BIOL 204: Blood (chapter 17)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:47 PM on 1/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
1
New cards
what is blood?
fluid that acts as a transport system for the body
2
New cards
functions of blood
transport, regulation, protection
3
New cards
transport of blood function
Delivering o2 and nutrients to body cells, transporting metabolic. transporting hormones from endocrine organs to target organs
4
New cards
what organs are part of transport of blood?
wastes to lungs and kidneys for elimination
5
New cards
which organs do hormones get transported to?
endocrine organs to target organs
6
New cards
regulation of blood function
maintaining body temperature by absorbing and distributing heat, maintaining normal pH using buffers; alkaline reserve of bicarbonate ions, maintaining adequate fluid volume in circulatory system
7
New cards
what instrument is used to normalize pH?
buffers
8
New cards
protection of blood
preventing blood loss, preventing infection
9
New cards
preventing blood loss
plasma proteins and platelets in blood initiate clot formation
10
New cards
preventing infection
agents of immunity are carried in blood (antibodies, complement proteins, white blood cells= leukocytes)
11
New cards
what agents are carried in blood
antibodies, complement proteins, and WBC’s
12
New cards
blood is the only tissue ______
that is fluid
13
New cards
blood is a mix of
matrix and cellular components
14
New cards
matrix is also?
plasma
15
New cards
cellular components is also?
formed elements
16
New cards
the color of blood varies with
\n o2 content
17
New cards
T/F: de-oxygenated blood is blue
false
18
New cards
what is the pH range of blood
\n 7.35-7.45
19
New cards
volume of blood in males
5-6L
20
New cards
volume of blood in females
4-5L
21
New cards
Red blood cells (RBC)
erythrocytes- 45% of whole blood
22
New cards
what is hematocrit?
percent of blood volume that is erythrocytes
23
New cards
what is buffy coat?
White blood cells and platelets (1%)
24
New cards
white blood cells (WBC)
leukocytes
25
New cards
how much blood is in plasma?
55% in blood
26
New cards
spun tube of blood yields three layers
plasma on top, buffy coat, erythrocytes on bottom
27
New cards
composition of plasma
\n straw-colored sticky fluid, about 90% water
28
New cards
most abundant solutes
plasma proteins
29
New cards
plasma proteins produced mostly by
liver
30
New cards
albumin
makes up 60% of plasma proteins, functions as carrier of other molecules as blood buffer and contributes to plasma osmotic pressure
31
New cards
formed elements
erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets
32
New cards
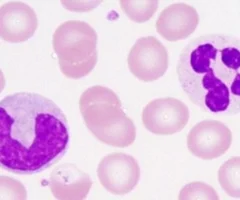
leukocytes
complete cells
33
New cards
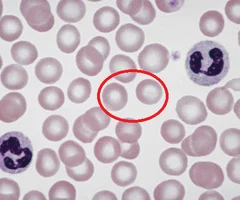
erythrocytes
no nuclei or organelles
34
New cards
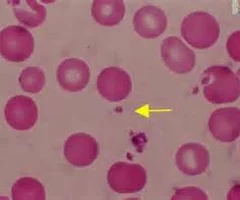
platelets
cell fragments
35
New cards
most formed elements survive in bloodstream for
only a few days
36
New cards
most blood cells originate in
bone marrow and do not divide
37
New cards
what is an erythrocytes
small cells that contribute to gas transport
38
New cards
erythrocytes are filled with
hemoglobin (Hb) for gas transport
39
New cards
hemoglobin
red heme pigment bound to protein globin
40
New cards
globin
is composed of four polypeptide chains
41
New cards
heme pigment
is bonded to each globin chain
\-gives blood red color
\-gives blood red color
42
New cards
each heme's central iron atom
binds one o2
43
New cards
each Hb carries
four o2
44
New cards
cycle of Hb
Hb gets o2 in lungs, unloads o2 in tissues, picks up some co2 to release in lungs
45
New cards
hematopoiesis
formation of all blood cells, occurs in red bone marrow
46
New cards
hematopoiesis in adults
found in axial skeleton, girdles, and proximal epiphyses of humerus and femur
47
New cards
hematopoietic stem cells (hemocytoblasts)
stem cells that gives rise to all formed elements
48
New cards
producing erythrocytes takes
15 days
49
New cards
why do some athletes abuse artificial erythropoietin (EPO)
increases hematocrit which increase stamina and performance
50
New cards
dangers of abusing EPO
increasing hematocrit thickens blood which causes clotting, stroke, or heart failure
51
New cards
life span of erythrocytes
100-120 days
52
New cards
erythrocyte do not
grow, divide, make new proteins
53
New cards
when erythrocytes are aged
become fragile, Hb degenerates
54
New cards
macrophages in spleen
break down these RBCs
55
New cards
two erythrocyte disorders
anemia and polycythemia
56
New cards
anemia
blood does not carry enough o2
57
New cards
cause of anemia
blood loos, not enough RBCs produced, too many RBCs being destroyed
58
New cards
hemorrhagic anemia
rapid blood loss- trauma
59
New cards
chronic hemorrhagic anemia
slight but persistent blood loss
60
New cards
not enough RBCs produced
iron-deficiency anemia, low iron intake, poor absorption, kidney disfunction
61
New cards
too many RBCs destroyed
premature lysis of RBCs, incompatible transfusions or infections
sickle cell anemia
sickle cell anemia
62
New cards
sickle cell anemia
RBCs become crescent shaped when o2 levels are low, misshape RBCs rupture easily and block small vessels
63
New cards
polycythemia
excess of RBCs; increases blood viscosity, causing blood flow
64
New cards
polycythemia vera
bone marrow cancer leading to excess RBCs, hematocrit may go as high as 80%
65
New cards
treatment for polycythemia vera
therapeutic phlebotomy
66
New cards
secondary polycythemia
caused by low o2 levels (example: high altitude) or increased EPO production
67
New cards
leukocytes
function in defense against disease
68
New cards
leukocytes increase in number
in response to infection
69
New cards
two major categories O leukocytes
granulocytes and agranulocytes
70
New cards
which contain visible cytoplasmic granules (granulocytes or agranulocytes)
granulocytes
71
New cards
granulocytes
larger and shorter lived than RBCs, contain lobed nuclei, all are phagocytic to some degree
72
New cards
life span of granulocytes
hours to days
73
New cards
three types of granulocytes
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
74
New cards
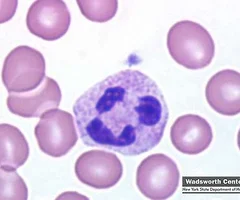
neutrophils
most numerous WBCs- 50-70%, kill microbes by process called respiratory burst
75
New cards
eosinophils
2-4% of all leukocytes, Red-staining granules contain digestive
enzymes• Release enzymes on large parasitic worms,
digesting their surface• Also play role in allergies and immune response
enzymes• Release enzymes on large parasitic worms,
digesting their surface• Also play role in allergies and immune response
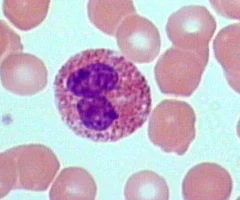
76
New cards
basophils
rarest WBCs, 0.5-1%, Nucleus deep purple with one to two
constrictions
Large, purplish black (basophilic) granules
contain histamine
constrictions
Large, purplish black (basophilic) granules
contain histamine
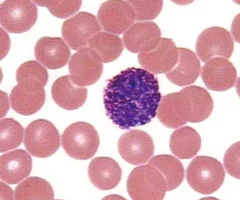
77
New cards
histamine
inflammatory chemical that acts as vasodilator and attracts WBCs to inflamed sites
78
New cards
Agranulocytes
lack visible cytoplasmic granules, both have spherical or kidney shaped nuclei
79
New cards
life span of arganulocytes
hours to years
80
New cards
two types of agranulocytes
lymphocytes and monocytes
81
New cards
lymphocytes
found in lymph tissue
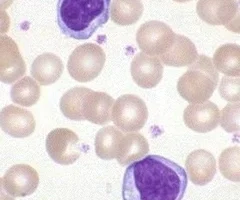
82
New cards
what are the two types of lymphocytes
T cells and B cells
83
New cards
T lymphocytes (T cells)
act against virus- infected cells and tumor cells
84
New cards
B lymphocytes (B cells)
give rise to plasma cells which produce antibodies
85
New cards
monocytes
abundant pale blue cytoplasm, dark purple-staining, U- or kidney-shaped nuclei, leave circulation, enter tissues, and differentiate into macrophages, actively phagocytic, activate lymphocytes to mount an immune response
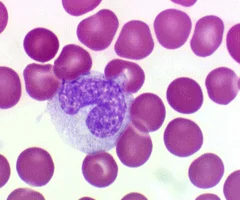
86
New cards
leukocyte production
all originate from hemocytoblast stem cell that branches into two pathways
87
New cards
lymphoid stem cells
produces lymphocytes
88
New cards
myeloid stem cells
produce all other elements
89
New cards
leukemia
immature, nonfunctional WBCs flood bloodstream, cancerous cells fill red bone marrow, crowding out other cell lines, leads to anemia and bleeding
90
New cards
mononucleosis
highly contagious viral disease, usually seen in young adults, caused by Epstein-Barr virus, results in high numbers of typical aranuocytes,
91
New cards
platelets
cytoplasmic fragments of megakaryocytic
92
New cards
function of platelets
form temporary platelet plug that helps seal breaks in blood vessels
93
New cards
Platelets life span
age quickly and degenerate in about 10 days
94
New cards
hemostasis
processes that stop bleeding
95
New cards
first step of clot formation
vascular spasm- smooth muscle contracts causing vasoconstriction
96
New cards
second step of clot formation
platelet plug formation- injury to lining of vessel exposes collagen fibers; platelets adhere, platelets release chemicals that make nearby platelets sticky; plates plug forms
97
New cards
third step of clot formation
coagulation- fibrin forms a mesh that traps red blood cells and platelets forming the clot
98
New cards
thromboembolic disorders
undesirable clot formation
99
New cards
thrombus
clot that develops and persists in unbroken blood vessel, may block circulation, leading to tissue death
100
New cards
embolus
thrombus freely floating in bloodstream