manifestation of respiratory disease
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
reflex response to irritation in UPPER respiratory tract to try and remove irritant (associated with inflammation or foreign material)
sneezing
irritation caused by nasal discharge from inhaled irritants with inflammation or foreign material in LOWER respiratory tract
coughing
yellow green cloudy thick mucous sputum indicates
bacterial infection
rusty or dark sputum indicates
pneumococcal pneumonia
large amounts of purulent sputum with foul odor is associated with
bronchiectasis
thick, tenacious mucus sputum is from what conditions
asthma or cystic fibrosis
think, tenacious with blood mucus sputum is from what conditions
chronic cough, tumor, or tuberculosis
hemoptysis (and what is it associated with)
blood tinged (bright red) frothy sputum associated with pulmonary edema
normal breathing rate
eupnea
Deep rapid respirations—typical for acidosis; may follow strenuous exercise
**trying to expel CO2
kussmauls respirations
labored respiration or prolonged inspiration or expiration is often associated with an obstruction of
obstruction of airways
wheezing or whistling sounds indicate an obstruction here
obstruction in small airways
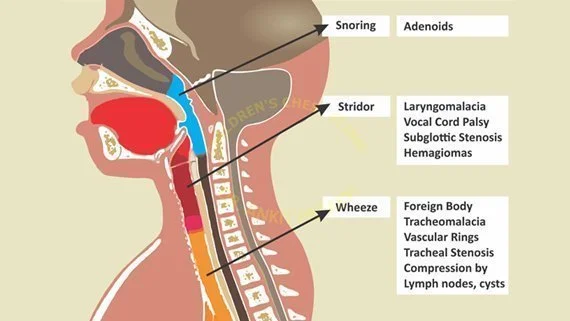
stridor (and what does it indicate)
high pitched crowing noise
usually indicates upper airway obstruction
cessation of breathing
apnea
hyperpnea
increase in depth and rate of breathing
bradypnea and tachypnea
slow and fast breathing but with normal rhythm
periods of apnea with irregular shallow breaths of equal depths
ataxic breathing
long, gasping inspiratory phase followed by a short, inadequate expiratory phase
apneusis
long, ineffective expiratory phase with shallow, increased respirations
obstructed breathing
Periodic breathing associated with periods of apnea, alternating regularly with a series of respiratory cycles; the respiratory cycle gradually increases, then decreases in rate and depth
cheyne stokes respiration
light bubbly or crackling breathing sounds with serous secretions
rales
deeper or harsher breathing sounds from thicker mucus
rhonchi
nonaeration or collapse of lungs
absence
Subjective feeling of discomfort
May be caused by increased carbon dioxide or hypoxemia
Often noted on exertion, such as climbing stairs
dyspnea
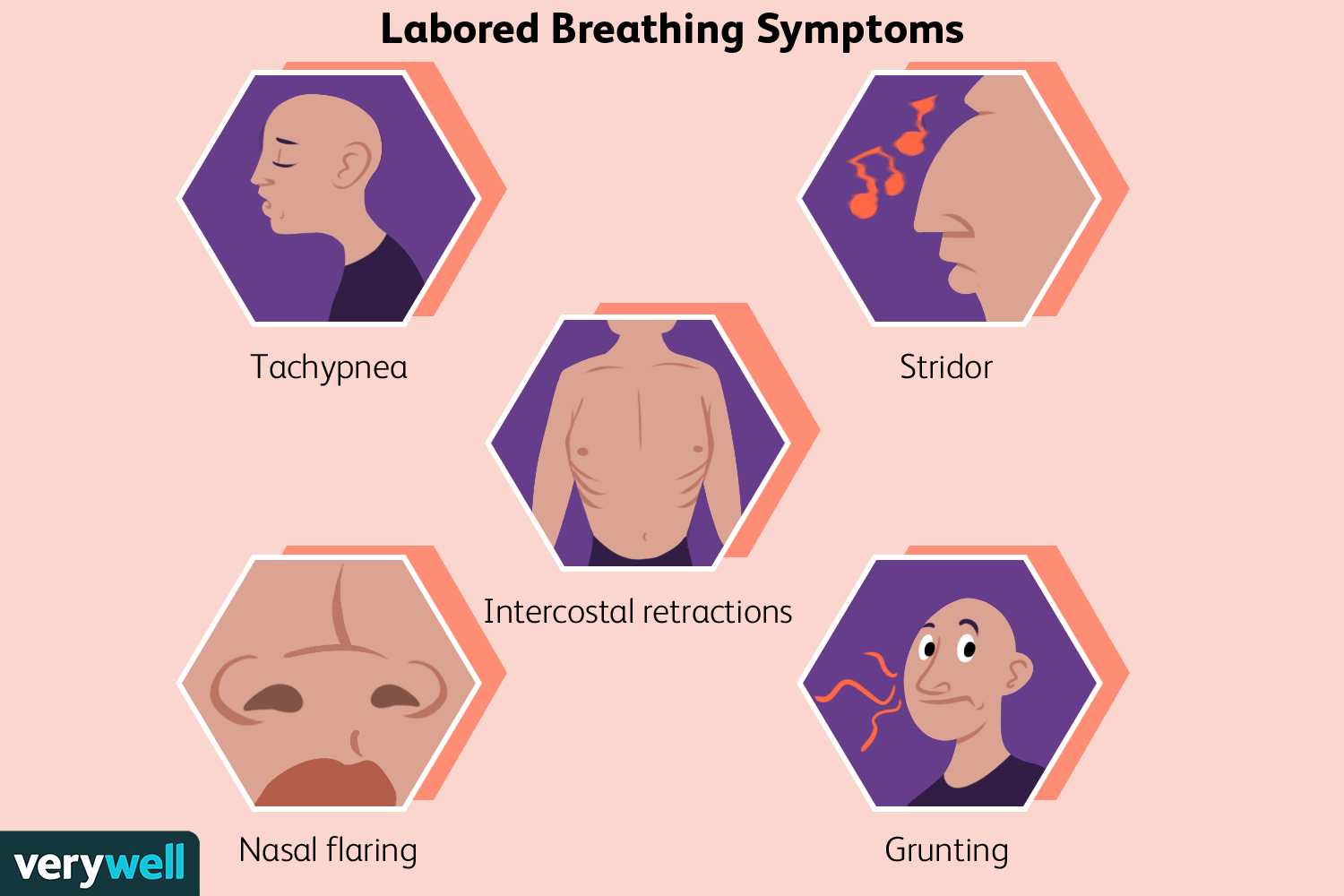
signs of severe dyspnea of respiratory distress
flaring nostrils, using accessory resp. muscles, retract muscles between or above ribs
when does orthopnea occur and with what position
lying down
caused by pulmonary congestion
sudden acute type of dyspnea common in patients with left sided congestive heart failure
paroxysmal noctunal dyspnea
bluish coloring of skin and mucous membranes caused by large amounts of unoxygenated hemoglobin in blood
cyanosis
what causes pleural pain
inflammation or infection of parietal pleura
soft sound produced as rough, inflamed, or scarred pleural move against each other
friction rub
what is clubbed digits
painless, firm, fibrotic enlargement at the end of the digit
what do clubbed digits result from
chronic hypoxia associated with respiratory or cardiovascular diseases