3.1 Periodicity, with exercises
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
metalloid
elemelons with characteristics of both metals and non metals; physical properties & appearance like metals, chemically more in common with non metals, in PSE form a staircase between metals and non metals, from silicon to polonium
semi conductor
refers to physical properties of materials (including alloys and compounds)





what d block contains
includes transition metals, but not exclusively







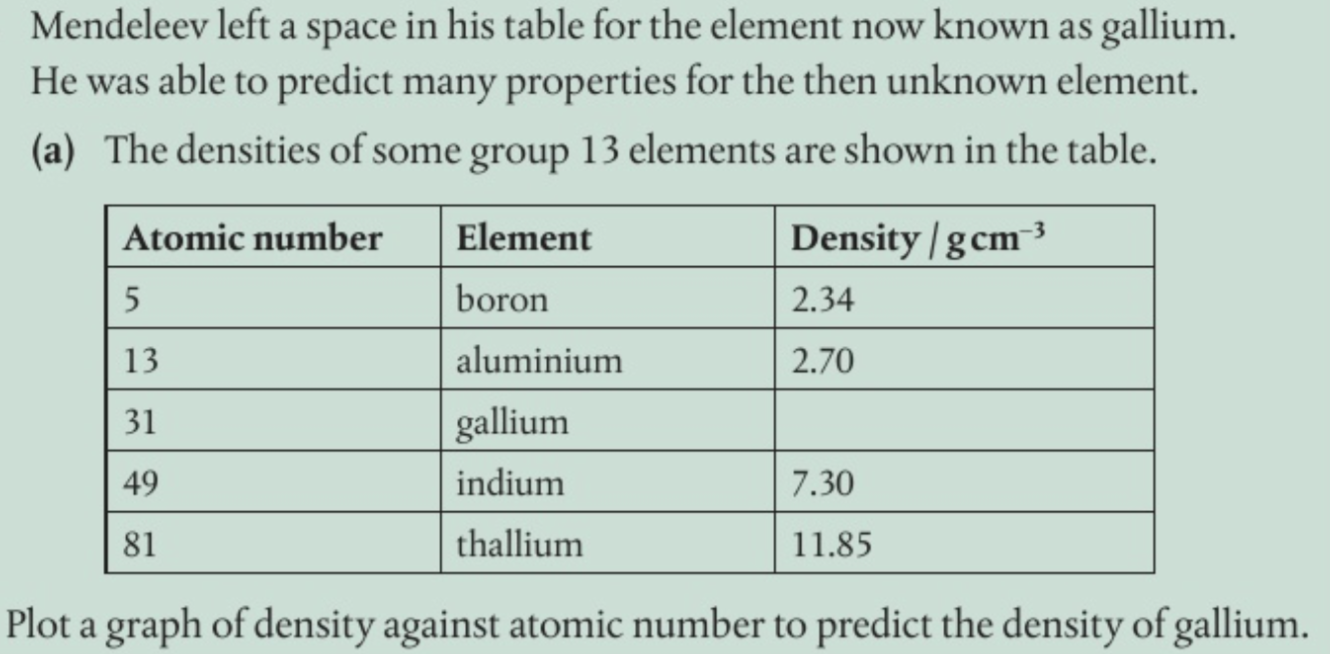
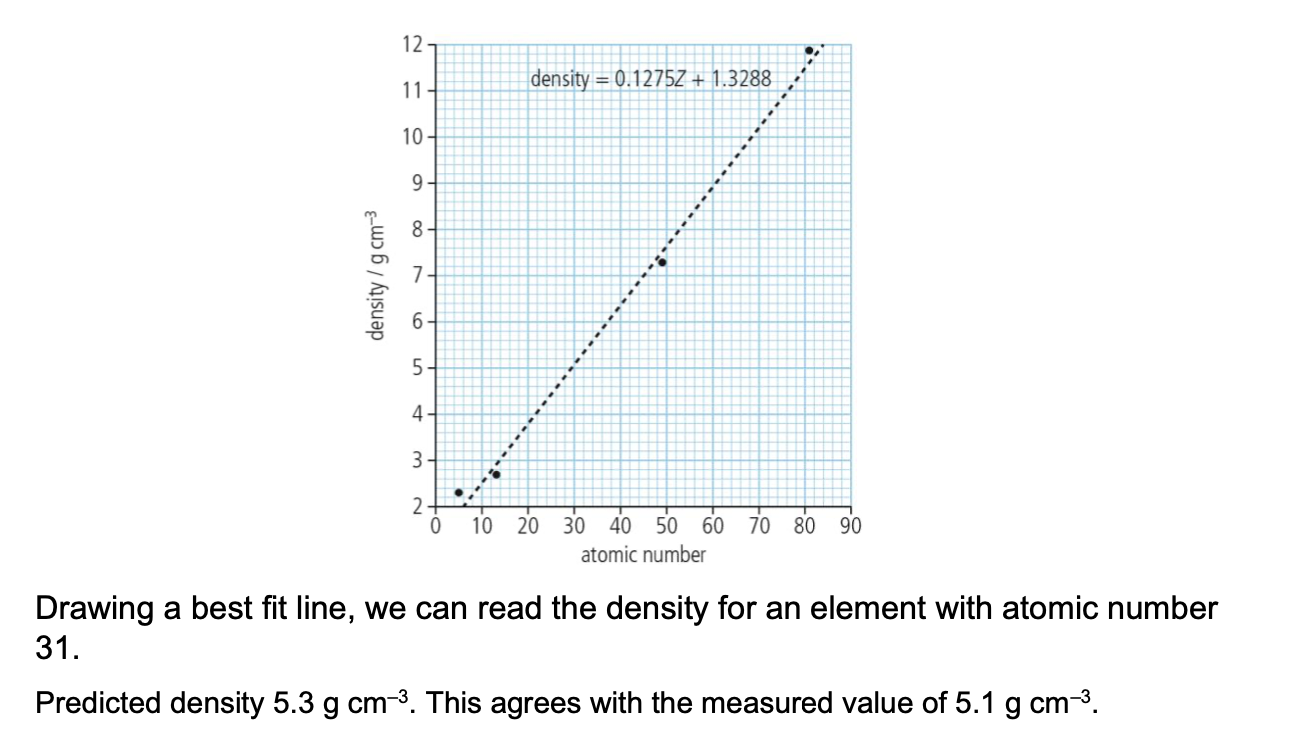
what periodicity is reflected in
properties (atomic and ionic radii, IE, EN, electron affinity especially )
what explains these trends
effective nuclear charge
effective nuclear charge trends
increasing across a period, approx the same down a group.
atomic radius trends
increasing down a group (number of occ electron levels increasing), decreasing across a period (eff nuclear charge rising) = significant impact
what ar is measured as
half the distance between neighbouring nucleii in a covalent bond; but can be considered as distance of nucleus to outermost electrons
ionic radius trends
increasing down a group, decreasing across a period
5 ionic radius trends
positive ions are smaller than parent atoms due to loss of an occ electron level
negative ions are larger than parent atoms due to the addition of an electron to the outer occ electron level = increasing repulsion between the outer electrons
decrease from groups 1-14 for positive ions due to increasing effective nuclear charge
decrease from groups 14-17 for negative ions due to increasing effective nuclear charge
increasing down a group as the number of occ electron levels increases


IE trends
decreasing down a group, increasing across a period
first IE def
amount of energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms in their ground state
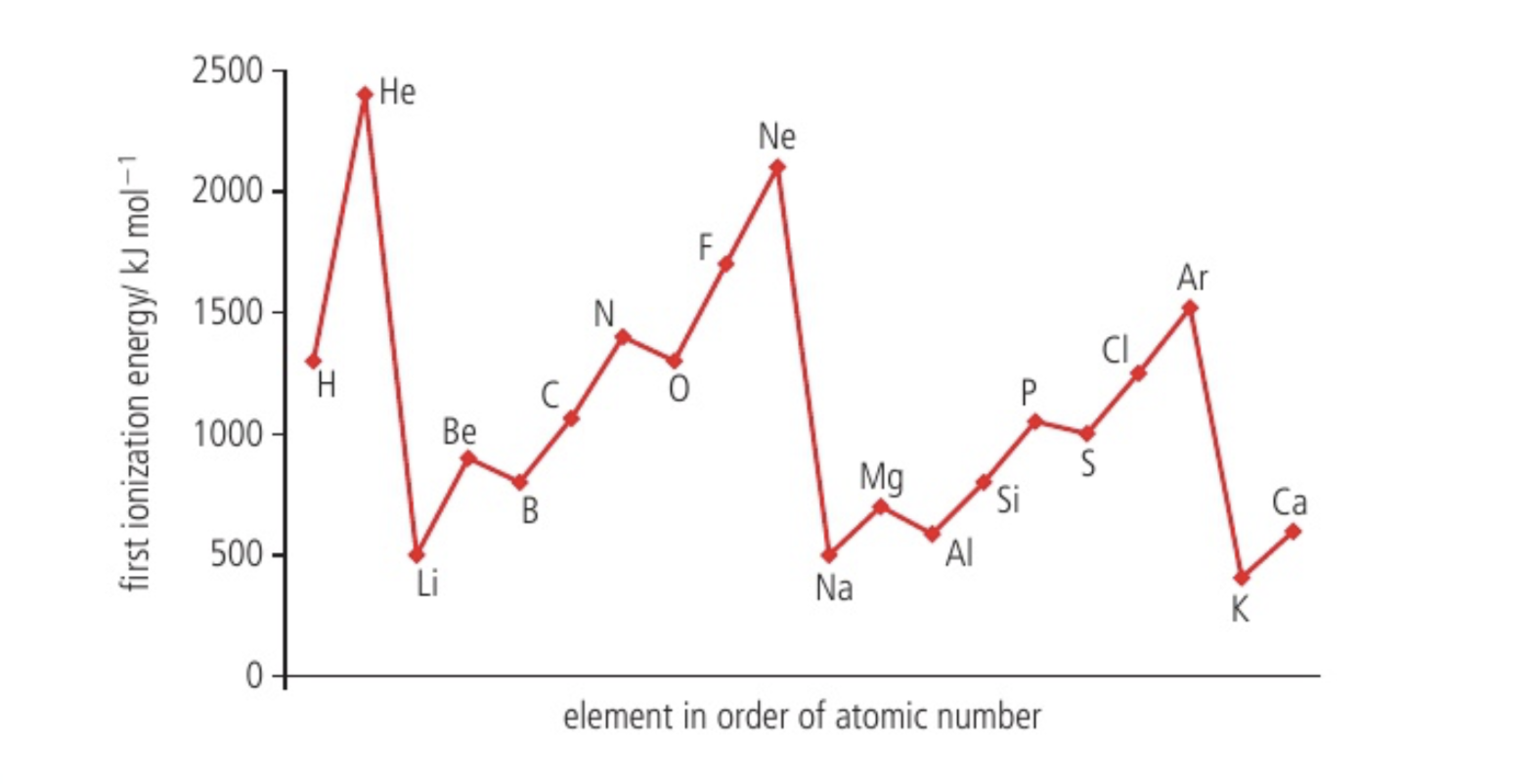
two IE trends
increasing across a period due to increasing effective nuclear charge creating a stronger attraction ie making them harder to remove
decreasing down a group because removed electron is from the furthest occupied electron level; although nuclear charge increasing, effective nuclear charge stays abt the same due to shielding, and so increasing distance reduces attraction
what indicates attraction to outer electrons except ie
atomic radius
electron affinity def
energy change that occurs when one mole of electrons is added to one mole of gaseous atoms in their ground state