Physics CSEC - Section D
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Explain the charging of objects
Electrons transfer from the surface of the glass rod onto the cloth, leaving the glass with excess positive charge and the cloth with excess negative charge.
Describe the forces that electric charges exert on each other
Like charges repel each other, while opposite charges attract. The strength of these forces depends on the magnitude of the charges and the distance between them.

Explain charging by induction
Charging by induction occurs when a charged object is brought near a neutral object, causing a redistribution of charges within the neutral object. This results in the neutral object becoming charged without direct contact.
Define an electric field
The region in which a body experiences a force due its charge. It is represented by electric field lines that show the direction in which a positive charge would move. It measured in volt metres
Describe one hazard and one useful application of static charge
Hazard: Lightning
Uses: Spray Painting (As the paint passes through a nozzle it becomes charged positively by friction. The positive droplets then induce opposite charge on the metal to be painted and are attracted to it. To increase the attraction, the metal can be connected to a negative potential)
Distinguish between conductors and insulators
Conductors are materials that allow electric charges to flow easily, while insulators are materials that resist the flow of electric charges.
Which conductors consist of the movement of both negative and positive charge carriers?
Metal : consists of a flow of electrons (only negative)
In semiconductors like silicon and germanium, electrons move through the material, but there are also holes that behave like positive charges
In electrolytes positive ions and negative ions move toward opposite electrodes, carrying electric current through the solution.
Differentiate between electron flow and conventional current
Electron flow refers to the movement of electrons from the negative terminal to the positive terminal of a circuit, while conventional current is defined as the flow of positive charge from the positive terminal to the negative terminal, which is opposite to the direction of electron flow.
Unit of electrical current
Ampere, A
Difference between direct and alternating currents
In direct current (D/C), the voltage is always constant, and the electricity flows in a certain direction.
In alternating current (A/C), the voltage periodically changes from positive to negative and from negative to positive, and the direction of the current also periodically changes accordingly.
Frequency = ?
1/Period (T)
Cite examples of the conversion of electrical energy to other forms and vice versa
Light: A light bulb (electrical → light + heat)
Heat: An electric heater or electric stove (electrical → heat)
Sound: A speaker (electrical → sound)
Chemical energy: A rechargeable battery (electrical → chemical)
Mechanical to electrical: A generator (movement of turbines produces electricity)Light to electrical: A solar panel (sunlight is converted into electricity)
Power = ?
Current x Voltage
Voltage = ?
Energy/ Coulombs
Discuss the importance of conserving electrical energy
Limited reserves of fossil fuel hence the need to conserve. Conserving electrical energy minimizes environmental impact and reduces energy costs. It also extends the lifespan of energy resources and enhances sustainability.
How to conserve electrical energy
Use energy-efficient appliances and LED lights to reduce electricity consumption.
Install solar panels (photovoltaic panels) to generate electricity from sunlight.
Install solar water heaters to use sunlight to heat water, instead of using electricity or gas.
Wash only full loads in the washing machine to save water and electricity.
Air-dry clothes on a line or rack instead of using electric dryers to save electricity.
Turn off electrical devices when not in use to avoid wasting electricity.
Carpool and keep your car engine tuned to save fuel (gasoline) and reduce pollution.
Differentiate between series and parallel circuits
Series : All components connected end to end to form a single path for current to flow
Parallel : Components connected in parallel. They have separate branches for current to flow, allowing multiple pathways.
What is a primary cell?
Converts chemical energy to electrical energy by a non reversible chemical reaction
What is a secondary cell/accumulator?
Converts chemical energy to electrical energy and vice versa through a reversible chemical reaction, allowing it to be recharged.
Function of the parts of a zinc carbon cell

Distinguish between primary and secondary cells
Characteristic | Primary Cells | Secondary Cells |
|---|---|---|
Terminal Voltage | ~1.5 V | ~2.0 V |
Maximum Current | Low | >400 A |
Internal Resistance | ~0.5 Ω | ~0.01 Ω |
Portability | More portable | Less portable |
Rechargeability | Not rechargeable | Rechargeable |
Ohms law?
V = IR
Investigate the relationship between current and potential difference
If a material is an ohmic conductor, a graph against I/V or vice versa is a straight line
investigate the relationship between current and potential difference; (a) Metallic conductors at constant temperature.
Ohmic conductor so the graph is a straight line
Filament lamps
Non-ohmic because their resistance changes with temperature. As the current flows through the filament, it heats up, causing its resistance to increase
Semi-Conductor diodes
When the diode is forward biased (its polarity such that it conducts), a small initial voltage is needed before a current flows. When it is reverse biased, conduction is almost zero.
Solutions of copper sulphate in water using copper electrodes
An ohmic conductor so the graph is straight
Explain the concept of resistance
Resistance is the measure of how much a conductor opposes the flow of electric current.
A resistor is a component in a circuit designed specifically to have a certain resistance.
R = V/I
Why does an ammeter need a very low resistance?
An ammeter needs very low resistance to ensure it doesn't significantly affect the current it’s reading
Why does a voltmeter need a high resistance?
Otherwise current will divert through it leaving a small voltage through the component it is measuring
Resistance formula for a series circuit?
The total resistance in a series circuit is the sum of the individual resistances: R_total = R1 + R2 + R3 + … + Rn.
Resistance formula for a parallel circuit?
The total resistance in a parallel circuit is given by the formula: 1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 + … + 1/Rn.
Discuss the reasons for using parallel connections of domestic appliances
Appliances could be switched off individually
Appliances can be made me to operate on one voltage
Explain the purpose of a fuse or circuit breaker
A fuse is thin wire which breaks when the current of the appliance gets too high and starts to overheat to prevent damage to the circuit and reduce the risk of fire. A fuse is always placed in an live wire
Explain the purpose of an earth wire
An earth wire is a safety feature in electrical systems that provides a path for electric current to dissipate safely into the ground in case of a fault, reducing the risk of electric shock or fire. If a fault occurs, the earth wire provides a low resistance pathway.
What is a current rating?
The current rating is the maximum amount of electric current, measured in amperes (A), that a fuse or circuit can safely carry without overheating or causing damage.
State the adverse effects of connecting electrical appliances to incorrect or fluctuating voltage supplies
Appliance will overheat
Appliance will malfunction
Can cause permanent damage
What is half wave rectification?
Half-wave rectification is the process of converting ac to dc by preventing one half of each cycle from being applied to the load.
Describe how a semiconductor dioxide can be used in half wave rectification
Since diodes only carry current in one direction, they can serve as a simple half-wave rectifier. Only passing half of an AC current causes irregularities, so a capacitor is usually used to smooth out the rectified signal before it can be usable.
Define logic gate
A logic gate is an idealised or physical electronic device that processes one or more input states (low or high, logic states 0 or 1) to produce a single output state (low or high, logic states 0 or 1)
Logic gate symbols
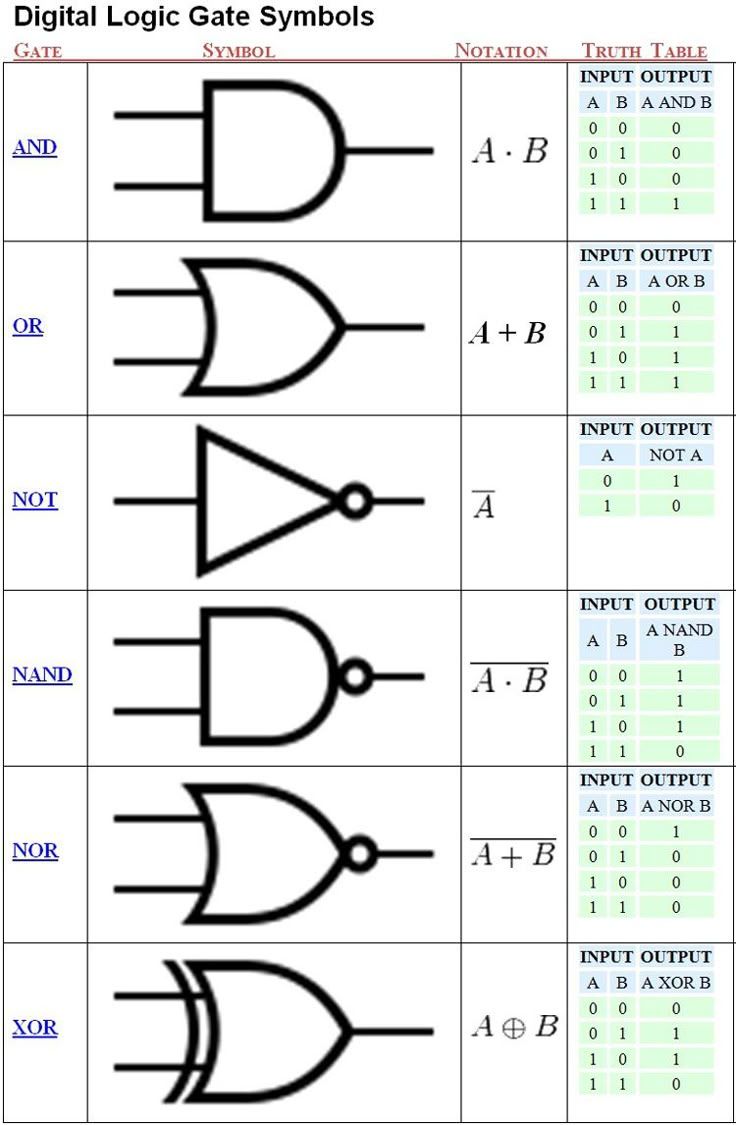
AND?
TWO 1s produce a 1; OTHERWISE, the output is 0
NAND?
TWO 1s produce a 0; OTHERWISE, the output is 1
OR
ANY 1s produce a 1; OTHERWISE, the output is 0
NOR
ANY 1s produce a 0; OTHERWISE, the output is 1
OR
1 produces a 0; 0 produces a 1
Pros of the impact of electronic and technological advances on society
• Businesses get a competitive edge when they use advanced technologies. • The global pooling of information increases the rate of research and development.• Improved transport through airplanes and trains, as well as better communicating devices such ascell phones and computers, has led to more efficient business transactions and to an increase insocial contact. • Better machinery leads to increased and improved productivity. • Electronic banking has facilitated the process of financial transactions
Cons of the impact of electronic and technological advances on society
• Incorrect information is common on the internet. • Individuals can be addicted to social networking to such an extent that their productivity decreases. • Excessive virtual communication may lead to lack of real communication and to a fall in social skills.• Exposure to movies with immoral sexual content and violence can eventually lead to some persons accepting these acts as the norm. • Hackers can intrude on computers and manipulate information such as bank accounts. • More efficient machinery can result in a decrease in available jobs.
Non Magnetic vs Magnetic materials
Magnetic materials are those which are attracted or repelled by magnets
Explain how a magnet can attract an unmagnetised object
In the presence of a magnetic material, the electrons in that material will align in such a way that makes them magnetic
Distinguish between materials used to make "permanent" and "temporary" magnets
Permanent magnets: steel and magnadur. Temporary magnets: iron and mumetal
Define a magnetic field
A magnetic field is the region in which a body experiences a force due to its magnetic polarity.
Apply suitable rules which relate the direction of current flow to the direction of the magnetic field
1. For a straight conductor: Imagine gripping the wire with the right hand such that the thumb is in the direction of the current; thefingers will then be in the direction of the magnetic field. 2. For a coil: Imagine gripping the coil with the fingers of the right hand in the direction of the current; the thumb will then indicate thedirection of the magnetic field (the end of the coil which acts as a north pole)
Identify the factors that affect the force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field
Strength of the field and on the magnitude of the current.
Explain the action of a D.C. motor
Current in the left hand part of the coil causes a downward force, and current in the right hand part of the coil causes an upward force
the coil rotates anti-clockwise because of the forces described above
When the coil is vertical, it moves parallel to the magnetic field, producing no force. This would tend to make the motor come to a stop, but two features allow the coil to continue rotating:
the momentum of the motor carries it on round a little
a split ring commutator changes the current direction every half turn
Once the conducting brushes reconnect with the commutator after a half turn:
current flows in the opposite direction through the wire in the coil
each side of the coil is now near the opposite magnetic pole
This means that the motor effect forces continue to cause anti-clockwise rotation of the coil.
Explain the action of the A.C. generator
As one side of the coil moves up through the magnetic field, a potential difference is induced in one direction. As the rotation continues and that side of the coil moves down, the induced potential difference reverses direction. This means that the alternator produces a current that is constantly changing. This is alternating current or ac.
Explain the principle of operation of a transformer
Transformers are used to increase or decrease the voltage of alternating currents. A transformer consists of two coils of wire wound on a metal core.An alternating voltage is applied to one coil (the primary coil). This causes a changing (alternating) magnetic field to be set up in the core. The other coil (the secondary coil) is in this changing magnetic field and so it has an alternating voltage induced in it.
The size of the secondary voltage depends on the number of turns on both the primary and the secondary coils, and on the size of the a.c. voltage applied across the primary coil.
State the advantages of using a.c. for transferring electrical energy
• Consumer appliances operate on several different voltages, which can easily be obtained from anac mains supply by use of a transformer. • Transformers step up and down ac with minimum energy loss. • The ac can be transferred from the power station at small currents, resulting in minimum energy being wasted as heat in the resistance of the transmitting cables. • By stepping down the transmission current from the power station, thinner cables can be used and therefore the material cost is reduced.
Apply the ideal transformer formula
Vs/Vp=Ns/Np