Oxy/Circ FA23 Lecture
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
186 Terms
Oral temperature range
96.4 - 99.5°F
Rectal temperature range
97.4 - 100.5°F
axillary temperature range
95.6 - 98.5°F
Tympanic temperature range
98.2 - 100.9°F
Temporal temperature range
98.7 - 100.5°F
Normal HR
60-100 bpm at rest
Normal respiratory rate
12-20 breaths per minute
Normal blood pressure
>90/60 and
normal oxygen saturation
95-100%
Afebrile
without fever
Pyrexia
fever
intermittent fever
temperature returns to normal at least once every 24 hours
Remittent fever
temperature does not return to normal and fluctuates a few degrees up and down
sustained/continuous fever
temperature remains above normal with minimal variations
relapsing/recurrent fever
The body temperature returns to normal for one or more days with one or more episodes of fever, each as long as several days.
Equipment for assessing temperature
-Electronic and digital thermometers
-Tympanic membrane thermometers
-Disposable single-use thermometers
-Temporal artery thermometers
-Automated monitoring devices
pulse points in the body
Temporal, Carotid, Brachial, Radial, Femoral, Popliteal, Posterior Tibial, Dorsalis Pedis
Pulse is regulated by
autonomic nervous system through cardiac sinoatrial node
parasympathetic simulation
decreases heart rate
sympathetic simulation
increases heart rate
Layers of the heart wall
epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
Vital exchange of gases
Alveoli -> vascular system (capillaries)
Think about grapes touching a hammock. If they are not touching, gas exchange is not happening
Oxygen is carried in the blood by
hemoglobin
Electrical impulses of the heart
SA node (pacemaker) --> AV node --> atrioventricular bundle (Bundle of His) --> Purkinje fibers
dysrhythmia
not in normal sinus rhythm
myocardial ischemia
blockage of blood to the heart muscle
Angina
chest pain caused by decreased blood flow to heart muscle
myocardial infarction (MI)
Death of cardiac muscle due to ischemia
(heart attack)
heart failure
heart can't pump enough blood to meet the body's needs
Modifiable risk factors
changeable or controllable
Ex. Diet, smoking, activity level, obesity, alcohol/drug use, etc.
unmodifiable risk factors
cannot be altered
Ex. age, genetics, gender
Chest pain/discomfort locations
-under the jaw
-in the arms
-behind the back
-other areas of upper body
diabetic neuropathy can result in
silent heart attacks
Physical assessment of CV system
-General appearance
-Skin and extremities
-Pulse pressure
-Blood pressure; orthostatic changes
-Arterial pulses
-Jugular venous pulsations
-Heart inspection, palpation, auscultation
-Assessment of other systems
Cardiac biomarkers
troponin and creatine kinase
-elevated levels can indicate heart damage or even heart attack
kidney function tests
BUN, creatinine, GFR
Normal sodium levels
136-144 mmol/L
normal potassium levels
3.7 - 5.1 mmol/L
High potassium = peak t wave
Low potassium = flat t wave or inversion
normal calcium levels
8.5 - 10.2 mg/dL
normal chloride levels
97 - 105 mmol/L
Normal magnesium levels
1.7-2.2 mg/dL
normal phosphate levels
2.5-4.8 mg/dL
normal bicarbonate levels
22-30 mmol/L
normal fasting blood glucose level
70-100 mg/dL (3.9-5.6 mmol/L)
Normal RBC count
3.93 to 5.69 million/mm3
Normal Hgb (hemoglobin) lab value:
males: 12.6-17.5 g/dL
females: 12-16 g/dL
normal HCT (hematocrit)
38% to 47.7%
Normal platelet count
150,000-450,000/mm3
clotting test for warfarin
PT/INR (prothrombin time test and international normalized ratio)
clotting test for heparin
PTT (partial thromboplastin time test)
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)
1/3 systolic + 2/3 diastolic
Regulation of blood pressure
-body fluids
-cardiac output (strength of heart contractions)
- renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system raises pressure
Factors affecting blood pressure
Age, gender, race
Circadian rhythm
Food intake
Exercise
Weight
Emotional state
Body position
Drugs/medications
hypotension
orthostatic hypotension
Decrease in blood pressure related to positional or postural changes from lying to sitting or standing positions
Normal blood pressure
Systolic
elevated blood pressure
systolic: 120-129
diastolic: less than 80
Stage 1 hypertension
Systolic: 130-139
Diastolic: 80-89
Stage 2 hypertension
Systolic > 140
Diastolic > 90
Manifestations of hypertension
Usually no symptoms other than elevated blood pressure
Symptoms seen related to organ damage are seen late and are serious
Retinal and other eye changes
Renal damage
Myocardial infarction
Cardiac hypertrophy
Stroke
Measuring blood pressure
-Correct arm cuff size
-Sit quietly with arm at the level of the heart
-Confirmation of diagnosis by average of two blood pressure readings
-Can also evaluate lifestyle modifications and success of prescription medications
Major risk factors
Hypertension
Smoking
Obesity
Physical inactivity
Dyslipidemia
Diabetes mellitus
Microalbuminuria or GFR
Loop Diuretics
Furosemide (Lasix)
-reduces fluid volume
Thiazide diuretics
Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)
-reduces fluid volume
ACE inhibitors
lisinopril, enalapril
-Reduces BP and afterload
ARBs (angiotensin II receptor blockers)
valsartan, losartan
-reduces BP and afterload
Beta Blockers
Metoprolol, Bisoprolol
-dilates vessels and reduces afterload
Calcium Channel Blockers
Amlodipine, Diltiazem, Nifedipine, Verapamil
-Decrease heart rate by limiting use of calcium
Digitalis
Digoxin
-improves contractility and slows heart rate
Cardiac Output (CO)
Amount of blood pumped in 1 minute (~5 L)
CO = HR x SV (Heart Rate x Stroke Volume
Preload
degree of stretch of the cardiac muscle fibers at the end of diastole
Afterload
the amount of resistance to ejection of blood from the ventricle
Cardiac Cycle: Diastole
relaxation
Cardiac Cycle: Systole
contraction
Stroke volume
The amount of blood pumped out of the heart with each contraction.
Indicators of the Heart's Effectiveness
Pulse rate, strength, and rhythm
Blood pressure
Skin color and temperature
Level of consciousness
iron deficiency anemia
anemia caused by inadequate iron intake (most common)
iron deficiency anemia treatment
iron supplements and dietary changes(green leafy vegetables and meat)
macrocytic anemia
bone marrow produces abnormally large RBCs
megaloblastic anemia
red blood cells are larger than normal because of deficiency of folic acid or vitamin B12
manifestations of anemias
fatigue, pallor, faster HR, tongue changes, nail changes, angular cheilitis, pica
diagnostic testing for anemia
-Hemoglobin and hematocrit
-Reticulocyte count
-Iron studies
-Vitamin B12
-Folate
treatment of anemia
-dietary therapy
-iron or vitamin supplementation: iron, folate, B12
-Transfusion of packed RBCs
-Immunosuppressive therapy
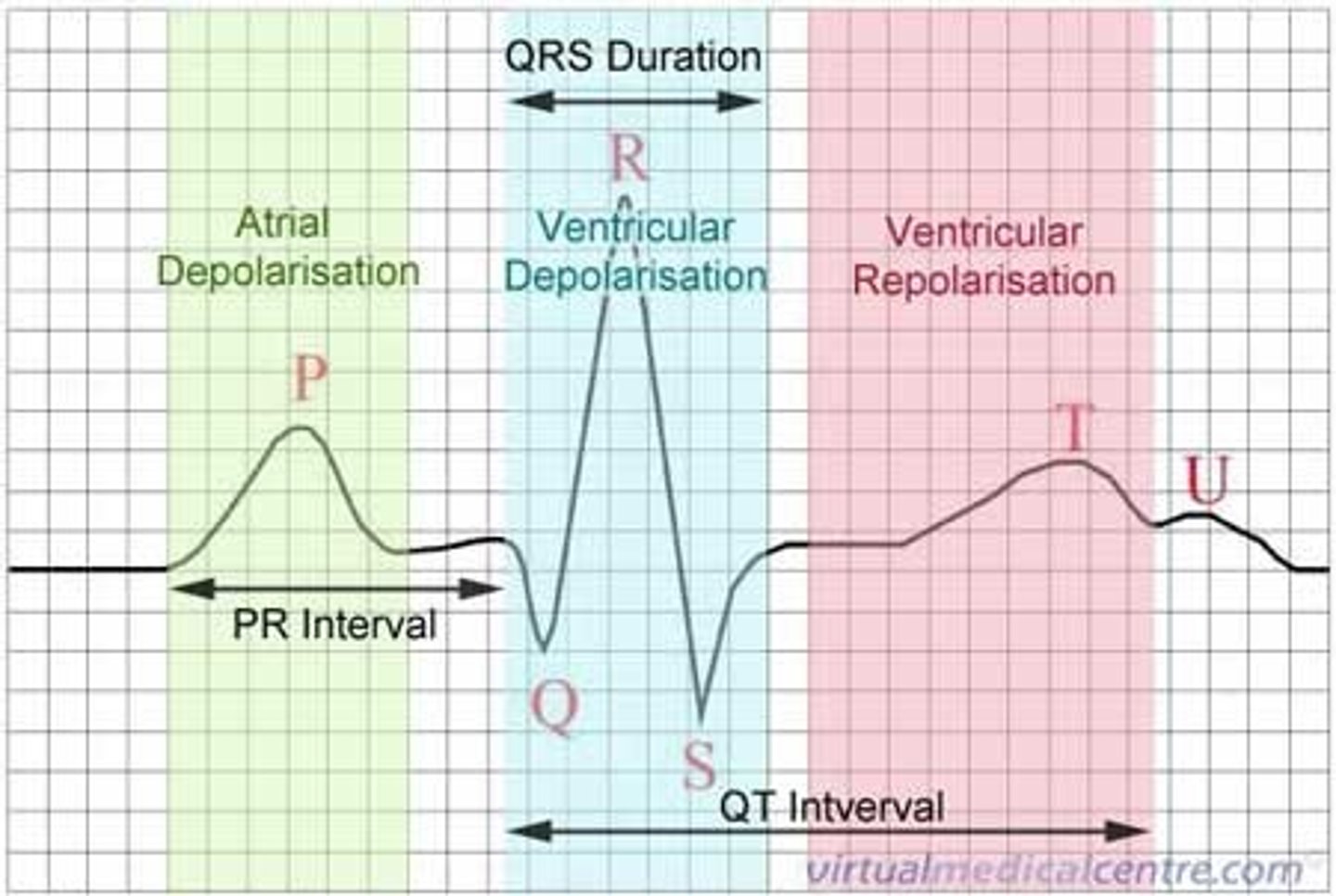
P wave
atrial depolarization
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization (contraction)
T wave
ventricular repolarization
Depolarization
influx of sodium into cell while potassium exits cell
Repolarization
reentry of potassium into cell while sodium exits
Normal Electrical Conduction
SA Node→
AV node→
Conduction→
bundle of his→
R and L bundle branches→
Purkinje fibers
P wave characteristics
Amplitude: 2-3 mm
Duration: 0.08-0.10 seconds (2 - 2.5 small squares)
PR interval duration
0.12-0.20 seconds (3-5 small boxes)
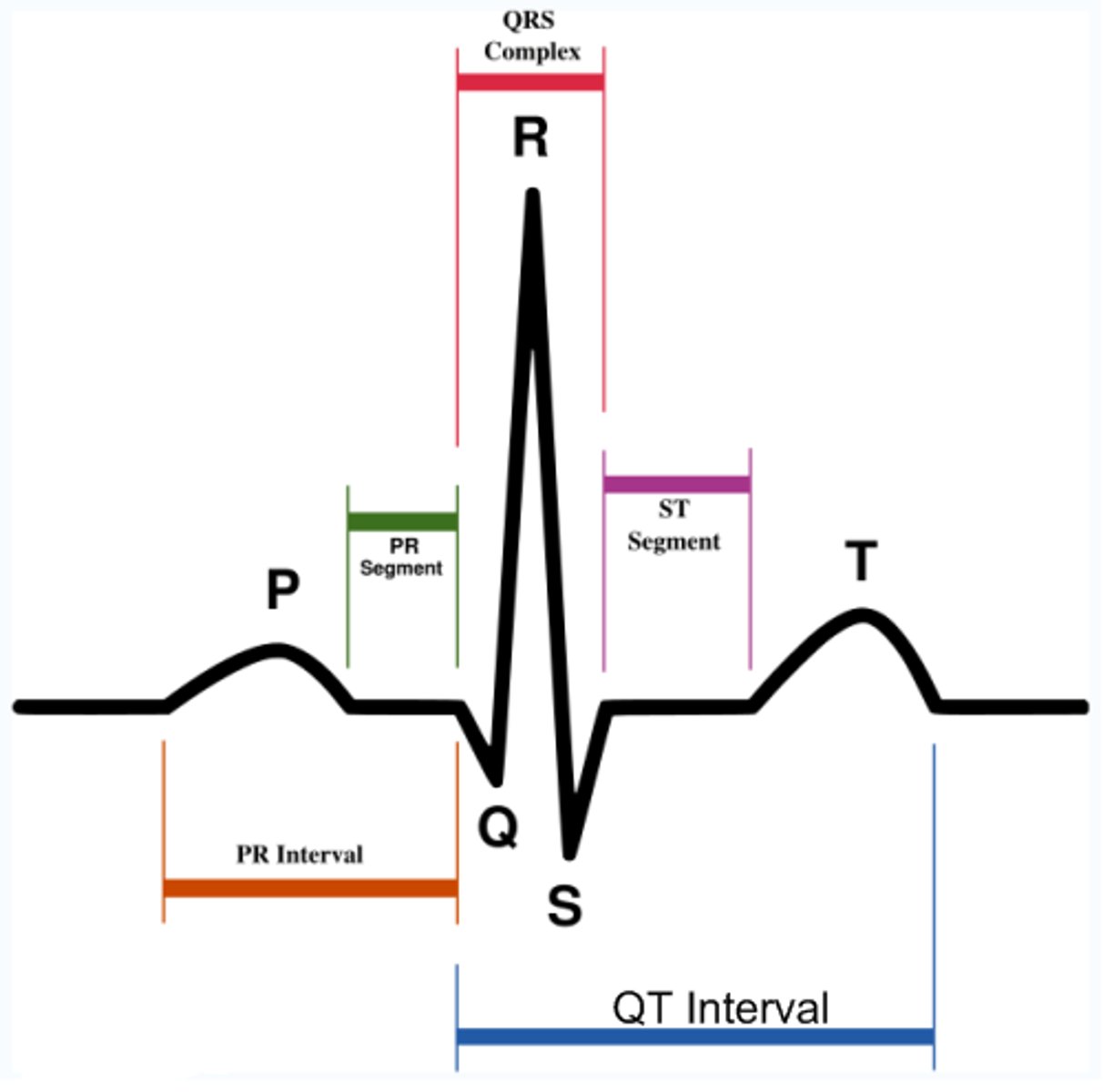
QRS complex characteristics
Duration: 0.08 - 0.12 seconds (2 - 3 small squares)
Amplitude: 5-30 mm high
QT interval
should be 0.35 - 0.43 seconds (1.5 to 2.5 big boxes)
T wave characteristics
Amplitude: 0.5 mm (half a small square)
Duration: 0.1 - 0.25 seconds
Sinus Bradycardia manifestations
-Hypotension
-Pale, cool skin
-Weakness
-Angina
-Dizziness or syncope
-Confusion or disorientation
-Shortness of breath
Sinus Bradycardia Treatment
-Atropine
-Avoid Valsalva
-Hold Rate Slowing Drugs (Digoxin, Beta Blockers)
-dopamine or epinephrine infusion
Sinus tachycardia manifestations
-dizziness
-dyspnea
-hypotension
-angina in pt with CAD
Sinus Tachycardia Treatment
-vagal maneuver
-beta blockers, adenosine, or CCBs
-synchronized cardioversion
physical assessment of arrhythmia
-skin (pale and cool)
-signs of fluid retention (jugular vein distention and lung auscultation)
-rate + rhythm of apical pulse
-heart sounds
-blood pressure
Upper airway function
warm, filter, humidify inspired air