ANAPHY LAB: Lymphatic System
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Capsule
1
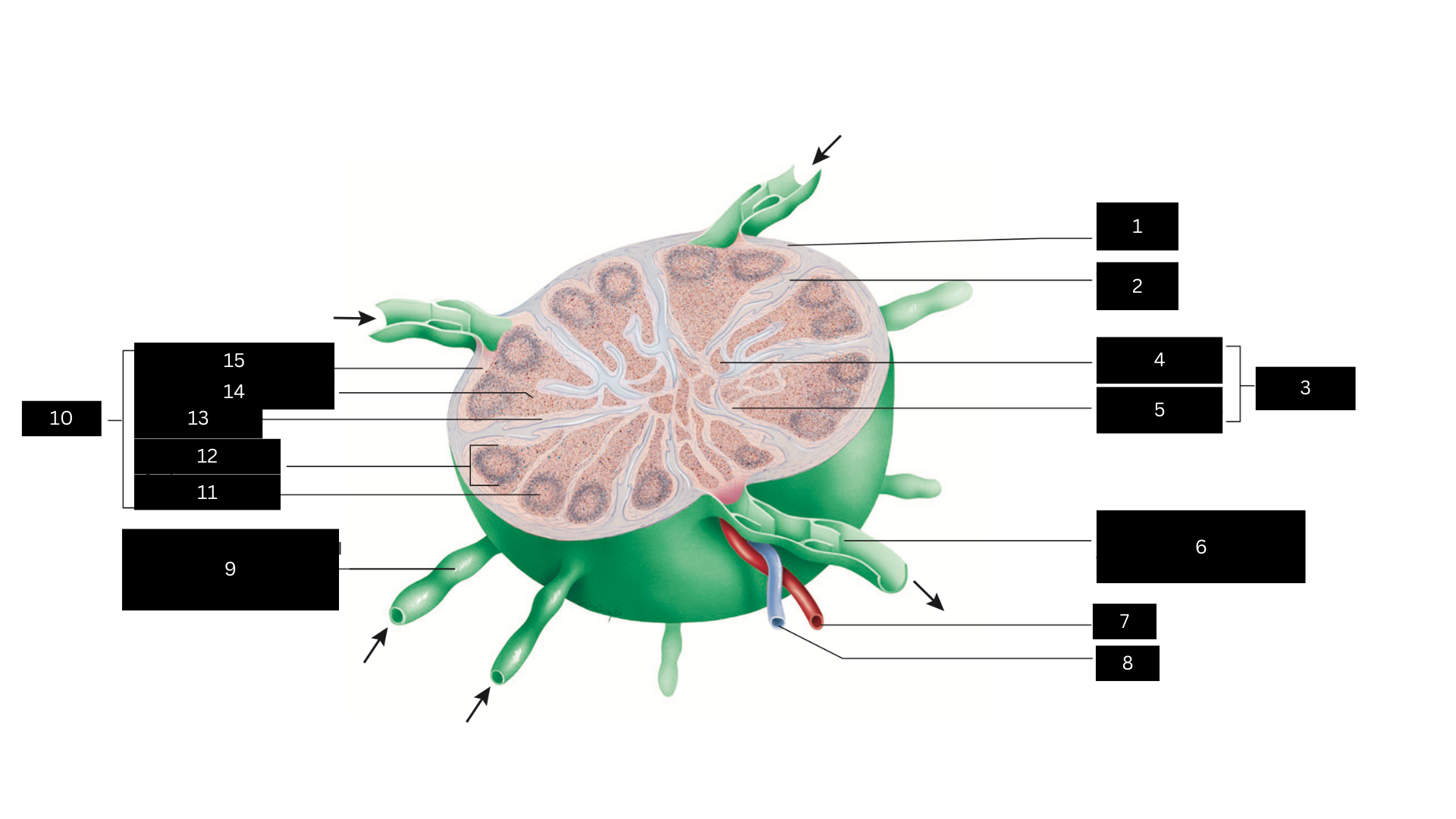
Trabecula
2
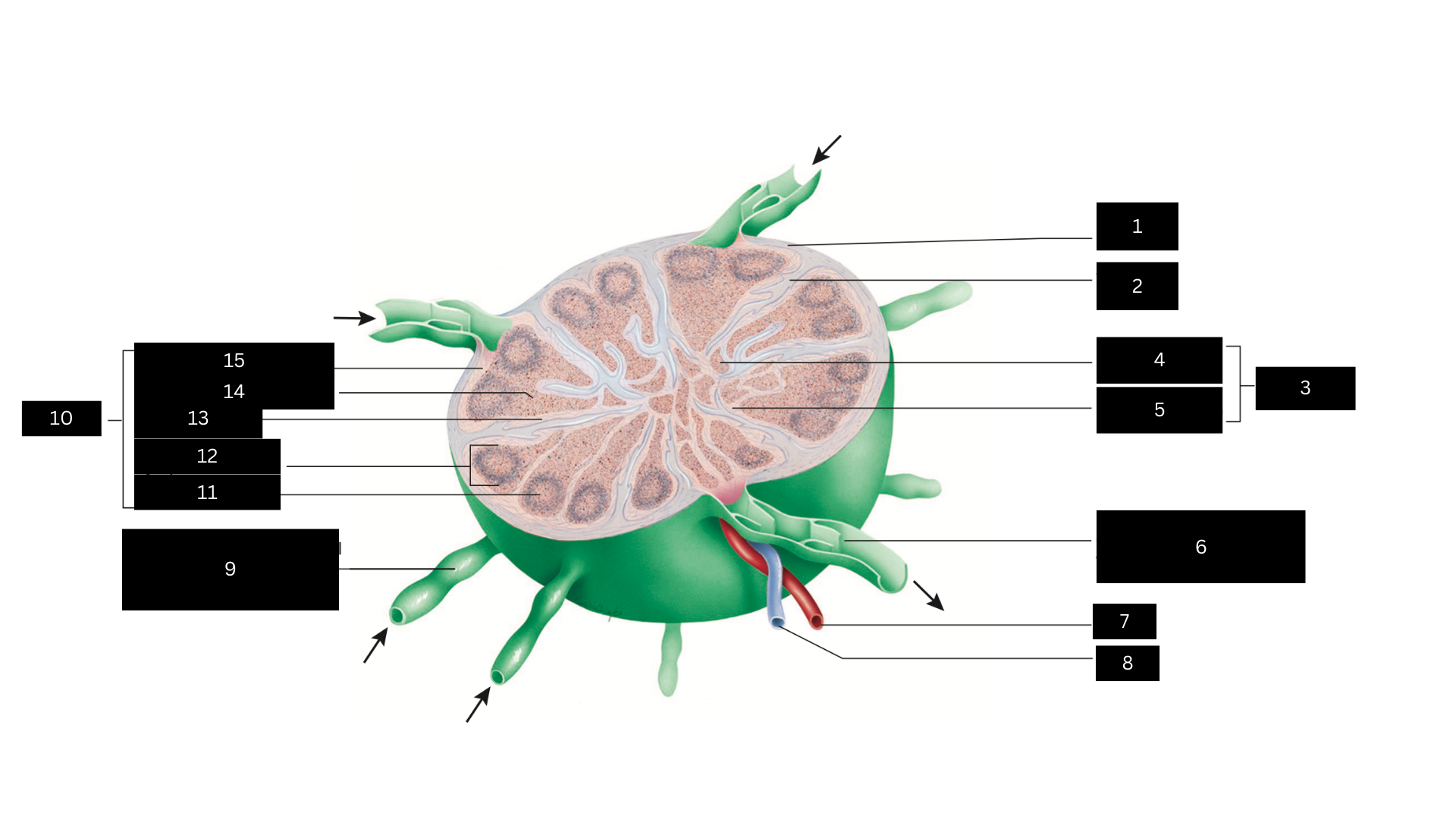
Medulla
3
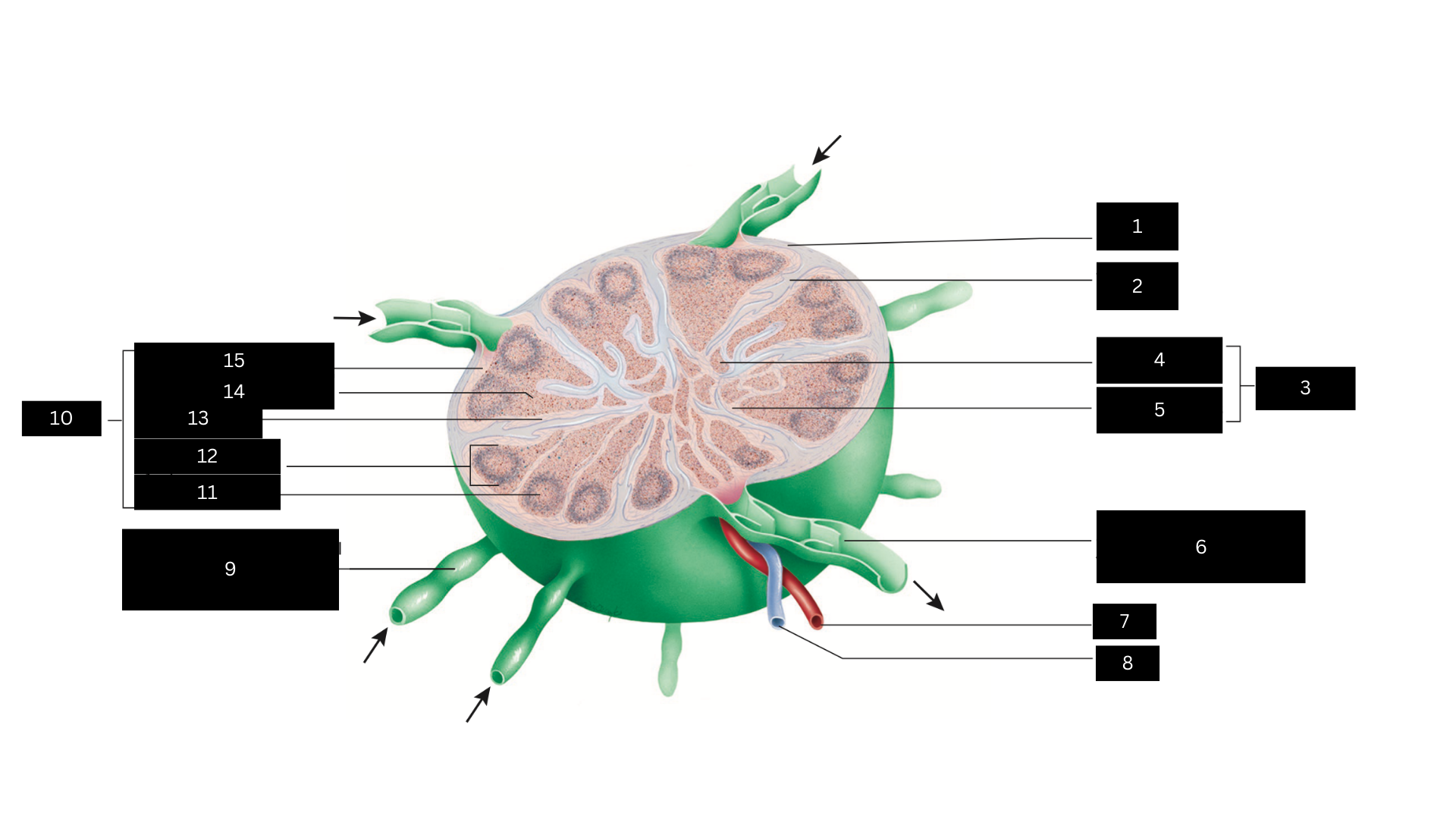
Medullary cord
4
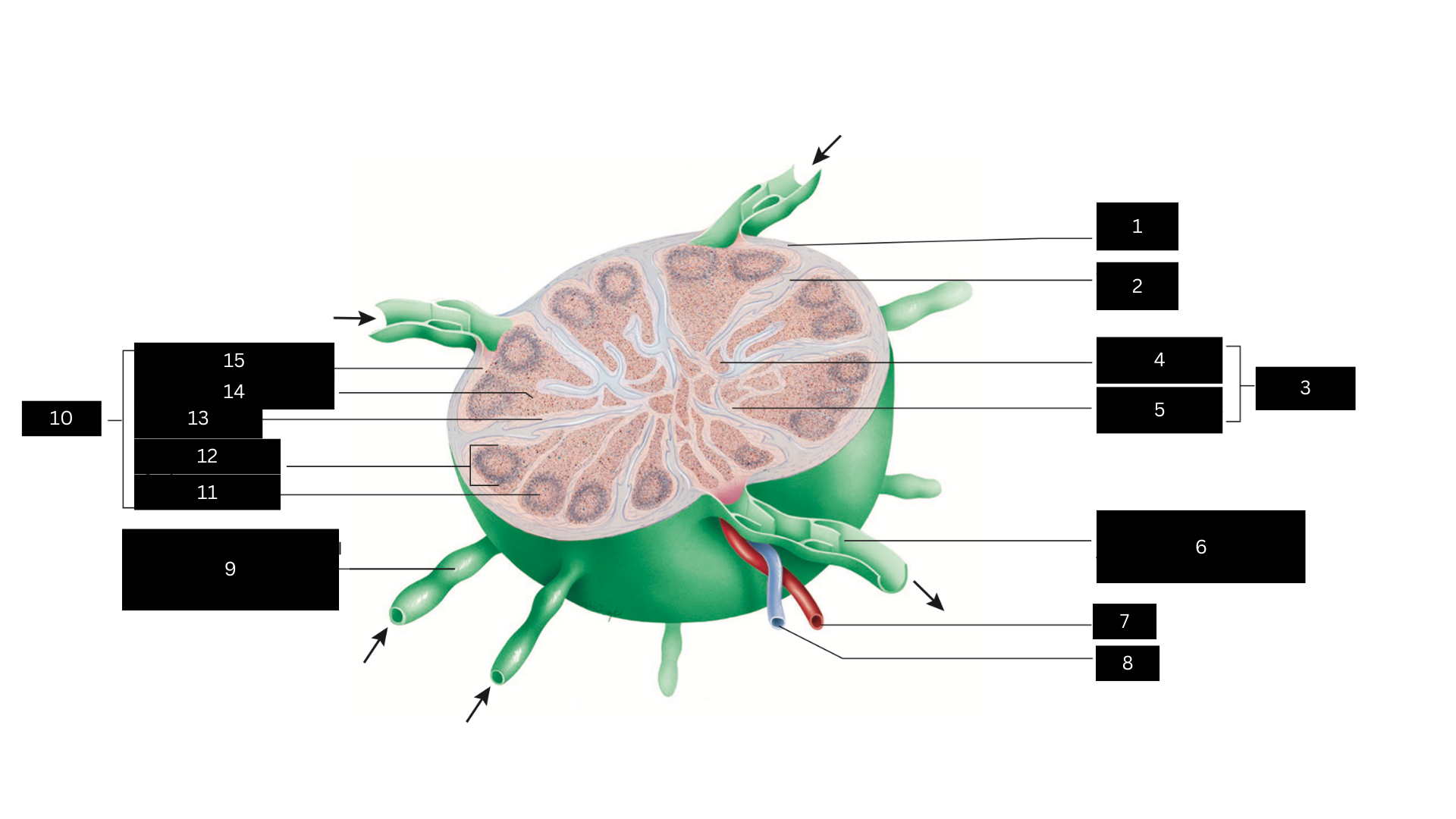
Medullary sinus
5
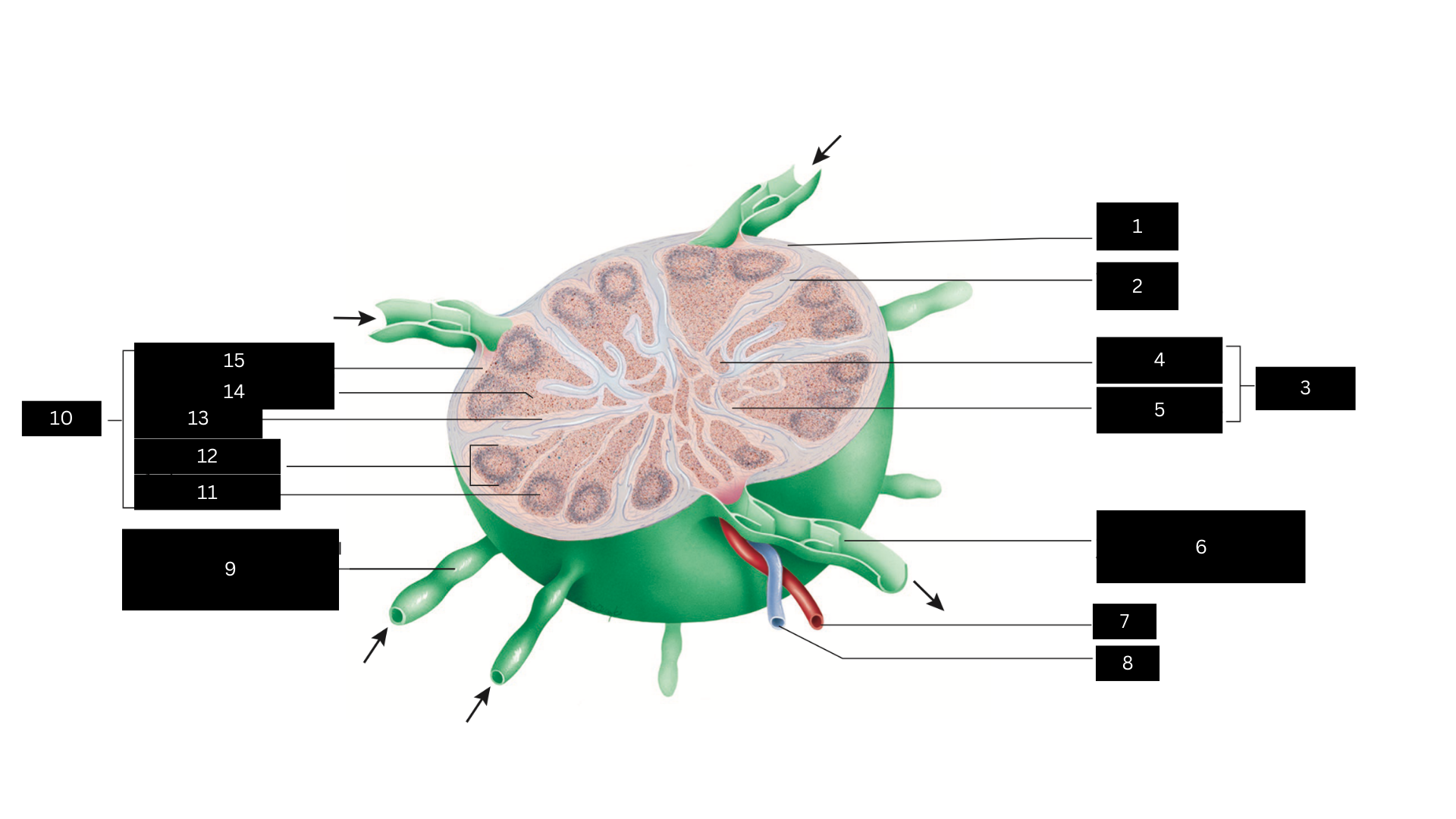
Efferent lymphatic vessel carrying lymph away from the lymph node
6
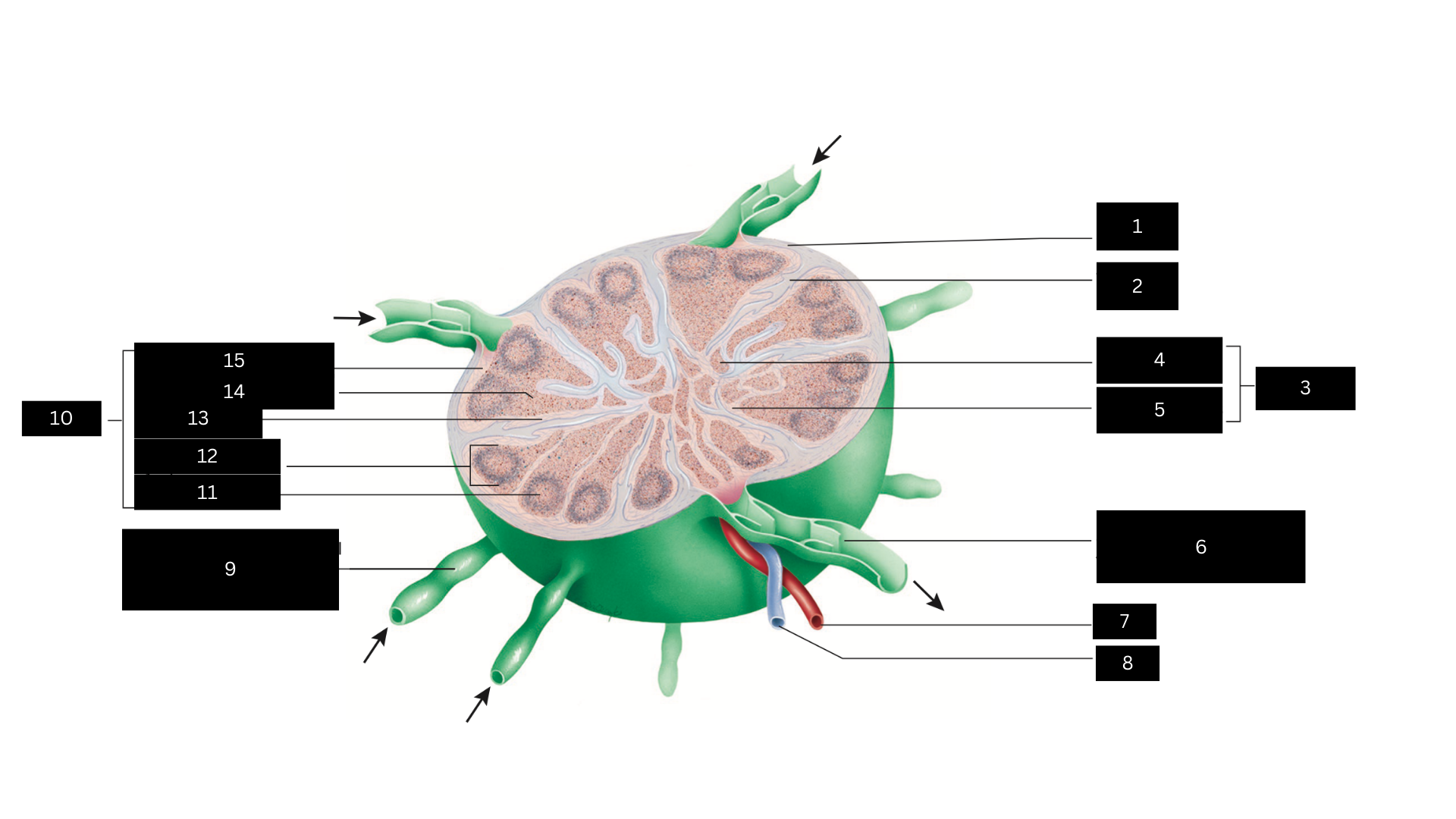
Artery
7
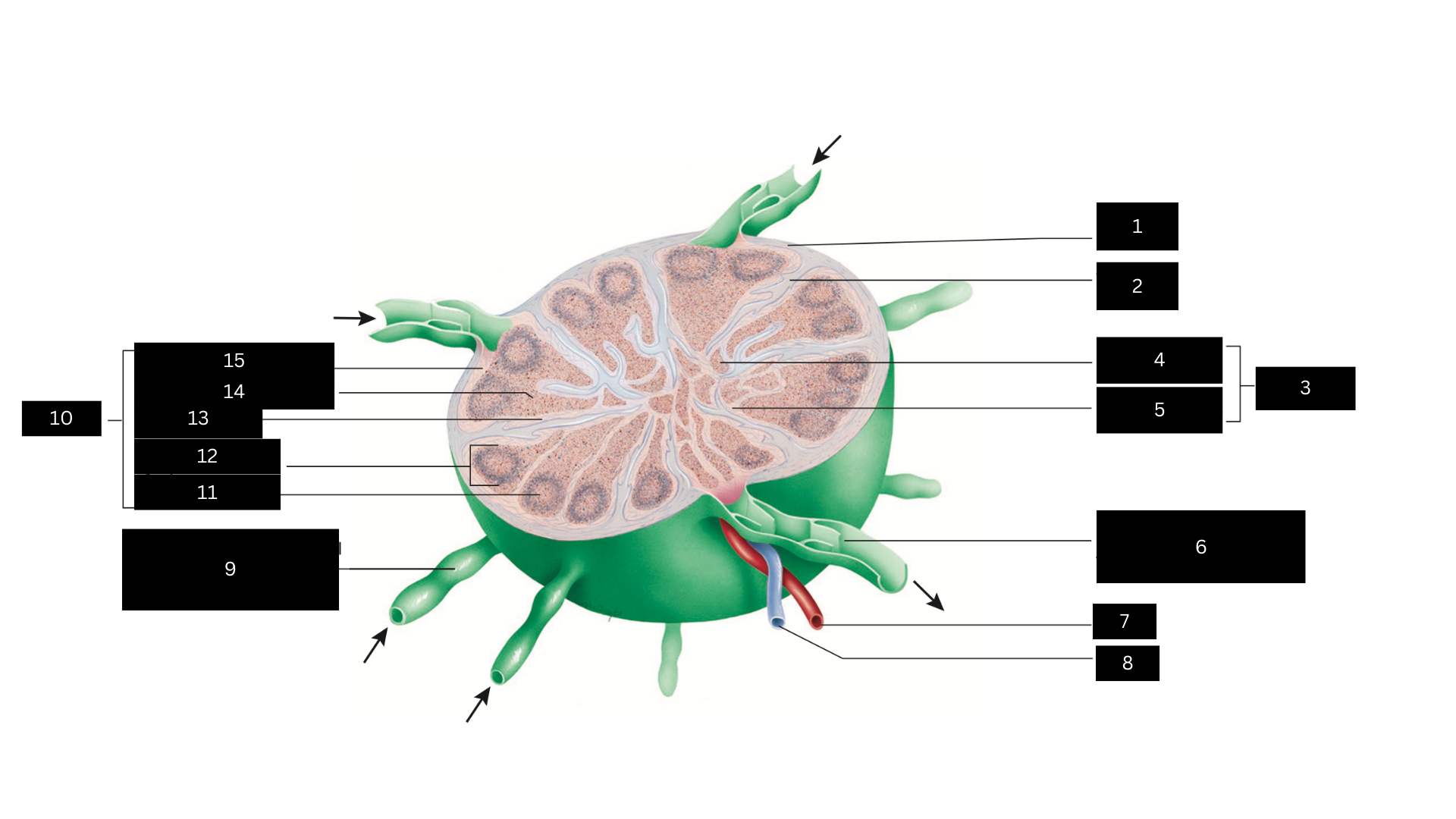
Vein
8
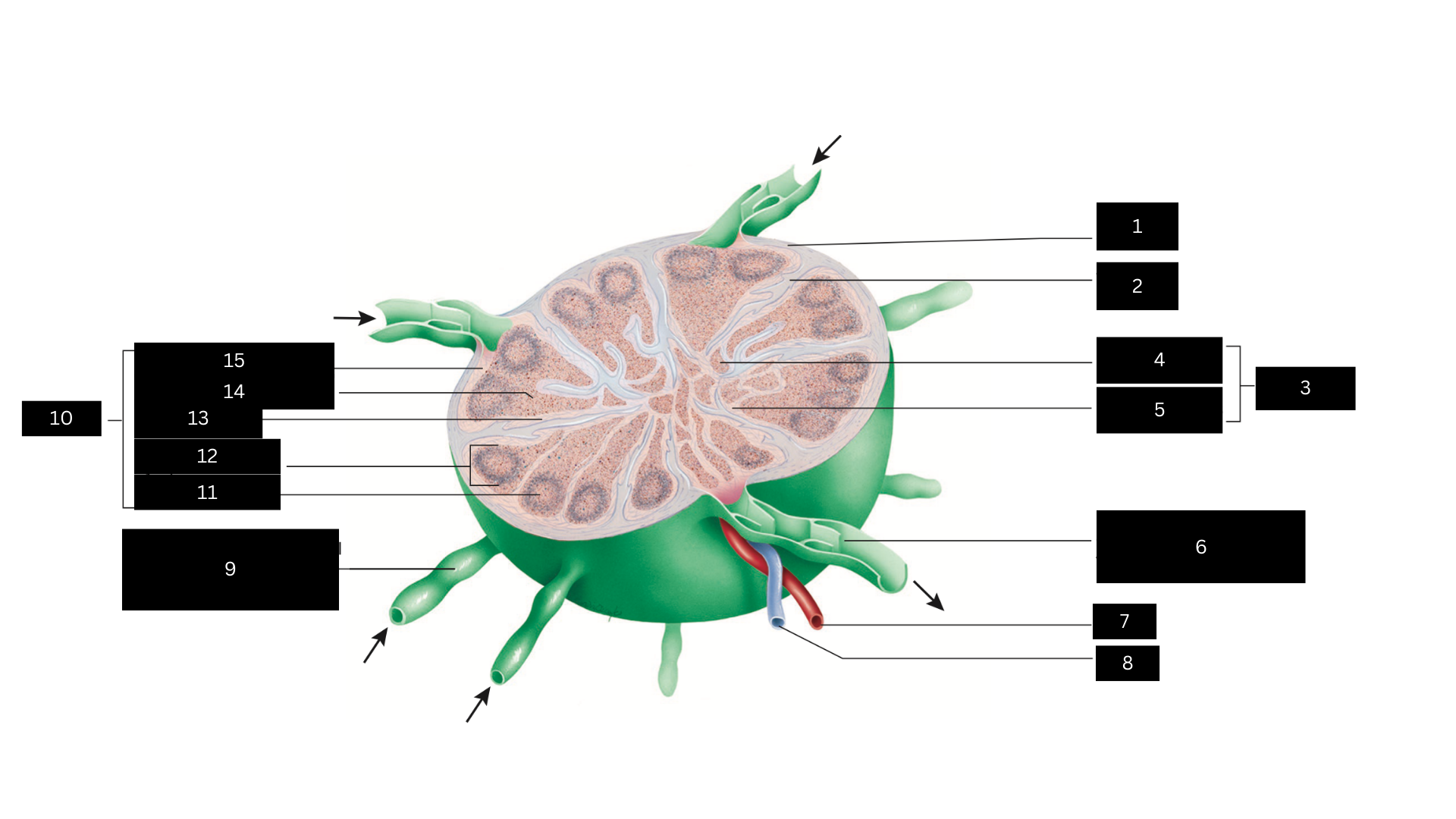
Afferent lymphatic vessel carrying lymph to the lymph node
9
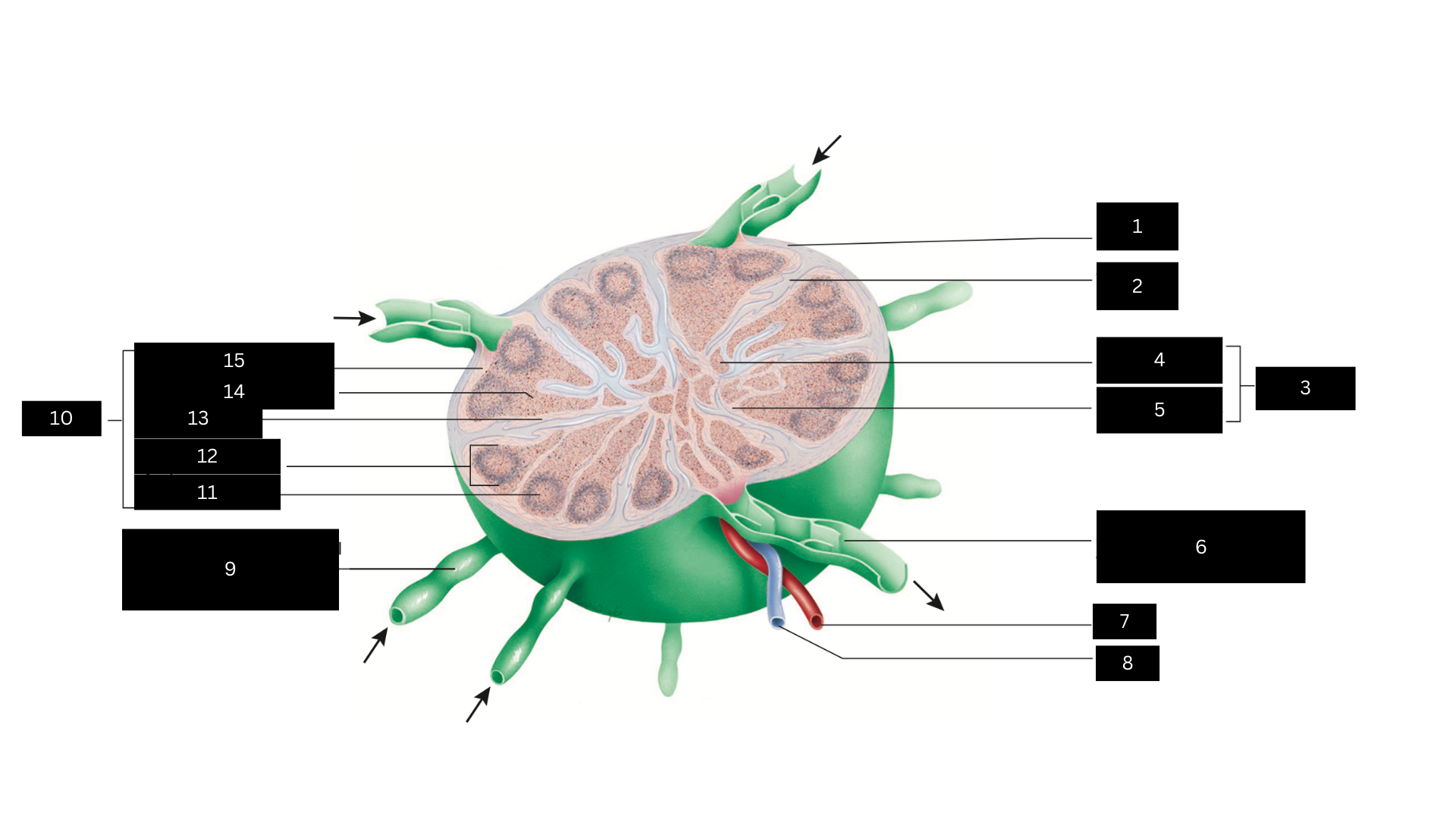
Cortex
10
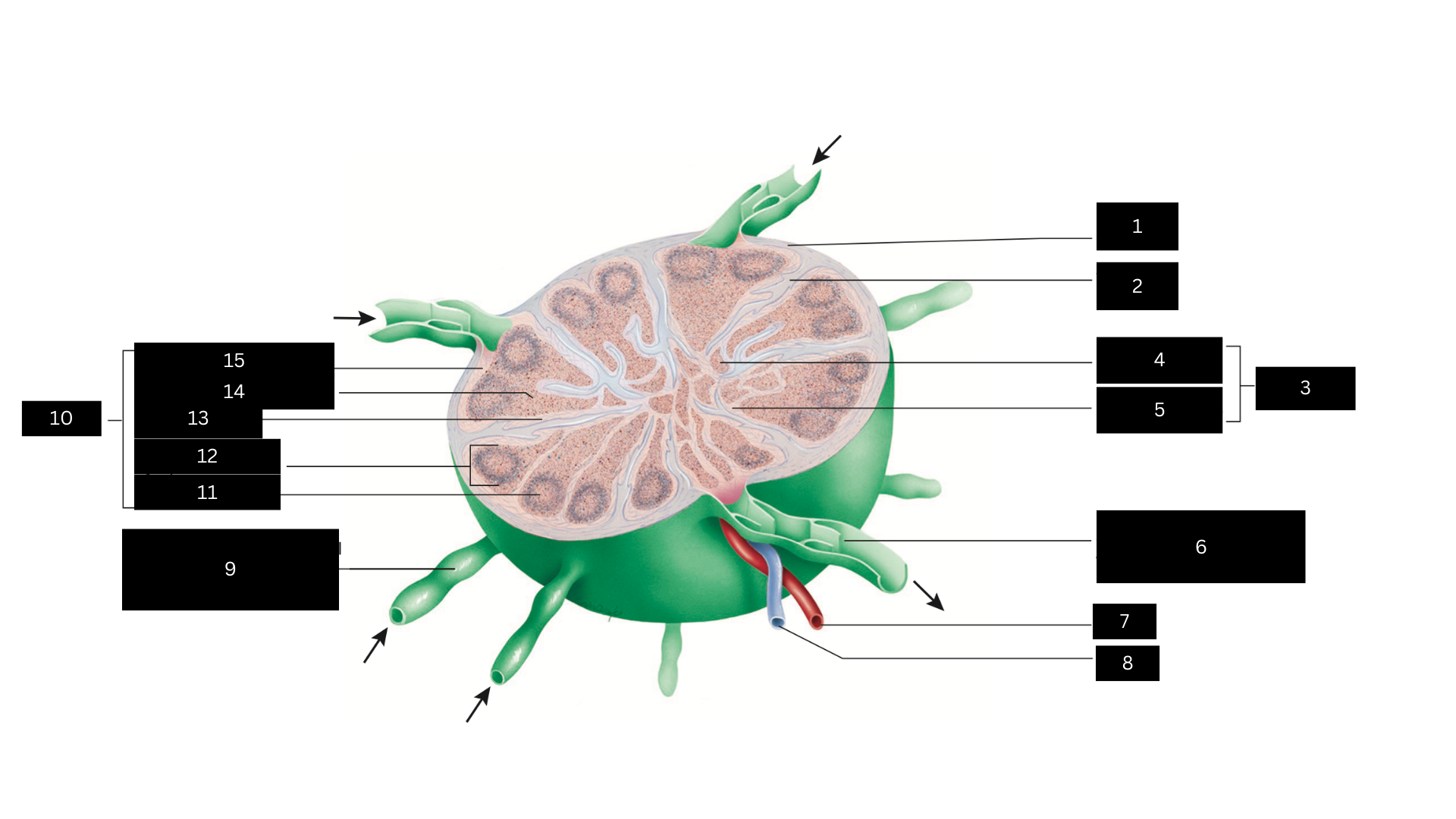
Germinal center
11
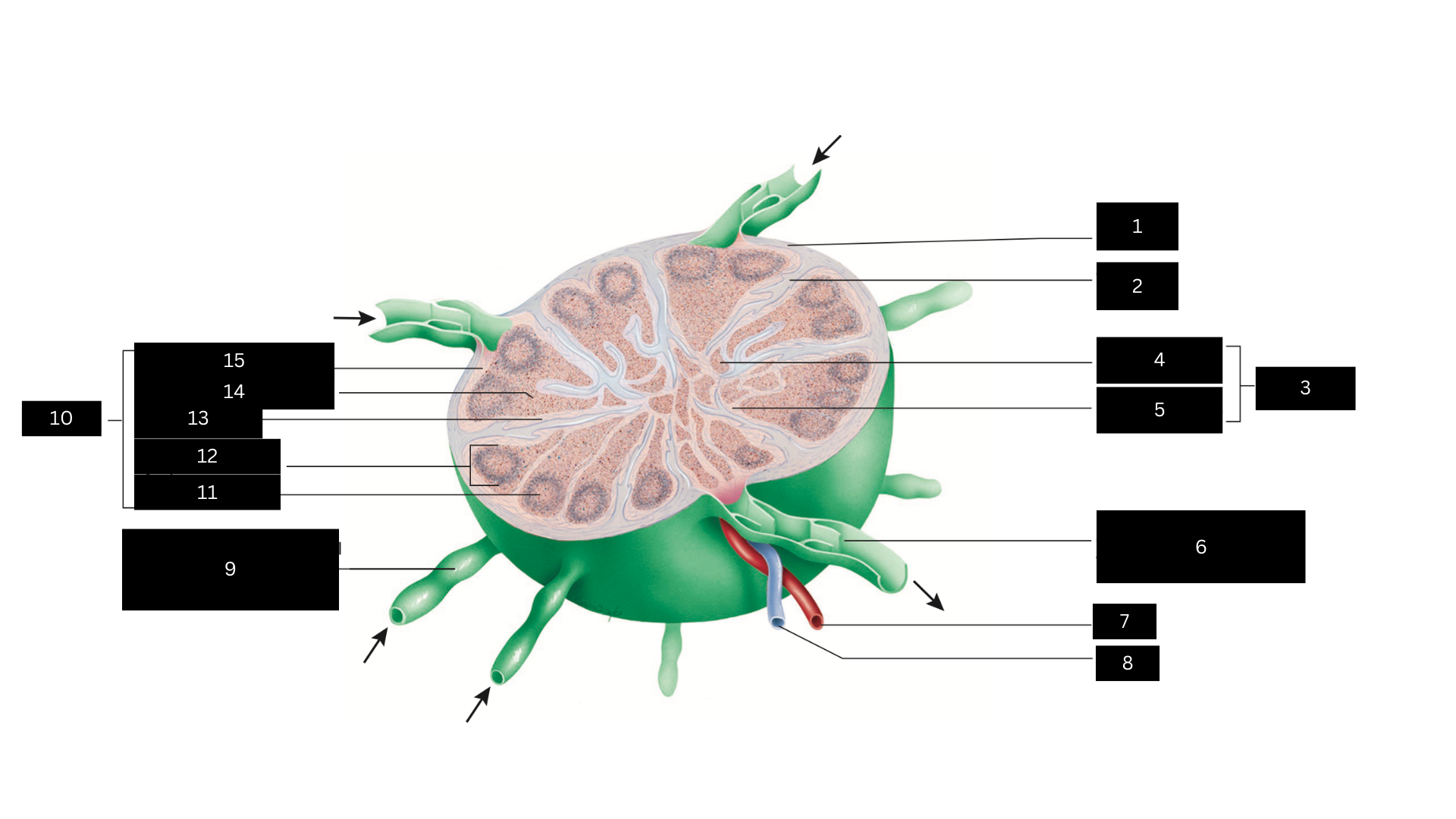
Lymphatic nodule
12
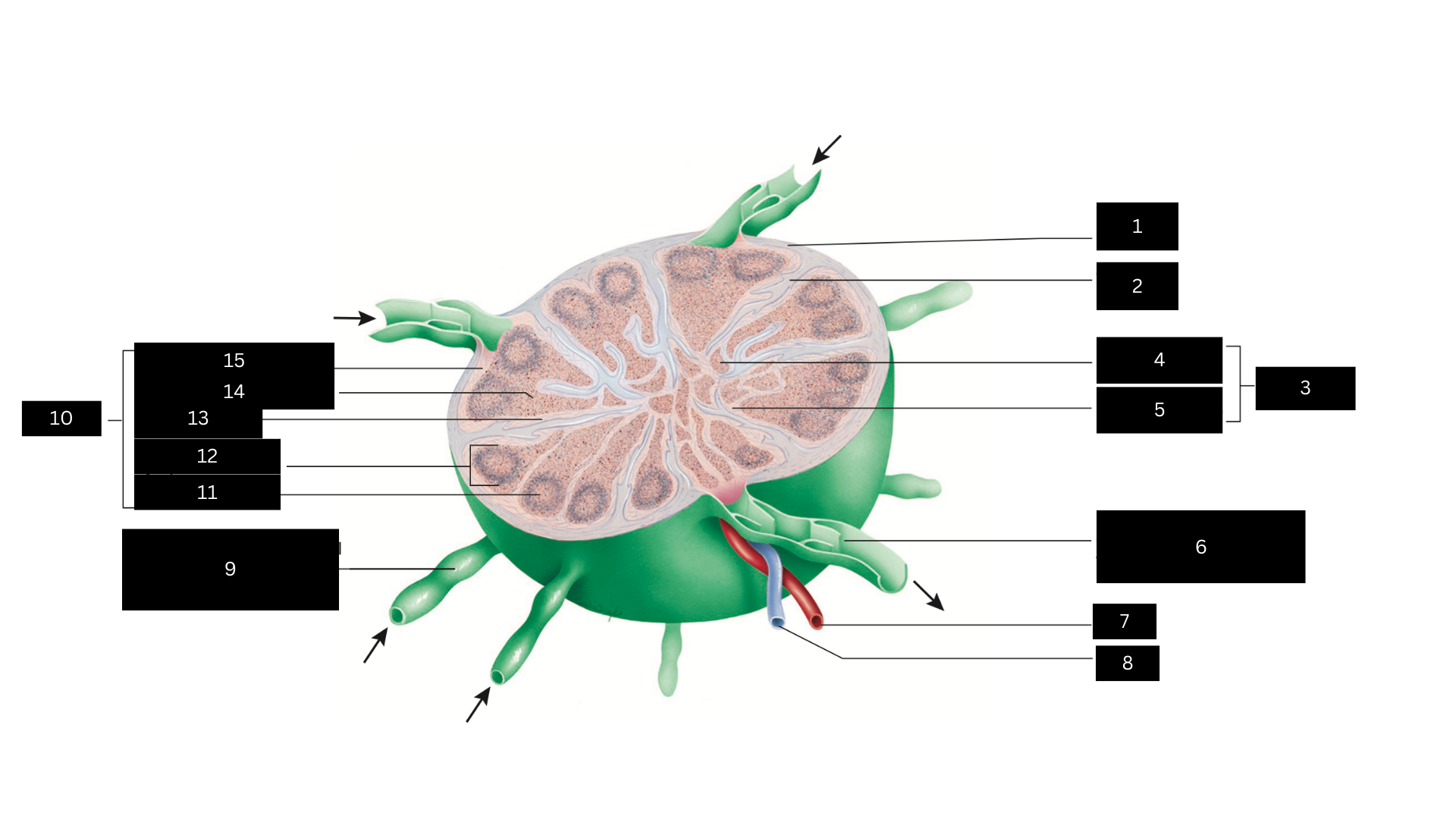
Cortical sinus
13
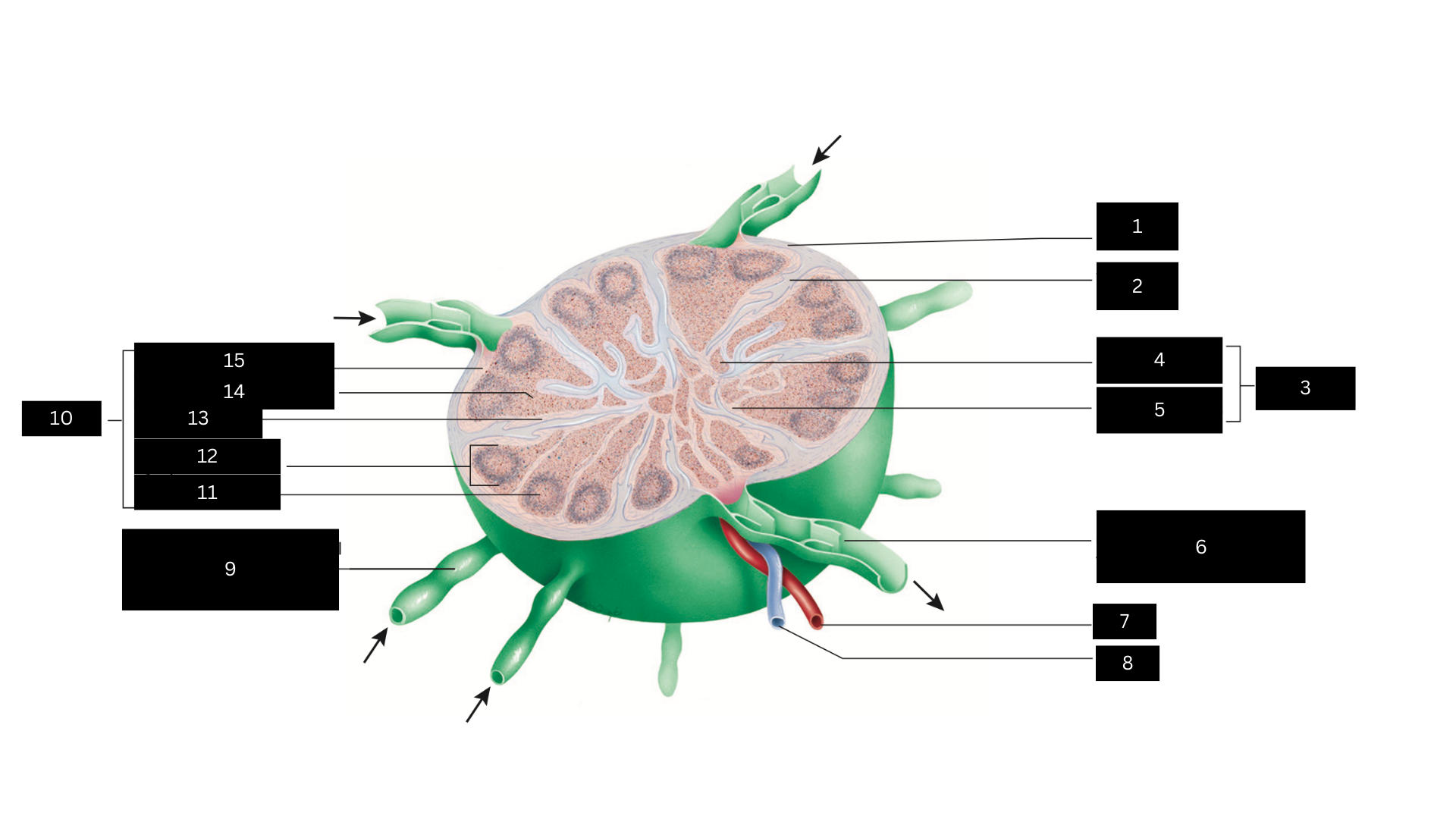
Diffuse lymphatic tissue
14
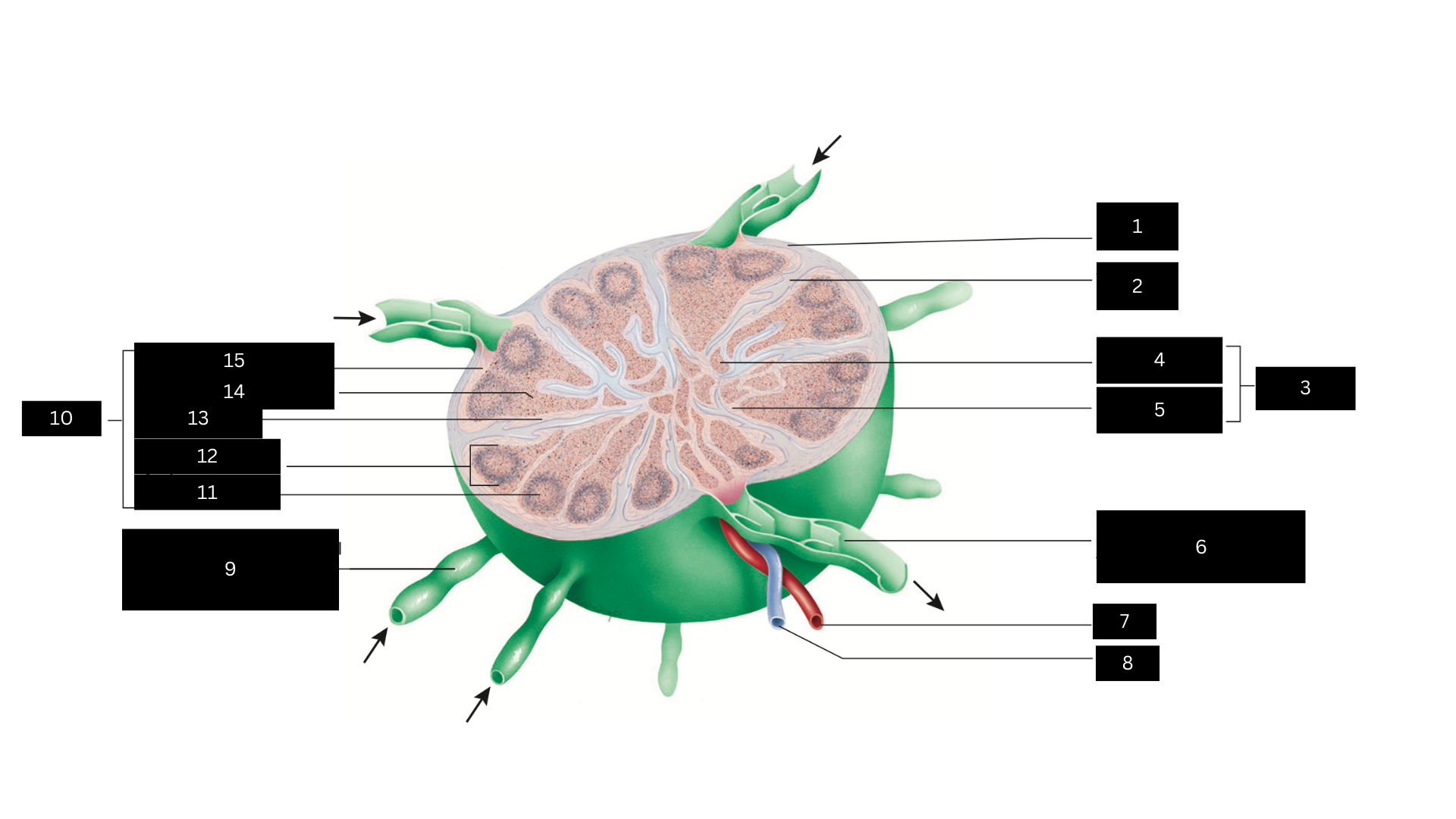
Subcapsular sinus
15
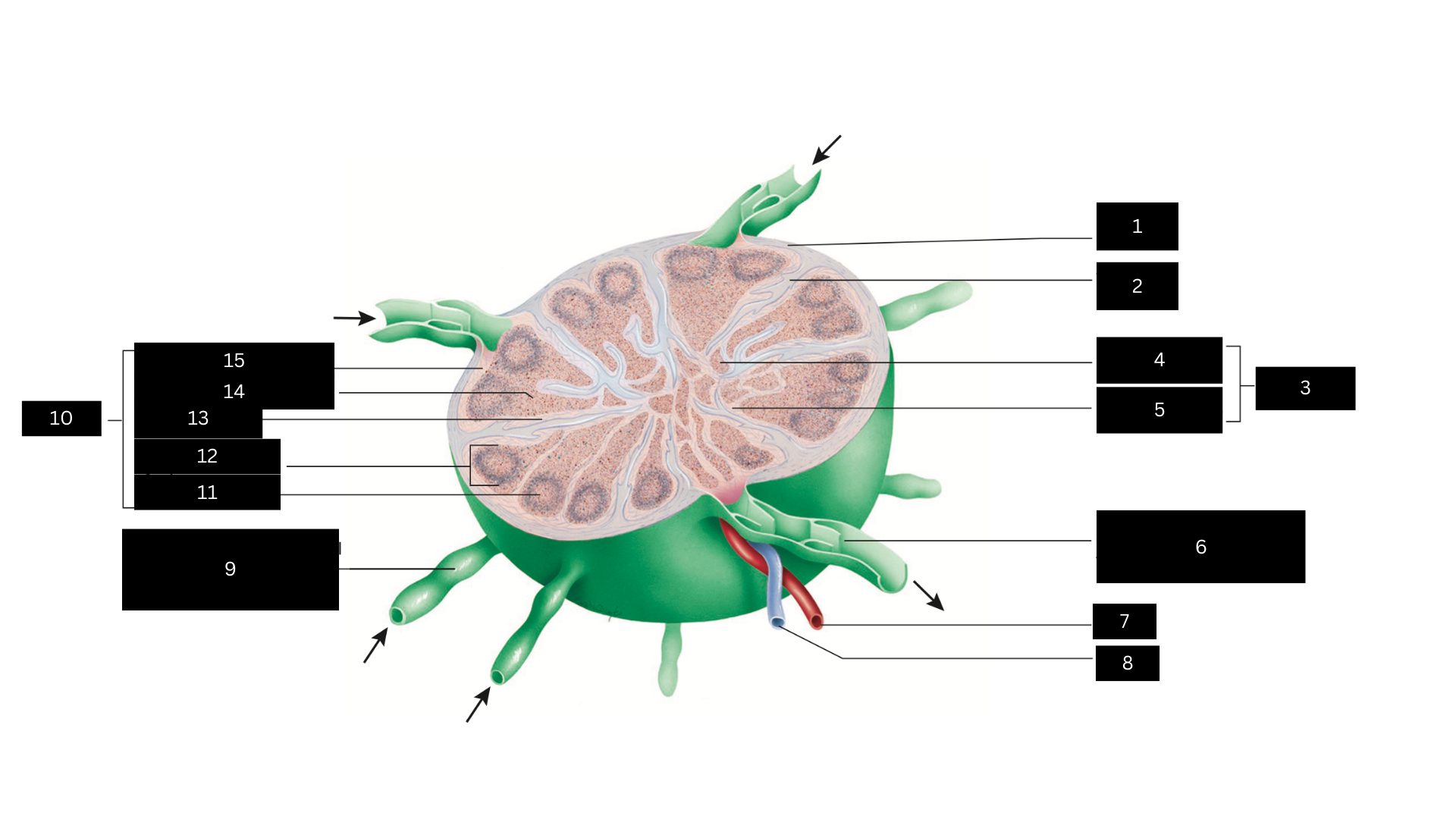
Lymph
1
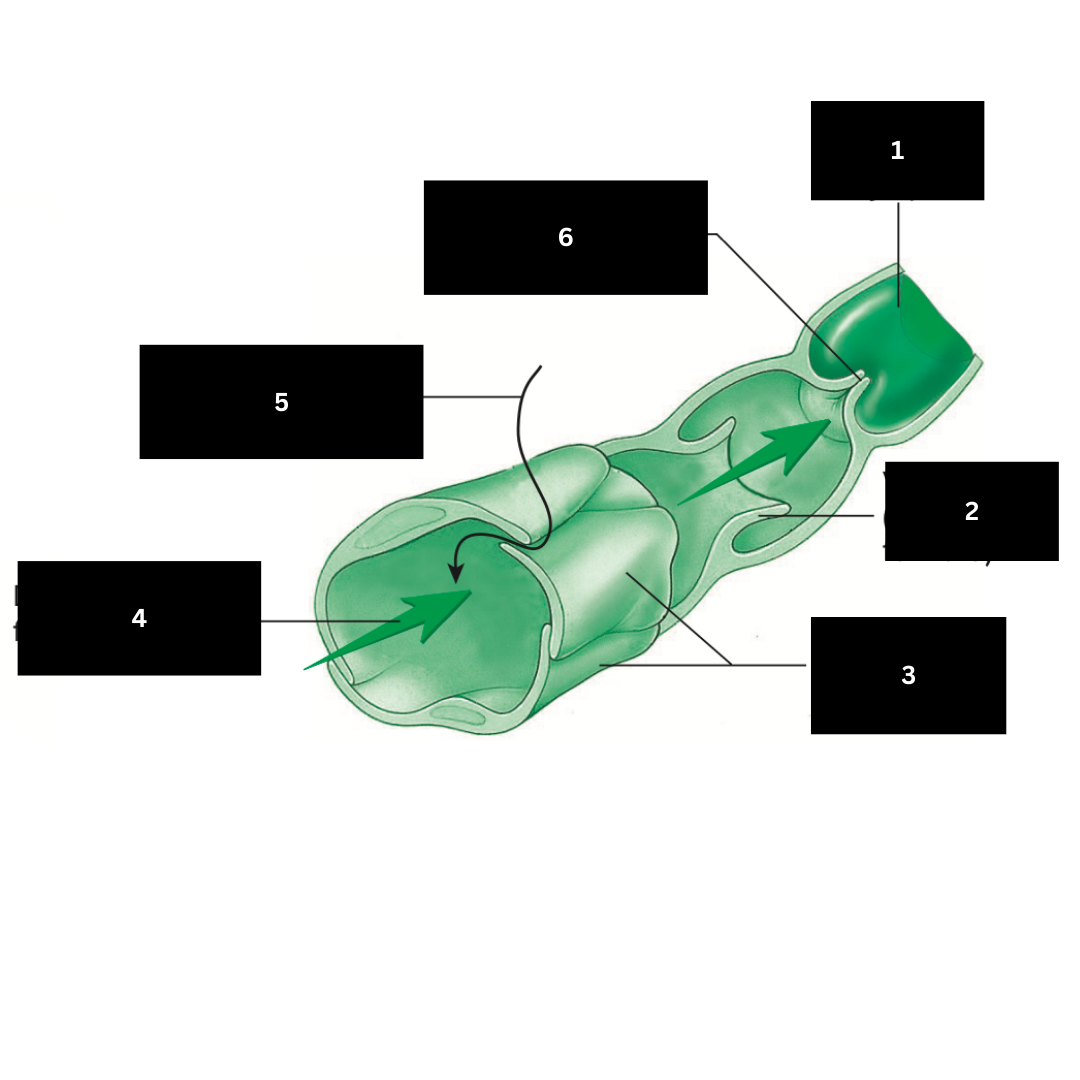
Valve open (lymph flows forward)
2
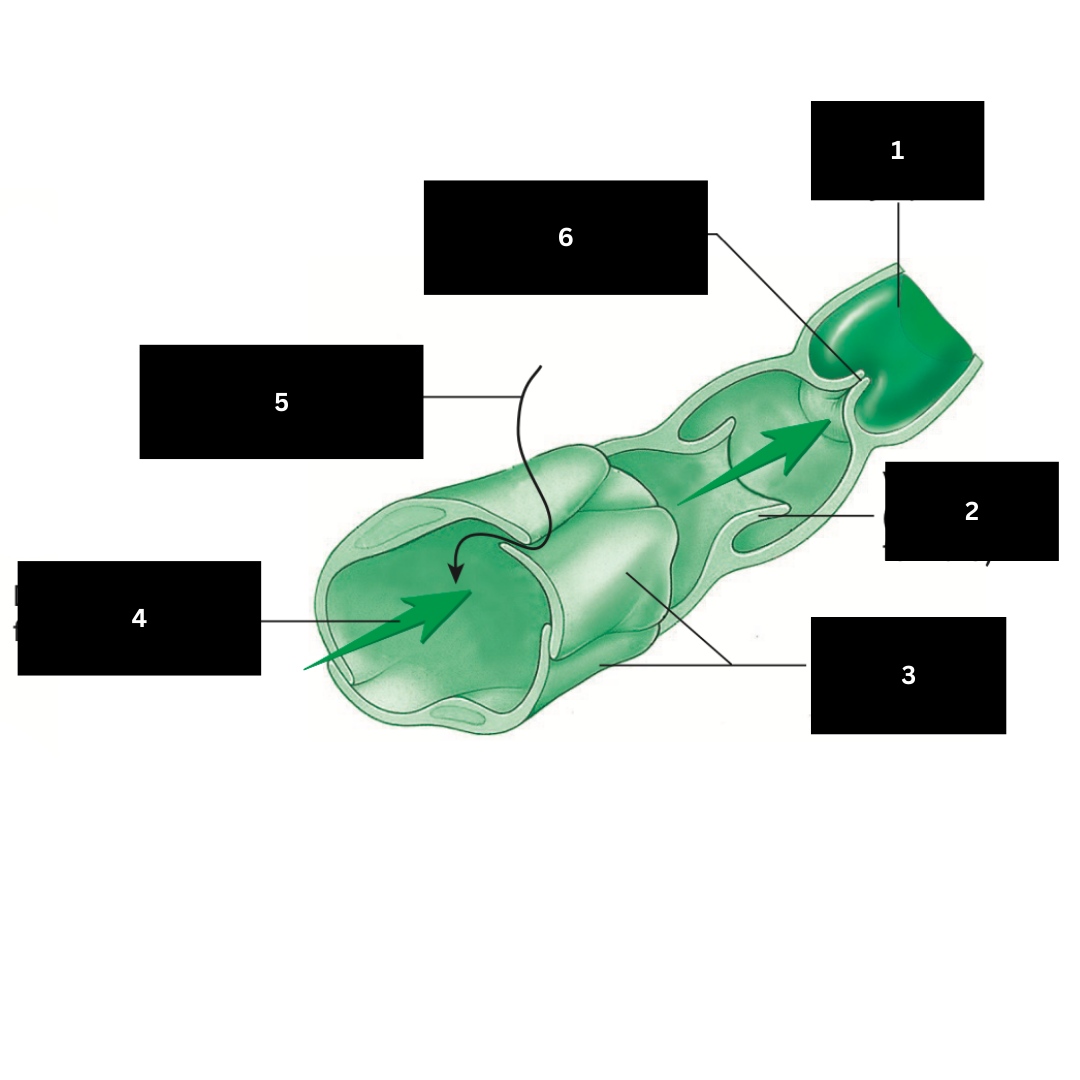
Overlapping endothelial cells
3
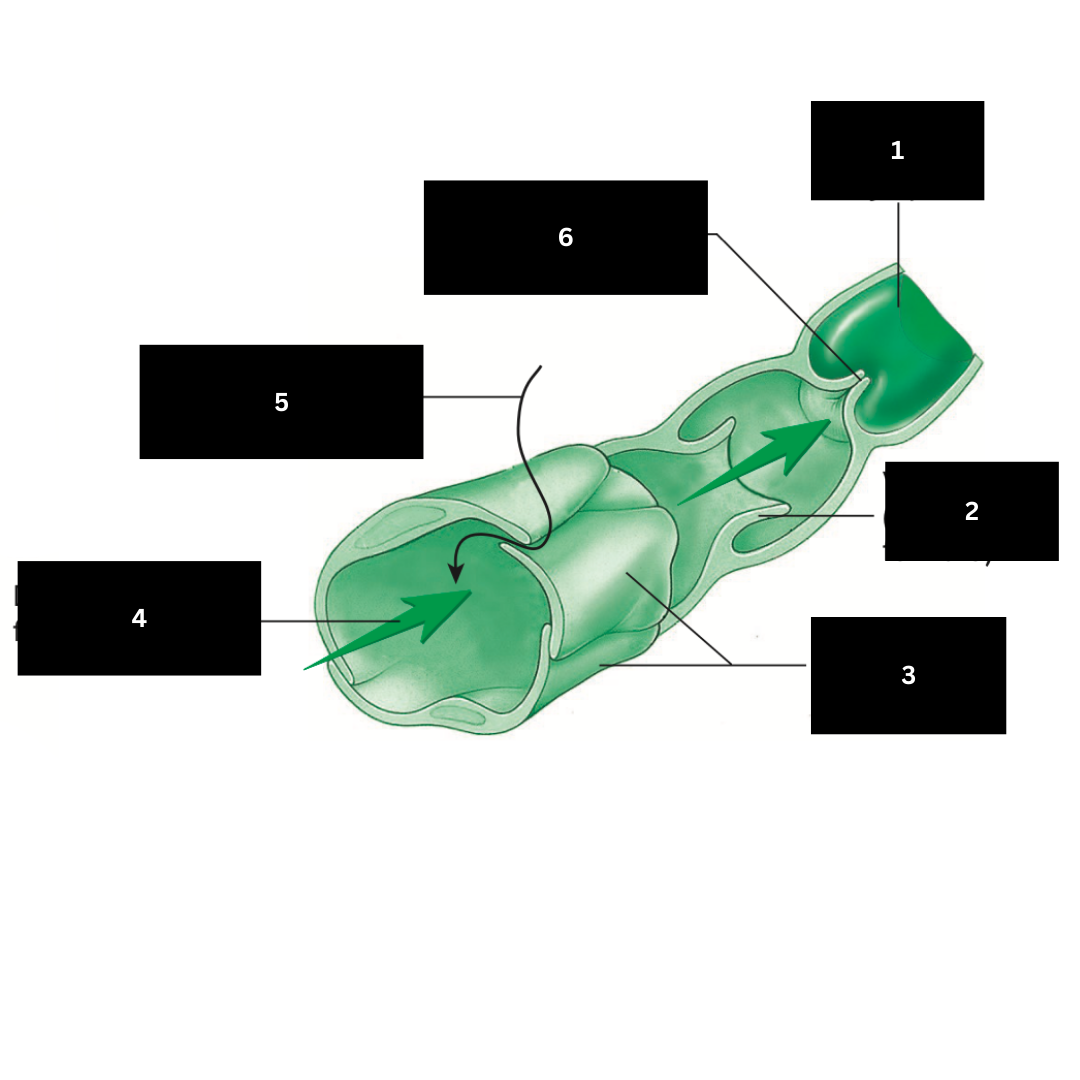
Direction of lymph flow in capillary
4
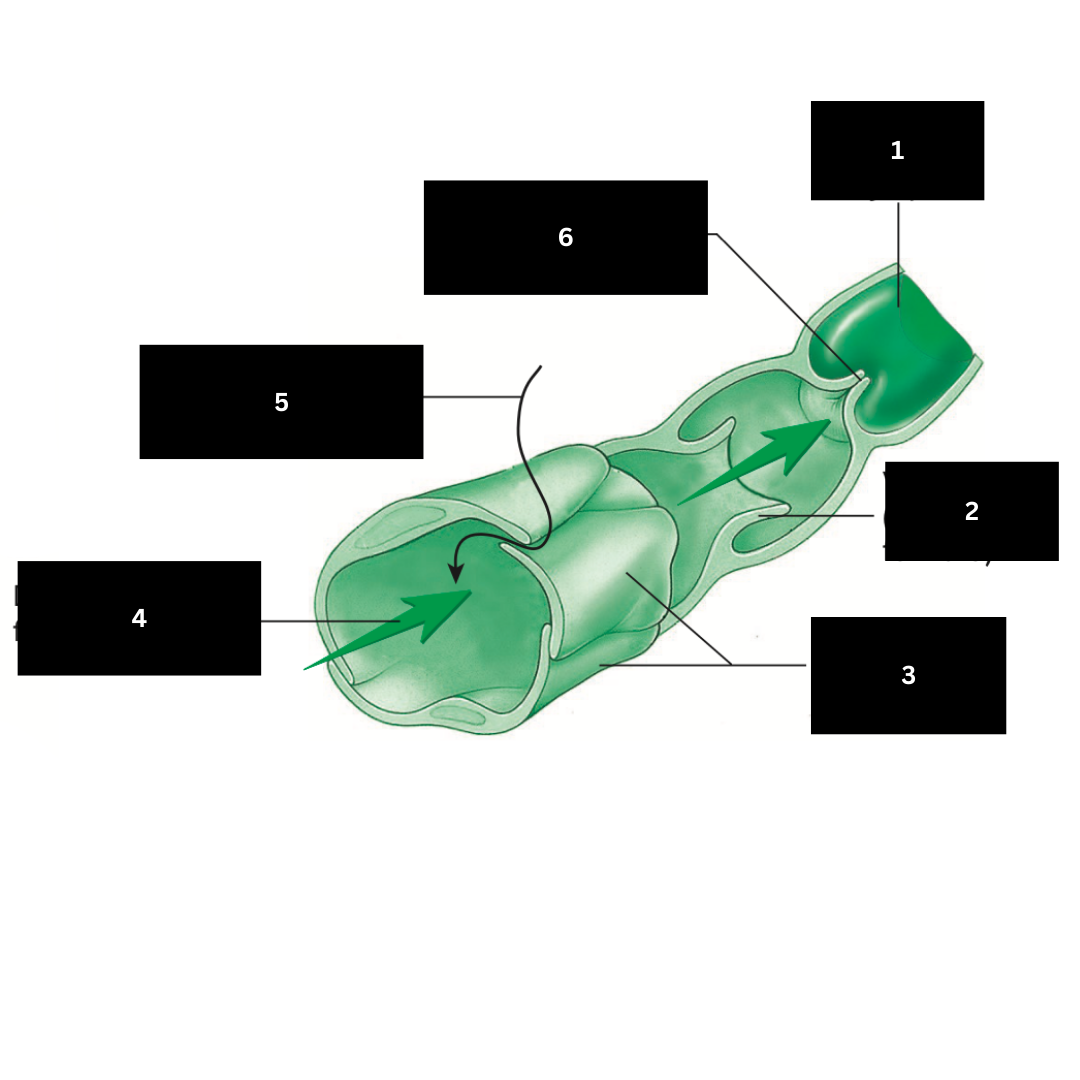
Fluid entering lymphatic capillary
5
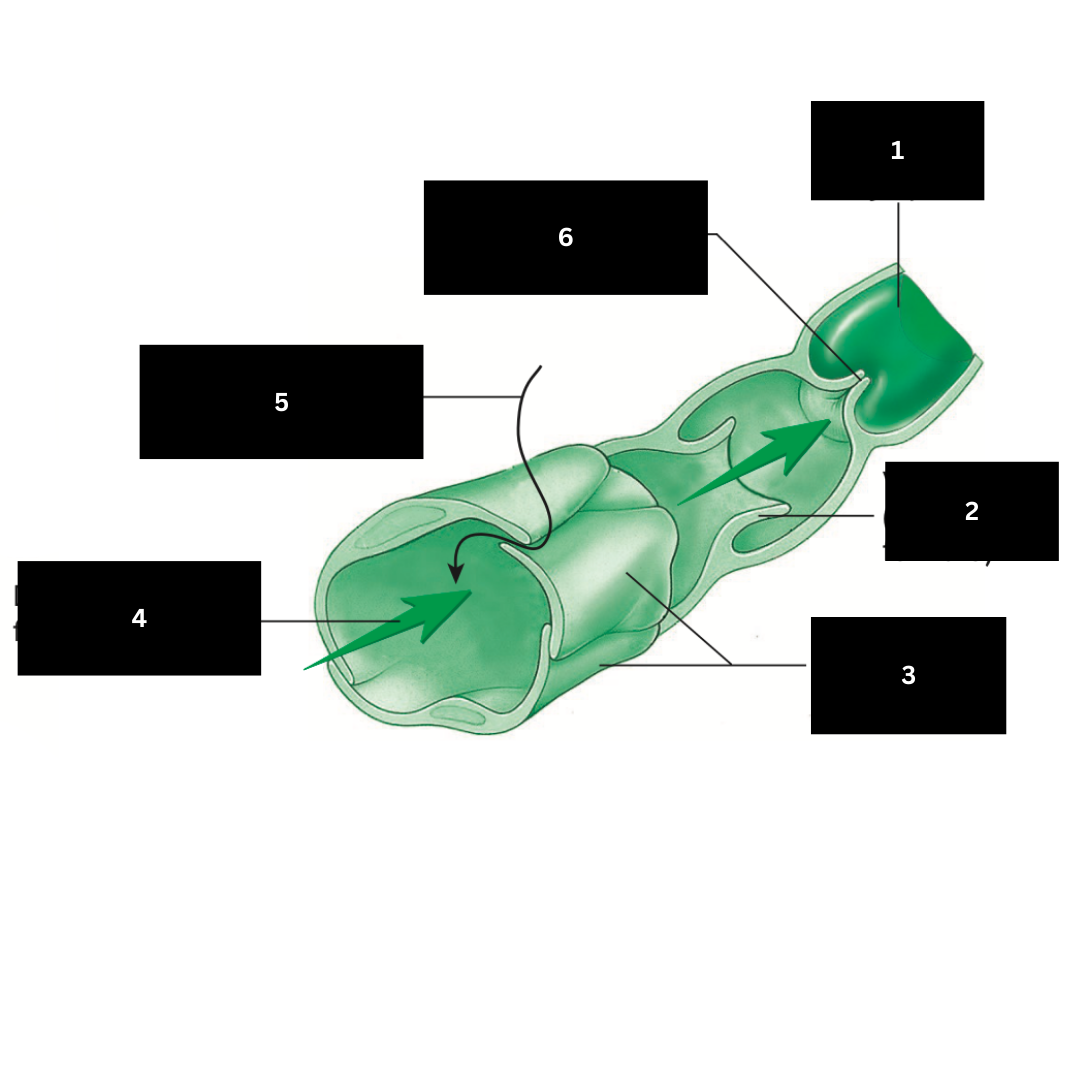
Valve closed (backflow of lymph is prevented)
6
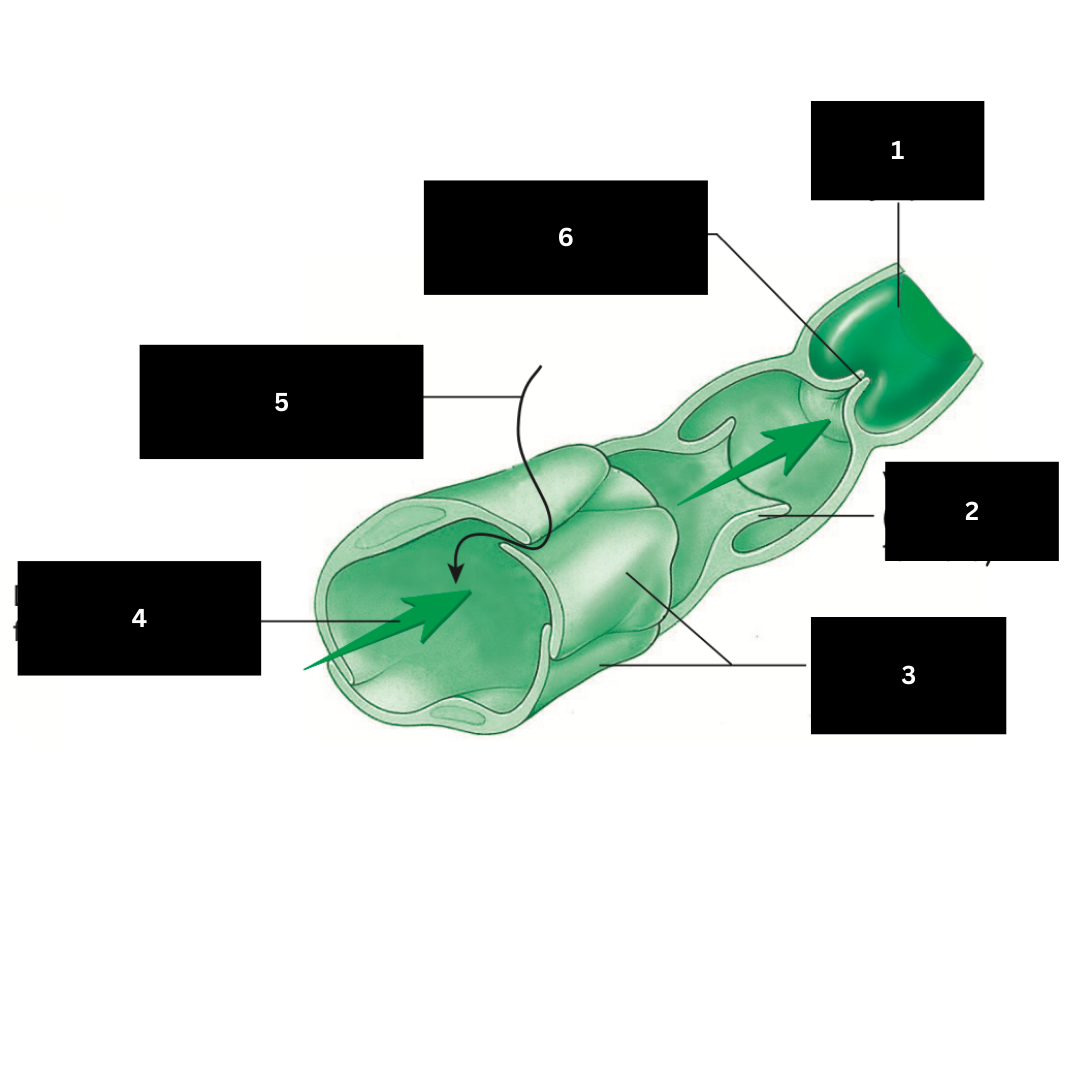
Hilum
1
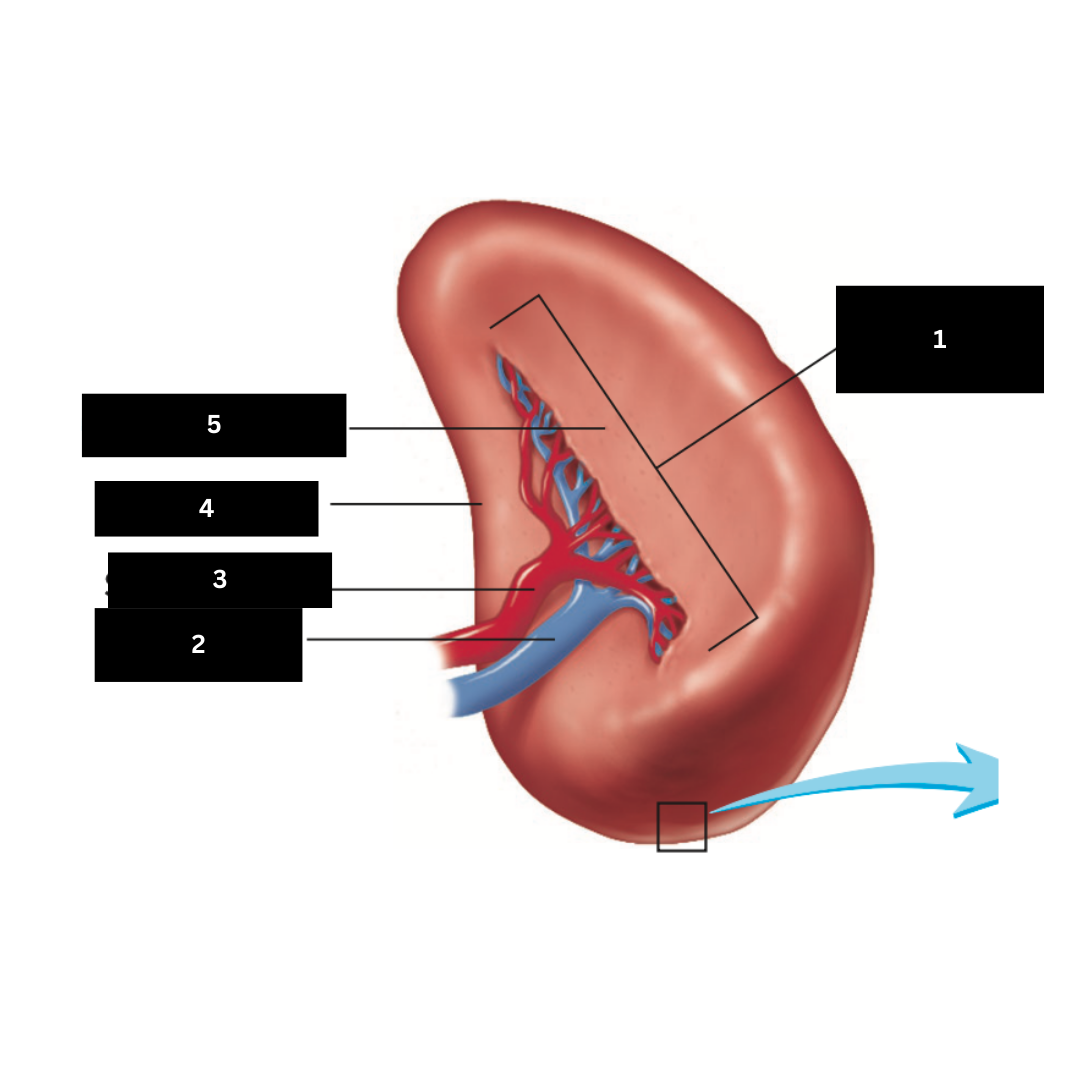
Splenic vein
2
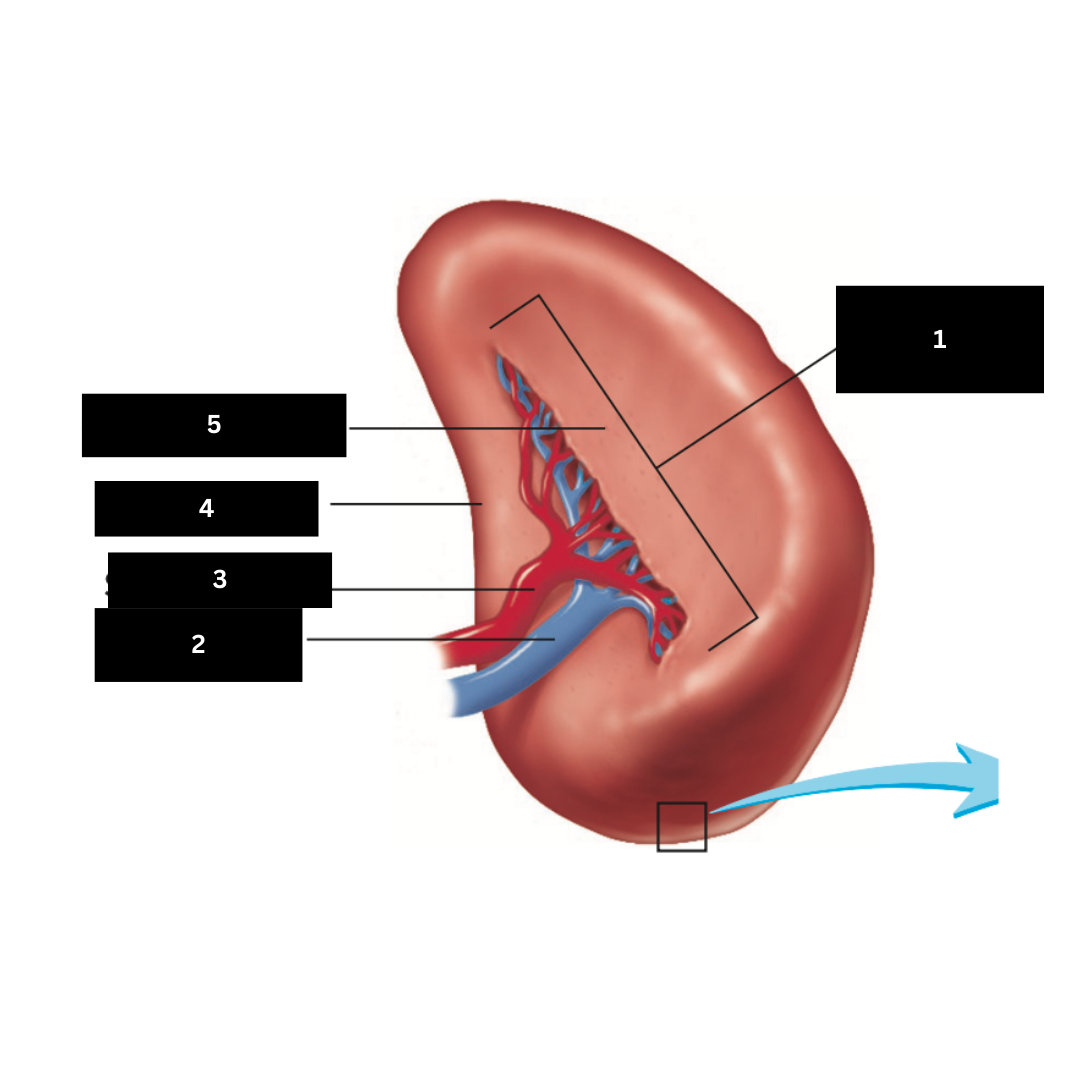
Splenic artery
3
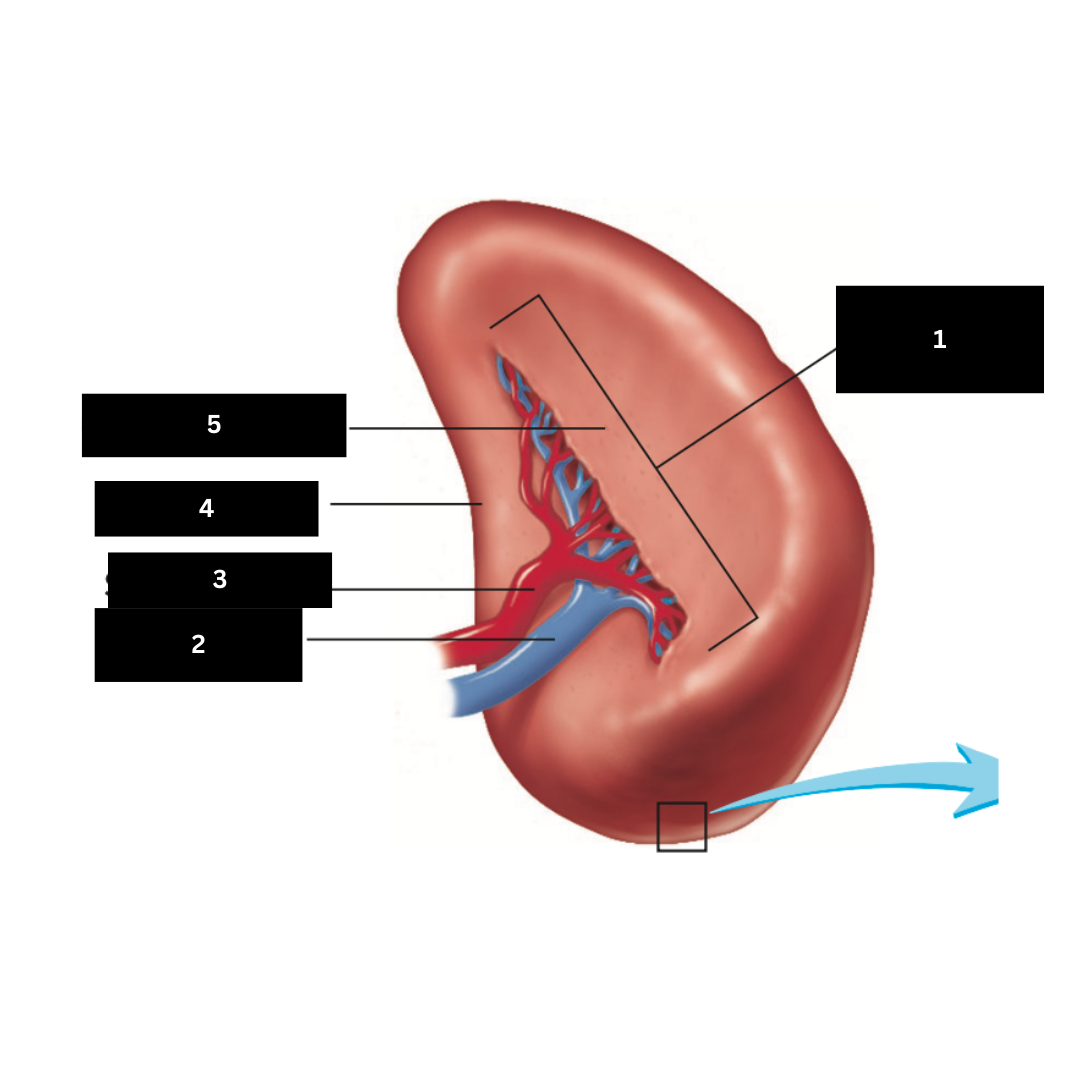
Renal surface
4
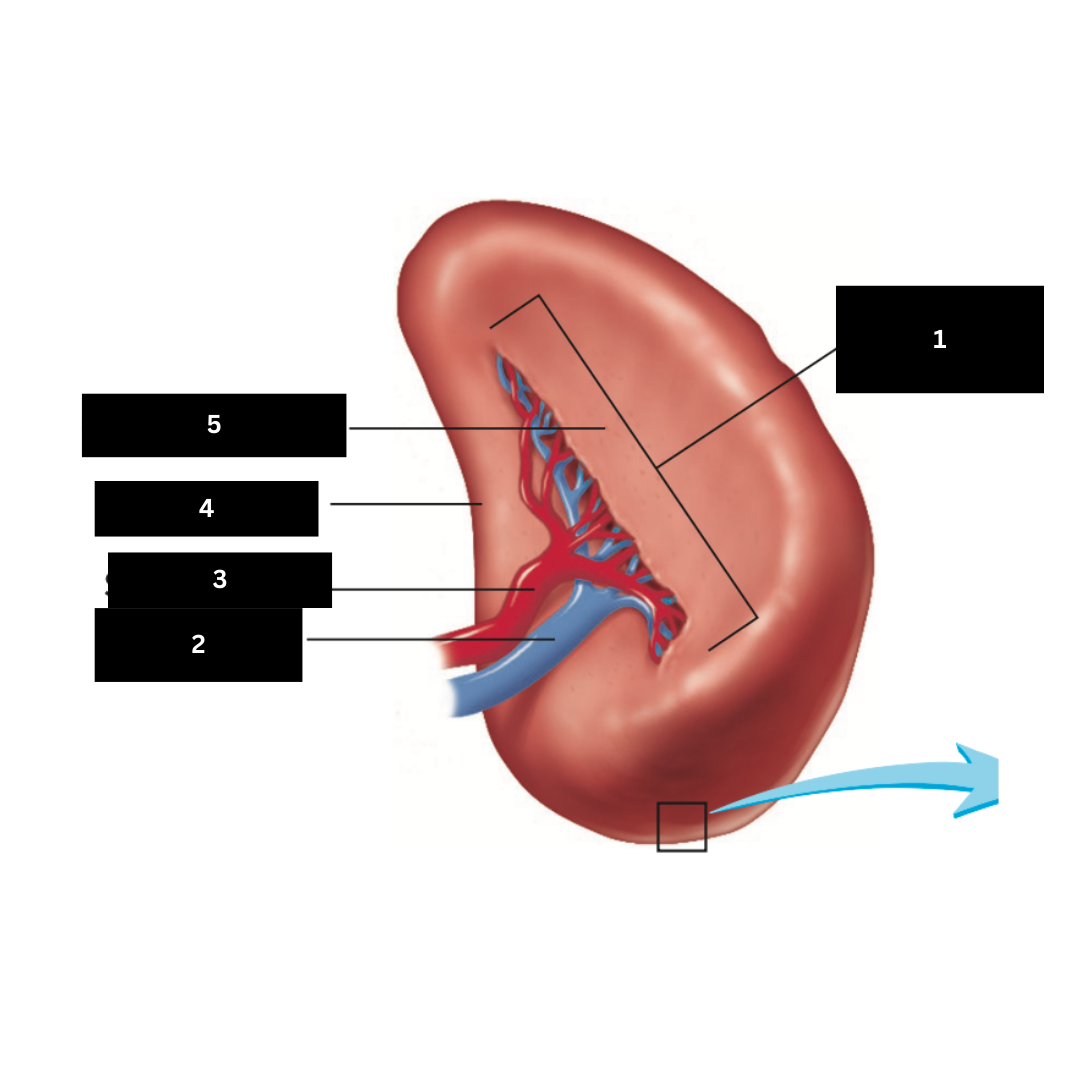
Gastric surface
5
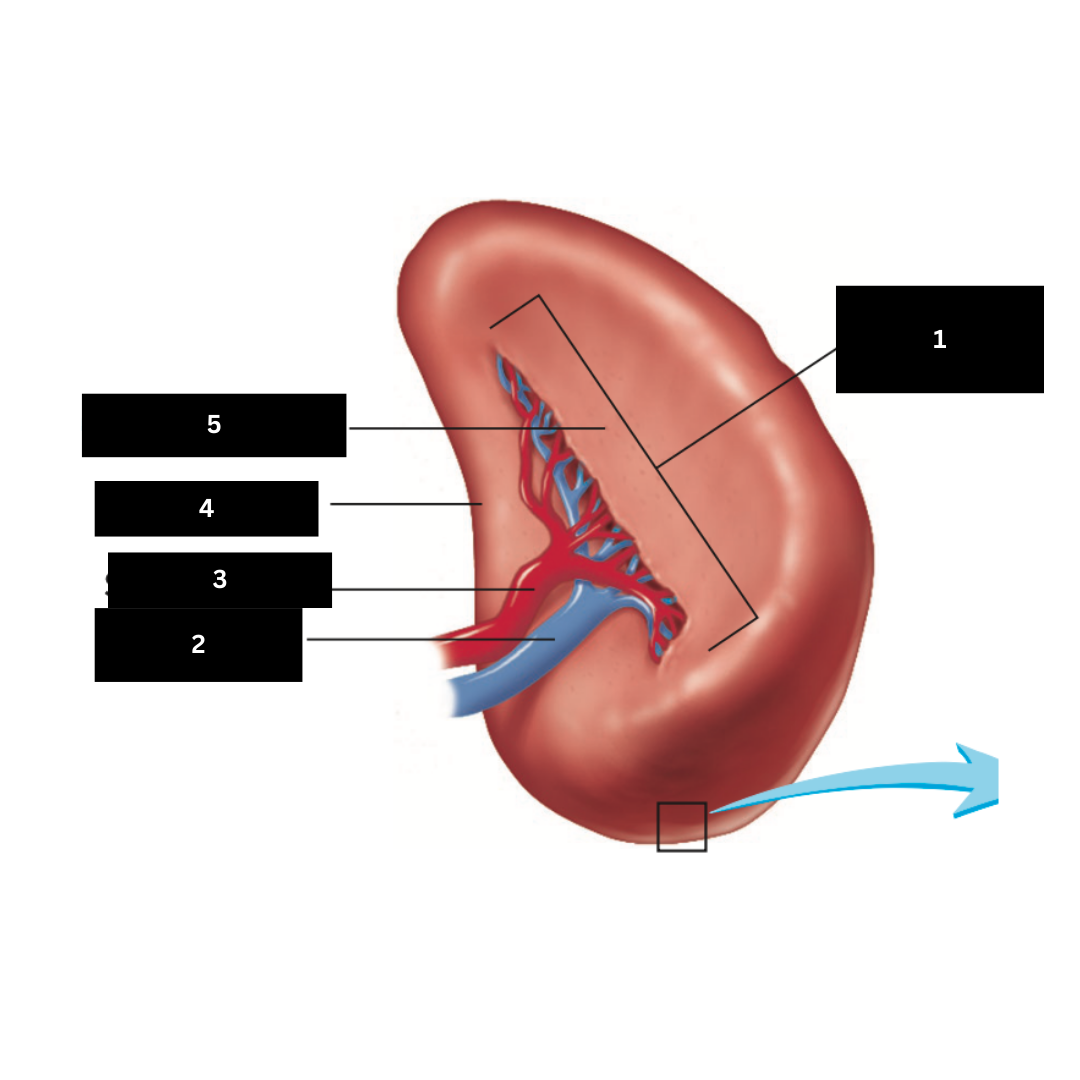
Trachea
1
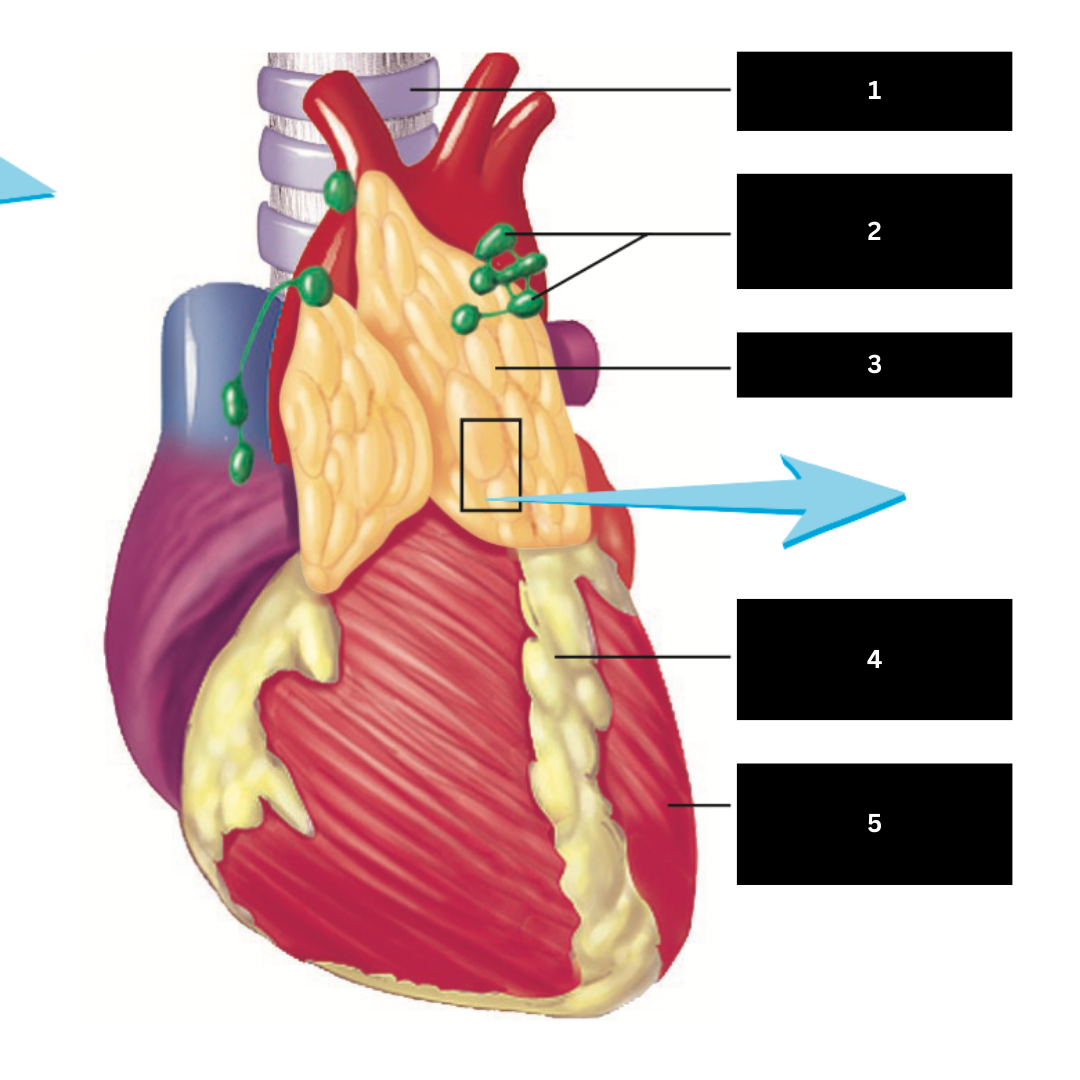
Lymph Nodes
2
Thymus
3
Adipose Tissue
4
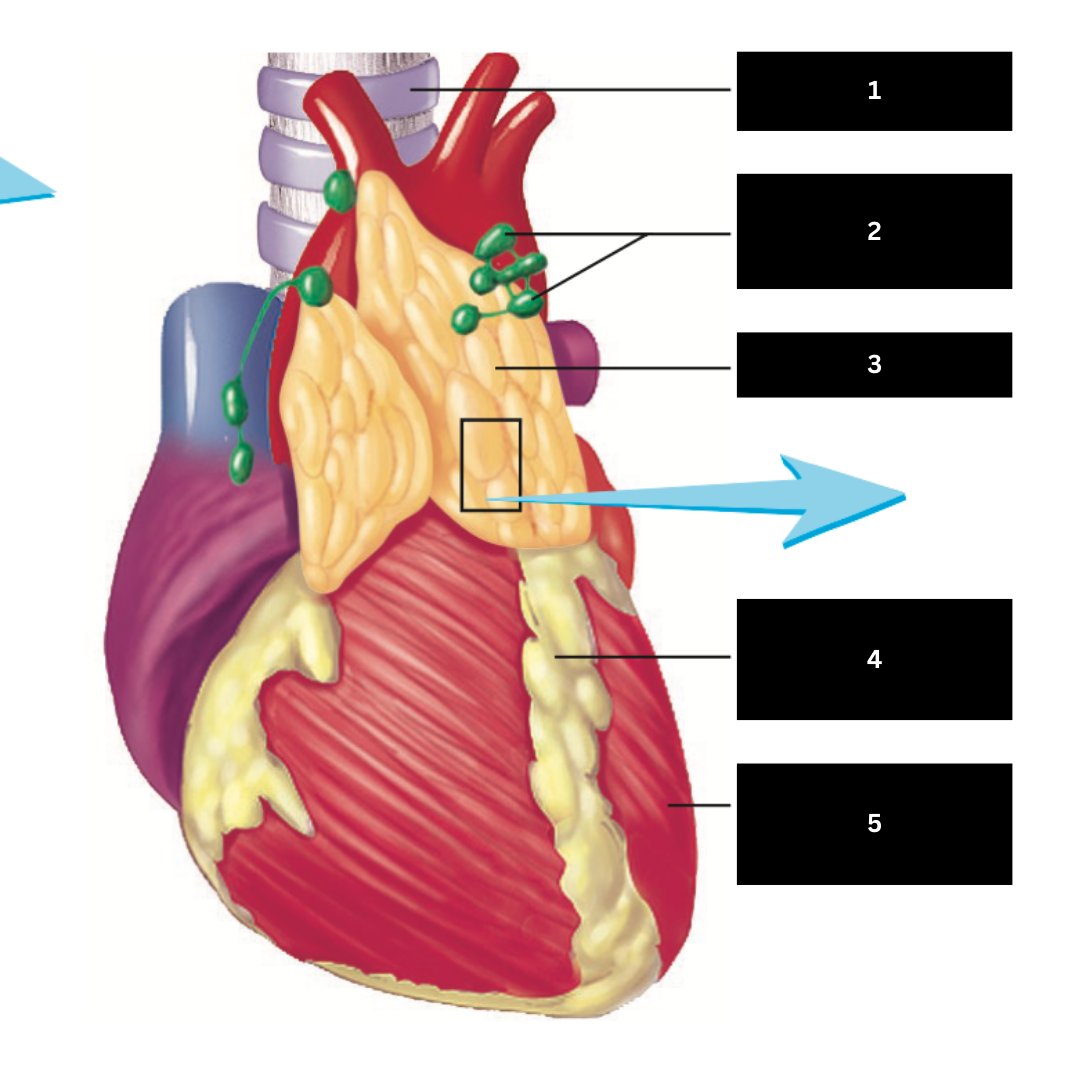
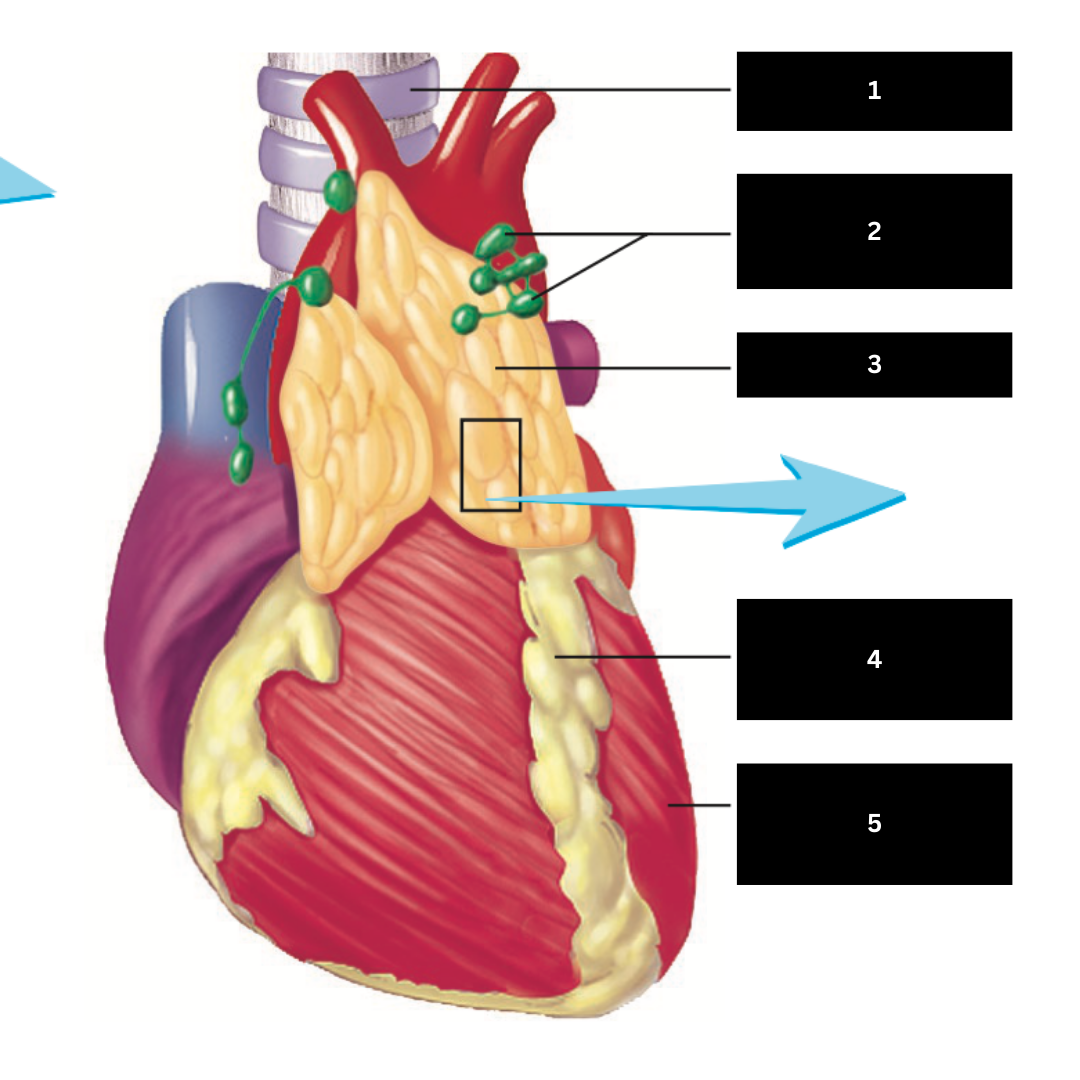
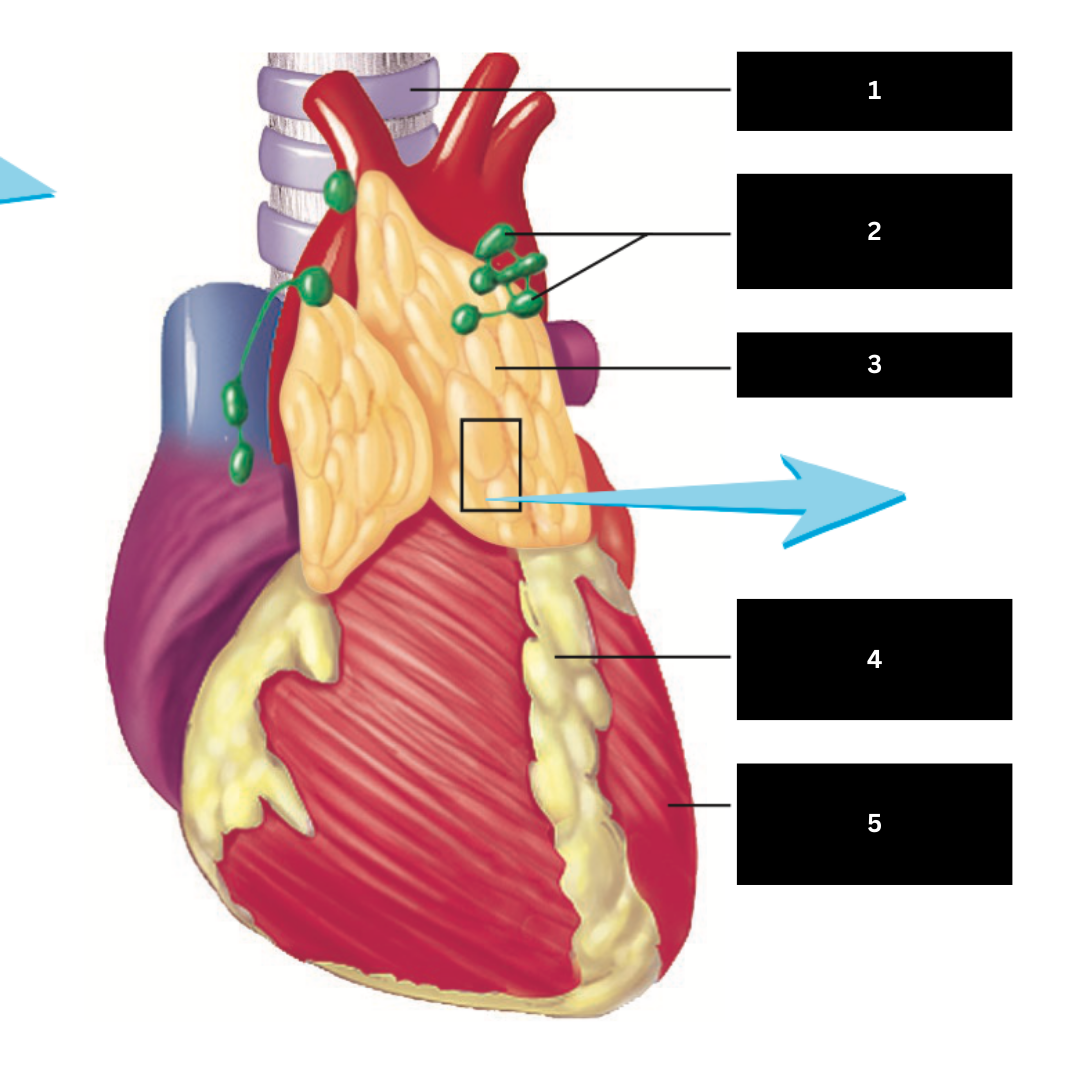
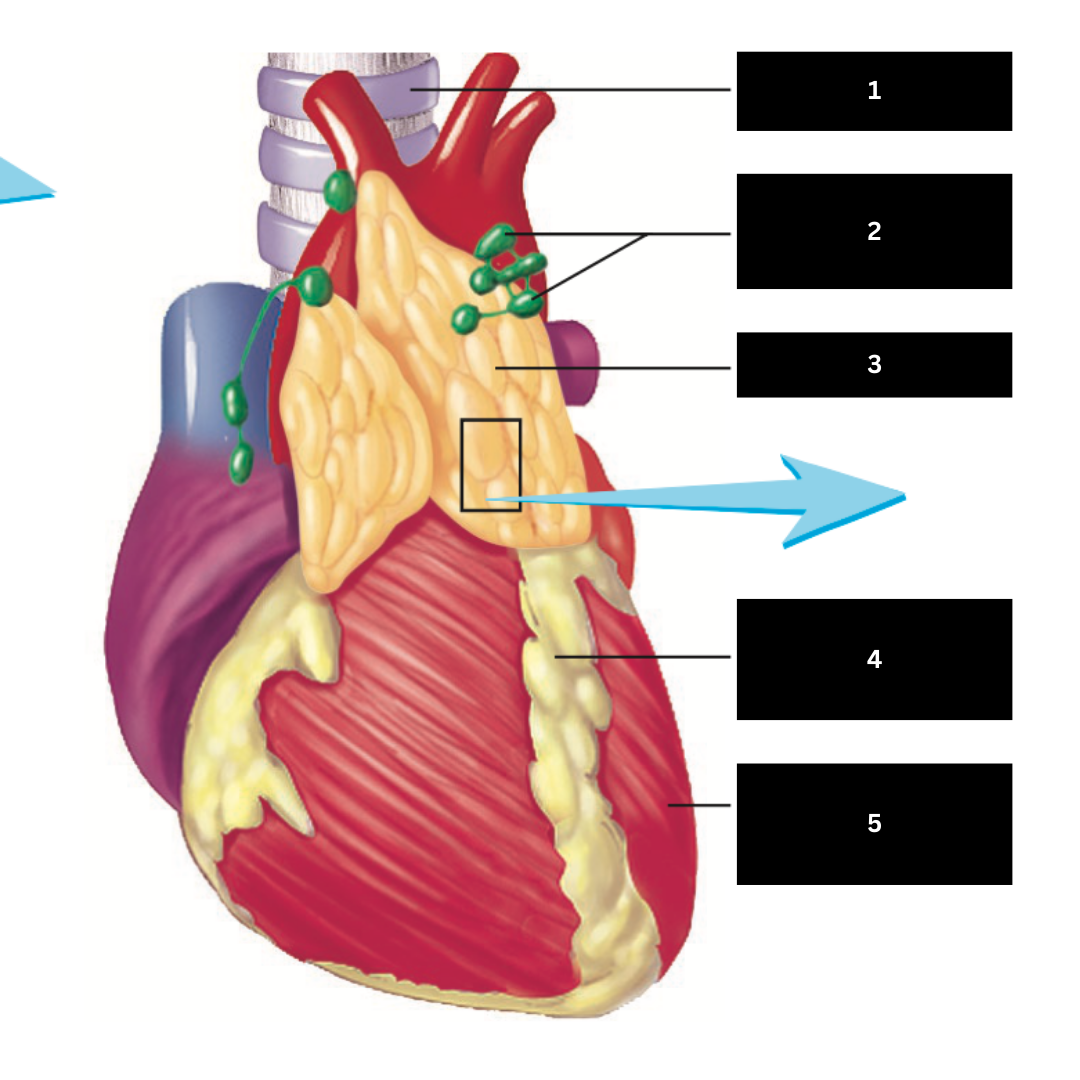
Heart
5
Pharyngeal Tonsil
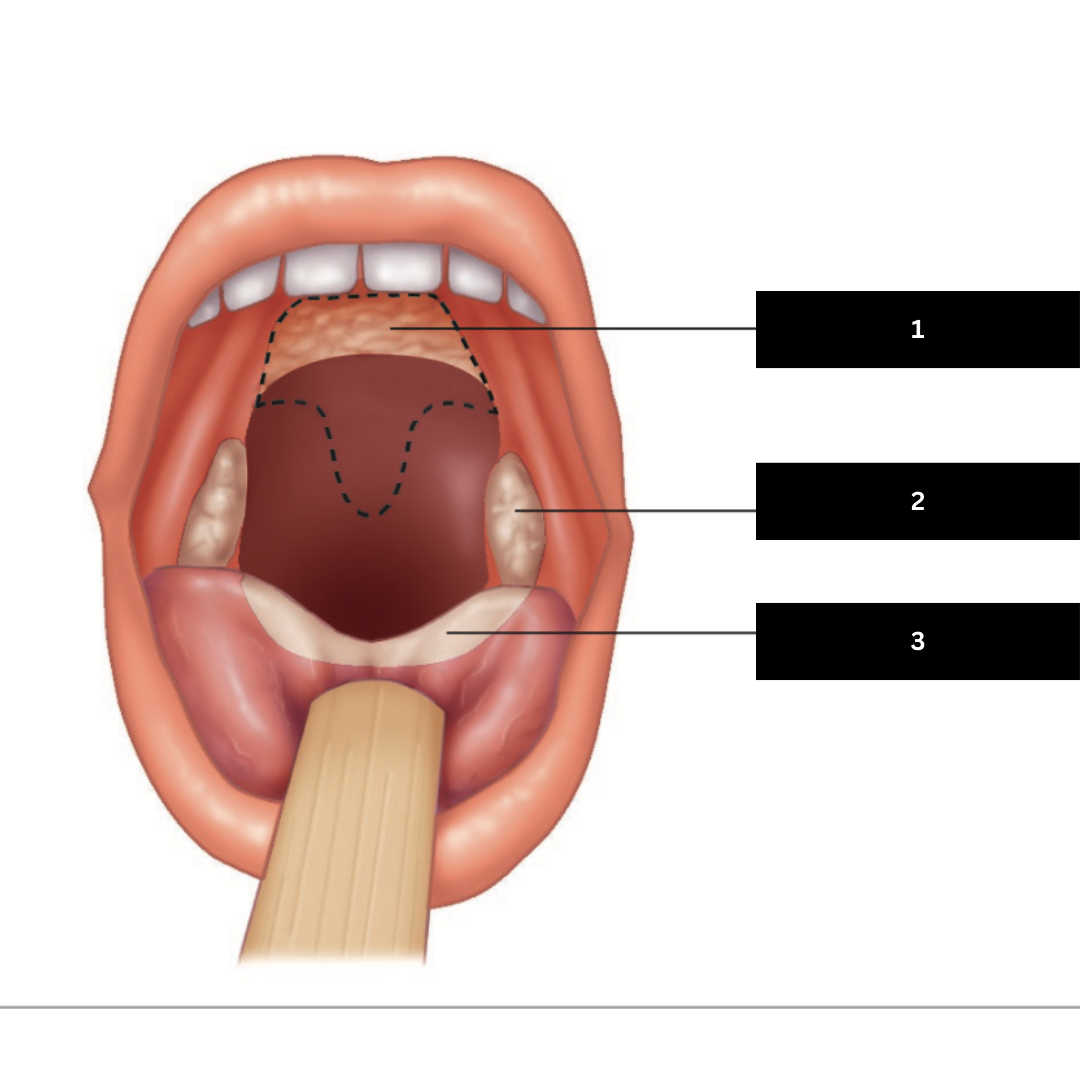
1
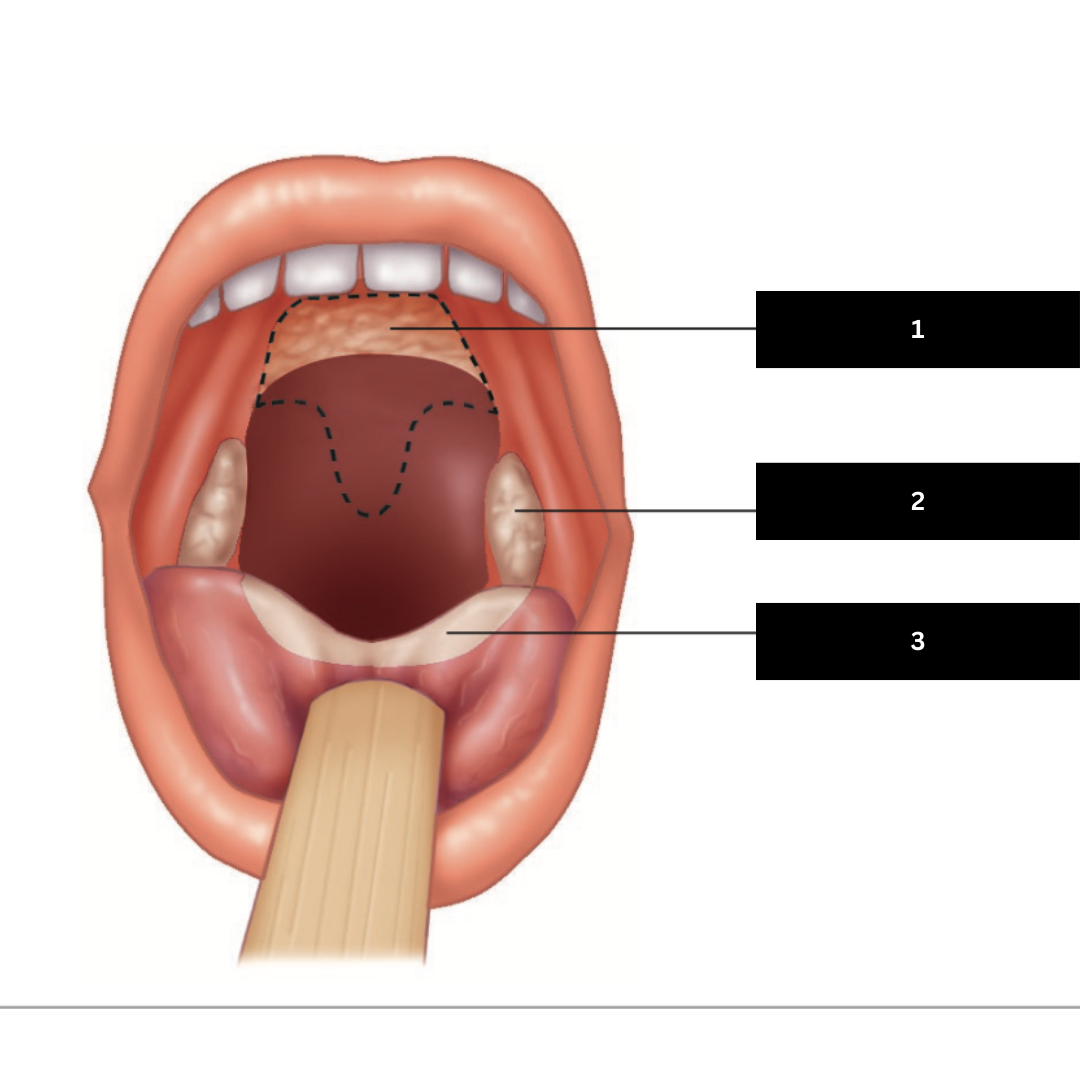
Palatine Tonsil
2
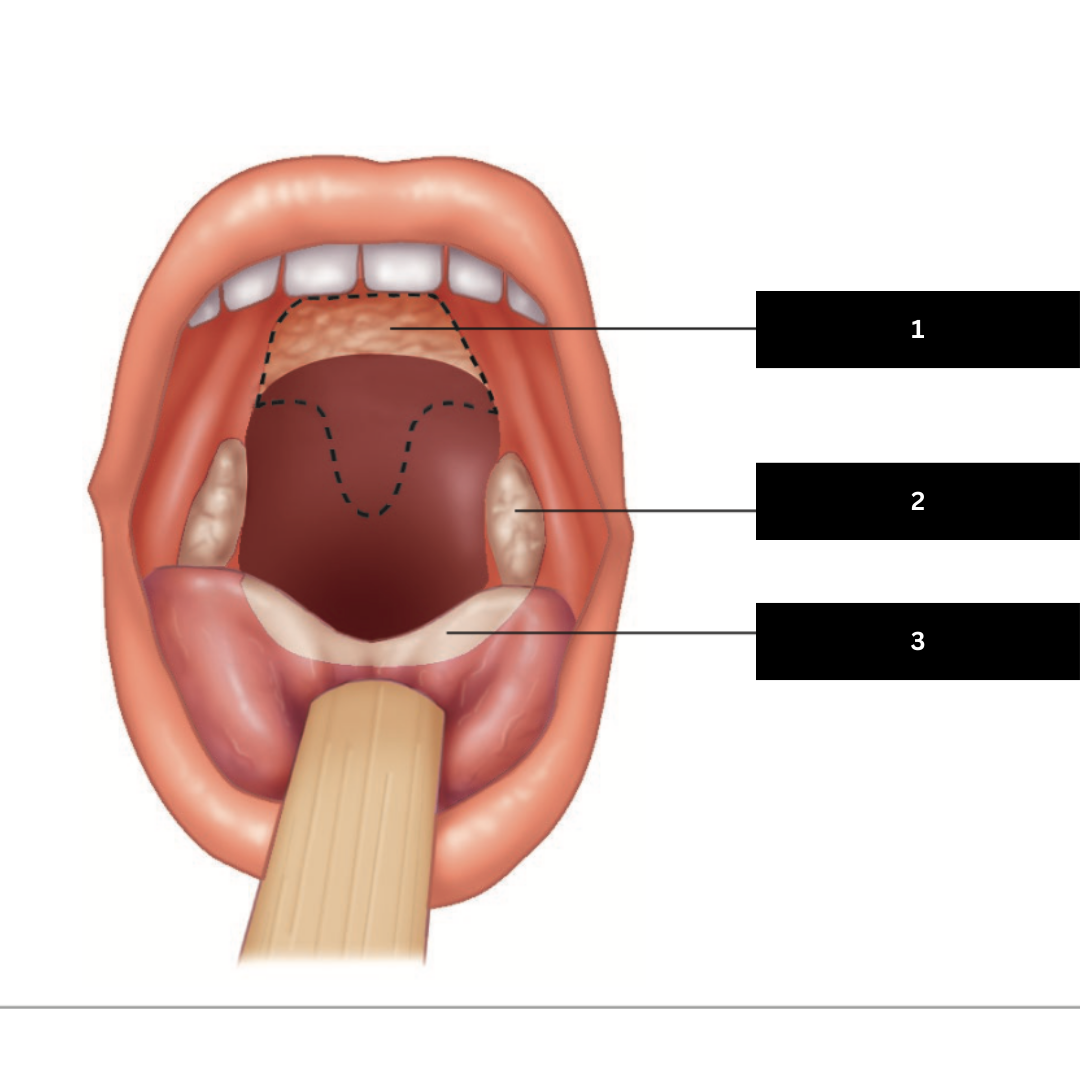
Lingual Tonsil
3
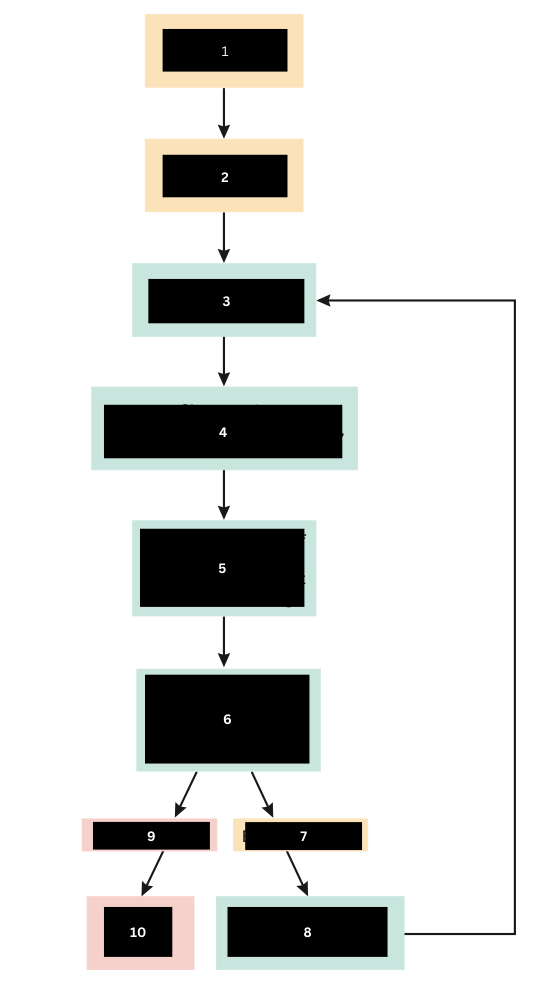
Bacteria enter the tissue
What triggers the inflammatory response
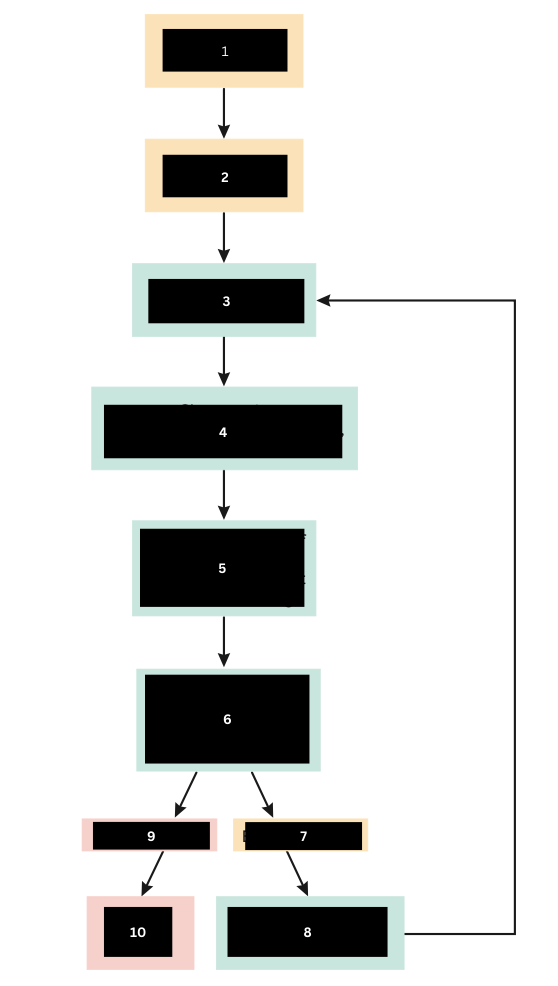
Tissue damage occurs
What does number 1 do?
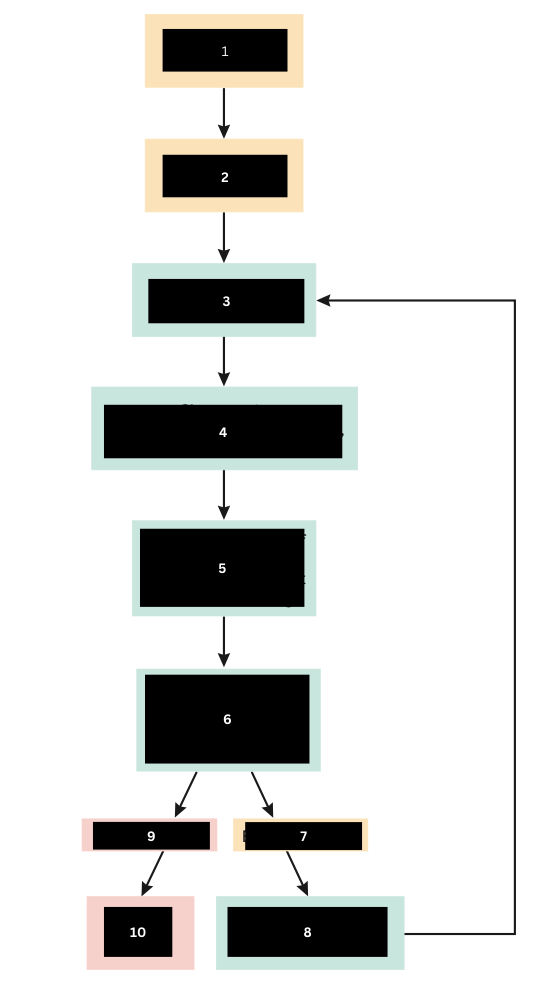
Chemical Mediators are released
What is released in response to number 2?
Increased vascular permiability
Increased bloodflow
Chemotaxis
What is triggered from the release of number 3?
Increased numbers of WBC and chemical mediators at the site of tissue damage
What happens at the site of tissue damage?
Bacteria are contained, destroyed, and phagocytized
What does the event in number 5 lead to?
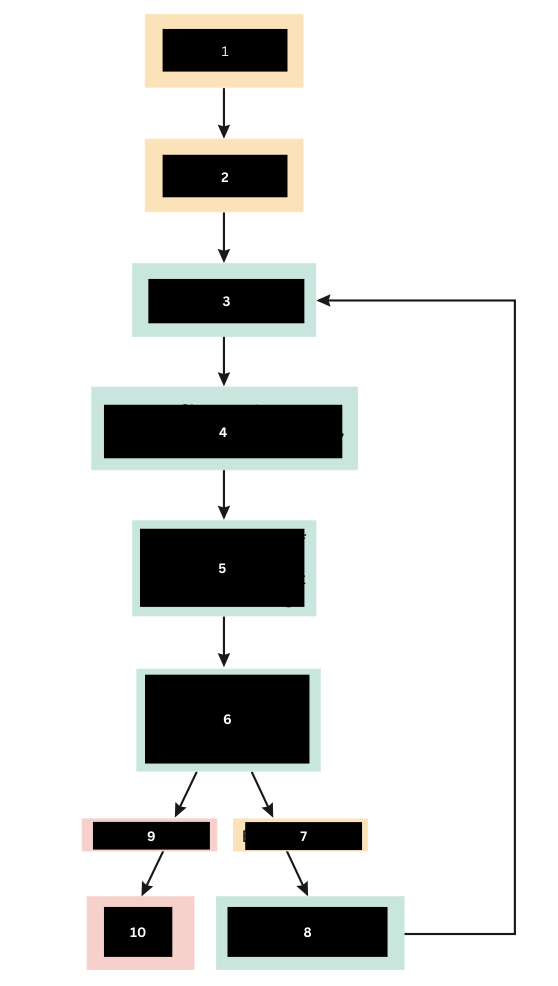
Bacteria Remain
If the immune response is not strong enough what happens? (Scroll down)
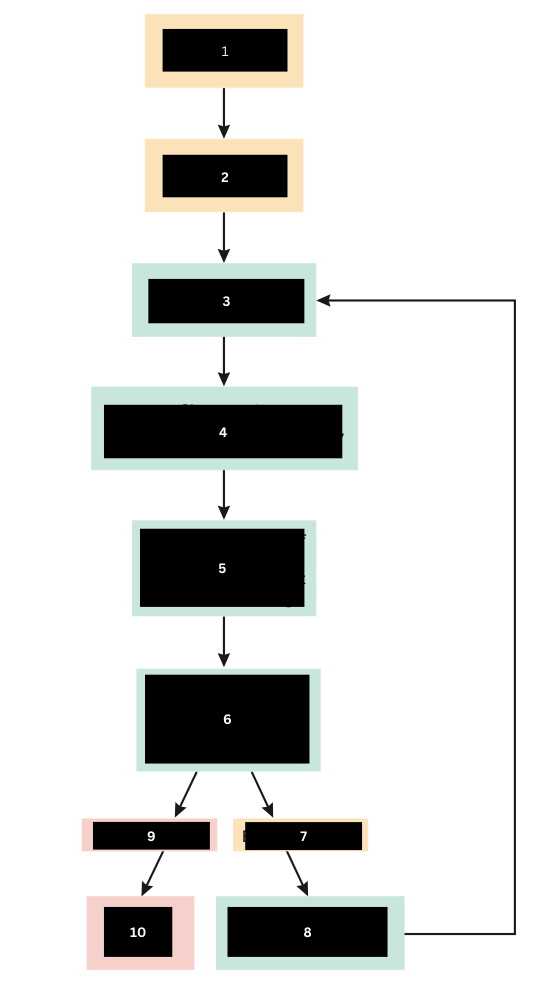
Additional chemical mediators are activated
What is the immune response to number 7?
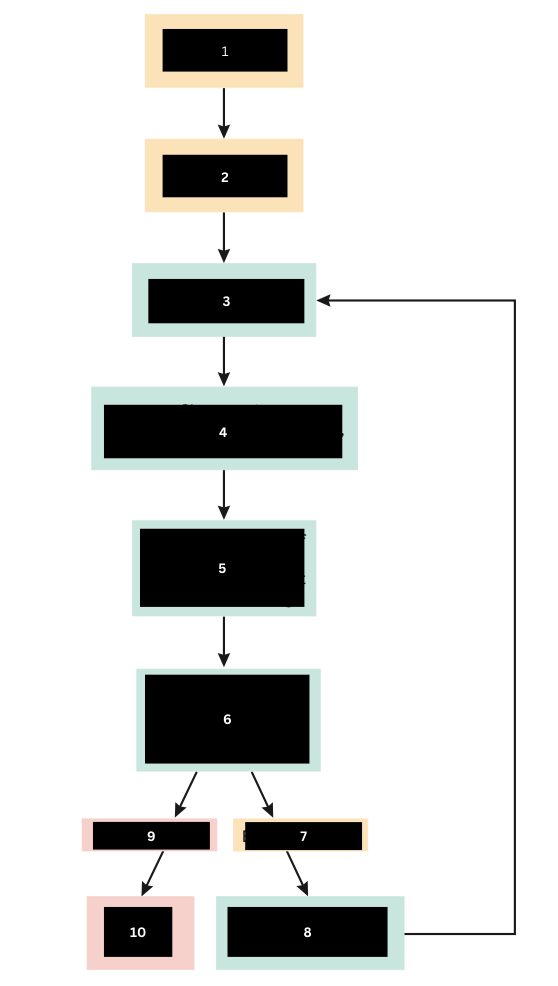
Bacteria are gone
When immune response is sufficient what happens to the bacteria?
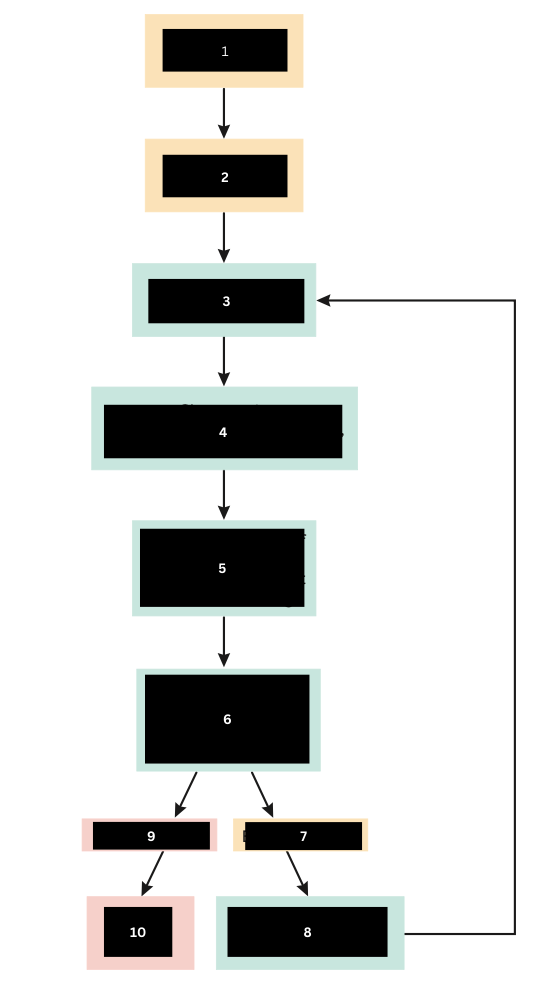
Tissue Repair
What then happens after number 9?
Celluar Immunity: Immunity is mediated by T cells that attack infected or abnormal cells directly
Humoral Immunity: Immunity is mediated by B cells and antibodies that target pathogens in body fluids
Difference Between Celluar Immunity and Humoral Immunity’s Definition?
Celluar Immunity: T-lymphocytes (T-cells), Helper T-cells (CD4), Cytotoxic T-cells (CD8)
Humoral Immunity: B-lymphocytes (B-cells), Plasma cells, memory B cells
Difference Between Celluar Immunity and Humoral Immunity’s Primary Cells?
Celluar Immunity: T cells recognize antigens presented by abnormal/infected cells via MHC molecules
Cytotoxic T cells destroy infected cells
Helper T cells stimulate other immune cells
Humoral Immunity: B cells cells recognize antigens and differentiate into plasma cells, producing antibodies
The antibodies bind to the antigens and mark them for destruction buy the immune system
Difference Between Celluar Immunity and Humoral Immunity’s Mechanism of Action?
Celluar Immunity: Intracelluar pathogens such as bacteria and virsuses.
-Cancer cells
-Transplanted tissue
Humoral Immunity: Extracelluar pathogens
-bacteria, toxins, and viruses before entering cells
Difference Between Celluar Immunity and Humoral Immunity’s Target?
Celluar Immunity: T-cells do not produce antibodies
Humoral Immunity: Plasma cells produce antibodies
Difference Between Celluar Immunity and Humoral Immunity’s Antibody Production?
Celluar Immunity: Memory T-cells provide faster responses to the same pathogens
Humoral Immunity: Memory B-cells provide quicker antibody production from the same pathogen
Difference Between Celluar Immunity and Humoral Immunity’s Memory Function?
Celluar Immunity:
Cytokines are the signal molecules of T-cells
Major Histocompatability Complex- antigen presentation to T-cells
Humoral Immunity:
Immunoglobins (Antibodies) - Neutralize pathogens and facilitate their clearance
Difference Between Celluar Immunity and Humoral Immunity’s Key Molecules?
Celluar Immunity: Slower initial response, needs to be activated and T-cells must proliferate
Humoral Immunity: Faster initial response, antibodies already ciruclate because of plasma cells
Difference Between Celluar Immunity and Humoral Immunity’s Response Time?
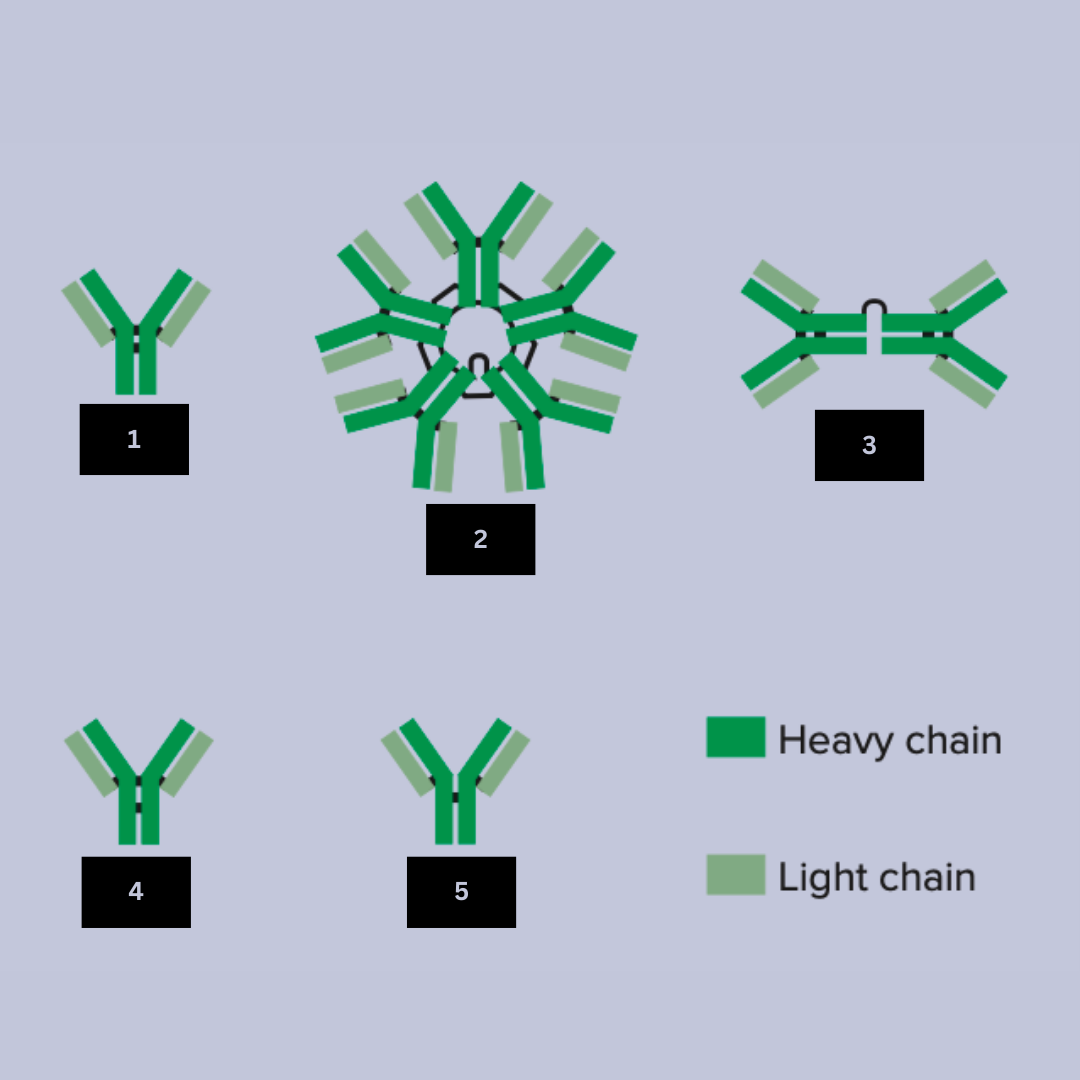
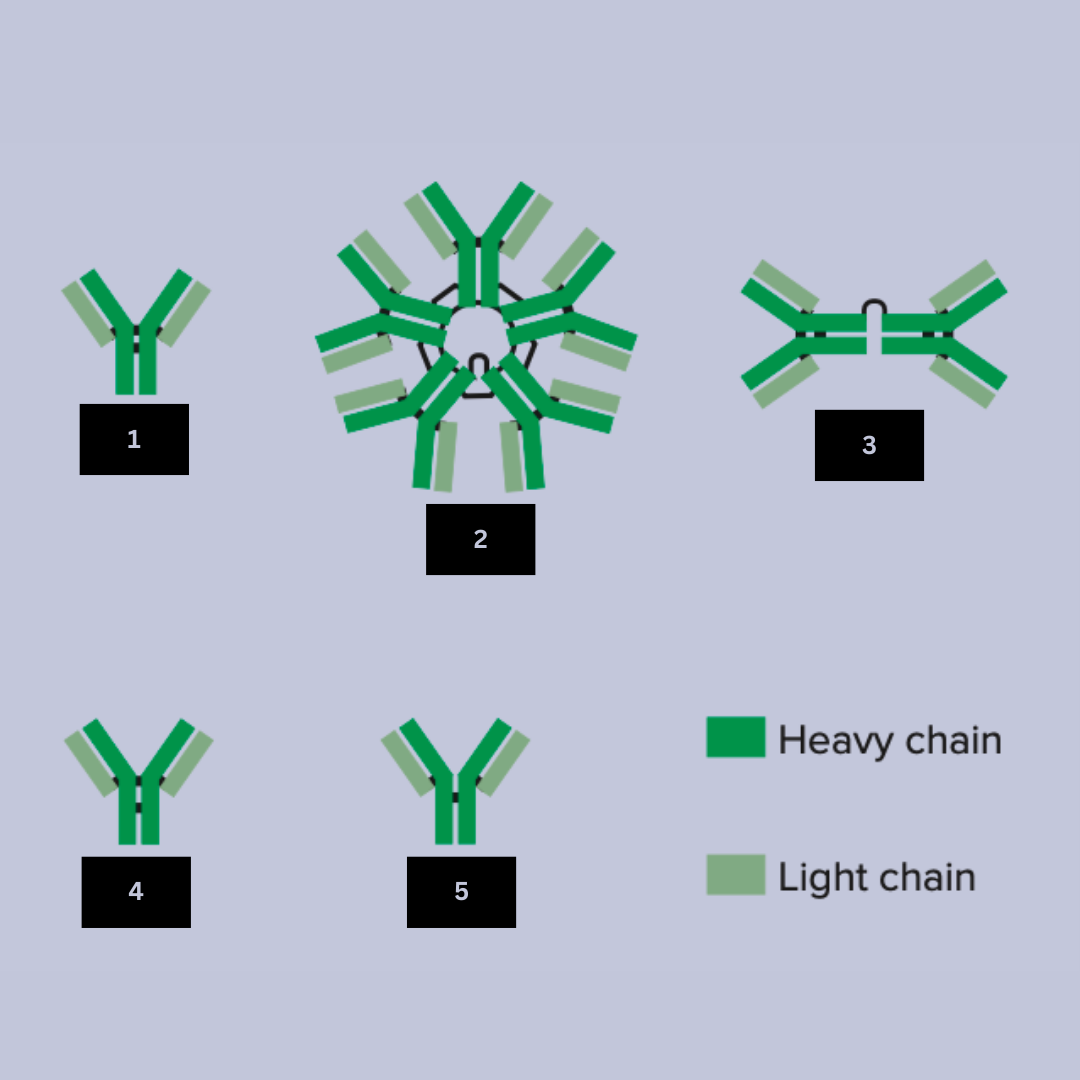
IgG
Antibody name (Look at the black lines to differentiate)
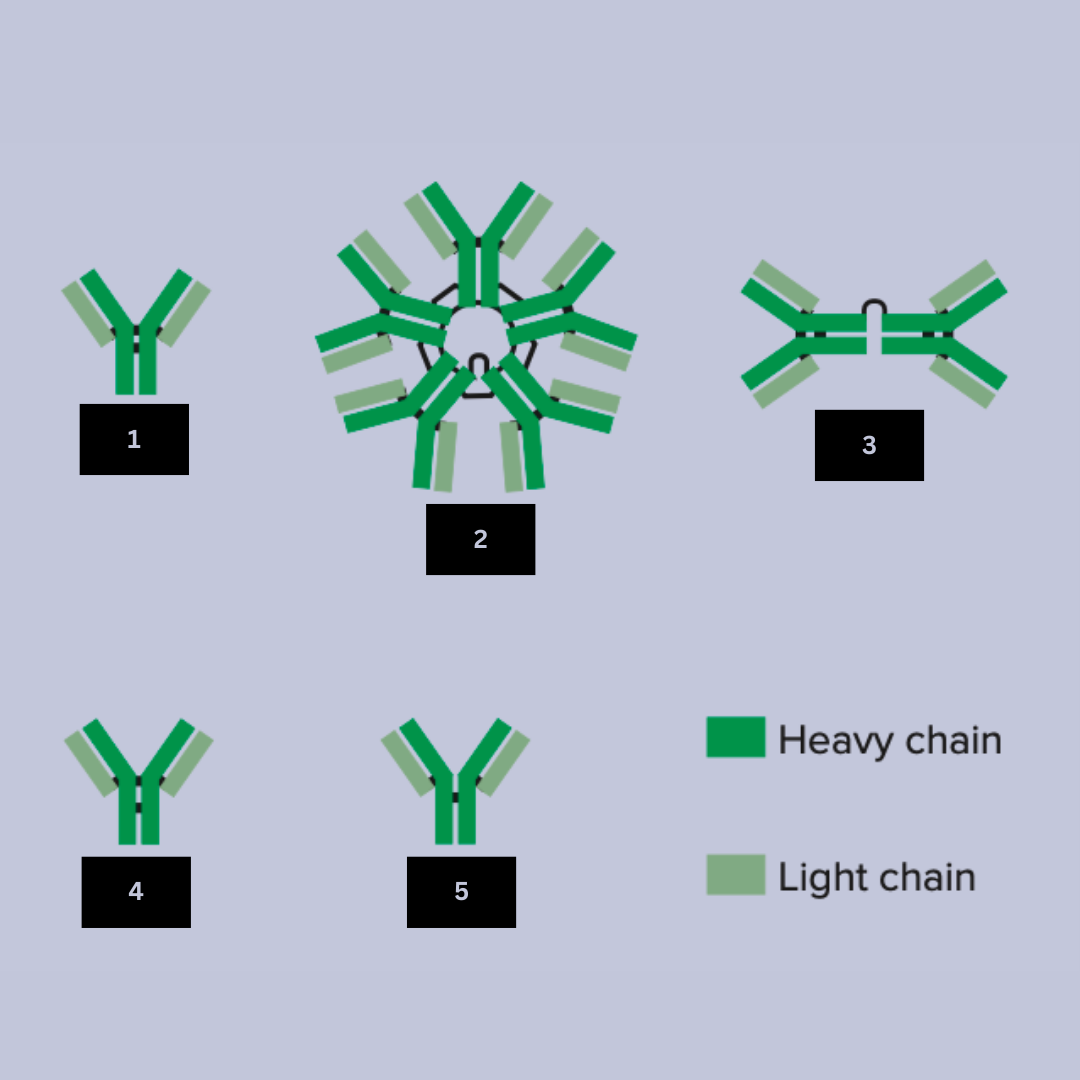
Provides long-term immunity after infection or vaccination
Neutralizes toxins or viruses
Activates the complementary system
Facilitates opsonization (marking pathogens for phagocytosis)
Antibody function
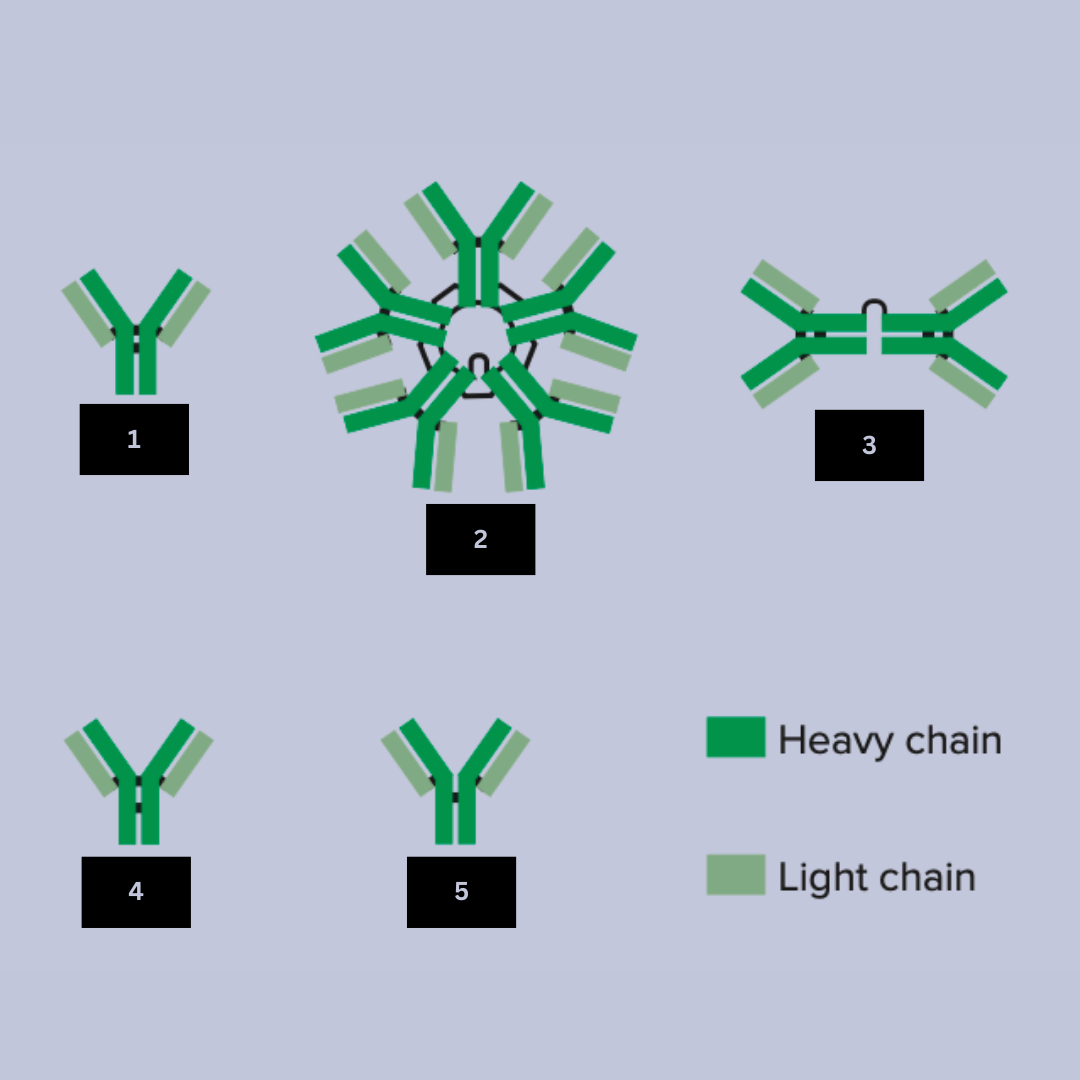
IgM
Antibody name
Primary responder in the early stages of infection
Excellent at Agglutination (clumping of pathogens)
Activates the complementary sytem
Antibody function
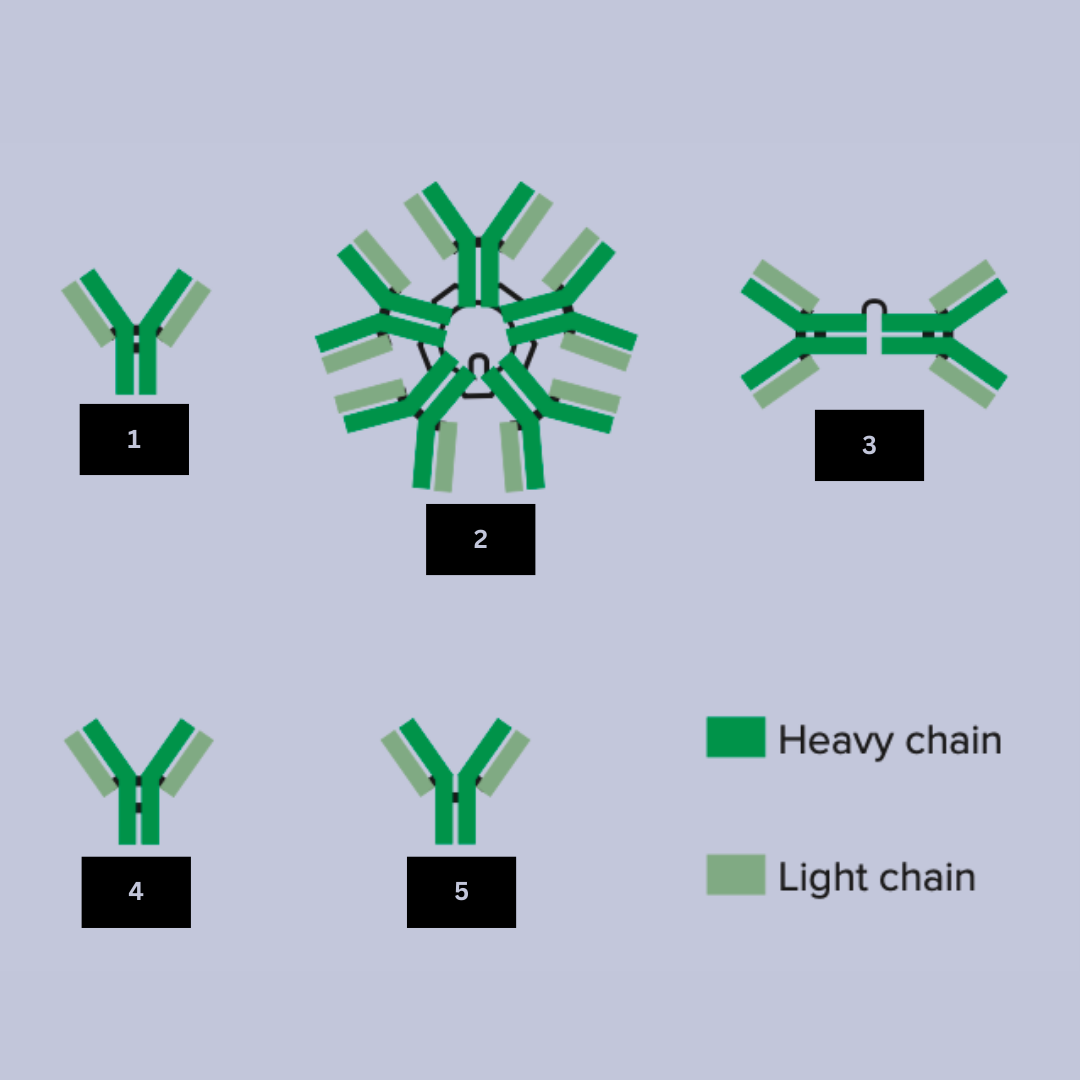
IgA
Antibody name
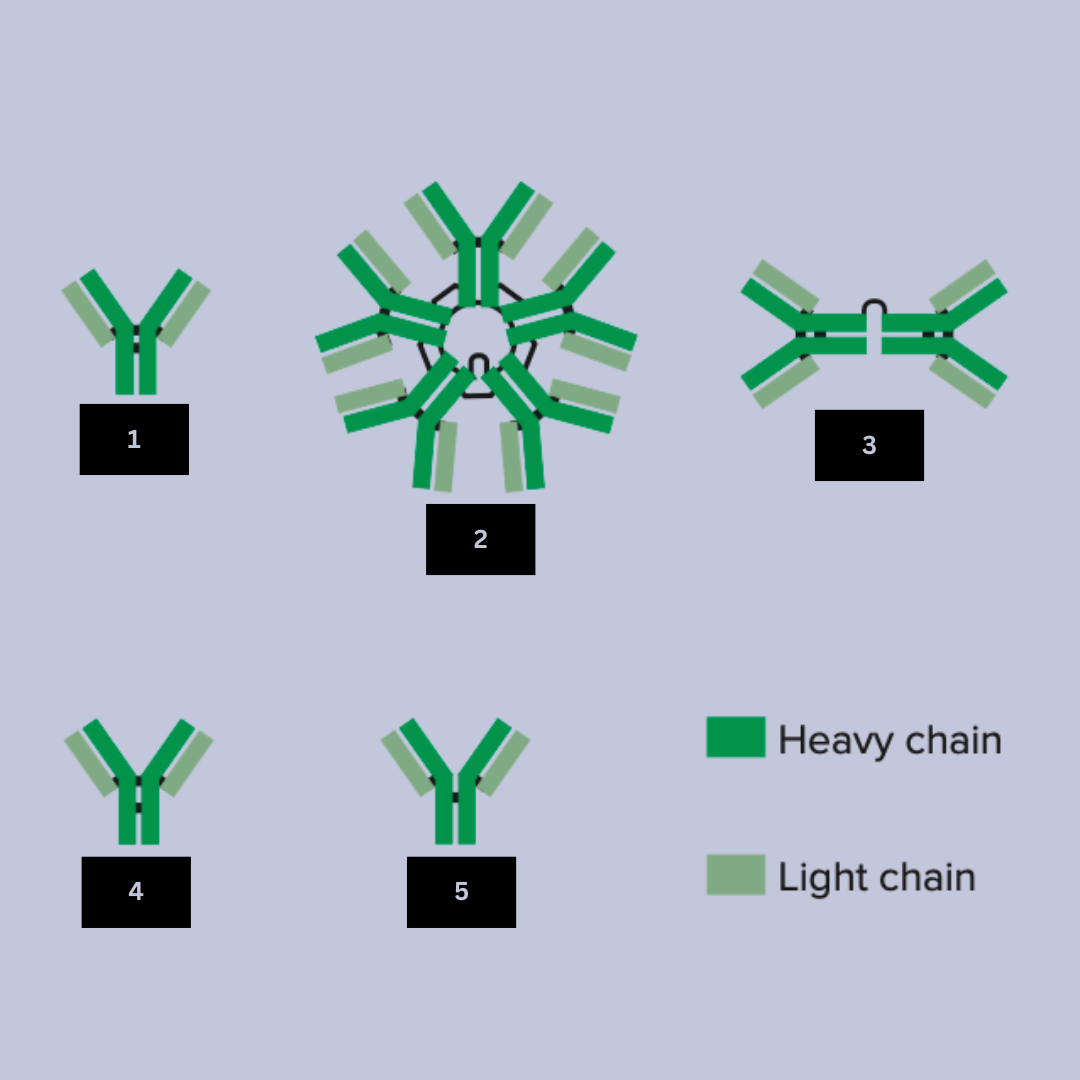
Protects mucousal surfaces
Provides passive immunity via breast milk
Antibody function
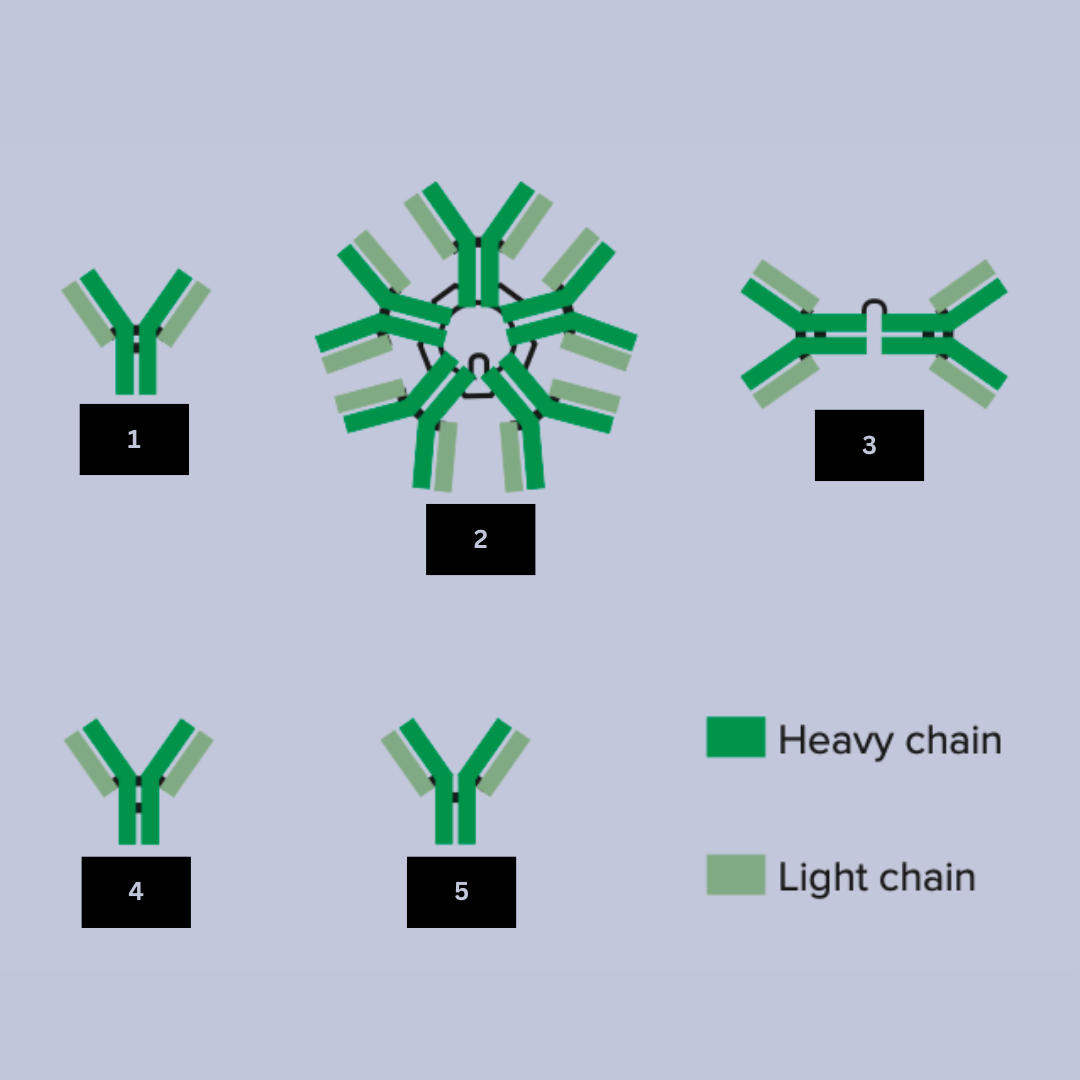
IgE
Antibody name
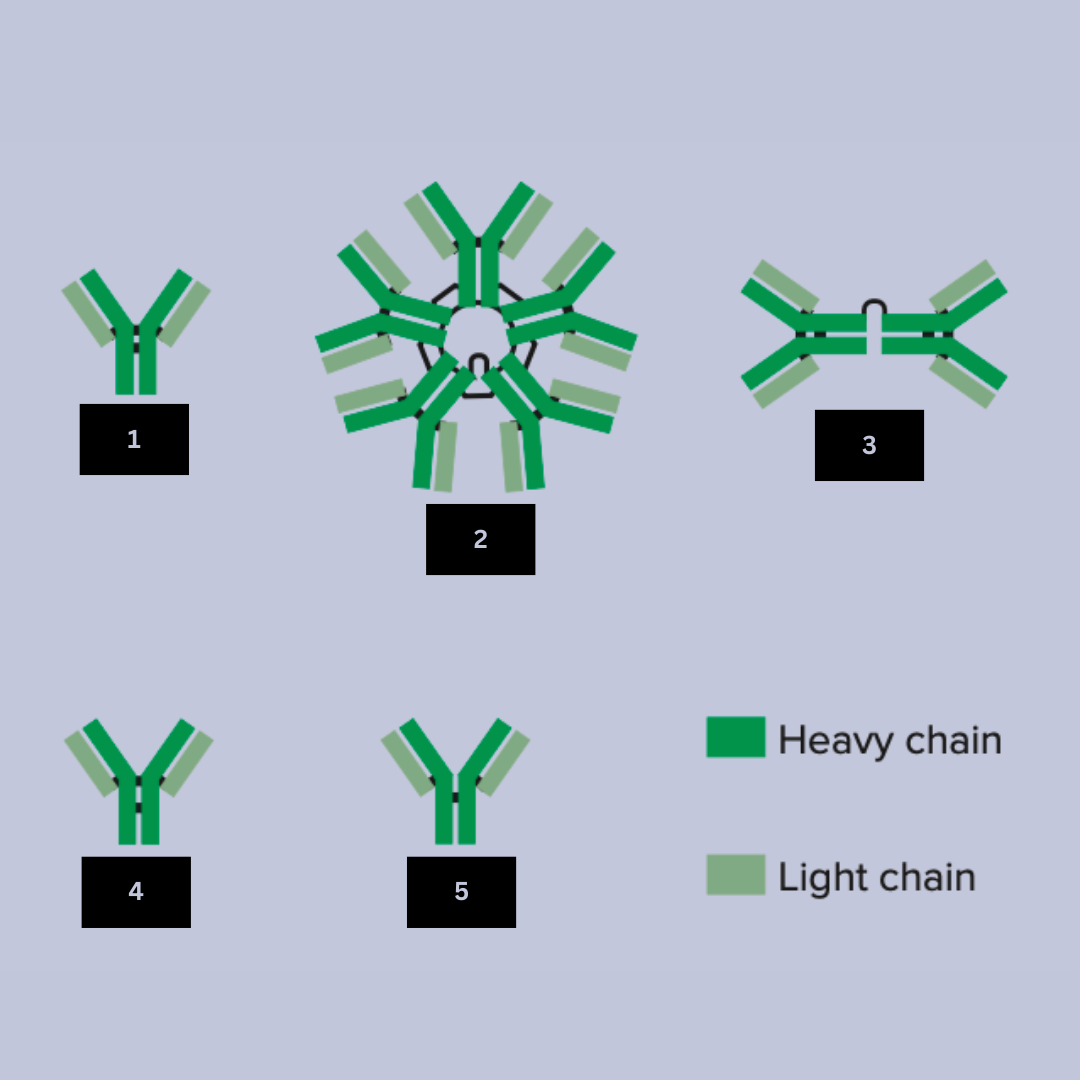
Triggers allergic responses by binding to allergens and activating mast cells and basophils, releasing histamine
Antibody function
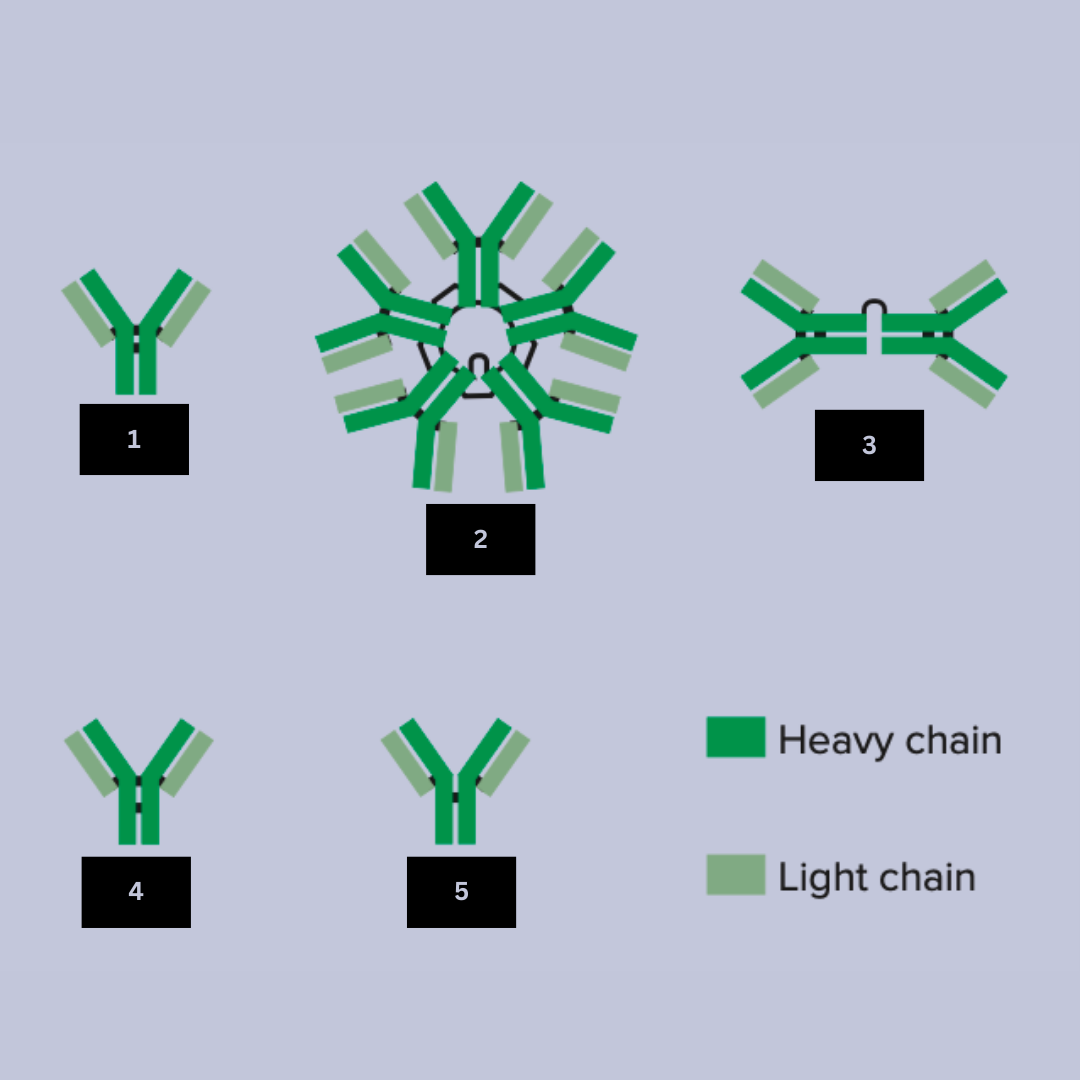
IgD
Antibody name
Plays a role in the activation and regulation of B cells
Function is less understood compared to other antibodies
Antibody funtion