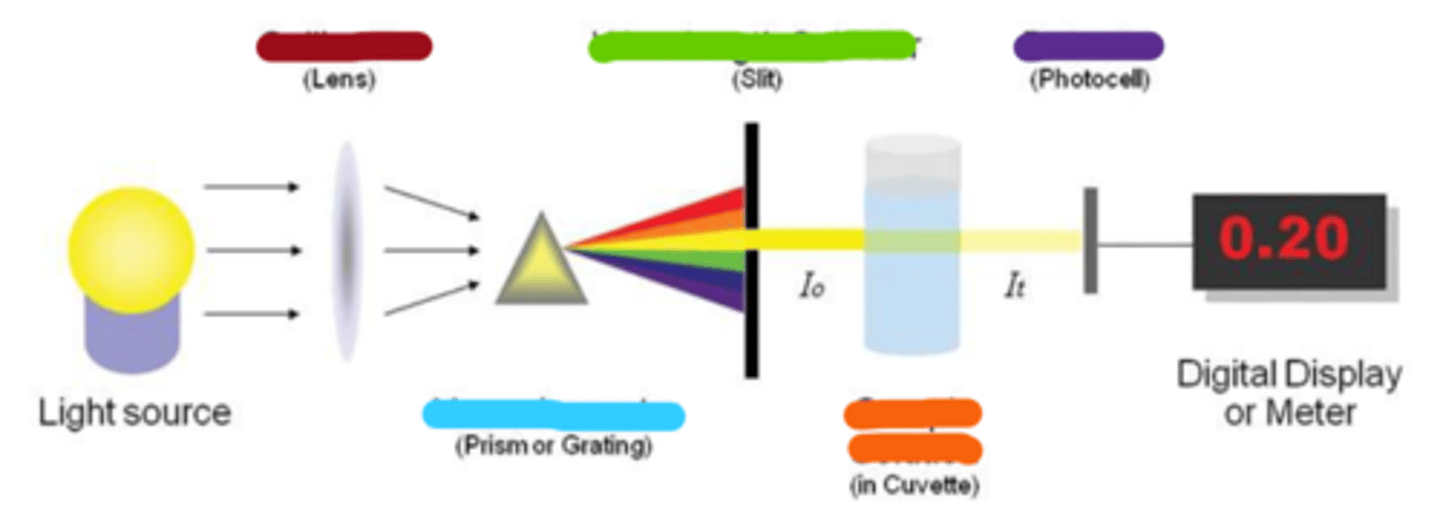
monochromator
blue
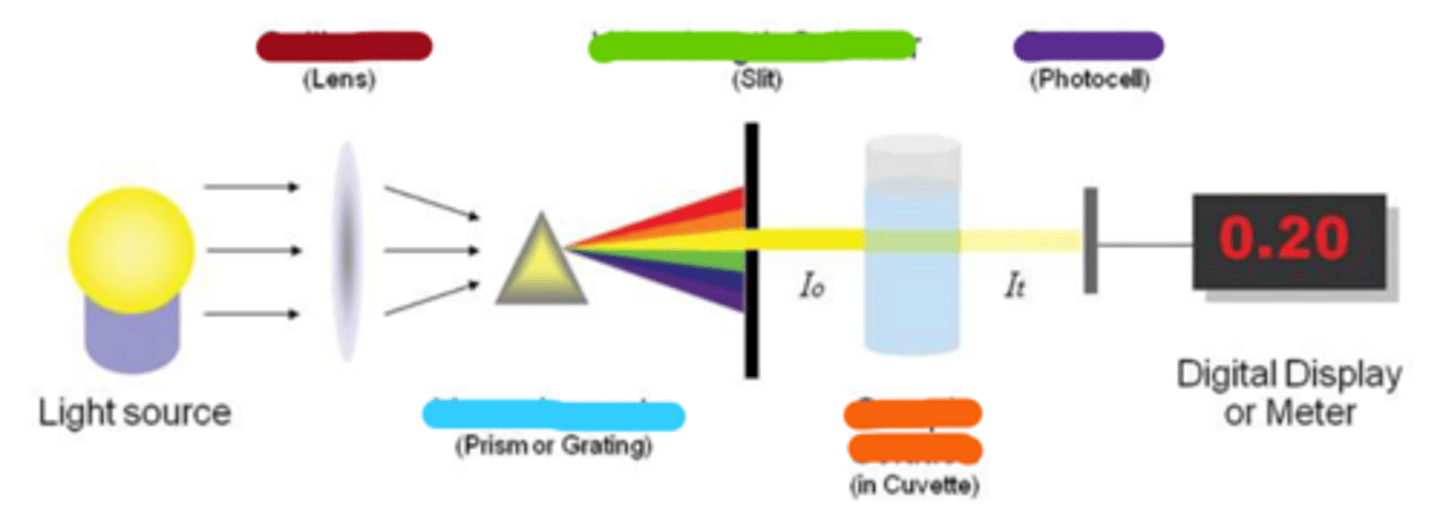
sample solution
orange
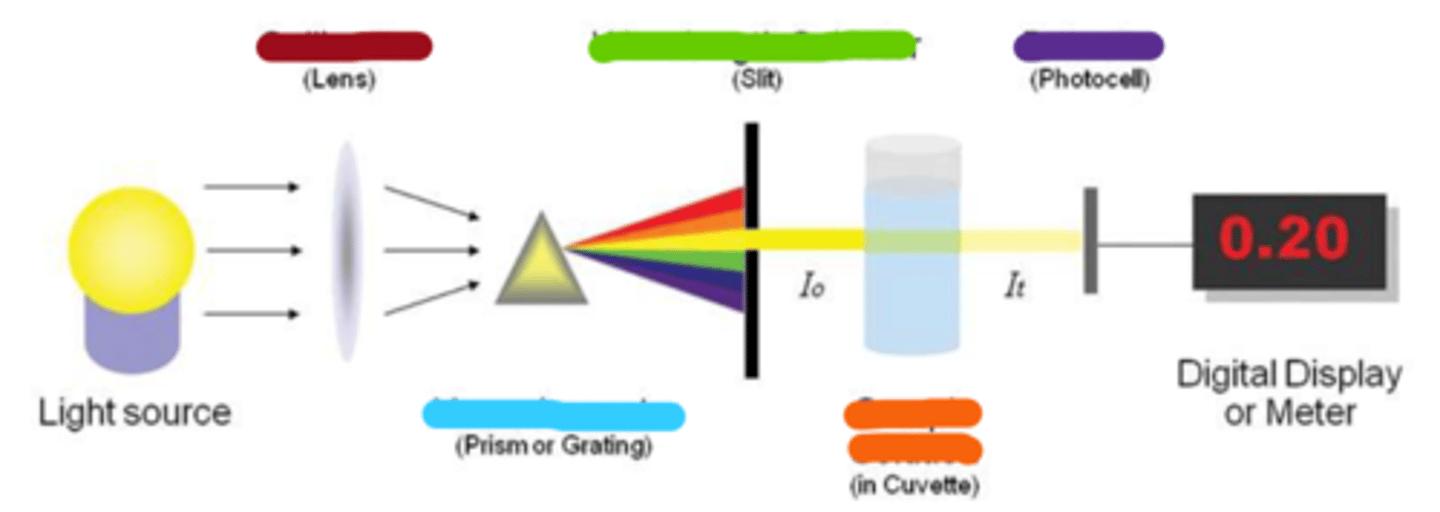
detector
purple
energies
spectroscopy: tune input light to evaluate specific attributes of sample based on spectrum of _____________
detector
spectroscopy: tune output ___________ to determine specified characteristics
frequency, wavelength
higher energies result in higher _____________ and shorter _____________
orbitals, matches
UV-VIS light can push electrons to higher energy _________ only when energy ____________ the energy difference between orbitals
absorbed
UV-VIS: when electrons are pushed to higher energy orbitals, that energy is ____________ by the compound
wavelengths
different compounds will absorb different _______________
light
UV-VIS measurements: expose sample to increasing wavelengths of __________
absorbance
UV-VIS measurement: capture the ________________ of light (done by detecting the amount of transmitted light)
peaks
UV-VIS measurement: ________ correspond to specific chemical compounds
UV-VIS measurement
can also be useful to quantify the concentration of a specific compound
beer-lambert's law
equation name?
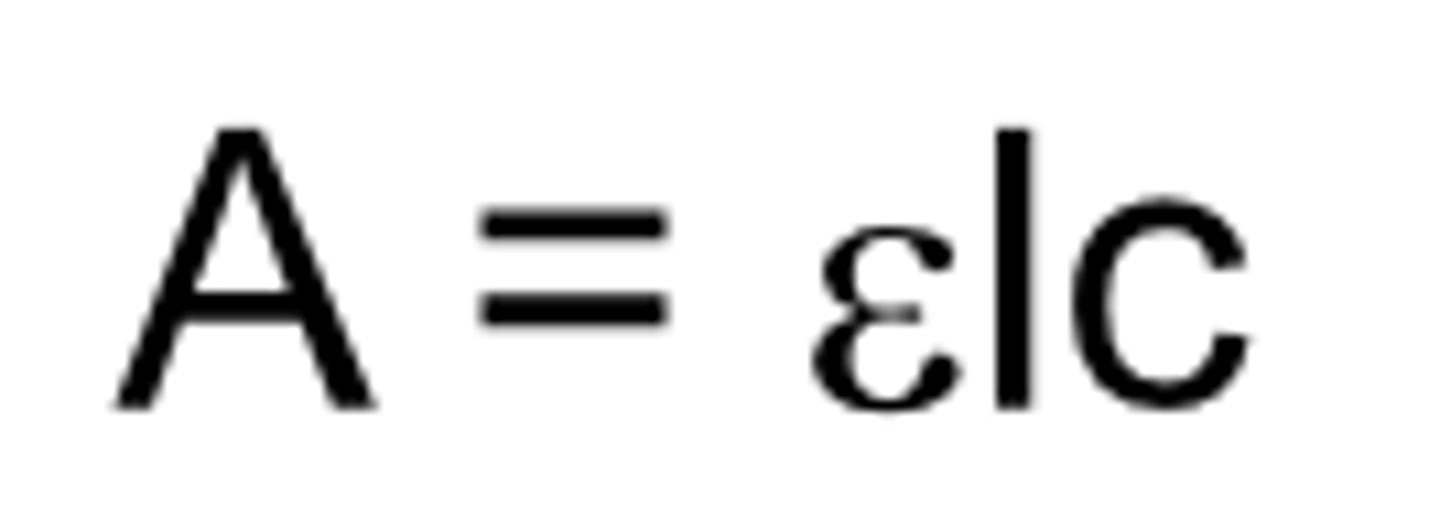
A
beer-lambert's law: absorbance
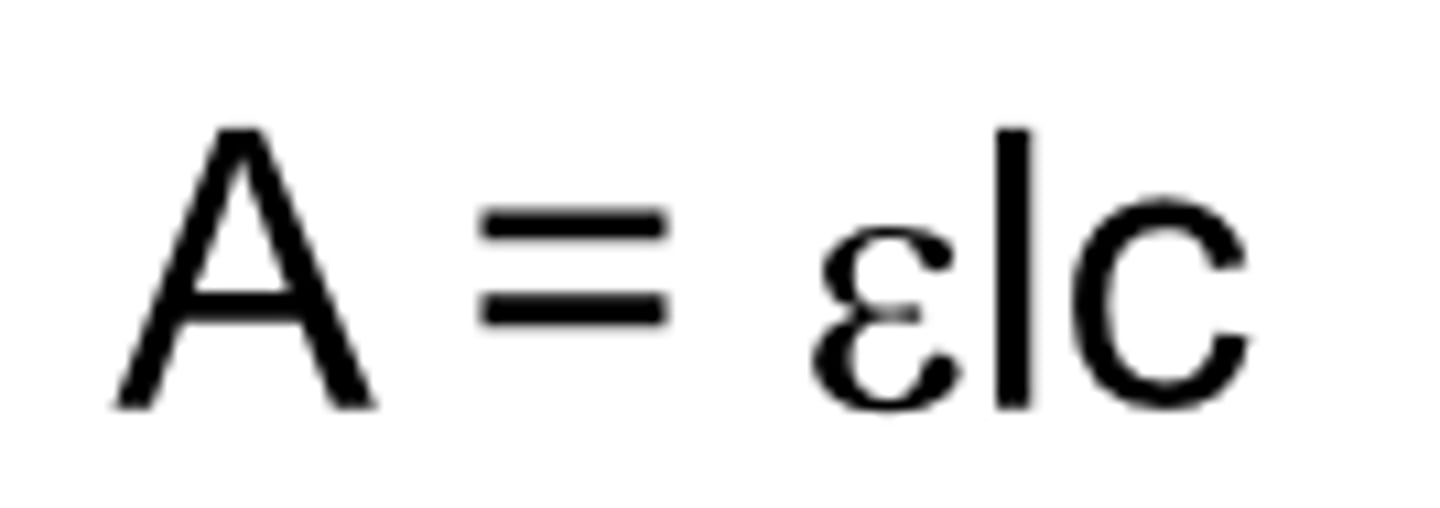
E
beer-lambert's law: molar attenuation coefficient
c
beer-lambert's law: concentration
l
beer-lambert's law: optical pathlength
protein
BCA assay quantifies __________ content
infrared
type of spectroscopy? radiation of wavelengths of 0.78-1000nm
ball and spring model
represents a bond between 2 atoms, single, double, and triple bonds have characteristic vibrational behavior
detection
infrared (IR) spectroscopy: different bonds will absorb specific wavelengths of light, allowing for ____________
nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
uses radiation in the radio-frequency region (0.5-75nm) to excite molecules
nucleus
NMR: induces changes in the _________ rather than electrons
transitions
NMR: the presence of a strong magnetic field is needed to observe the nuclear ____________
positively
nuclei are _____________ charged
magnetic
nuclei spin creates a small __________ field
2
nuclei have ___ orientations to the spin
unequal
nuclei must have _________ numbers of protons and neutrons to produce a signal in NMR analysis
spin
NMR: when protons are placed in a larger, external magnetic field, H0, they ______ one of two ways
favorable
NMR: proton in magnetic field spinning the same direction as the field is energetically ________________
unfavorable
NMR: proton in magnetic field spinning the opposite direction as the field is energetically ________________
lower
NMR: proton in magnetic field spinning the same direction as the field has a _________ energy state (alpha)
higher
NMR: proton in magnetic field spinning the opposite direction as the field has a _________ energy state (beta)
hv
the difference in energy between these 2 states is
increases
the difference in these 2 energy states ___________ with increasing strength of the magnetic field
resonance frequency
proton spin will flip from alpha to beta, or vice versa, if exposed to radio energy of frequency (n) ____________ _____________
energy
when exposed to the same magnetic field (H0), various molecules require different amounts of ___________ to resonate
local environment
the resonance frequency depends strongly on the ______ _____________ of each nucleus
compound
the local environment changes depending on the chemical ____________
electrons
energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy: X-ray ejects ___________
characteristic energy
higher energy electrons fill ejected electron position, leading to emission of ___________________ __________
elemental
energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy: ____________ information gathered about material
high performance liquid chromatography
provides information based on separation of substances by chemical properties (size or charge)
size-exclusion chromatography
high-performance liquid chromatography: SEC meaning?
gel permeation chromatography
size-exclusion chromatography (SEC): GPC meaning
gel filtration chromatography
size-exclusion chromatography (SEC): GFC meaning
refractive
size-exclusion chromatography (SEC): eluted compounds change the ___________ index of solvent
mass spectroscopy
does NOT involve measurement of absorption of electromagnetic radiation
mass spectroscopy
determines atomic and molecular masses of various species
high energy
mass spectroscopy: first the sample is ionized through bombardment with _____ _________ particles (usually electrons)
magnetic field
mass spectroscopy: charged species are forced through a ____________ ________
linear
mass spectroscopy: interaction deflects species from a ________ path
more
mass spectroscopy: lighter species deflected _______ than heavier ones
mass
mass spectroscopy: species are separated by differences in ______
isotopes
mass spectroscopy: extremely sensitive to difference between __________ of the same element
inorganic, organic
information given from mass spec: qualitative and quantitative assessment of ____________ and ___________ molecules
polymers
information given from mass spec: primarily used for natural and synthetic ___________
isotopes
information given from mass spec: used to identify ____________ ratios within a substance
bonds
information given from mass spec: can provide information on strength of various _______ in a molecule
exposure, delivered
two types of biocompatibility testing considerations
exposure (in vivo tests)
amount the while animal/person is exposed to (inhaled, skin exposure, swallowed, injected, or ingested)
delivered dose (in vitro)
amount arriving at the cell: absorption > circulation and distribution > delivery to organs > delivery to cells
toxicity
cell death through inhibition of key metabolic pathways
in vitro
(cell exposure tests) target cell doses using delivered dosage
cytotoxicity assays
screening tool for raw materials or component products before they are put into the design of a medical device
direct contact, agar diffusion, elution
three types of cytotoxicity assays
direct contact
confluent monolayer + sample > 24 hr > assay
agar diffusion
agar added above culture + sample > 1-3 days > assay
elution
extract of the material using PBS or media added to culture > evaluate after 24 hr > stain for viability
leachable
elution: determines whether a product or compound will have any toxic effect due to _______________ on living cells
cell
evaluate effect through: ______ cytotoxicity and behavior
cell behavior
adhesion, spreading, migration, invasion, changes in mRNA and protein
Calcein-AM
live/dead stain: enters cytoplasm and is cleaved by esterases (only present in living cells) > cleavage leads to green fluorescence
ethidium homodimer
live/dead stain: enters nucleus of compromised (dead) cells, intercalating agent, fluoresces red
vital stain
taken up and retained by healthy cells (dead cells appear colorless)
MTT assay
cytotoxicity assessment assay - indication of mitochondrial activity
adhesion and spreading
cell behavior?
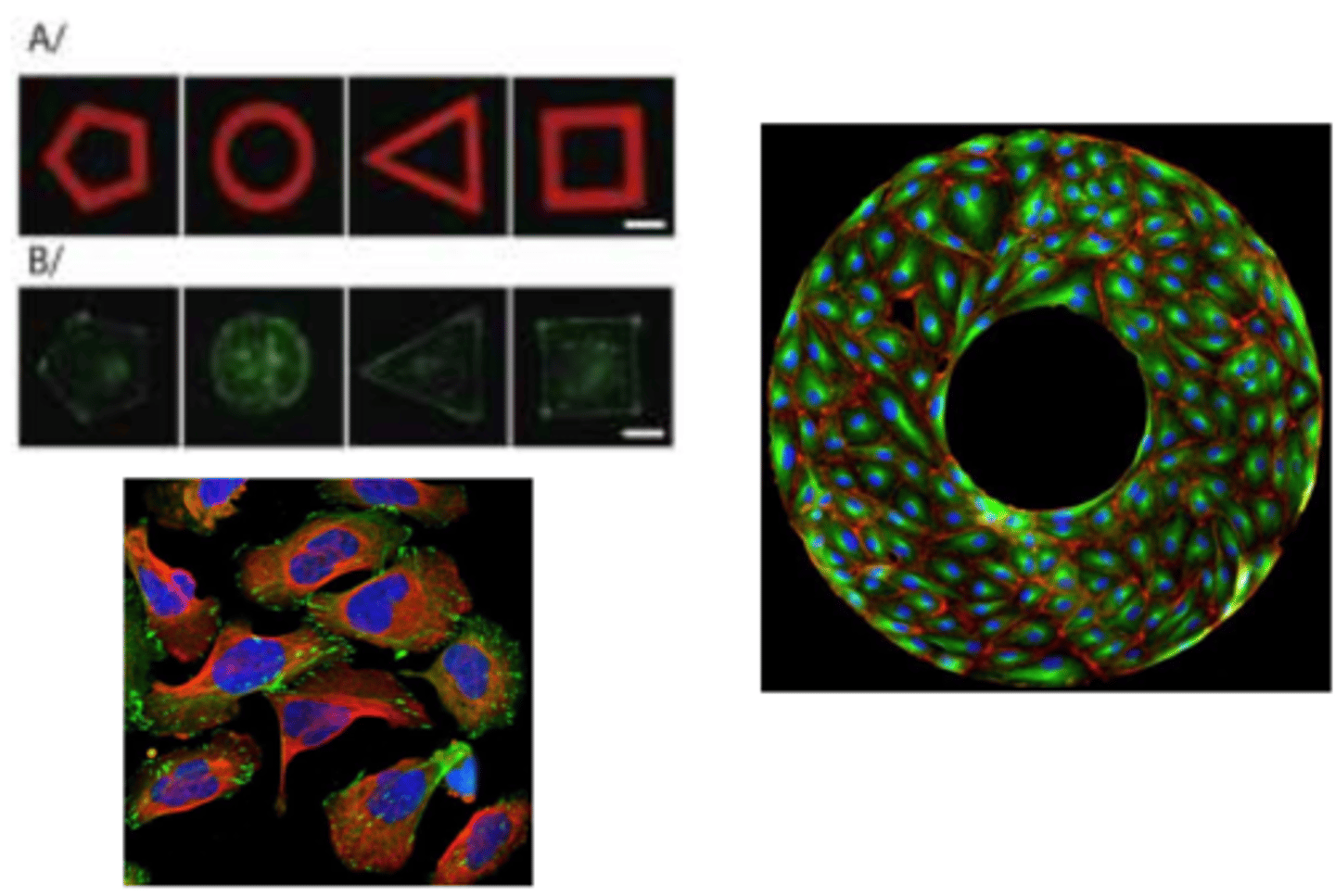
cell mobility
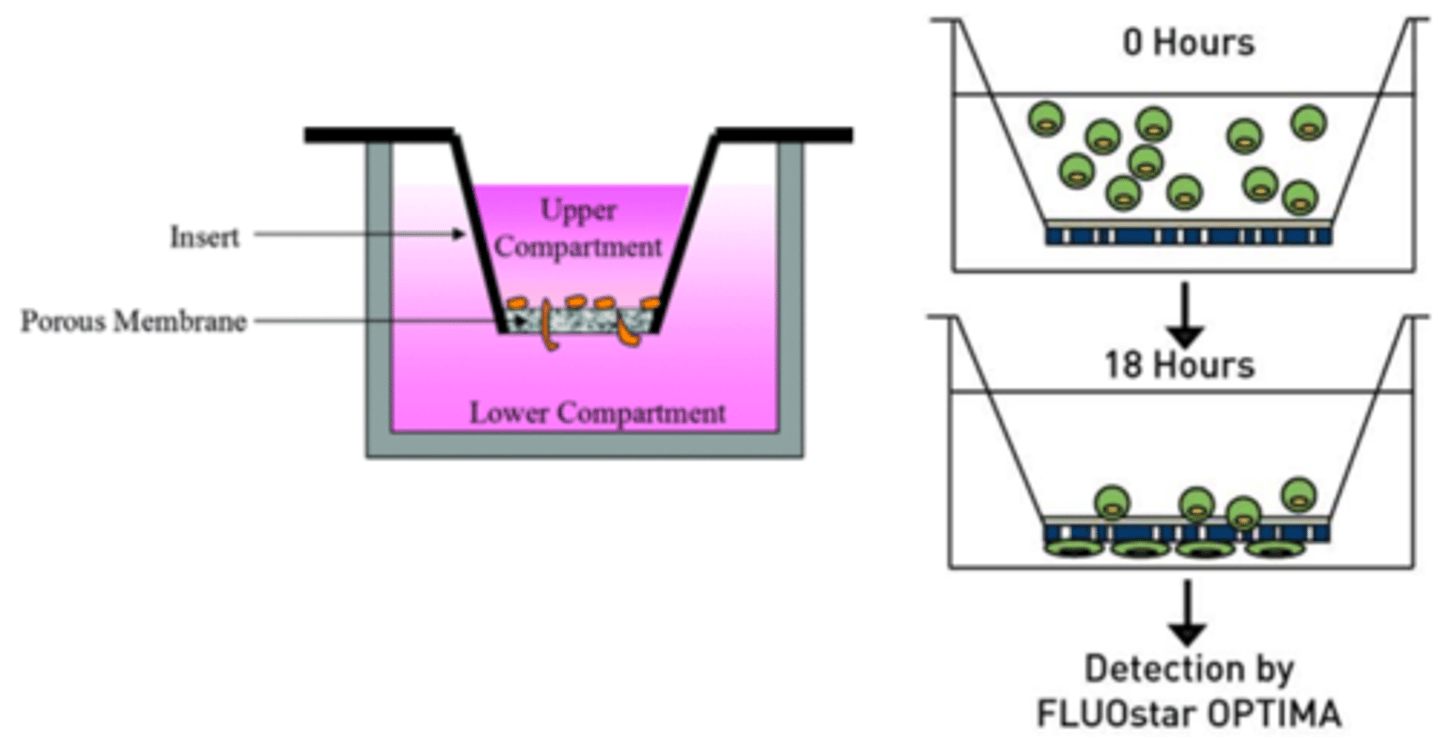
cell behavior?
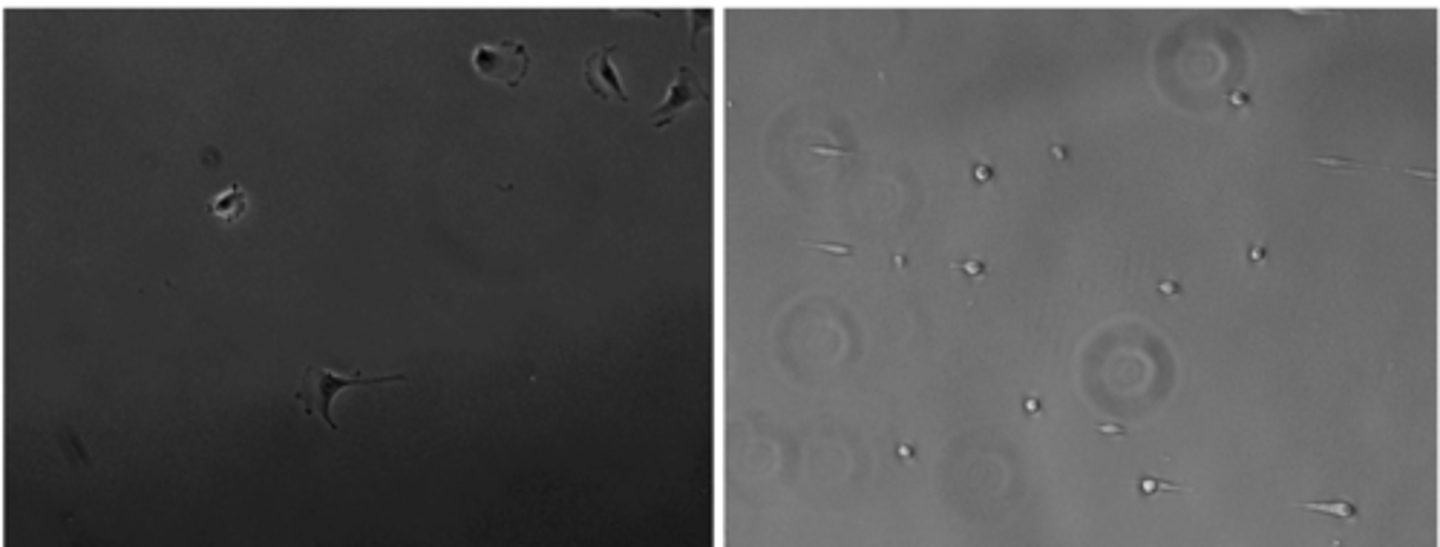
migration assay (Boyden chamber)
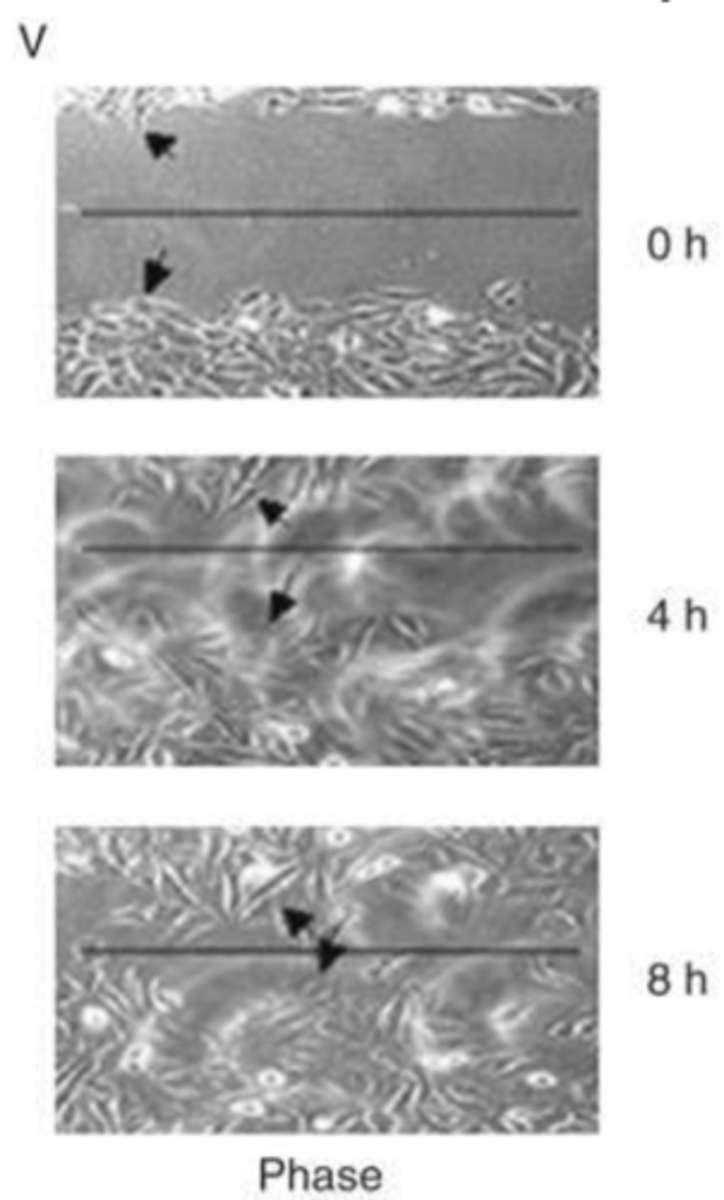
cell behavior?
scratch wound assay
cell behavior?
phenotype
toxins can alter the cell ________________, which can be determined through DNA/RNA, Protein Assays
DNA/RNA
type of assay? PCR/qPCR
DNA/RNA
type of assay? micro-array testing
protein
type of assay? western blotting
protein
type of assay? immuno-staining
protein
type of assay? ELISA
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
quick, easy method for generating unlimited copies of any fragment of DNA
denaturation, annealing, extension
3 major steps in PCR repeated in 30 or 40 cycles?
denaturation
open strands, stops enzymatic actions > ready to copy (94-95C)
annealing
using polymerase (enzyme which assembles DNA base pairs) using primers (base pairs which fit exactly) (54-60C)
extension
ideal working temperature for polymerase, bases are added complementary to the template from 5' to 3' (68-74C)
gene expression microarrays
to determine which genes are suppressed and which are turned on after a treatment
gene expression microarrays
based on tracing mRNA, a chip made from an array of DNA sequences corresponding to known gene
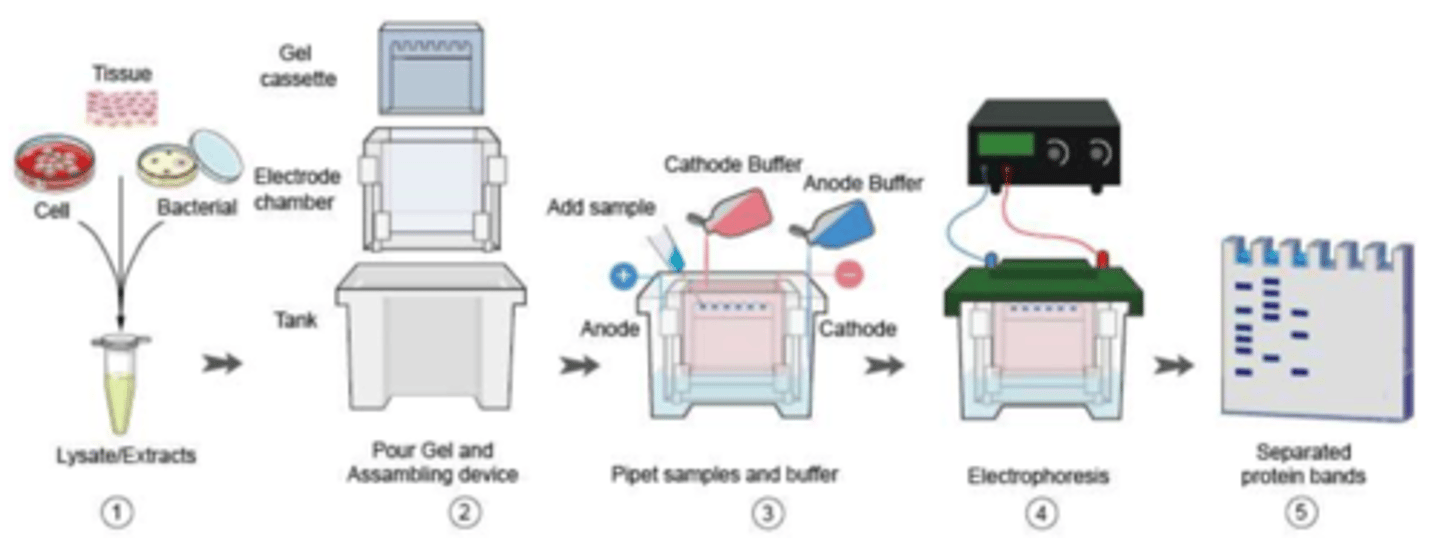
electrophoresis
western blotting - ____________________