Physics Midterm
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
When force is held constant…
mass and acceleration are inversely proportional (as mass increases, acceleration decreases) (as mass decreases, acceleration increases)
when mass is held constant…
force and acceleration are directly proportional (as one increases so does the other, as one decreases so does the other)
system
a collectin of interacting objects
area under the curve for a Force-Time graph
impulse = change in momentum
area under the curve for a Velocity-Time graph
displacement (vector)
determining direction of acceleration
when velocity and acceleration are same sign they are speeding up and when they are opposite the object is slowing down
constant velocity
0 = acceleration
position vs time graphs
positive slope means positive velocity which means positive direction. a straight line means velocity is constant and acceleration is 0. y-intercept is the starting position of the object
velocity vs time graphs
slope is acceleration, y-int = initial velocity, direction of motion is determined by y value, under the x axis is negative dir, straight line is consant velocity
ticker tapes
if the dots are getting farther apart the object is speeding up, if they are getting closer it is slowing down, and if they are the same the velocity is constant
free fall
acceleration due to gravity, no air resistence, a = g = -10m/s²
frictional force - Ff
a force caused by 2 surfaces sliding past eachother, friction opposes an object’s direction of motion
tension force - Ft
the force transmitted through a string, rope, cable, wire etc. it is directed along the length of the wire and pulls equally on the objects on the opposite ends of the wire.
spring force - Fspring
the force exerted by a compressed or stretched spring. the spring force acts in the opposite direction of the stretching or compression to bring the spring back to equilibrium.
applied force - Fa
a force applied to an object by another object
gravitational force - Fg
the force that pulls objects toward the center of the other massive objects(like planets). Fg is equal to an (object’s weight * g) and is always directed downward toward the center of the earth or other planet
normal force - Fn
a support force exerted on an object when it is in contact with another stable surface like a table, this force acts on the object perpendicular to the surface it is in contact with
force
vector quantity measured in Newtons(N) that causes a change in acceleration (change in velocity). Net Force is equal to the sum of all the forces acting on an object. Not required to keep an object in motion or constant velocity only to make it accelerate
balanced forces
when all the forces acting on an object cancel out or there are no forces at all
unbalanced forces
object is accelerating, forces don’t cancel out (Net Force doesn’t = 0), change in velocity
Inertia
NOT A FORCE, a tendency for an object to reisist changes in motion, depends only on an object’s mass, more mass more inertia
Newton’s First Law: Law of Inertia
An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced force
Newton’s Third Law: Force Pairs
For every action force, there is a reaction force that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, this is called a force pair.
N3L force pairs don’t cancel out because they act on different objects
The force pair to an object’s weight is the gravitational force of the object pulling on the earth
force pair to gravity is always gravity, NOT NORMAL FORCE
internal force
interactions that produce forces within a defined system that cancel out
external force
interactions and forces that are caused by objects outside the system boundry. if these forces are not balanced, the system will accelerate.
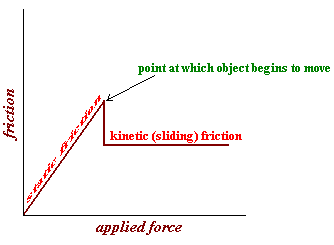
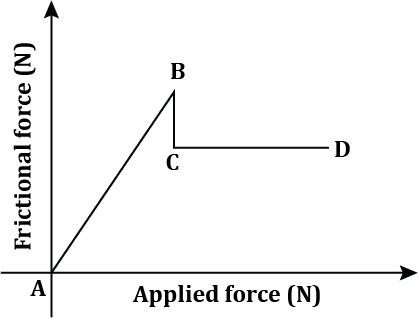
static friction
frictional force that prevents an object from moving
kinectic friction
the frictional force that opposes motion once an object is moving
friction vs applied force graph
weight
mass * g(accel due to grav)
mass
amount while weight is a force
momentum (p)
mass in motion (vector) - kg * m/s
impulse (I)
a force applied to an object for an amount of time that results in a change in a momentum (vector) - N * s
conservation of momentum
for collisions, the total initial momentum of a system before a collision will be equal to the total final momentum of a system when there are no other forces present
if there are any external forces other than collision, momentum is not conserved
both objects experience the same change in momentum/impulse/force during and after the collision
the smaller mass object experiences the greater acceleration (change in velocity)
inelastic collision or hit and stick
objects collide and stick together to form a single object with combined mass and shared velocity “bug hits windshield”
m1 vi + m2 vi = (m1 + m2) vf
elastic or bounce collision
separate final velocity, not one combined object post-collision
m1 v1 initial+ m2 v2 initial = m1 v1 final + m2 v2 final
explosion
start at rest, in contact, pushed apart by “explosion,” force acts equally on both objects
(m1 + m2) vi = m1 v1 final + m2 v2 final